文章目录
本文不推荐看,我整理得不好
上篇我们结合循环依赖讲了getBean,但还没有讲其中的动态代理的具体逻辑。前面说,不管如何代理最后的逻辑都是wrapIfNecessary()这个方法起作用。
此文我们先说说相关内容,然后聚焦wrapIfNecessary
⑪finishBeanFactoryIntialization
一、引入
第一部分是早期按后置处理器的getBean写的,很乱,只是舍不得删,勿看,直接去看二吧
1 preInstantiateSingletons
preInstantiateSingletons是finish阶段的最后一步,遍历获取容器中所有的Bean定义信息(一般的bean定义到这里已经都有了),依次创建对象getBean(beanName);
类DefaultListableBeanFactory;
public void preInstantiateSingletons() throws BeansException {
// Iterate over a copy to allow for init methods which in turn register new bean definitions.
// While this may not be part of the regular factory bootstrap, it does otherwise work fine.
// 拿到所有的bean定义
List<String> beanNames = new ArrayList<String>(this.beanDefinitionNames);//10个
/*
beanDefinitionNames包括:
internalConfigurationAnnotationProcessor、
inernalAutowiredAnnotationProcessor、
internalRequiredAnnationProcessor、
internalCommonAnnotationProcessor、
internalEventListenerProcessor、
internalEventListenerFactory、
mainConfigOfAOP、
calculator、
logAspects、
internalProxyCreater
*/
// 遍历实例化所有非加载的单例bean
// Trigger initialization of all non-lazy singleton beans...
for (String beanName : beanNames) {
//遍历一次获取
RootBeanDefinition bd = getMergedLocalBeanDefinition(beanName);
if (!bd.isAbstract() && bd.isSingleton() && !bd.isLazyInit()) {
if (isFactoryBean(beanName)) {
//如果是工厂bean的话;我们finish阶段的10个都不是工厂bean//internalEventListenerFactory也不是工厂bean
final FactoryBean<?> factory = (FactoryBean<?>) getBean(FACTORY_BEAN_PREFIX + beanName);
boolean isEagerInit;
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null && factory instanceof SmartFactoryBean) {
isEagerInit = AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction<Boolean>() {
@Override
public Boolean run() {
return ((SmartFactoryBean<?>) factory).isEagerInit();
}
}, getAccessControlContext());
}else {
//10个都不是工厂bean
isEagerInit = (factory instanceof SmartFactoryBean &&
((SmartFactoryBean<?>) factory).isEagerInit());
}
if (isEagerInit) {
//恶汉模式初始化
getBean(beanName);
}
}else {
// 重点//不是工厂bean
/*会进入else的有下面10个,即我们前面的都会进入这里getBean
internalConfigurationAnnotationProcessor、inernalAutowiredAnnotationProcessor、internalRequiredAnnationProcessor、internalCommonAnnotationProcessor、internalEventListenerProcessor、internalEventListenerFactory、mainConfigOfAOP、calculator、logAspects、internalProxyCreater
*/
// 下面进行我们之前就讲过的getBean流程。包括先从缓存中拿,缓存中没有就去创建新的bean// 一般在容器创建阶段都是创建的,我们创建完自己getBean才能从缓存中拿到
getBean(beanName);
// getBean{dogetBean()、第一个getSingleton()、第二个getSingleton()}
}
}
}
// 回调post-init
// Trigger post-initialization callback for all applicable beans...
for (String beanName : beanNames) {
Object singletonInstance = getSingleton(beanName);//10个都在前面创建过了,此时10个都能从缓存中拿到
if (singletonInstance instanceof SmartInitializingSingleton) {
// 上篇我们有个SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor,他是用来提前代理的
//只有internalEventListenerProcessor会进入第1层if,然后进入第二层的else
final SmartInitializingSingleton smartSingleton = (SmartInitializingSingleton) singletonInstance;
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction<Object>() {
@Override
public Object run() {
smartSingleton.afterSingletonsInstantiated();
return null;
}
}, getAccessControlContext());
}
else {
smartSingleton.afterSingletonsInstantiated();
}
}
}
}//执行完后退出finishBeanFactoryIntialization(),去执行refresh()的最后一个finishRefresh();
2 重温createBean
我们在这里重温创建bean的流程,但又不只是重复上面创建后置处理器bean的流程。我们这次主要是关注代理对象是在哪里创建的
AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory类;
protected Object createBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, Object[] args) throws BeanCreationException {
RootBeanDefinition mbdToUse = mbd;//要创建的bean的定义信息
// Make sure bean class is actually resolved at this point, and
// clone the bean definition in case of a dynamically resolved Class
// which cannot be stored in the shared merged bean definition.
Class<?> resolvedClass = resolveBeanClass(mbd, beanName);
if (resolvedClass != null && !mbd.hasBeanClass() && mbd.getBeanClassName() != null) {
mbdToUse = new RootBeanDefinition(mbd);
mbdToUse.setBeanClass(resolvedClass);
}
// Prepare method overrides.
try {
mbdToUse.prepareMethodOverrides();
}
catch (BeanDefinitionValidationException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(mbdToUse.getResourceDescription(),
beanName, "Validation of method overrides failed", ex);
}
try {
//resolveBeforeInstantiation只是针对有自定义的targetsource,因为自定义的targetsource不是spring的bean那么肯定不需要进行后续的一系列的实例化、初始化。所以可以在resolveBeforeInstantiation直接进行proxy,但初次接触我们还是大概略过即可,我们普通的动态代理不是在这里创建的
Object bean = resolveBeforeInstantiation(beanName, mbdToUse);
if (bean != null) {
//calculator时为空
return bean;
}
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw ... }
// 创建对象, 动态代理也是这里面创建的
Object beanInstance = doCreateBean(beanName, mbdToUse, args);//创建CreateBeanInstance、populateBean属性赋值、initializeBean(Aware,before,init,after)
return beanInstance;
}
3 resolveBeforeInstantiation
无用功,即本函数返回不了什么,不看也罢
resolveBeforeInstantiation就是创建代理对象的地方
//实例化前给后置处理器一个返回代理对象的机会
protected Object resolveBeforeInstantiation(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd) {
Object bean = null;
if (!Boolean.FALSE.equals(mbd.beforeInstantiationResolved)) {
// Make sure bean class is actually resolved at this point.
if (!mbd.isSynthetic() && hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors()) {
Class<?> targetType = determineTargetType(beanName, mbd);
if (targetType != null) {
// 用BeforeInstantiation类型的后置处理器调用 BeforeInstantiation+BeforeInitializition后置处理器
// 我们的后置处理器是SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor,所以并不会操作
bean = applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInstantiation(targetType, beanName);//BeforeInstantiation实例化前
//如果返回值不为null,那么就沿用PostBeanProcessor
if (bean != null) {
//calculator这里会为null
// 下面这个里的会拿到cacheKey后判断!earlyProxyReferences.contains(cacheKey);这是循环引用的关键,没有才进入wrapIfNecessary
bean = applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(bean, beanName);//AfterInitialization初始化后//调用完Calculator后 来到这里
}
}
}
mbd.beforeInstantiationResolved = (bean != null);
}
return bean;
}
3.1 applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInstantiation():
无用功,不用看3.1。而且是早期按后置处理器的getBean写的,很乱,只是舍不得删,勿看
其实后置处理器也分多种,一种分类方式是作用于初始化前的还是实例化前的。
我们用的后置处理器AbstractAutoProxyCreater实现了SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor,即代表他是一个实例化前的后置处理器,但不巧的是我们测试用例的时候没有写实例化前的逻辑,所以这也返回不了bean对象,而是推迟到了我们第一次提到getBean中在"AfterInitialization"时形成代理。
AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory;
protected Object applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInstantiation(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) {
for (BeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
//拿到所有后置处理器
/*在registerBeanPostProcessors阶段:
- 对于internalAutowiredAnnotationProcessor、internalRequiredAnnotationProcessor、internalCommonAnnotationProcessor这3个bean而言,通过getBeanPostProcessors()可以获取到4个后置处理器:ApplicationContextAwareProcessor、ApplicationListenerDetector、ConfigurationClassPostProcessor$importAwareBeanPostProcessor、PostProcessorRegisAnootrationDelegate$BeanPostProcessorChecker
而对于internalAutoProxyCreator,是前面4+3=7个:
旧的4个:ApplicationContextAwareProcessor、ApplicationListenerDetector、ConfigurationClassPostProcessor$importAwareBeanPostProcessor、PostProcessorRegisAnootrationDelegate$BeanPostProcessorChecker、
还有新增的3个:CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor、AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor、RequiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor
====================================
finishBeanFacoryInitialization阶段就有4+3+1=8个后置处理器,加了个AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreater
在finish阶段,getBeanPostProcessors有8个:ApplicationContextAwareProcessor、ConfigurationClassPostProcessor$importAwareBeanPostProcessor、PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate$BeanPostProcessorChecker、AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreater、CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor、AutoWiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor、RequiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor、ApplicationListenerDetector
*/
if (bp instanceof InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) {
//如果该后置处理器是应用到实例
/*
register阶段:
对于internalAutowiredAnnotationProcessor、internalRequiredAnnotationProcessor、internalCommonAnnotationProcessor这三个后置处理器bean,只有ConfigurationClassPostProcessor$importAwareBeanPostProcessor满足if
对于internalAutoProxyCreator来说,满足的有ConfigurationClassPostProcessor$importAwareBeanPostProcessor、CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor、AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor、RequiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor
=============================
在finish阶段:
对于internalEventListenerProcessor、internalEventListenerFactory、mainOfAOP、calculator、logAspects有5个满足:ConfigurationClassPostProcessor$importAwareBeanPostProcessor、AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreater、CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor、AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor、RequiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor
*/
//我们讲解的是形参beanName=Calculator,且for遍历到AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreater的情况,此时才能进入我们想要的postProcessBeforeInstantiation()
// 这里要注意的是调用的后置处理器的postProcessBeforeInstantiation
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor ibp = (InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) bp;
Object result = ibp.postProcessBeforeInstantiation(beanClass, beanName);//每个后置处理器重写了该方法//注意是instance之前,而不是initial之前,所以才是ibp//一个是BeanPostProcessor(bean创建初始化前后调用),一个是InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor(创建bean实例之前先尝试用后置处理器返回对象的)
//对于postProcessBeforeInstantiation()而言,因为其子类有的重写了该方法,所以上个语句调用的并不都是都是一个相同的方法,对于这些后置处理器(4个)来说,他们的postProcessBeforeInstantiation()只是return null:InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessorAdapter类,ConfigurationClassPostProcessor$ImportAwareBeanPostProcessor、CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor、AutoAnnotationPostProcessor、RequiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor、AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor
//而对于AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreater这个后置处理器来说,他调用的是AbstractAutoProxyCreator类的他们的postProcessBeforeInstantiation()方法 // 第一次进去了
if (result != null) {
return result;
}
}
}
return null;
}
可见和我们原来beforeInitialize方法一样,都是遍历后置处理器以在bean上操作before方法
AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreater这个后置处理器就是类型的,会进入applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInstantiation()方法
3.2 ibp.postProcessBeforeInstantiation
无用功
AbstractAutoProxyCreator;关注计算器类和切面类;意思是后置处理器或者普通bean创建的时候对于那个bean他的后置处理器哪个会在实例化前起作用;
public Object postProcessBeforeInstantiation(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) throws BeansException {
//MathCalculator//LogAspect//对应AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreater
Object cacheKey = getCacheKey(beanClass, beanName);//根据bean的类型和名字拿到bean对应的缓存key
if (beanName == null || !this.targetSourcedBeans.contains(beanName)) {
//false//calculator时候targetSourcedBeans为空,根据后一个条件进入了if
// 判断有没有在需要增强都是bean里
if (this.advisedBeans.containsKey(cacheKey)) {
//已经增强的bean//看计算器和切面类是否在advisedBeans(保存了已经需要增强的bean?),false不包含//我们的简单测试用例不会进入,即使多些个ac.getBean(MathCalculator.class);也不会进入//都不会进入
return null;
}
if (isInfrastructureClass(beanClass) || shouldSkip(beanClass, beanName)) {
//isInfrastructureClass判断当前bean是否是基础类型(Advice、Pointcut、Advisor、AopInfratrutureBean) 或者 是否是切面(@Aspect),我们这里当beanName=="logAspect"时才为true。这个shouldSkip最后还会调用super.shouldSkip,返回false
//shouldSkip是否应该跳过//判断是不是AspectJPointcutAdvisor这个类型的增强器,我们是InstantiationModelAwarePointcutAdvisor这个类型的所以跳过了//就是增强器LogStart..LogEnd//只有logAspect时会进入,且为true、false
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE);//cacheKey=="logAspect"
return null;
}
}
// Create proxy here if we have a custom TargetSource.
