【项目】编写一个在线OJ的项目
1.项目目标
做出一个在线oj系统,支持查看题目列表,支持点击单个题目,支持代码块书写代码,支持提交书写的代码到后端,支持后端编译+运行,支持返回结果
2.项目环境
1.利用开源库cpp-httplib中的httplib.h头文件链接如下:
https:llgitee.comliqxglcpp-httplib?_from=gitee_search
2.安装jsoncpp:
yum install jsoncpp
yun install jsoncpp-devel
3.安装boost环境:
sudo yum install -y snappy-devel boost-devel zlib-devel.x86_64 python-pip
sudo pip install BeautifulSoup4
git clone https://gitee.com/HGtz2222/ThirdPartLibForCpp.git
cd ./ThirdPartLibForCpp/el7.x86_64/
sh install.sh
3.模快划分
B/S浏览器+服务器模式

1.试题模块

- 获取所有试题信息,返回上层调用
- 获取单个试题信息,返回上层调用
2. 编译模块

1.编译运行,将结果返回上层调用
3.http模块

提供三个接口, 分别处理三个请求:
- 请求显示所有试题:获取整个试题列表,回复响应
- 请求显示单个试题:获取单个试题信息,回复响应
- 请求显示编译运行:获取编译运行结果,回复响应
4.工具模块
提供加载文件、字符串切割、解码辅助、html页面填充渲染方法等等
4.各模块具体实现:
4.1 http模块
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include "httplib.h"
#include "oj_model.hpp"
#include "oj_view.hpp"
int main()
{
using namespace httplib;
OjModel model;
//1.初始化httplib库的server对象
Server svr;
//2.提供三个接口, 分别处理三个请求
//2.1 获取整个试题列表, get
svr.Get() {
};
//2.2 获取单个试题
svr.Get(){
};
//2.3 编译运行
svr.Post(){
};
svr.listen("0.0.0.0", 17878);
return 0;
}
4.1.1 响应获取整个试题列表的请求

svr.Get("/all_questions", [&model](const Request& req, Response& resp){
//1.返回试题列表
std::vector<Question> questions;
model.GetAllQuestion(&questions);
std::string html;
OjView::DrawAllQuestions(questions, &html);
resp.set_content(html, "text/html");
});
- 调用试题模板的
GetAllQuestion方法获取所有题目信息,存储于vector< Question > questions中 - 调用工具模板的
DrawALLQuestion方法,questions中保存的题目信息渲染到HTML页面中,响应用户
4.1.2 响应获取单个试题的请求

// 浏览器提交的资源路径是 /question/[试题编号]
// \d+ : 正则表达式:表示多位数字
svr.Get(R"(/question/(\d+))", [&model](const Request& req, Response& resp){
//1.获取url当中关于试题的数字 & 获取单个试题的信息
std::cout << req.version << " " << req.method << std::endl;
std::cout << req.path << std::endl;
Question ques;
model.GetOneQuestion(req.matches[1].str(), &ques);
//2.渲染模版的html文件
std::string html;
OjView::DrawOneQuestion(ques, &html);
resp.set_content(html, "text/html");
});
- 调用试题模板的
GetOneQuestion方法获取单个题目信息,存储于Question ques中 - 调用工具模板的
DrawOneQuestion方法,ques中保存的题目信息渲染到HTML页面中,响应用户
4.1.3 响应编译运行请求

svr.Post(R"(/compile/(\d+))", [&model](const Request& req, Response& resp){
//1.获取试题编号 & 获取试题内容
Question ques;
model.GetOneQuestion(req.matches[1].str(), &ques);
//ques.tail_cpp_ ==> main函数调用+测试用例
//post 方法在提交代码的时候, 是经过encode的, 要想正常获取浏览器提交的内容, 需要进行
//decode, 使用decode完成的代码和tail.cpp进行合并, 产生待编译的源码
std::unordered_map<std::string, std::string> body_kv;
UrlUtil::PraseBody(req.body, &body_kv);
std::string user_code = body_kv["code"];
//2.构造json对象, 交给编译运行模块
Json::Value req_json;
req_json["code"] = user_code + ques.tail_cpp_;
req_json["stdin"] = "";
std::cout << req_json["code"].asString() << std::endl;
Json::Value resp_json;
Compiler::CompileAndRun(req_json, &resp_json);
//获取的返回结果都在 resp_json当中
std::string err_no = resp_json["errorno"].asString();
std::string case_result = resp_json["stdout"].asString();
std::string reason = resp_json["reason"].asString();
std::string html;
OjView::DrawCaseResult(err_no, case_result, reason, &html);
resp.set_content(html, "text/html");
});
- 根据URL的后缀名
http://192.168.21.129:17878/question/1,最后数字为题目编号,因此通过正则表达(/compile/(\d+)进行路径匹配。 - 通过
req.matches[1].str(),找到试题编号。接着调用试题模块的GetOneQuestion方法获取该试题的所有信息 - 对数据包进行拆分
PraseBody获取未解码的代码,解码后与tail.cpp文件组合成待编译的文件 - 构造
json对象,进行组织管理,交给编译模块运行CompileAndRun - 获取编译运行的返回结果存储在
resp_json当中 DrawCaseResult将结果填充给html页面,返回响应set_content
4.2 试题模块
4.2.0 试题保存形式及其内容
1.由各个试题序号命名的文件夹 + 共用一个config文件组成:

2.config文件包含所有试题信息:题目序号、题目名字、题目难易程度、以题目序号命名的文件夹路径(以tab键分隔)

3.以题目序号命名的文件夹包含:
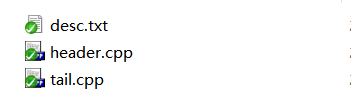
以文件1中的三个文件为例子:
- header.cpp[保存文件头部]
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <map>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
bool isPalindrome(int x) {
return true;
}
};
- desc.txt[题目的描述]
判断一个整数是否是回文数。回文数是指正序(从左向右)和倒序(从右向左)读都是一样的整数。
示例 1:
输入: 121
输出: true
示例 2:
输入: -121
输出: false
解释: 从左向右读, 为 -121 。 从右向左读, 为 121- 。因此它不是一个回文数。
示例 3:
输入: 10
输出: false
解释: 从右向左读, 为 01 。因此它不是一个回文数。
进阶:
你能不将整数转为字符串来解决这个问题吗?
- tail.cpp[文件末尾,包含测试用例以及调用逻辑]
#ifndef CompileOnline
// 这是为了编写用例的时候有语法提示. 实际线上编译的过程中这个操作是不生效的.
#include "header.cpp"
#endif
///
// 此处约定:
// 1. 每个用例是一个函数
// 2. 每个用例从标准输出输出一行日志
// 3. 如果用例通过, 统一打印 [TestName] ok!
// 4. 如果用例不通过, 统一打印 [TestName] failed! 并且给出合适的提示.
///
void Test1() {
bool ret = Solution().isPalindrome(121);
if (ret) {
std::cout << "Test1 ok!" << std::endl;
} else {
std::cout << "Test1 failed! input: 121, output expected true, actual false" << std::endl;
}
}
void Test2() {
bool ret = Solution().isPalindrome(-10);
if (!ret) {
std::cout << "Test2 ok!" << std::endl;
} else {
std::cout << "Test2 failed! input: -10, output expected false, actual true" << std::endl;
}
}
int main() {
Test1();
Test2();
return 0;
}
4.2.1 试题模块模板
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <unordered_map>
#include <fstream>
#include <vector>
#include "tools.hpp"
struct Question
{
std::string id_; //题目id
std::string title_; //题目标题
std::string star_; //题目的难易程度
std::string path_; //题目路径
std::string desc_; //题目的描述
std::string header_cpp_; //题目预定义的头
std::string tail_cpp_; //题目的尾, 包含测试用例以及调用逻辑
};
class OjModel
{
public:
OjModel()
{
//加载config文件
Load("【config文件路径】");
}
~OjModel()
{
}
//从config文件夹当中获取题目信息
bool Load(const std::string& filename)
{
}
//提供给上层调用这一个获取所有试题的接口
bool GetAllQuestion(std::vector<Question>* questions)
{
}
//提供给上层调用者一个获取单个试题的接口
bool GetOneQuestion(const std::string& id, Question* ques)
{
}
private:
std::unordered_map<std::string, Question> ques_map_;
};
- 采用
Question结构体存储一道题目的所有信息 - 采用
unordered_map将每道题目以id为键,Question为值,组织管理所有试题
4.2.2 加载config文件,获取题目信息
bool Load(const std::string& filename)
{
//fopen open C++ fstream
std::ifstream file(filename.c_str());
if(!file.is_open())
{
std::cout << "config file open failed" << std::endl;
return false;
}
std::string line;
while(std::getline(file, line))
{
std::vector<std::string> vec;
StringUtil::Split(line, "\t", &vec);
//boost::spilt分割函数,line中字符串以tab进行分割
Question ques;
ques.id_ = vec[0];
ques.title_ = vec[1];
ques.star_ = vec[2];
ques.path_ = vec[3];
std::string dir = vec[3];
FileUtil::ReadFile(dir + "/desc.txt", &ques.desc_);
FileUtil::ReadFile(dir + "/header.cpp", &ques.header_cpp_);
FileUtil::ReadFile(dir + "/tail.cpp", &ques.tail_cpp_);
