文章目录
1、axios与fetch实现数据请求
(1)fetch
<body>
<div id="box">
<button @click="handleClick()">正在热映</button>
<ul>
<li v-for="data in datalist">
<!--获取json中影片的图像-->
<img :src="data.poster" alt=""/>
<!--获取json中影片的名称-->
<h2>{
{data.name}}</h2>
<!-- {
{data}}-->
</li>
</ul>
</div>
<script type="text/javascript">
new Vue({
el:'#box',
data:{
datalist:[]
},
methods:{
handleClick(){
fetch("json/test.json").then(res=>res.json()).then(res=>{
console.log(res);
this.datalist = res.data.films;
})
}
}
})
</script>
</body>
实现效果:

post格式
1
fetch("**",{
method:'post',
headers:{
"Content-Type":"application/x-www-form-urlencoded"
},
body:"name=kerwin&age=100"
}).then(res=>res.json()).then(res=>{
console.log(res)});
2
fetch("**",{
method:'post',
headers:{
"Content-Type":"application/json"
},
body:JSON.stringify({
name:"kerwin",
age:100
})
}).then(res=>res.json()).then(res=>{
console.log(res)});
注意:
Fetch请求默认是不带cookie的,需要设置fetch(url,(credentials:'include))
(2)axios
data是真实后端数据
与fetch的区别
- 要引入axios.min.js
handleClick(){
axios.get('json/test.json').then(res=>{
console.log(res.data);
this.datalist = res.data.data.films;
})
//----此方法和上面axios.get相同-----
axios({
url:"json/test.json",
method:'get' //get post根据method进行修改
}).then(res=>{
console.log(res.data)
})
}
实现效果与fetch相同
Post/delete
axios.delete("****",{
//可以在此处传参
myname:'zyy',
myage:18
}).then(res=>{
console.log(res.data)
})
2、计算属性
<script type="text/javascript">
var vm = new Vue({
el:'...',
data:{
},
computed:{
changeword(){
return ''
}
}
})
</script>
复杂逻辑,模版难以维护的放在计算属性内,使得模版、代码更好维护些。
(1)基础例子
用 computed
<body>
<div id="box">
<!--千万不要加小括号 -->
{
{changeword}}
</div>
<script type="text/javascript">
var vm = new Vue({
el:'#box',
data:{
myname:'zmy'
},
computed:{
changeword(){
return this.myname.substring(0,1).toUpperCase() + this.myname.substring(1,)
}
}
})
</script>
</body>
显示效果:
Zmy
(2)计算属性 VS methods
<body>
<div id="box">
<!--千万不要加小括号 -->
{
{changeword}}
<!--methods 方法-->
{
{changewordmethods()}}
</div>
<script type="text/javascript">
var vm = new Vue({
el:'#box',
data:{
myname:'zmy'
},
methods:{