// Suppresses unnecessary default instantiation of the target bean:
// The TargetSource will handle target instances in a custom fashion.
if (beanName != null) {
//如果我们有自定义目标源码的话我们就创建代理对象,这里我们没有
TargetSource targetSource = getCustomTargetSource(beanClass, beanName);//null
if (targetSource != null) {
//calculator时候targetSourced为空
this.targetSourcedBeans.add(beanName);
Object[] specificInterceptors = getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(beanClass, beanName, targetSource);
Object proxy = createProxy(beanClass, beanName, specificInterceptors, targetSource);//创建代理对象
this.proxyTypes.put(cacheKey, proxy.getClass());
return proxy;
}
}
return null;//calculator时候因为前面好多null,所以会执行到这里返回空
}
//
protected boolean isInfrastructureClass(Class<?> beanClass) {
boolean retVal = Advice.class.isAssignableFrom(beanClass) || //Advice
Pointcut.class.isAssignableFrom(beanClass) || //PointCut
Advisor.class.isAssignableFrom(beanClass) || //Advisor
AopInfrastructureBean.class.isAssignableFrom(beanClass);
return retVal;
}
//
protected boolean shouldSkip(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) {
// TODO: Consider optimization by caching the list of the aspect names
List<Advisor> candidateAdvisors = findCandidateAdvisors();//增强器,就是我们切面里的通知方法//把通知方法封装在了Advisor增强器里//4个logstart logend ...//每个封装的通知方法的增强器是InstantiationModelAwarePointcutAdvisor
for (Advisor advisor : candidateAdvisors) {
if (advisor instanceof AspectJPointcutAdvisor) {
//判断增强器是不是这个类型的,而是InstantiationModelAwarePointcutAdvisor类型的,所以不进入
if (((AbstractAspectJAdvice) advisor.getAdvice()).getAspectName().equals(beanName)) {
return true;
}
}
}
return super.shouldSkip(beanClass, beanName);//调用父类的showSkip,而父类直接return false;//所以calculator时返回false
}
从上步到下步中间还有挺多步骤,尚硅谷没有讲清。我们从postProcessBeforeInstantiation出来后,没有处理bean,所以bean还是为null。回到applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInstantiation后,for完还是为null,所以回到resolveBeforeInstantiation。而因为applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInstantiation的结果bean为null,所以resolveBeforeInstantiation方法中的postProcessAfterInitialization执行不到,直接跳出resolveBeforeInstantiation回到createBean,因为resolve结果为null所以中间不会调出,往下执行doCreateBean。然后doCreateBean经过了createBeanInstance、populateBean、initializeBean,然后进入initializeBean方法。initializeBean方法中依次执行invokeAwareMethods、applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization、invokeInitMethods、postProcessAfterInitialization,我们执行的是这里的postProcessAfterInitialization。
4 postProcessAfterInitialization
虽然这个方法挺有用,但不是在这里很有用,我们放到后面吧,
注意正是在这里完成动态代理的
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
if (bean != null) {
// 用给定bean的name和class封装为一个cacheKey
Object cacheKey = getCacheKey(bean.getClass(), beanName);//bean的名字
// 1.判断当前bean是否需要被代理,如果需要则进行封装
if (!this.earlyProxyReferences.contains(cacheKey)) {
//早期代理引用?之前代理过没有,这里calculator从docreateBean走过来之后,为null,进入if
// 封装
return wrapIfNecessary(bean, beanName, cacheKey);//如果需要就包装,calculator进入//返回了采用CGLIB增强了的代理对象
}
}
return bean;//给容器中返回当前组件使用cglib增强了的代理对象,执行目标方法的时候,代理对象就会执行通知方法的流程
}
- postProcessAfterInitialization
- wrapIfNecessary 如果需要代理就包装成代理
- isInfrastructureClass
- shouldSkip
- getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean 获取当前bean的所有Advisor增强器
- findEligibleAdvisors
- findAdvisorsThatCanApply
- findEligibleAdvisors
- createProxy 创建代理替换原来的bean
- wrapIfNecessary 如果需要代理就包装成代理
二、wrapIfNecessary
1 doCreateBean
- createBean
- resolveBeforeInstantiation
- applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInstantiation:实例化前处理,这里大多数没有返回值
- applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization:如果上一步有返回值才调用这个
- doCreateBean,
- createBeanInstance:创建实例,
- populateBean:属性赋值
- initializeBean:初始化,而我们的后置处理器就是在初始化前后进行工作的,所以我们点进去这个方法
- invokeAwareMethods:注入set方法
- applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization:初始化前
- invokeInitMethods:正常实例化功能
- applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization:初始化后
- resolveBeforeInstantiation
2 wrapIfNecessary
本方法的作用是看看当前bean需不需要被动态代理
//AbstractAutoProxyCreator.java
protected Object wrapIfNecessary(Object bean, String beanName, Object cacheKey) {
// 1.判断当前bean是否在targetSourcedBeans缓存中存在(已经处理过),如果存在,则直接返回当前bean
// 已经代理过
if (beanName != null && this.targetSourcedBeans.contains(beanName)) {
//calculator不进入
return bean;
}
// 2.在advisedBeans缓存中存在,并且value为false,则代表无需处理 // 无需代理
if (Boolean.FALSE.equals(this.advisedBeans.get(cacheKey))) {
//calculator不进入,增强过的bean里没有calculator
return bean;
}
// 3.bean的类是aop基础设施类,基础类不应代理 || 指定了bean不需要自动代理
if (isInfrastructureClass(bean.getClass()) ||
shouldSkip(bean.getClass(), beanName)) {
//calculator不进入if
// 标记为false,放到缓存中就知道他无需代理了
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE);
return bean;
}
// 4.获取当前bean适用的Advices和Advisors 拦截器 // ExposeInvocationInterceptor、InstantiationModelAwarePointcutAdvisorImpl(这个类型是我们标注的通知。有属性aspectJAdviceMethod/aspectJAdvisorFactory/instantiatedAdvice)
Object[] specificInterceptors = getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(bean.getClass(), beanName, null);//拦截器,拦截目标方法执行
// 5.如果存在增强器则创建代理
if (specificInterceptors != DO_NOT_PROXY) {
//上个结果不为"不代理",即该bean需要代理
// 拦截器链不为空,标记当前bean需要代理,放到已增强缓存列表中,为true
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.TRUE);
// 5.1 创建代理对象:
// 用于最后增加逻辑执行完毕后,通过反射执行我们真正的方法时使用(method.invoke(bean, args))
Object proxy = createProxy(
bean.getClass(),
beanName,
specificInterceptors, // 处理逻辑
new SingletonTargetSource(bean));// 传入被代理对象,即我们前面已经创建的bean对象
//得到的是一个MathCalculator$$EnhanceBySpringBGLIB 或者 Proxy$XX之类的
// 5.2 创建完代理后,将cacheKey -> 代理类的class放到缓存
this.proxyTypes.put(cacheKey, proxy.getClass());//如果当前bean需要增强,创建代理对象
return proxy;
}
// 6.标记为无需处理 // 没有拦截器链
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE);//放到增强bean中
return bean;
}
InstantiationModelAwarePointcutAdvisorImpl.java
// 作为拦截器(实例)的通知类(类型)
final class InstantiationModelAwarePointcutAdvisorImpl
implements InstantiationModelAwarePointcutAdvisor, AspectJPrecedenceInformation, Serializable {
private static final Advice EMPTY_ADVICE = new Advice() {
};
private final AspectJExpressionPointcut declaredPointcut;
private final Class<?> declaringClass;
private final String methodName;
private final Class<?>[] parameterTypes;
private transient Method aspectJAdviceMethod;
private final AspectJAdvisorFactory aspectJAdvisorFactory;
private final MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory aspectInstanceFactory;
private final int declarationOrder;
private final String aspectName;
private final Pointcut pointcut;
private final boolean lazy;
@Nullable
private Advice instantiatedAdvice;
@Nullable
private Boolean isBeforeAdvice;
@Nullable
private Boolean isAfterAdvice;
1 获取可用增强器getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean
获取该bean所有的增强器
拿到符合条件的通知
//AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator
protected Object[] getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName, TargetSource targetSource) {
// 上面第三个参数传入null
// 1.找到符合条件的Advisor // 已排好序
List<Advisor> advisors = findEligibleAdvisors(beanClass, beanName);
// 2.如果没有符合条件的Advisor,则返回null
if (advisors.isEmpty()) {
return DO_NOT_PROXY;//即null//上面没有找到适合当前对象的通知方法,自然不创建代理对象了
}
return advisors.toArray();//有增强器,返回该bean的通知(增强器)
}
findEligibleAdvisors
- findCandidateAdvisors
- findAdvisorsThatCanApply
protected List<Advisor> findEligibleAdvisors(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) {
//找哪些通知方法是需要切入当前bean方法的
// 1.查找所有的候选Advisor
List<Advisor> candidateAdvisors = findCandidateAdvisors();
// 2.从所有候选的Advisor中找出符合条件的
List<Advisor> eligibleAdvisors = findAdvisorsThatCanApply(candidateAdvisors, beanClass, beanName);
// 3.扩展方法,留给子类实现
extendAdvisors(eligibleAdvisors);
// 4.如果找到了符合条件的Advisor,还要将这些Advisor排序
if (!eligibleAdvisors.isEmpty()) {
eligibleAdvisors = sortAdvisors(eligibleAdvisors);//调用通知方法是由顺序的
}
return eligibleAdvisors;
}
1.1findCandidateAdvisors()
- 获取所有beanName,这一步骤中所有beanFactory中注册的bean都会被提取出来
- 遍历所有beanName,并找出声明AspectJ注解的类,进行进一步的吹了
- 对标记为AspectJ注解的类进行增强器的获取
- 将提取结果加入缓存
//AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator
@Override
protected List<Advisor> findCandidateAdvisors() {
// 根据父类的规则添加配置文件中的AOP声明
List<Advisor> advisors = super.findCandidateAdvisors();//AstractAdvisorAutoProxyCreater
// 在获取增强的方法中除了保留父类的获取配置文件中定义的增强外,同时添加了获取Bean的注解增强的功能,那么其实现正是由this.aspectJAdvisors.buildAspectJAdvisors()
// 添加bean工厂中所有标记为Apsect类中的所有通知
if (this.aspectJAdvisorsBuilder != null) {
advisors.addAll(this.aspectJAdvisorsBuilder.buildAspectJAdvisors());
}
return advisors;
}
protected List<Advisor> findCandidateAdvisors() {
Assert.state(this.advisorRetrievalHelper != null, "No BeanFactoryAdvisorRetrievalHelper available");
return this.advisorRetrievalHelper.findAdvisorBeans();
}
//BeanFactoryAspectJAdvisorsBuilder
public List<Advisor> buildAspectJAdvisors() {
List<String> aspectNames = this.aspectBeanNames;
if (aspectNames == null) {
synchronized (this) {
aspectNames = this.aspectBeanNames;
if (aspectNames == null) {
List<Advisor> advisors = new ArrayList<>();
aspectNames = new ArrayList<>();
// 获取所有beanName
String[] beanNames = BeanFactoryUtils.beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors(
this.beanFactory, Object.class, true, false);
// 循环所有的beanName找出对应的增强方法
for (String beanName : beanNames) {
// 不合法的bean则略过,由子类定义规则,默认返回true
if (!isEligibleBean(beanName)) {
continue;
}
// 获取beanName对应的bean的类型 // 别饿汉式实例化bean,以防他们还没被织入就被容器缓存
Class<?> beanType = this.beanFactory.getType(beanName);
if (beanType == null) {
continue;
}
// 如果存在AspectJ注解
if (this.advisorFactory.isAspect(beanType)) {
// 把切面bean的name假如到aspectNames列表中
aspectNames.add(beanName);
AspectMetadata amd = new AspectMetadata(beanType, beanName);
if (amd.getAjType().getPerClause().getKind() == PerClauseKind.SINGLETON) {
MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory factory =
new BeanFactoryAspectInstanceFactory(this.beanFactory, beanName);
// 解析标记AspectJ注解中的增强方法 // 重要 // 解析的是指定的beanName
List<Advisor> classAdvisors = this.advisorFactory.getAdvisors(factory);
if (this.beanFactory.isSingleton(beanName)) {
// 放入到通知缓存中
this.advisorsCache.put(beanName, classAdvisors);
}
else {
this.aspectFactoryCache.put(beanName, factory);
}
// 添加到总的通知列表中 // 保存了全部bean的通知
advisors.addAll(classAdvisors);
}
else {
// Per target or per this.
if (this.beanFactory.isSingleton(beanName)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Bean with name '" + beanName +
"' is a singleton, but aspect instantiation model is not singleton");
}
MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory factory =
new PrototypeAspectInstanceFactory(this.beanFactory, beanName);
this.aspectFactoryCache.put(beanName, factory);
advisors.addAll(this.advisorFactory.getAdvisors(factory));
}
}
}
this.aspectBeanNames = aspectNames;
return advisors;
}
}
}
}
下面getAdvisors()函数中首先完成了堆增强器的获取,包括获取注解以及根据注解生成增强的步骤,然后考虑到在配置中可能会将增强配置成延迟初始化,那么需要在首位加入同步实例化增强器以保证增强使用之前的实例化,最后是对DeclareParents注解的获取
//ReflectiveAspectJAdvisorFactory
@Override
public List<Advisor> getAdvisors(MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory aspectInstanceFactory) {
// 获取标记为AspectJ的类
Class<?> aspectClass = aspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().getAspectClass();
// 获取标记为AspectJ的name
String aspectName = aspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().getAspectName();
// 验证
validate(aspectClass);
// We need to wrap the MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory with a decorator
// so that it will only instantiate once.
MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory lazySingletonAspectInstanceFactory =
new LazySingletonAspectInstanceFactoryDecorator(aspectInstanceFactory);
List<Advisor> advisors = new ArrayList<>();
// 循环遍历除pointcuts之外的方法
for (Method method : getAdvisorMethods(aspectClass)) {
// 壹>> 普通增强器的获取
Advisor advisor = getAdvisor(method, lazySingletonAspectInstanceFactory, advisors.size(), aspectName);
if (advisor != null) {
advisors.add(advisor);
}
}
// 如果寻找的增强器不为空而且又配置了增强延迟初始化,那么需要在首位加入同步实例化增强器
// If it's a per target aspect, emit the dummy instantiating aspect.
if (!advisors.isEmpty() && lazySingletonAspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().isLazilyInstantiated()) {
Advisor instantiationAdvisor = new SyntheticInstantiationAdvisor(lazySingletonAspectInstanceFactory);
advisors.add(0, instantiationAdvisor);
}
// 获取DeclareParents注解
// Find introduction fields.
for (Field field : aspectClass.getDeclaredFields()) {
Advisor advisor = getDeclareParentsAdvisor(field);
if (advisor != null) {
advisors.add(advisor);
}
}
return advisors;
}
//--------------
private List<Method> getAdvisorMethods(Class<?> aspectClass) {
final List<Method> methods = new ArrayList<>();
ReflectionUtils.doWithMethods(aspectClass, method -> {
// Exclude pointcuts // 声明为PiontCut的方法不处理
if (AnnotationUtils.getAnnotation(method, Pointcut.class) == null) {
methods.add(method);
}
}, ReflectionUtils.USER_DECLARED_METHODS);
methods.sort(METHOD_COMPARATOR);
return methods;
}
//--------------
寻找增强器之 — 壹 普通增强器的获取
// ReflectiveAspectJAdvisorFactory
@Override
@Nullable
public Advisor getAdvisor(Method candidateAdviceMethod, MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory aspectInstanceFactory,
int declarationOrderInAspect, String aspectName) {
validate(aspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().getAspectClass());
// 对切点注解的获取
AspectJExpressionPointcut expressionPointcut = getPointcut(
candidateAdviceMethod,
aspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().getAspectClass());
if (expressionPointcut == null) {
return null;
}
// 根据切点信息生成增强器
return new InstantiationModelAwarePointcutAdvisorImpl(
expressionPointcut,
candidateAdviceMethod,
this,
aspectInstanceFactory,
declarationOrderInAspect,
aspectName);
}
壹.1 切点信息的获取
所有获取切点信息就是获取注解的表达式信息的获取,如@Before(“test()”)
// ReflectiveAspectJAdvisorFactory
@Nullable
private AspectJExpressionPointcut getPointcut(Method candidateAdviceMethod, Class<?> candidateAspectClass) {
// 获取方法上的注解
AspectJAnnotation<?> aspectJAnnotation =
AbstractAspectJAdvisorFactory.findAspectJAnnotationOnMethod(candidateAdviceMethod);
if (aspectJAnnotation == null) {
return null;
}
// 使用AspectJExpressionPointcut实例封装获取的信息
AspectJExpressionPointcut ajexp =
new AspectJExpressionPointcut(candidateAspectClass, new String[0], new Class<?>[0]);
// 提取得到的注解中的表达式:如@PointCut("execution(* *.*test*(..))")中的"execution(* *.*test*(..))"
ajexp.setExpression(aspectJAnnotation.getPointcutExpression());
if (this.beanFactory != null) {
ajexp.setBeanFactory(this.beanFactory);
}
return ajexp;
}
//----------AbstractAspectJAdvisorFactory
@Nullable
protected static AspectJAnnotation<?> findAspectJAnnotationOnMethod(Method method) {
// 设置敏感的注解类
for (Class<?> clazz : ASPECTJ_ANNOTATION_CLASSES) {
/*
private static final Class<?>[] ASPECTJ_ANNOTATION_CLASSES =
new Class<?>[] {
Pointcut.class,
Around.class,
Before.class,
After.class,
AfterReturning.class,
AfterThrowing.class};
*/
AspectJAnnotation<?> foundAnnotation = findAnnotation(method, (Class<Annotation>) clazz);
if (foundAnnotation != null) {
return foundAnnotation;
}
}
return null;
}
// AbstractAspectJAdvisorFactory
@Nullable // 获取指定的方法的注解并使用AspectJAnnotation封装
private static <A extends Annotation> AspectJAnnotation<A> findAnnotation(Method method, Class<A> toLookFor) {
A result = AnnotationUtils.findAnnotation(method, toLookFor);
if (result != null) {
return new AspectJAnnotation<>(result);
}
else {
return null;
}
}
壹.2 根据切点信息生成增强
所有的增强都由Advisor的实现类InstantionModelAwarePointcutAdvisorImpl统一封装的
// InstantiationModelAwarePointcutAdvisorImpl
// 构造器
public InstantiationModelAwarePointcutAdvisorImpl(AspectJExpressionPointcut declaredPointcut,
Method aspectJAdviceMethod, AspectJAdvisorFactory aspectJAdvisorFactory,
MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory aspectInstanceFactory, int declarationOrder, String aspectName) {
this.declaredPointcut = declaredPointcut;
this.declaringClass = aspectJAdviceMethod.getDeclaringClass();
this.methodName = aspectJAdviceMethod.getName();
this.parameterTypes = aspectJAdviceMethod.getParameterTypes();
this.aspectJAdviceMethod = aspectJAdviceMethod;
this.aspectJAdvisorFactory = aspectJAdvisorFactory;
this.aspectInstanceFactory = aspectInstanceFactory;
this.declarationOrder = declarationOrder;
this.aspectName = aspectName;
if (aspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().isLazilyInstantiated()) {
// Static part of the pointcut is a lazy type.
Pointcut preInstantiationPointcut = Pointcuts.union(
aspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().getPerClausePointcut(), this.declaredPointcut);
// Make it dynamic: must mutate from pre-instantiation to post-instantiation state.
// If it's not a dynamic pointcut, it may be optimized out
// by the Spring AOP infrastructure after the first evaluation.
this.pointcut = new PerTargetInstantiationModelPointcut(
this.declaredPointcut, preInstantiationPointcut, aspectInstanceFactory);
this.lazy = true;
}
else {
// A singleton aspect.
this.pointcut = this.declaredPointcut;
this.lazy = false;
//
this.instantiatedAdvice = instantiateAdvice(this.declaredPointcut);
}
}
// InstantiationModelAwarePointcutAdvisorImpl
private Advice instantiateAdvice(AspectJExpressionPointcut pointcut) {
Advice advice = this.aspectJAdvisorFactory.getAdvice(this.aspectJAdviceMethod, pointcut,
this.aspectInstanceFactory, this.declarationOrder, this.aspectName);
return (advice != null ? advice : EMPTY_ADVICE);
}
//---------------
//ReflectiveAspectJAdvisorFactory
@Override
@Nullable
public Advice getAdvice(Method candidateAdviceMethod, AspectJExpressionPointcut expressionPointcut,
MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory aspectInstanceFactory, int declarationOrder, String aspectName) {
Class<?> candidateAspectClass = aspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().getAspectClass();
validate(candidateAspectClass);
AspectJAnnotation<?> aspectJAnnotation =
AbstractAspectJAdvisorFactory.findAspectJAnnotationOnMethod(candidateAdviceMethod);
if (aspectJAnnotation == null) {
return null;
}
// If we get here, we know we have an AspectJ method.
// Check that it's an AspectJ-annotated class
if (!isAspect(candidateAspectClass)) {
throw new AopConfigException("Advice must be declared inside an aspect type: " +
"Offending method '" + candidateAdviceMethod + "' in class [" +
candidateAspectClass.getName() + "]");
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Found AspectJ method: " + candidateAdviceMethod);
}
AbstractAspectJAdvice springAdvice;
switch (aspectJAnnotation.getAnnotationType()) {
case AtPointcut:
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Processing pointcut '" + candidateAdviceMethod.getName() + "'");
}
return null;
case AtAround:
springAdvice = new AspectJAroundAdvice(
candidateAdviceMethod, expressionPointcut, aspectInstanceFactory);
break;
// @Before
case AtBefore:
springAdvice = new AspectJMethodBeforeAdvice(
candidateAdviceMethod, expressionPointcut, aspectInstanceFactory);
break;
case AtAfter:
springAdvice = new AspectJAfterAdvice(
candidateAdviceMethod, expressionPointcut, aspectInstanceFactory);
break;
case AtAfterReturning:
springAdvice = new AspectJAfterReturningAdvice(
candidateAdviceMethod, expressionPointcut, aspectInstanceFactory);
AfterReturning afterReturningAnnotation = (AfterReturning) aspectJAnnotation.getAnnotation();
if (StringUtils.hasText(afterReturningAnnotation.returning())) {
springAdvice.setReturningName(afterReturningAnnotation.returning());
}
break;
case AtAfterThrowing:
springAdvice = new AspectJAfterThrowingAdvice(
candidateAdviceMethod, expressionPointcut, aspectInstanceFactory);
AfterThrowing afterThrowingAnnotation = (AfterThrowing) aspectJAnnotation.getAnnotation();
if (StringUtils.hasText(afterThrowingAnnotation.throwing())) {
springAdvice.setThrowingName(afterThrowingAnnotation.throwing());
}
break;
default:
throw new UnsupportedOperationException(
"Unsupported advice type on method: " + candidateAdviceMethod);
}
// Now to configure the advice...
springAdvice.setAspectName(aspectName);
springAdvice.setDeclarationOrder(declarationOrder);
String[] argNames = this.parameterNameDiscoverer.getParameterNames(candidateAdviceMethod);
if (argNames != null) {
springAdvice.setArgumentNamesFromStringArray(argNames);
}
springAdvice.calculateArgumentBindings();
return springAdvice;
}
//AspectJMethodBeforeAdvice
public class AspectJMethodBeforeAdvice extends AbstractAspectJAdvice implements MethodBeforeAdvice, Serializable {
public AspectJMethodBeforeAdvice(
Method aspectJBeforeAdviceMethod, AspectJExpressionPointcut pointcut, AspectInstanceFactory aif) {
super(aspectJBeforeAdviceMethod, pointcut, aif);
}
@Override
public void before(Method method, Object[] args, @Nullable Object target) throws Throwable {
//
invokeAdviceMethod(getJoinPointMatch(), null, null);
}
@SuppressWarnings("serial")
public class MethodBeforeAdviceInterceptor implements MethodInterceptor, BeforeAdvice, Serializable {
private final MethodBeforeAdvice advice;
/**
* Create a new MethodBeforeAdviceInterceptor for the given advice.
* @param advice the MethodBeforeAdvice to wrap
*/
public MethodBeforeAdviceInterceptor(MethodBeforeAdvice advice) {
Assert.notNull(advice, "Advice must not be null");
this.advice = advice;
}
@Override
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation mi) throws Throwable {
// 重要方法
this.advice.before(mi.getMethod(), mi.getArguments(), mi.getThis());
return mi.proceed();
}
}
//-------------AspectJMethodBeforeAdvice-
@Override
public void before(Method method, Object[] args, @Nullable Object target) throws Throwable {
invokeAdviceMethod(getJoinPointMatch(), null, null);
}
protected Object invokeAdviceMethod(
@Nullable JoinPointMatch jpMatch, @Nullable Object returnValue, @Nullable Throwable ex)
throws Throwable {
return invokeAdviceMethodWithGivenArgs(argBinding(getJoinPoint(), jpMatch, returnValue, ex));
}
protected Object invokeAdviceMethodWithGivenArgs(Object[] args) throws Throwable {
Object[] actualArgs = args;
if (this.aspectJAdviceMethod.getParameterCount() == 0) {
actualArgs = null;
}
try {
ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(this.aspectJAdviceMethod);
// TODO AopUtils.invokeJoinpointUsingReflection
return this.aspectJAdviceMethod.invoke(this.aspectInstanceFactory.getAspectInstance(), actualArgs);
}
catch (IllegalArgumentException ex) {
throw new AopInvocationException("Mismatch on arguments to advice method [" +
this.aspectJAdviceMethod + "]; pointcut expression [" +
this.pointcut.getPointcutExpression() + "]", ex);
}
catch (InvocationTargetException ex) {
throw ex.getTargetException();
}
}
寻找增强器之 — 贰 增加同步实例化增强器
如果寻找的增强器不为空并且又配置了增强延迟初始化,那么就需要在首位加入同步实例化增强器。同步实例化增强器SyntheticInstantiationAdvisor
// ReflectiveAspectJAdvisorFactory内部类
protected static class SyntheticInstantiationAdvisor extends DefaultPointcutAdvisor {
public SyntheticInstantiationAdvisor(final MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory aif) {
super(aif.getAspectMetadata().getPerClausePointcut(), (MethodBeforeAdvice)
(method, args, target) -> aif.getAspectInstance());
}
}
寻找增强器之 — 叁 获取DeclareParents注解
DeclareParents主要用于音节增强的注解形式的实现,而其实现方式与普通增强很类似,只不过使用DeclareParentsAdvisor对功能进行封装
@Nullable
private Advisor getDeclareParentsAdvisor(Field introductionField) {
DeclareParents declareParents = introductionField.getAnnotation(DeclareParents.class);
if (declareParents == null) {
// Not an introduction field
return null;
}
if (DeclareParents.class == declareParents.defaultImpl()) {
throw new IllegalStateException("'defaultImpl' attribute must be set on DeclareParents");
}
return new DeclareParentsAdvisor(
introductionField.getType(), declareParents.value(), declareParents.defaultImpl());
}
1.2findAdvisorsThatCanApply
前面的函数中已经完成了所以所以增强器的解析,但是对于增强器来讲,并不一定都适用于当前bean,还要挑取出是适合的增强器,也就是满足我们配置的通配符的增强器
----AopUtils.java----;
public static List<Advisor> findAdvisorsThatCanApply(List<Advisor> candidateAdvisors, Class<?> clazz) {
if (candidateAdvisors.isEmpty()) {
return candidateAdvisors;
}
List<Advisor> eligibleAdvisors = new LinkedList<Advisor>();
// 1.首先处理引介增强(@DeclareParents)用的比较少可以忽略,有兴趣的参考:https://www.cnblogs.com/HigginCui/p/6322283.html
for (Advisor candidate : candidateAdvisors) {
if (candidate instanceof IntroductionAdvisor && canApply(candidate, clazz)) {
//不是这个类型的//进不来
eligibleAdvisors.add(candidate);
}
}
boolean hasIntroductions = !eligibleAdvisors.isEmpty();
// 2.遍历所有的candidateAdvisors
for (Advisor candidate : candidateAdvisors) {
// 2.1 引介增强已经处理,直接跳过
if (candidate instanceof IntroductionAdvisor) {
//不是这个类型的,不进入
continue;
}
// 2.2 正常普通bean增强处理,判断当前bean是否可以应用于当前遍历的增强器(bean是否包含在增强器的execution指定的表达式中)
if (canApply(candidate, clazz, hasIntroductions)) {
//匹不匹配,这里用切入点表达式算能不能切入//LogStart等能切入calculator
eligibleAdvisors.add(candidate);//加入到可用通知集合中
}
}
return eligibleAdvisors;
}
----AopUtils.java----;
public static boolean canApply(Advisor advisor,
Class<?> targetClass,
boolean hasIntroductions) {
//false
if (advisor instanceof IntroductionAdvisor) {
return ((IntroductionAdvisor) advisor).getClassFilter().matches(targetClass);
}
// 我们一般进入的是这里
else if (advisor instanceof PointcutAdvisor) {
PointcutAdvisor pca = (PointcutAdvisor) advisor;
return canApply(pca.getPointcut(), targetClass, hasIntroductions);
}
else {
// It doesn't have a pointcut so we assume it applies.
return true;
}
}
----AopUtils.java----;
public static boolean canApply(Pointcut pc, // 重载,一个是advisor,一个是Pointcut
Class<?> targetClass,
boolean hasIntroductions) {
//false
Assert.notNull(pc, "Pointcut must not be null");
if (!pc.getClassFilter().matches(targetClass)) {
return false;
}
MethodMatcher methodMatcher = pc.getMethodMatcher();
if (methodMatcher == MethodMatcher.TRUE) {
// No need to iterate the methods if we're matching any method anyway...
return true;
}
IntroductionAwareMethodMatcher introductionAwareMethodMatcher = null;
if (methodMatcher instanceof IntroductionAwareMethodMatcher) {
introductionAwareMethodMatcher = (IntroductionAwareMethodMatcher) methodMatcher;
}
Set<Class<?>> classes = new LinkedHashSet<Class<?>>(ClassUtils.getAllInterfacesForClassAsSet(targetClass));
classes.add(targetClass);
for (Class<?> clazz : classes) {
Method[] methods = ReflectionUtils.getAllDeclaredMethods(clazz);
for (Method method : methods) {
if ((introductionAwareMethodMatcher != null &&
introductionAwareMethodMatcher.matches(method, targetClass, hasIntroductions)) ||
methodMatcher.matches(method, targetClass)) {
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
三、创建代理createProxy
步骤为:
- 拿到上面可用的拦截器链、
- 创建代理工厂、
- 代理工厂生产代理类配置(根据有没有接口选择创建的代理类型)
- 代理类配置生成代理对象
下面主要是
1创建代理工厂createProxy
要搞懂工厂,我们最好先去看下https://blog.csdn.net/hancoder/article/details/107259143
注意:createProxy()里面也有创建代理对象的逻辑,但是为了学习方法,我们暂且只认为他是创建代理工厂。而创建代理对象的逻辑我们就认为他是拿工厂去创建代理对象即可。
//AbstractAutoProxyCreator.java
protected Object createProxy(//当前bean需要增强,创建代理对象
Class<?> beanClass,
String beanName,
Object[] specificInterceptors,
TargetSource targetSource) {
if (this.beanFactory instanceof ConfigurableListableBeanFactory) {
AutoProxyUtils.exposeTargetClass((ConfigurableListableBeanFactory) this.beanFactory, beanName, beanClass);
}
// 1.创建proxyFactory,proxy的生成主要就是在proxyFactory做的//每组被代理对象和它的advisors都有属于他们组的代理工厂,只要拿到他的代理工厂,就知道要做什么事
ProxyFactory proxyFactory = new ProxyFactory();//代理对象的创建工厂,里面有目标对象+advisors
// 从当前对象复制属性值
proxyFactory.copyFrom(this);
// 检查proxyTargetClass属性,判断对于给定的bean使用类代理还是接口代理,
// proxyTargetClass值默认为false,可以通过proxy-target-class属性设置为true
if (!proxyFactory.isProxyTargetClass()) {
// 检查preserveTargetClass属性,判断beanClass是应该基于类代理还是基于接口代理
if (shouldProxyTargetClass(beanClass, beanName)) {
// 如果是基于类代理,则将proxyTargetClass赋值为true
proxyFactory.setProxyTargetClass(true);
}
else {
// 评估bean的代理接口
evaluateProxyInterfaces(beanClass, proxyFactory);
}
}
// 2.将当前bean适合的advice,重新封装下,封装为Advisor类,然后添加到ProxyFactory中
Advisor[] advisors = buildAdvisors(beanName, specificInterceptors);// 拦截器包装为Advisor[]
// 将advisors添加到proxyFactory
proxyFactory.addAdvisors(advisors);//把advisors增强器保存在代理工厂中
// 设置要代理的类,将targetSource赋值给proxyFactory的targetSource属性,之后可以通过该属性拿到被代理的bean的实例
proxyFactory.setTargetSource(targetSource);
// 自定义ProxyFactory,空方法,留给子类实现
customizeProxyFactory(proxyFactory);
// 用来控制proxyFactory被配置之后,是否还允许修改通知。默认值为false(即在代理被配置之后,不允许修改代理类的配置)
proxyFactory.setFrozen(this.freezeProxy);
if (advisorsPreFiltered()) {
proxyFactory.setPreFiltered(true);
}
// 3.调用getProxy获取bean对应的proxy
return proxyFactory.getProxy(getProxyClassLoader());//用代理工厂帮我们创建对象
}
对于代理类的创建及处理,Spring委托给了ProxyFactory去处理,而在次函数中主要是对ProxyFactory的初始化操作,进而对真正的创建代理做准备,这些初始化操作包括如下内容:
- 获取当前类中的属性
- 添加代理接口
- 封装Advisor并加入到ProxyFactory中
- 设置要代理的类
- 当然在spring中还为子类提供了定制的函数customizeProxyFactory,子类可以在此函数中进行对ProxyFactory的进一步封装
- 进行获取代理操作
代理工厂里封装了advisors、被代理对象的封装targetSource
//ProxyFactory
public Object getProxy(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
return createAopProxy().//生成代理配置类
getProxy(classLoader);//生成代理对象
}
2生成代理类配置createAopProxy()
工厂可以根据我们传入的信息自动判断是创建JDK动态代理还是CGLIB动态代理,我们把选择的信息保存好,然后直接new就出来代理对象了
//-----ProxyCreatorSupport是ProxyFactory的父类----;
protected final synchronized AopProxy createAopProxy() {
// 创建代理
if (!this.active) {
// 1.激活此代理配置
activate();
}
// 2.创建AopProxy
return getAopProxyFactory().createAopProxy(this);//传入ProxyFactory,他是ProxyCreatorSupport的子类
}
//---DefaultAopProxyFactory---;
@Override
public AopProxy createAopProxy(AdvisedSupport config) throws AopConfigException {
//传入ProxyFactory,他是ProxyCreatorSupport的子类
// 1.判断使用JDK动态代理还是Cglib代理
if (config.isOptimize() || // optimize:用于控制通过cglib创建的代理是否使用激进的优化策略。除非完全了解AOP如何处理代理优化,否则不推荐使用这个配置,目前这个属性仅用于cglib代理,对jdk动态代理无效
config.isProxyTargetClass() || // proxyTargetClass:默认为false,设置为true时,强制使用cglib代理,是目标类本身被代理而不是目标类的接口。设置方式:<aop:aspectj-autoproxy proxy-target-class="true" />
hasNoUserSuppliedProxyInterfaces(config)) {
//config是否存在代理接口或者只有SpringProxy一个接口
// 拿到要被代理的对象的类型
Class<?> targetClass = config.getTargetClass();
if (targetClass == null) {
throw ...;}
// 要被代理的对象是接口 || targetClass是Proxy class
// 当且仅当使用getProxyClass方法或newProxyInstance方法动态生成指定的类作为代理类时,才返回true。
if (targetClass.isInterface() || Proxy.isProxyClass(targetClass)) {
//第二个可以在Enable中设置
// JDK动态代理,这边的入参config(AdvisedSupport)实际上是ProxyFactory对象
// 具体为:AbstractAutoProxyCreator中的proxyFactory.getProxy发起的调用,在ProxyCreatorSupport使用了this作为参数,
// 调用了的本方法,这边的this就是发起调用的proxyFactory对象,而proxyFactory对象中包含了要执行的的拦截器
return new JdkDynamicAopProxy(config);//jdk动态代理//需要实现接口 // 传入了代理对象
}
return new ObjenesisCglibAopProxy(config);//CGlib代理//没有实现接口,jdk也没法让他使用动态代理。也可以让他强制使用CGlib
}
else {
return new JdkDynamicAopProxy(config);
}
}
JDK和CGLIB使用方法总结为:
- 如果目标对象实现了接口,默认情况下回采用JDK的动态代理实现AOP
- 如果目标对象实现了接口,可以强制使用CGLIB实现AOP。如
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy proxy-target-class="true" />- 添加CGLIB库放到classpath
- 如果目标对象没有实现接口,必须采用CGLIB库,spring会自动在JDK动态代理和CGLIB之间转换
我们把JDK动态代理和CGLIB的区别放到后面讲,或者可以看https://blog.csdn.net/hancoder/article/details/107259143
3 new代理对象getProxy()
在这里就需要分支了,上一步代理类的配置已经决定了它是JDK动态代理还是CGLIB代理,当然他们创建的对象的类型就不一样的了,但两种代理里面都有getProxy()这个函数,所以两个对象才都能通过getProxy()返回代理对象
- JDK的getProxy()直接就在JdkDynamicAopProxy中
// JdkDynamicAopProxy
public Object getProxy(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Creating JDK dynamic proxy: " + this.advised.getTargetSource());
}
Class<?>[] proxiedInterfaces = AopProxyUtils.completeProxiedInterfaces(this.advised, true);
findDefinedEqualsAndHashCodeMethods(proxiedInterfaces);
// 用jdk自带的动态代理创建代理对象
return Proxy.newProxyInstance(classLoader,
proxiedInterfaces,
this);// 传入JdkDynamicAopProxy对象
}
- CGLIB的getProxy()不在ObjenesisCglibAopProxy中,而是在ObjenesisCglibAopProxy的父类中。
@Override//ObjenesisCglibAopProxy
public Object getProxy(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Creating CGLIB proxy: " + this.advised.getTargetSource());
}
try {
Class<?> rootClass = this.advised.getTargetClass();
Assert.state(rootClass != null, "Target class must be available for creating a CGLIB proxy");
Class<?> proxySuperClass = rootClass;
if (rootClass.getName().contains(ClassUtils.CGLIB_CLASS_SEPARATOR)) {
proxySuperClass = rootClass.getSuperclass();
Class<?>[] additionalInterfaces = rootClass.getInterfaces();
for (Class<?> additionalInterface : additionalInterfaces) {
this.advised.addInterface(additionalInterface);
}
}
// Validate the class, writing log messages as necessary.
validateClassIfNecessary(proxySuperClass, classLoader);
// Configure CGLIB Enhancer...
Enhancer enhancer = createEnhancer();
if (classLoader != null) {
enhancer.setClassLoader(classLoader);
if (classLoader instanceof SmartClassLoader &&
((SmartClassLoader) classLoader).isClassReloadable(proxySuperClass)) {
enhancer.setUseCache(false);
}
}
enhancer.setSuperclass(proxySuperClass);
enhancer.setInterfaces(AopProxyUtils.completeProxiedInterfaces(this.advised));
enhancer.setNamingPolicy(SpringNamingPolicy.INSTANCE);
enhancer.setStrategy(new ClassLoaderAwareGeneratorStrategy(classLoader));
Callback[] callbacks = getCallbacks(rootClass);
Class<?>[] types = new Class<?>[callbacks.length];
for (int x = 0; x < types.length; x++) {
types[x] = callbacks[x].getClass();
}
// fixedInterceptorMap only populated at this point, after getCallbacks call above
enhancer.setCallbackFilter(new ProxyCallbackFilter(
this.advised.getConfigurationOnlyCopy(), this.fixedInterceptorMap, this.fixedInterceptorOffset));
enhancer.setCallbackTypes(types);
// Generate the proxy class and create a proxy instance.
return createProxyClassAndInstance(enhancer, callbacks);
}
catch (CodeGenerationException | IllegalArgumentException ex) {
throw new AopConfigException("Could not generate CGLIB subclass of " + this.advised.getTargetClass() +
": Common causes of this problem include using a final class or a non-visible class",
ex);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
// TargetSource.getTarget() failed
throw new AopConfigException("Unexpected AOP exception", ex);
}
}
//---------------------------
protected Object createProxyClassAndInstance(Enhancer enhancer, Callback[] callbacks) {
enhancer.setInterceptDuringConstruction(false);
enhancer.setCallbacks(callbacks);
return (this.constructorArgs != null && this.constructorArgTypes != null ?
enhancer.create(this.constructorArgTypes, this.constructorArgs) :
enhancer.create());
}
四、动态代理
对动态代理不熟悉的看这里:https://blog.csdn.net/hancoder/article/details/107259143
首先,我们知道Spring AOP的底层实现有两种方式:一种是JDK动态代理,另一种是CGLib的方式。
- JDK动态代理:其代理读一下必须是某个接口的实现,它是通过在运行期间创建一个接口的实现类来完成对目标对象的代理。意思是说,运行期间会在内存中生成一个代理类,他实现了接口,并没有实现我们原来的目标类。
- spring中先创建最初的目标对象,然后生成新的目标对象class,然后注册到容器中,代替原来的bean。beanName不变,而BeanClass改变
- 涉及java.lang.reflect包下边的两个类:Proxy和InvocationHandler。其中,InvocationHandler是一个接口,可以通过实现该接口定义横切逻辑,并通过反射机制调用目标类的代码,动态地将横切逻辑和业务逻辑贬值在一起。
- CGLIB动态代理:实现原理类似于JDK动态代理,只是它在运行期间生成的代理对象是目标类的子类,覆盖其中的方法。意思是说,他的父类是目标类,我们就能用目标类接收(多态),而JDK动态代理只能动接口接收,不能用目标类接收。因为是继承,所以改类和方法最好不要声明为final
- Code Generation Library
- 底层依赖ASM(开源的Java字节码编辑类库)操作字节码
- CGLib可以为一个类创建一个子类,在子类中采用方法拦截的技术拦截所有父类方法的调用并顺势织入横切逻辑。
需要先看一看这篇jdk动态代理博客:https://blog.csdn.net/hancoder/article/details/107259143
然后看spring的步骤才比较简单
动态代理jdk/cglib区别
- JDK动态代理:通过反射来接收被代理的类,并且被代理的类必须实现接口;
核心是:java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler接口 与 java.lang.reflect.Proxy类; - CGLIB动态代理:目标类没有实现接口,Spring AOP会选择使用CGLIB在运行时动态的生成某个类的子类,因此,CGLIB是通过继承的方式,用子类实现对目标类的增强,final class不可继承的类,无法使用CGLIB做动态代理。
- Spring的AOP与IOC:Spring AOP对象由Spring IOC容器自动生成、管理,其依赖关系也由IOC容器负责管理,那么AOP对象可以直接使用容器中的其他Bean实例作为被代理对象,所以此时使用SpringAOP只需要定义切点(pointcut)和 增强(advice)即可。
- AOP代理的方法通过在目标对象的切入点动态的织入增强处理,完成对目标方法的增强。
AOP继承树
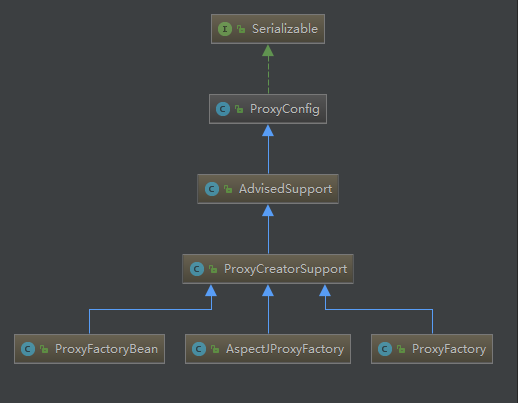
-
ProxyConfig类:所有Spring AOP生成的代理对象的基类,主要为其AOP代理对象工厂实现类提供配置属性。
-
AdvisedSupport类:ProxyConfig类的子类,封装了AOP中通用的对增强(Advice)和通知器(Advisor)的相关操作,对于所有生成AOP代理对象都通用,而代理对象的生成由子类完成;
-
ProxyCreatorSupport类:AdvisedSupport类的子类,一个AOP对象创建的辅助类,提供不同的AOP代理对象生成的通用方法,而代理对象的生成由其子类完成。
- 属性:aopProxyFactory
-
实际创建AOP对象的类:AspectJProxyFactory、ProxyFactory、ProxyFactoryBean;工厂类;ProxyCreatorSupport的子类;
-
AspectJProxyFactory:创建AspectJ的AOP对象,用于Spring集成AspectJ的作用,此时,就不需要使用AspectJ特定的编译器了。
-
ProxyFactory:创建编程式的AOP对象;
-
ProxyFactoryBean:创建声明式的AOP对象,通过配置创建AOP对象
-
ProxyFactoryBean的功能: 初始化通知器链 获取单例、原型的Aop代理对象 <!-- 切面 --> <bean id="logAdvice" class="com.test.advice.LogAdvice"/> <!--配置AOP代理工厂,封装AOP功能的主要类--> <bean id="requestProxy" class="org.springframework.aop.framework.ProxyFactoryBean"> <!-- AOP 代理接口 --> <property name="proxyInterfaces"> <value>com.test.Request</value> </property> <!-- 需要增强的对象 --> <property name="target"> <bean class="com.test.StringRequest" /> </property> <!--代理拦截器,配置通知器的名称,即通知器在AOP代理的配置下通过使用代理对象的拦截机制发挥作用--> <property name="interceptorNames"> <list> <value>logAdvice</value> </list> </property> <!-- 是否接口类:true说明ProxyFactoryBean要代理的不是接口类,而是CGLIB方式来进行代理 --> <property name="proxyTargetClass" value="false"/> </bean>
-
-
(1)创建代理对象JdkDynamicAopProxy/ObjenesisCglibAopProxy
上面的invoke、register、finish都是我们AnnotationConfigApplicationContext ac = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(MainConfigOfAOP.class);这条语句中的fresh()中执行的,那么我们往下执行到mathCalculator.div(1, 1);会发生什么呢?
研究我们执行calculator.div()方法时的执行流程,给div打断点,然后我们进入div方法,实际上此时进入的并不是div方法,因为代理类只在内存中,你一般看不到,但为了容易理解,我们特意把内部中的内存保存下来,如下,你就看到了实际上执行的div
getBean拿到的是代理类
// 代理类:代理类会利用jdk动态代理类
public final class $Proxy33 extends Proxy implements CalculatorFather, SpringProxy, Advised, DecoratingProxy {
private static Method m3 = Class.forName("com.atguigu.aop.CalculatorFather").getMethod("div", Integer.TYPE, Integer.TYPE);
public final int div(int var1, int var2) throws {
try {
// 调用父类Proxy中的invocationHandler【h】
return (Integer)super.h.invoke(this, // 代理对象
m3, // 接口div方法
new Object[]{
var1, var2});// 传入的参数
} catch (RuntimeException | Error var4) {
throw var4;
} catch (Throwable var5) {
throw new UndeclaredThrowableException(var5);
}
}
可以看到他基本是一个空方法,除了一句super.h.invoke(),他是调用的父类Proxy中h属性的方法,也就是JdkDynamicAopProxy中的invoke。而JdkDynamicAopProxy的invoke会就是java底层的东西了,这在之前的文章里说过。
当我们调用了被 AOP 代理的方法时,使用 JDK 动态代理会走到 JdkDynamicAopProxy#invoke 方法,使用 cglib 代理会走到 DynamicAdvisedInterceptor#intercept 方法,两者的内容基本一样,下面我们分别说:
JdkDynamicAopProxy.invoke

我们之前helloworld的时候是自己写的handler,所以invoke比较简单,但也传入了3个参数:proxy将来的代理对象+method目标方法+方法参数,同时this里有目标方法
final class JdkDynamicAopProxy implements AopProxy, InvocationHandler, Serializable {
//InvocationHandler
// 构造器
public JdkDynamicAopProxy(AdvisedSupport config) throws AopConfigException {
Assert.notNull(config, "AdvisedSupport must not be null");
if (config.getAdvisors().length == 0 && config.getTargetSource() == AdvisedSupport.EMPTY_TARGET_SOURCE) {
throw new AopConfigException("No advisors and no TargetSource specified");
}
this.advised = config;
}
@Override // 关于代理对象的任何方法都会传到这里
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
MethodInvocation invocation;
Object oldProxy = null;
boolean setProxyContext = false;
// 1.advised就是proxyFactory,而targetSource持有目标对象的引用
TargetSource targetSource = this.advised.targetSource;
Class<?> targetClass = null;
Object target = null;
try {
// equals方法处理
if (!this.equalsDefined && AopUtils.isEqualsMethod(method)) {
// The target does not implement the equals(Object) method itself.
// 目标不实现equals(Object)方法本身。
return equals(args[0]);
}
// hashCode处理
else if (!this.hashCodeDefined && AopUtils.isHashCodeMethod(method)) {
// The target does not implement the hashCode() method itself.
return hashCode();
} else if (method.getDeclaringClass() == DecoratingProxy.class) {
// There is only getDecoratedClass() declared -> dispatch to proxy config.
// 只有getDecoratedClass()声明 - > dispatch到代理配置。
return AopProxyUtils.ultimateTargetClass(this.advised);
}
//Advised接口或者其父接口中定义的方法,直接反射调用
else if (!this.advised.opaque &&
method.getDeclaringClass().isInterface() &&
method.getDeclaringClass().isAssignableFrom(Advised.class)) {
// Service invocations on ProxyConfig with the proxy config...
// ProxyConfig上的服务调用与代理配置...
return AopUtils.invokeJoinpointUsingReflection(this.advised, method, args);
}
Object retVal;
// 目标对象内部调用是无法实现增强的,需要暴露代理,此时需要exposeProxy设置为true// 这个参数和事务有关,目标对象内部的自我调用将无法实施切面中的增强则需要通过此属性暴露代理
if (this.advised.exposeProxy) {
oldProxy = AopContext.setCurrentProxy(proxy);
setProxyContext = true;
}
// 2.拿到我们被代理的对象实例 //以防target来自对象池,所以在创建代理前调用get获取target
target = targetSource.getTarget();
if (target != null) {
targetClass = target.getClass();
}
// 3.获取拦截器链:例如使用@Around注解时会找到AspectJAroundAdvice,还有ExposeInvocationInterceptor
// 常见的有ExposeInvocationInterceptor、AspectJAroundAdvice、AspectJAfterAdvice、AspectJReturningAdvice、AspectJBeforeAdvice、AspectJAfterThrowingAdvice
List<Object> chain = this.advised.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(method, targetClass);
// advised:属性AdvisedSupport advised,构造函数传入的时候AdvisedSupport config自动复制给advised
// 4.检查我们是否有任何拦截器(advice)。 如果没有,直接反射调用目标,并避免创建MethodInvocation。
if (chain.isEmpty()) {
Object[] argsToUse = AopProxyUtils.adaptArgumentsIfNecessary(method, args);
// 5.不存在拦截器链,则直接进行反射调用切点方法
retVal = AopUtils.invokeJoinpointUsingReflection(target, method, argsToUse);
} else {
// ===========重点=====
// 6.如果存在拦截器,则创建一个ReflectiveMethodInvocation:代理对象、被代理对象、方法、参数、
// 被代理对象的Class、拦截器链封装为ReflectiveMethodInvocation
invocation = new ReflectiveMethodInvocation(proxy, target, method, args, targetClass,
chain);//传入所有拦截器
// Proceed to the joinpoint through the interceptor chain.
// 7.触发ReflectiveMethodInvocation的执行方法
retVal = invocation.proceed();// 触发拦截器链
}
// Massage return value if necessary.
// 8.必要时转换返回值
Class<?> returnType = method.getReturnType();
if (retVal != null && retVal == target &&
returnType != Object.class && returnType.isInstance(proxy) &&
!RawTargetAccess.class.isAssignableFrom(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
// Special case: it returned "this" and the return type of the method
// is type-compatible. Note that we can't help if the target sets
// a reference to itself in another returned object.
retVal = proxy;
} else if (retVal == null && returnType != Void.TYPE && returnType.isPrimitive()) {
throw new AopInvocationException(
"Null return value from advice does not match primitive return type for: " + method);
}
return retVal;
} finally {
if (target != null && !targetSource.isStatic()) {
// Must have come from TargetSource.
targetSource.releaseTarget(target);
}
if (setProxyContext) {
// Restore old proxy.
AopContext.setCurrentProxy(oldProxy);
}
}
}
上面有两个主要内容:
- 获取当前方法的拦截器链,并封装为ReflectiveMethodInvocation
- 使用封装的拦截器链执行proceed方法:invocation.proceed();
ReflectiveMethodInvocation.proceed();
new ReflectiveMethodInvocation(proxy, target, method, args, targetClass, chain);
//ReflectiveMethodInvocation.java;
public class ReflectiveMethodInvocation implements ProxyMethodInvocation, Cloneable {
protected final Object proxy;
protected final Object target;
protected final Method method;
protected Object[] arguments;
private final Class<?> targetClass;
private Map<String, Object> userAttributes;
protected final List<?> interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers;// 拦截器链
private int currentInterceptorIndex = -1;
protected ReflectiveMethodInvocation(Object proxy, Object target, Method method, Object[] arguments, Class<?> targetClass,
List<Object> interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers) {
//拦截器链
this.proxy = proxy;
this.target = target;
this.targetClass = targetClass;
this.method = BridgeMethodResolver.findBridgedMethod(method);
this.arguments = AopProxyUtils.adaptArgumentsIfNecessary(method, arguments);
this.interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers = interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers;
}
@Override
public Object proceed() throws Throwable {
// 执行完所有增强后执行切点方法
// 初始当前索引为-1,然后自增
if (this.currentInterceptorIndex == this.interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers.size() - 1) {
//-1是否等于5-1,即没有拦截器时if成立
//当前拦截器链为空 或 或者拦截器索引为拦截器链长度-1,即最后一个索引
return invokeJoinpoint();// 简单的method.invoke(target, args);
}
// 获取下一个要执行的拦截器
Object interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice =
this.interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers.get(++this.currentInterceptorIndex);//索引移动//把索引从-1变成0 //先获取到0号拦截器,即ExposeInvocationInterceptor,然后依次为AspectJAfterThrowingAdvice、AfterReturningAdviceInterceptor、AsoectJAfterAdvice、MethodBeforeAdviceInterceptor
// 动态匹配
if (interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice instanceof InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher) {
// Evaluate dynamic method matcher here: static part will already have
// been evaluated and found to match.
InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher dm =
(InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher) interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice;
if (dm.methodMatcher.matches(this.method, this.targetClass, this.arguments)) {
return dm.interceptor.invoke(this);
}
else {
// 不匹配则不执行拦截器
// Dynamic matching failed.
// Skip this interceptor and invoke the next in the chain.
return proceed();
}
}else {
/* 普通拦截器,直接调用拦截器,比如
- ExposeInvocationInterceptor、
- AspectJAfterThrowingAdvice、 抛异常
- AfterReturningAdviceInterceptor、 正常返回
- AspectJAfterAdvice、 后置
- MethodBeforeAdviceInterceptor 前置
*/
return ((MethodInterceptor) interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice).invoke(this);//this为CglibMethodInvocation//里面还会调用proceed
}
}
思路为虽然我们拦截器的顺序是反的,但是因为递归的原因,拦截器是能按序执行的
ExposeInvocationInterceptor.invoke()
//ExposeInvocationInterceptor.java @Override public Object invoke(MethodInvocation mi) throws Throwable { MethodInvocation oldInvocation = invocation.get();//ReflectiveMethodInvocation invocation.set(mi); try { return mi.proceed();// 执行代理对象,即执行cglib的proceed } finally { invocation.set(oldInvocation); } }proceed()
//CglibAopProxy内部类CglibMethodInvocation; public Object proceed() throws Throwable { try { return super.proceed();// 又回到了我们刚出现过的proceed //只不过这回索引也+1变成1了 } catch (RuntimeException ex) { throw ex; } catch (Exception ex) { if (ReflectionUtils.declaresException(getMethod(), ex.getClass())) { throw ex; } else { throw new UndeclaredThrowableException(ex); } } } /* ReflectiveMethodInvocation; @Override public Object proceed() throws Throwable { if (this.currentInterceptorIndex == this.interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers.size() - 1) { return invokeJoinpoint();//不满足 } Object interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice = this.interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers.get(++this.currentInterceptorIndex);//索引移动//把索引从0变成1 //获取到1号拦截器,即 AspectJAfterThrowingAdvice,然后依次为AfterReturningAdviceInterceptor、AsoectJAfterAdvice、MethodBeforeAdviceInterceptor */
然后AspectJAfterThrowingAdvice也重复上面过程
顺序为
- ExposeInvocationInterceptor、
- AspectJAfterThrowingAdvice、
- AfterReturningAdviceInterceptor、
- AspectJAfterAdvice、
- MethodBeforeAdviceInterceptor
直到最后一个MethodBeforeAdviceInterceptor,他的invoke方法与前面的不同
@Override // MethodBeforeAdviceInterceptor.java
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation mi) throws Throwable {
// 多了个before方法,去执行before方法
this.advice.before(mi.getMethod(), mi.getArguments(), mi.getThis());
// 继续执行,执行到下面的函数里的时候,因为索引为size-1了,就直接执行目标方法后return,return到下一个代码块
return mi.proceed(); // 又到ReflectiveMethodInvocation对象的proceed()中了,全局只有一个mi
// return后返回然后依次退栈往回走
}
一直return,知道return到AspectJAfterAdvice.java的时候,我们看看他的invoke方法
@Override
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation mi) throws Throwable {
try {
// 先往下执行,先去后面看正常结束还是异常退出,但无论怎么样都执行下面的后置通知
// 但这里要明确的是proceed是我们来的时候执行的内容,我们回去的时候实际上proceed已经执行完了,直接执行后置通知后返回即可
return mi.proceed();
}
finally {
// 执行后置通知
invokeAdviceMethod(getJoinPointMatch(), null, null);
}
}
执行到AfterReturningAdviceInterceptor时
//AfterReturningAdviceInterceptor
@Override
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation mi) throws Throwable {
//往上层抛异常
Object retVal = mi.proceed();
//开始执行返回通知了
// 上面没有异常才执行后置返回通知,否则执行不到这就直接往上层抛异常了
this.advice.afterReturning(retVal, mi.getMethod(), mi.getArguments(), mi.getThis());
return retVal;
}
//AspectJAfterThrowingAdvice
@Override
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation mi) throws Throwable {
try {
return mi.proceed();
}
// 回来了,看看有没有异常
catch (Throwable ex) {
if (shouldInvokeOnThrowing(ex)) {
invokeAdviceMethod(getJoinPointMatch(), null, ex);
}
throw ex;
}
}
(2)CGLIB动态代理对象的执行逻辑
intercept【cgllib】
CglibAopProxy.intercept()拦截目标方法执行
- intercept()
List<Object> chain = this.advised.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(method, targetClass);- 如果chain为空:methodProxy.invoke(target, argsToUse);
- 如果chain不为空:new CglibMethodInvocation(proxy, target, method, args, targetClass, chain, methodProxy).proceed();
CglibAopProxy内部类DynamicAdvisedInterceptor
private static class CglibAopProxy.DynamicAdvisedInterceptor
implements MethodInterceptor, Serializable {
private final AdvisedSupport advised;
public DynamicAdvisedInterceptor(AdvisedSupport advised) {
this.advised = advised;
}
public Object intercept(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args, MethodProxy methodProxy) throws Throwable {
Object oldProxy = null;
boolean setProxyContext = false;
Class<?> targetClass = null;
Object target = null;
try {
if (this.advised.exposeProxy) {
// Make invocation available if necessary.
oldProxy = AopContext.setCurrentProxy(proxy);
setProxyContext = true;
}
// May be null. Get as late as possible to minimize the time we
// "own" the target, in case it comes from a pool...
target = getTarget();
if (target != null) {
targetClass = target.getClass();
}
// 根据ProxyFactory对象获取将要执行的目标方法拦截器链//获取拦截器和动态拦截通知 //this为proxyFactory // Object类型为MethodInterceptor
List<Object> chain = this.advised.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(method, targetClass);//拦截器链:每一个通知方法又被包装为方法拦截器,方法的执行都是利用MethodInterceptor机制
//拦截器有ExposeInvocationInterceptor、AspectJAfterThrowingAdvice、AfterReturningAdviceInterceptor、AsoectJAfterAdvice、MethodBeforeAdviceInterceptor
Object retVal;
//没有拦截器链,直接执行目标方法
// Check whether we only have one InvokerInterceptor: that is,
// no real advice, but just reflective invocation of the target.
if (chain.isEmpty() && Modifier.isPublic(method.getModifiers())) {
// We can skip creating a MethodInvocation: just invoke the target directly.
// Note that the final invoker must be an InvokerInterceptor, so we know
// it does nothing but a reflective operation on the target, and no hot
// swapping or fancy proxying.
Object[] argsToUse = AopProxyUtils.adaptArgumentsIfNecessary(method, args);
retVal = methodProxy.invoke(target, argsToUse);
}
else {
// 执行到这说明有拦截器链,创建cglib代理对象,值得注意的是java动态代理因为没有拦截器链,所以执行不到这里
//如果有拦截器链,把需要执行的目标对象,目标方法,拦截器链等信息传入创建一个CglibMethodInvocation对象,并调用retval=mi.proceed()方法
// CglibMethodInvocation即处理逻辑
retVal =
new CglibMethodInvocation(proxy, target, method, args, targetClass, chain, methodProxy)//创建对象,
.proceed();//调用proceed方法//拦截器链的触发过程//1
}
retVal = processReturnType(proxy, target, method, retVal);
return retVal;
}
finally {
if (target != null) {
releaseTarget(target);
}
if (setProxyContext) {
// Restore old proxy.
AopContext.setCurrentProxy(oldProxy);
}
}
}
@Override
public boolean equals(@Nullable Object other) {
return (this == other ||
(other instanceof DynamicAdvisedInterceptor &&
this.advised.equals(((DynamicAdvisedInterceptor) other).advised)));
}
/**
* CGLIB uses this to drive proxy creation.
*/
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return this.advised.hashCode();
}
}
(3)获取链getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice
intercept()
- List chain = this.advised.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(method, targetClass);
- List cached = this.advisorChainFactory.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(
- 遍历advisors都转成Interceptor类型
- Interceptor[] interceptors = registry.getInterceptors(advisor);
- interceptors.add((MethodInterceptor) advice);
- interceptors.add(adapter.getInterceptor(advisor));
- interceptorList.addAll(Arrays.asList(interceptors));
- Interceptor[] interceptors = registry.getInterceptors(advisor);
- 遍历advisors都转成Interceptor类型
- List cached = this.advisorChainFactory.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(
- 如果chain为空:methodProxy.invoke(target, argsToUse);
- 如果chain不为空:new CglibMethodInvocation(proxy, target, method, args, targetClass, chain, methodProxy).proceed();
// JdkDynamicAopProxy.advised
// AdvisedSupport;
public List<Object> getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(Method method, Class<?> targetClass) {
//获取目标方法拦截器链
// 拦截器链有缓存,用过一次就缓存起来了
MethodCacheKey cacheKey = new MethodCacheKey(method);//把获取都的信息保存起来方便下一次直接使用// 用method和method.hashCode组成cacheKey
// 从缓存中尝试获取该方法对于的拦截器链
List<Object> cached = this.methodCache.get(cacheKey);//保存所有拦截器5:=一个默认的ExposeInvocationInterceptor+4个增强器
// 缓存中没有获取到,根据方法和模板方法得到拦截器链。顺便放到缓存中
if (cached == null) {
//用通知链的工厂来获取目标方法的拦截器链
cached = this.advisorChainFactory.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(
this, method, targetClass);
this.methodCache.put(cacheKey, cached);
}
return cached;
}
// DefaultAdvisorChainFactory.java
public class DefaultAdvisorChainFactory implements AdvisorChainFactory, Serializable {
@Override
public List<Object> getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(
Advised config,
Method method,
Class<?> targetClass) {
//拦截器链被封装在list中,长度是通知的个数,一个是默认的ExposedInvocationIntercepter,剩下4个是我们自定义的
List<Object> interceptorList = new ArrayList<Object>(config.getAdvisors().length);
Class<?> actualClass = ( targetClass != null ? targetClass : method.getDeclaringClass());
boolean hasIntroductions = hasMatchingIntroductions(config, actualClass);
AdvisorAdapterRegistry registry = GlobalAdvisorAdapterRegistry.getInstance();
//遍历所有增强器,封装成Interceptor[]
for (Advisor advisor : config.getAdvisors()) {
//5个
if (advisor instanceof PointcutAdvisor) {
//如果是切入点的增强器//ExposedInvocationInterceptor
PointcutAdvisor pointcutAdvisor = (PointcutAdvisor) advisor;
if (config.isPreFiltered() || pointcutAdvisor.getPointcut().getClassFilter().matches(actualClass)) {
//包装增强器
MethodInterceptor[] interceptors = registry.getInterceptors(advisor);
MethodMatcher mm = pointcutAdvisor.getPointcut().getMethodMatcher();
if (MethodMatchers.matches(mm, method, actualClass, hasIntroductions)) {
if (mm.isRuntime()) {
// Creating a new object instance in the getInterceptors() method
// isn't a problem as we normally cache created chains.
for (MethodInterceptor interceptor : interceptors) {
interceptorList.add(new InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher(interceptor, mm));
}
}
else {
interceptorList.addAll(Arrays.asList(interceptors));
}
}
}
}
else if (advisor instanceof IntroductionAdvisor) {
IntroductionAdvisor ia = (IntroductionAdvisor) advisor;
if (config.isPreFiltered() || ia.getClassFilter().matches(actualClass)) {
//包装增强器
Interceptor[] interceptors = registry.getInterceptors(advisor);
interceptorList.addAll(Arrays.asList(interceptors));
}
}
else {
//包装增强器
Interceptor[] interceptors = registry.getInterceptors(advisor);
interceptorList.addAll(Arrays.asList(interceptors));
}
}
return interceptorList;//3、5是使用adapter重新装了的拦截器 ,2、4本来就是拦截器。反正都转成MethodInterceptor
}
将advisor封装为MethodInterceptor[]
DefaultAdvisorAdapterRegistry;
@Override
public MethodInterceptor[] getInterceptors(Advisor advisor) throws UnknownAdviceTypeException {
List<MethodInterceptor> interceptors = new ArrayList<MethodInterceptor>(3);
Advice advice = advisor.getAdvice();
//如果通知类型是MethodInterceptor,直接加入集合中
if (advice instanceof MethodInterceptor) {
interceptors.add((MethodInterceptor) advice);
}
//如果通知类型不是如果通知类型是MethodInterceptor,使用增强器适配器AdvisorAdapter将增强器转为MethodInterceptor拦截器,假如到集合中
for (AdvisorAdapter adapter : this.adapters) {
//MethodBeforeAdviceAdapter、AfterReturingAdviceInterceptor
if (adapter.supportsAdvice(advice)) {
//每个不一样 AspectAfterReturingAdvice
interceptors.add(adapter.getInterceptor(advisor));
}
}
if (interceptors.isEmpty()) {
throw new UnknownAdviceTypeException(advisor.getAdvice());
}
return interceptors.toArray(new MethodInterceptor[interceptors.size()]);//返回MethodInterceptor
}
new CglibMethodInvocation(proxy, target, method, args, targetClass, chain, methodProxy).proceed();
- intercept
- CGlibAopProxy.java
- retVal = new CglibMethodInvocation(proxy, target, method, args, targetClass, chain, methodProxy).proceed();
- return super.proceed();
- if (this.currentInterceptorIndex == this.interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers.size() - 1)
- return invokeJoinpoint();
- return dm.interceptor.invoke(this);