ques_map_[ques.id_] = ques;
}
file.close();
return true;
}
- 通过加载config文件获取所有试题信息:【id】 【名字】 【难易】 【路径】,将每一道题的信息存储在
Question结构体中的id_、title_、star_、path_中 - 调用工具模块的ReadFile函数分别读取【路径】下的desc.txt,header.cpp,tail.cpp文件,获取题目描述,题目预定义的头,测试用例,存储在
Question结构体中的desc_、header_cpp_、tail_cpp_中 - 这样我们读取了config文件中的一行信息,也就是一道题的所有信息存储在
Question结构体对象ques中。 - 将每道题目的
id作为键,ques对象作为值,存入unordered_map<std::string, Question> ques_map_当中进行组织管理
4.2.3 上层调用接口,获取所有试题接口
bool GetAllQuestion(std::vector<Question>* questions)
{
//1.遍历无序的map, 将试题信息返回给调用者
//对于每一个试题, 都是一个Question结构体对象
for(const auto& kv : ques_map_)
{
questions->push_back(kv.second);
}
//2.排序
std::sort(questions->begin(), questions->end(), [](const Question& l, const Question& r){
//比较Question当中的题目编号, 按照升序规则
return std::stoi(l.id_) < std::stoi(r.id_);
});
return true;
}
- 遍历
ques_map_中的值,通过questions作为出参存储所有试题信息,返还给上层调用
4.2.4 上层调用接口,获取单个试题接口
bool GetOneQuestion(const std::string& id, Question* ques)
{
auto it = ques_map_.find(id);
if(it == ques_map_.end())
{
return false;
}
*ques = it->second;
return true;
}
- 根据
ques_map_中的键(题目id)找到对应试题信息,通过ques存储试题信息作为出参,返还给上层调用
4.3 工具模板
4.3.1 读取文件内容
class FileUtil
{
public:
//读文件接口
//file_name: 文件名称
//content: 读到的内容, 输出参数, 返还调用者
static bool ReadFile(const std::string& file_name, std::string* content)
{
//1.清空content当中的内容
content->clear();
std::ifstream file(file_name.c_str());
if(!file.is_open())
{
return false;
}
//文件被打开了
std::string line;
while(std::getline(file, line))
{
(*content) += line + "\n";
}
file.close();
return true;
}
};
content作为出参,保存文件内容
4.3.2 字符串切割
class StringUtil
{
public:
static void Split(const std::string& input, const std::string& split_char, std::vector<std::string>* output)
{
boost::split(*output, input, boost::is_any_of(split_char), boost::token_compress_off);
}
};
- 根据字符切割字符串
4.3.3 解析数据包并解码
//body从httplib.h当中的request类的成员变量获得
// body:
// key=value&key1=value1 ===> 并且是进行过编码
// 1.先切割
// 2.在对切割之后的结果进行转码
static void PraseBody(const std::string& body, std::unordered_map<std::string, std::string>* body_kv)
{
std::vector<std::string> kv_vec;
StringUtil::Split(body, "&", &kv_vec);
for(const auto& t : kv_vec)
{
std::vector<std::string> sig_kv;
StringUtil::Split(t, "=", &sig_kv);
if(sig_kv.size() != 2)
{
continue;
}
//在保存的时候, 针对value在进行转码
(*body_kv)[sig_kv[0]] = UrlDecode(sig_kv[1]);
}
}
static std::string UrlDecode(const std::string& str)
{
std::string strTemp = "";
size_t length = str.length();
for (size_t i = 0; i < length; i++)
{
if (str[i] == '+') strTemp += ' ';
else if (str[i] == '%')
{
assert(i + 2 < length);
unsigned char high = FromHex((unsigned char)str[++i]);
unsigned char low = FromHex((unsigned char)str[++i]);
strTemp += high*16 + low;
}
else strTemp += str[i];
}
return strTemp;
}
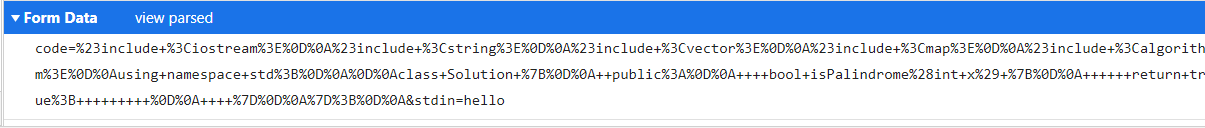
- 解析数据包
code=xxx&&stdin=xxx - 根据=拆分数据包,获得正文
- 正文进行解码,转化为代码
4.3.4 向HTML填充信息
class OjView
{
public:
static void DrawAllQuestions(std::vector<Question>& questions, std::string* html)
{
//1. 创建template字典
ctemplate::TemplateDictionary dict("all_questions");
//2.遍历vector, 遍历vector就相当于遍历多个试题, 每一个试题构造一个子字典
for(const auto& ques : questions)
{
TemplateDictionary* AddSectionDictionary(const TemplateString section_name);
ctemplate::TemplateDictionary* sub_dict = dict.AddSectionDictionary("question");
//void SetValue(const TemplateString variable, const TemplateString value);
/*
* variable: 指定的是在预定义的html当中的变量名称
* value: 替换的值
* */
sub_dict->SetValue("id", ques.id_);
sub_dict->SetValue("id", ques.id_);
sub_dict->SetValue("title", ques.title_);
sub_dict->SetValue("star", ques.star_);
}
//3.填充
ctemplate::Template* tl = ctemplate::Template::GetTemplate("./template/all_questions.html", ctemplate::DO_NOT_STRIP);
//all_questions.html内容被加载到内存中,以逐字逐句的方式,原文件未被修改
//渲染
tl->Expand(html, &dict);
}
static void DrawOneQuestion(const Question& ques, std::string* html)
{
ctemplate::TemplateDictionary dict("question");
dict.SetValue("id", ques.id_);
dict.SetValue("title", ques.title_);
dict.SetValue("star", ques.star_);
dict.SetValue("desc", ques.desc_);
dict.SetValue("id", ques.id_);
dict.SetValue("code", ques.header_cpp_);
ctemplate::Template* tl = ctemplate::Template::GetTemplate("./template/question.html", ctemplate::DO_NOT_STRIP);
//渲染
tl->Expand(html, &dict);
}
};
- 运用ctemplate创建根字典
- 根据每道题目创建子字典
- 依据关键字匹配,通过字典对html页面进行填充渲染。
4.3.5获取时间戳
//获取时间戳
class TimeUtil
{
public:
static int64_t GetTimeStampMs()
{
struct timeval tv;
gettimeofday(&tv, NULL);
return tv.tv_sec + tv.tv_usec / 1000;
}
//[年月日 时分秒]
static void GetTimeStamp(std::string* TimeStamp)
{
time_t st;
time(&st);
struct tm* t = localtime(&st);
char buf[30] = {
0 };
snprintf(buf, sizeof(buf) - 1, "%04d-%02d-%02d %02d:%02d:%02d", t->tm_year + 1900, t->tm_mon + 1, t->tm_mday, t->tm_hour, t->tm_min, t->tm_sec);
TimeStamp->assign(buf, strlen(buf));
}
};
4.3.6日志记录
enum LogLevel
{
INFO = 0,
WARNING,
ERROR,
FATAL,
DEBUG
};
const char* Level[] =
{
"INFO",
"WARNING",
"ERROR",
"FATAL",
"DEBUG"
};
/*
* lev:日志等级
* file: 文件名称
* line : 行号
* logmsg : 想要记录的日志内容
* */
inline std::ostream& Log(LogLevel lev, const char* file, int line, const std::string& logmsg)
{
std::cout << "begin log" << std::endl;
std::string level_info = Level[lev];
std::cout << level_info << std::endl;
std::string TimeStamp;
TimeUtil::GetTimeStamp(&TimeStamp);
std::cout << TimeStamp << std::endl;
std::cout << "[" << TimeStamp << " " << level_info << " " << file << ":" << line << "]" << " " << logmsg;
return std::cout;
}
#define LOG(lev, msg) Log(lev, __FILE__, __LINE__, msg)
4.4 编译运行模块
4.4.0 检查参数
if(Req["code"].empty())
{
(*Resp)["errorno"] = PRAM_ERROR;
(*Resp)["reason"] = "Pram error";
return;
}
- 参数是否是错误的, json串当中的code是否为空
4.4.1 将代码存入文件中
std::string code = Req["code"].asString();
std::string file_nameheader = WriteTmpFile(code);
if(file_nameheader == "")
{
(*Resp)["errorno"] = INTERNAL_ERROR;
(*Resp)["reason"] = "write file failed";
return;
}
- 文件命名约定: tmp_时间戳_src.cpp
4.4.2 编译
static bool Compile(const std::string& file_name)
{
int pid = fork();
if(pid > 0)
{
//father
waitpid(pid, NULL, 0);
}
else if (pid == 0)
{
//child
//进程程序替换--》 g++ SrcPath(filename) -o ExePath(filename) "-std=c++11"
int fd = open(CompileErrorPath(file_name).c_str(), O_CREAT | O_WRONLY, 0666);
if(fd < 0)
{
return false;
}
//将标准错误(2)重定向为 fd, 标准错误的输出, 就会输出在文件当中
dup2(fd, 2);
execlp("g++", "g++", SrcPath(file_name).c_str(), "-o", ExePath(file_name).c_str(), "-std=c++11", "-D", "CompileOnline", NULL);
close(fd);
//如果替换失败了, 就直接让子进程退出了,如果替换成功了, 不会走该逻辑了
exit(0);
}
else
{
return false;
}
//如果说编译成功了, 在tmp_file这个文件夹下, 一定会产生一个可执行程序, 如果
//当前代码走到这里,判断有该可执行程序, 则我们认为g++执行成功了, 否则, 认为执行失败
struct stat st;
int ret = stat(ExePath(file_name).c_str(), &st);
if(ret < 0)
{
return false;
}
return true;
}
- 创建子进程,子进程进行进程程序替换
- 将标准错误(2)重定向为 fd,将错误进行保存,如果编译失败,将其返回。
- 如果说编译成功了, 在tmp_file这个文件夹下, 一定会产生一个可执行程序
4.4.3 运行
static int Run(const std::string& file_name)
{
int pid = fork();
if(pid < 0)
{
return -1;
}
else if(pid > 0)
{
//father
int status = 0;
waitpid(pid, &status, 0);
return status & 0x7f;
}
else
{
//注册一个定时器, alarm
//[限制运行时间]
alarm(1);
//child
//进程程序替换, 替换编译创建出来的可执行程序
//[限制内存] // #include <sys/resource.h>
struct rlimit rlim;
rlim.rlim_cur = 30000 * 1024; //3wk
rlim.rlim_max = RLIM_INFINITY;
setrlimit(RLIMIT_AS, &rlim);
int stdout_fd = open(StdoutPath(file_name).c_str(), O_CREAT | O_WRONLY, 0666);
if(stdout_fd < 0)
{
return -2;
}
dup2(stdout_fd, 1);
int stderr_fd = open(StderrPath(file_name).c_str(), O_CREAT | O_WRONLY, 0666);
if(stderr_fd < 0)
{
return -2;
}
dup2(stderr_fd, 2);
execl(ExePath(file_name).c_str(), ExePath(file_name).c_str(), NULL);
exit(0);
}
return 0;
}
- 创建子进程,子进程进行进程程序替换
execl,进行运行编译产生的可执行程序 - 将运行结果重定向到
stdout_fd中 - 将标准错误重定向到
stderr_fd中
4.4.4 构造响应
(*Resp)["errorno"] = OK;
(*Resp)["reason"] = "Compile and Run ok";
std::string stdout_str;
FileUtil::ReadFile(StdoutPath(file_nameheader), &stdout_str);
(*Resp)["stdout"] = stdout_str;
std::string stderr_str;
FileUtil::ReadFile(StderrPath(file_nameheader), &stderr_str);
(*Resp)["stderr"] = stderr_str;
- 将所有结果放入json中进行组织,作为出参传递给上一层
4.4.5 删除临时文件
static void Clean(const std::string& filename)
{
unlink(SrcPath(filename).c_str());
unlink(CompileErrorPath(filename).c_str());
unlink(ExePath(filename).c_str());
unlink(StdoutPath(filename).c_str());
unlink(StderrPath(filename).c_str());
}