changewordmethods(){
return this.myname.substring(0,1).toUpperCase() + this.myname.substring(1,)
}
},
computed:{
changeword(){
return this.myname.substring(0,1).toUpperCase() + this.myname.substring(1,)
}
}
})
</script>
</body>
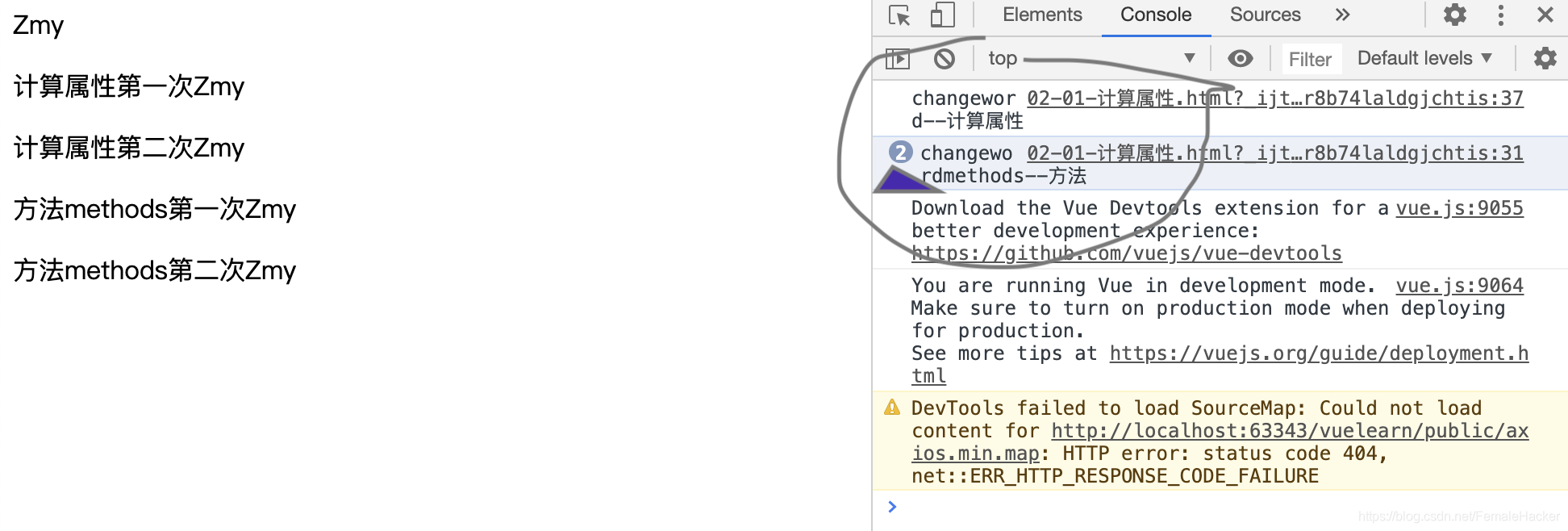
- 发现两者的实现效果相同
- 计算属性是基于它们的依赖进行缓存的
- 计算属性只有在它的相关依赖发生改变时才会重新求值
区别
-
计算属性有缓存,访问第一次时会调用,第二次的时候会直接告诉结果。
-
方法每次都需要重新调用。
模糊查询-计算属性实例
<body>
<div id="box">
<input type="text" v-model="mytext"/>
<ul>
<li v-for="data in computedlist" :key="data">
{
{data}}
</li>
</ul>
</div>
<script type="text/javascript">
var vm = new Vue({
el:"#box",
data:{
datalist:['aaa','bbb','ccc','ddd','add','cee','eee','aao','cce'],
mytext:''
},
computed:{
computedlist(){
return this.datalist.filter(item=>item.indexOf(this.mytext)>-1)
}
}
})
</script>
</body>
实现效果与之前“模糊查询实例”相同。
(3)计算属性 VS watch(监听器)
watch版----计算总金额简单例子
说明:如果金额小于1000,则添加10元邮费。
<body>
<div id="box">
<p>单价 <input type="text" v-model="price"/></p>
<p>数量 <input type="text" v-model="number"/></p>
<p>总金额:{
{sum}} (元)</p>
</div>
<script type="text/javascript">
var vm = new Vue({
el:'#box',
data:{
price:100,
number:0,
sum:0
},
//watch监听器
watch:{
//方法名称要和状态名称相同
price(){
if (this.price * this.number <1000){
this.sum = this.price * this.number + 10
}else{
this.sum = this.price * this.number
}
},
number(){
if (this.price * this.number <1000){
this.sum = this.price * this.number + 10
}else{
this.sum = this.price * this.number
}
},
}
})
</script>
</body>
实现效果:

计算属性版----计算总金额简单例子
<body>
<div id="box">
<p>单价 <input type="text" v-model="price"/></p>
<p>数量 <input type="text" v-model="number"/></p>
<p>总金额:{
{computedsum}} (元)</p>
</div>
<script type="text/javascript">
var vm = new Vue({
el:'#box',
data:{
price:100,
number:1,
},
computed:{
computedsum(){
var sum = 0
if (this.price * this.number <1000){
sum = this.price * this.number + 10
}else{
sum = this.price * this.number
}
return sum
}
}
})
</script>
</body>
实现效果相同。
区别
无论有多个值,计算属性只需要写一次;而watch需要写很多次。譬如price和number,watch写了两次,而计算属性computed只写了一次。
因此,状态特别多的时候,计算属性优势就很突出了。
3、Mixins
正在学,待更新…