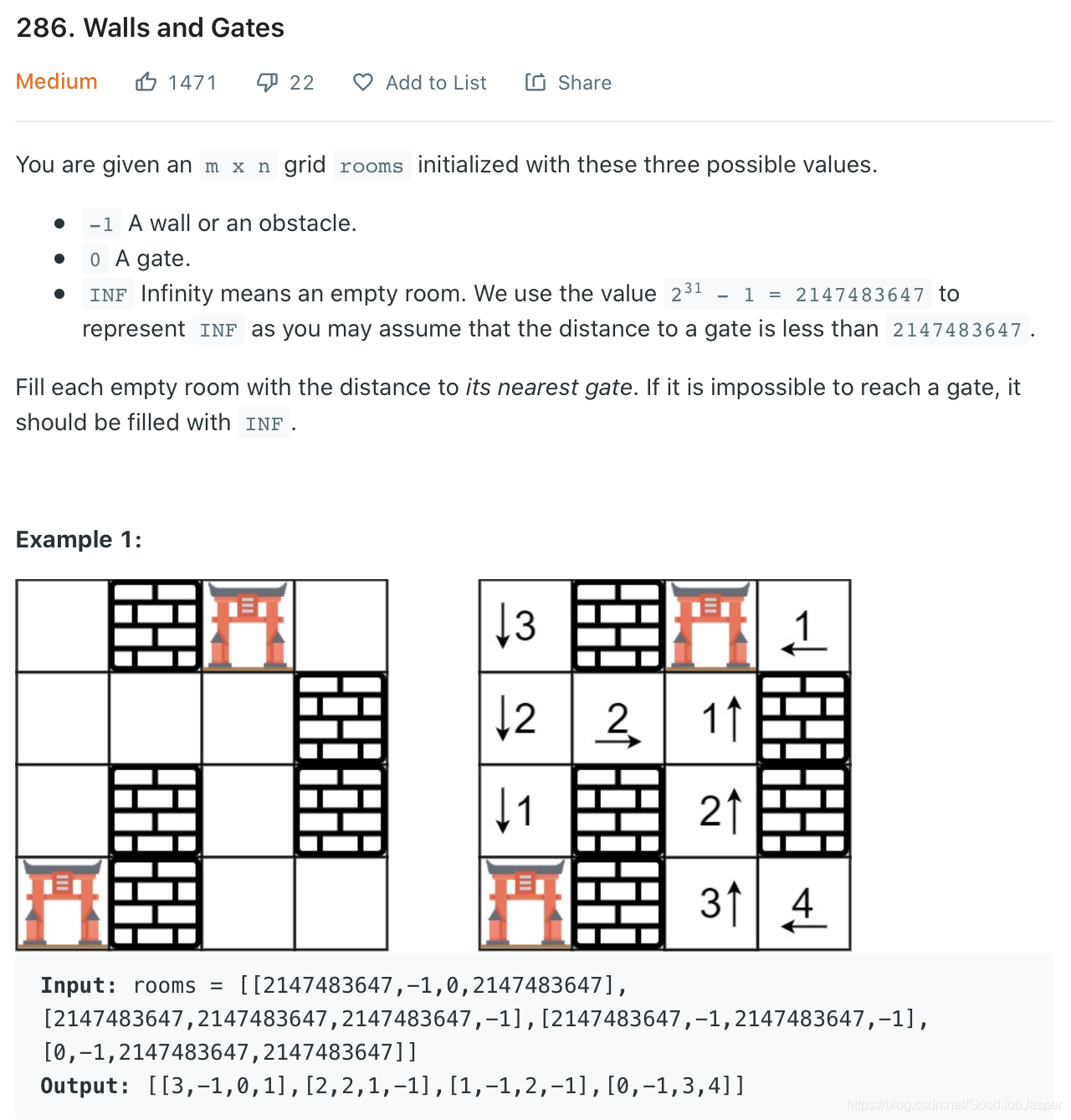
方法1: dfs/backtracking。做dfs应用题的时候还是比较模糊,不知道base case是什么,什么时候backtrack,还需加强锻炼啊!时间复杂(mn)^2,空间复杂mn。
class Solution {
public void wallsAndGates(int[][] rooms) {
int m = rooms.length;
int n = rooms[0].length;
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++){
for(int j = 0; j < n; j++){
if(rooms[i][j] == 0){
dfs(rooms, i, j, 0);
}
}
}
}
public void dfs(int[][] rooms, int i, int j, int k){
if(i < 0 || j < 0 || i >= rooms.length || j >= rooms[0].length) return;
if(rooms[i][j] == -1) return; //can remove
if(k <= rooms[i][j]){
rooms[i][j] = k;
dfs(rooms, i-1, j, k+1);
dfs(rooms, i+1, j, k+1);
dfs(rooms, i, j-1, k+1);
dfs(rooms, i, j+1, k+1);
}
}
}
方法2: bfs。这个方法直接看lc官方解答2,讲的不算很清楚,但是自己画个图,走一遍程序就懂了。时间复杂mn,空间复杂mn。
private static final int EMPTY = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
private static final int GATE = 0;
private static final List<int[]> DIRECTIONS = Arrays.asList(
new int[] {
1, 0},
new int[] {
-1, 0},
new int[] {
0, 1},
new int[] {
0, -1}
);
public void wallsAndGates(int[][] rooms) {
int m = rooms.length;
if (m == 0) return;
int n = rooms[0].length;
Queue<int[]> q = new LinkedList<>();
for (int row = 0; row < m; row++) {
for (int col = 0; col < n; col++) {
if (rooms[row][col] == GATE) {
q.add(new int[] {
row, col });
}
}
}
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
int[] point = q.poll();
int row = point[0];
int col = point[1];
for (int[] direction : DIRECTIONS) {
int r = row + direction[0];
int c = col + direction[1];
if (r < 0 || c < 0 || r >= m || c >= n || rooms[r][c] != EMPTY) {
continue;
}
rooms[r][c] = rooms[row][col] + 1;
q.add(new int[] {
r, c });
}
}
}
总结:
- 这道题可以和200题和在一起看。基本相同。
- 方法1的时间复杂度分析如下:
