文章目录
WOA
元启发式优化算法在工程应用中越来越受欢迎。
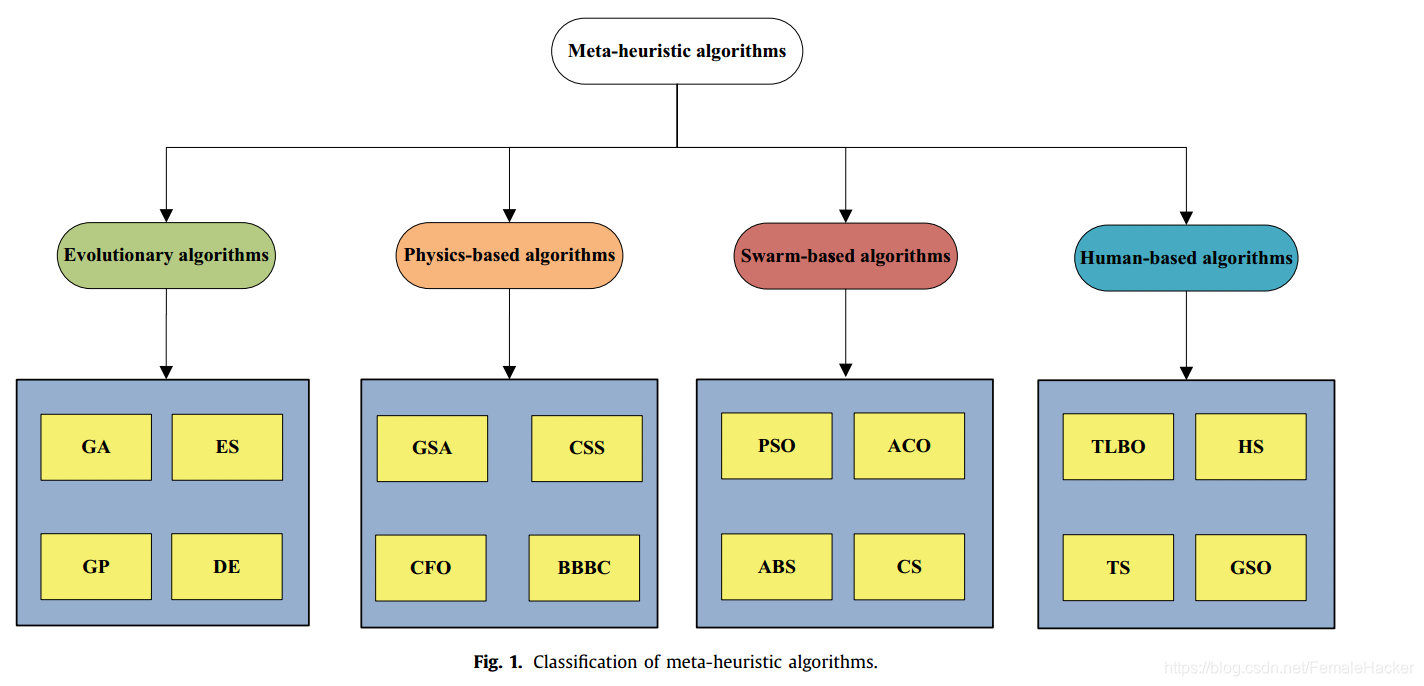
基于群体的元启发式优化算法不论其性质如何,都具有一个共同的特征。搜索过程分为e xploration和exploitation。
座头鲸的捕猎觅食行为被称为泡网取食法,座头鲸喜欢捕食一群靠近水面的磷虾或小鱼。这种觅食是通过下图所示的圆形或“9”形路径创建独特的气泡来完成。
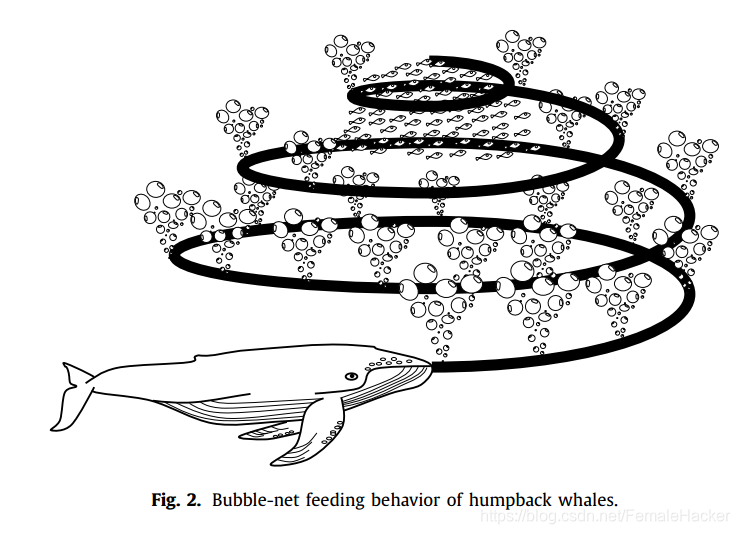
气泡网捕食是一种独特的行为,只能在座头鲸身上观察到。
Encircling prey
座头鲸能够识别猎物的位置并包围它们。WOA算法假设当前最优候选解是目标猎物或接近最优。在定义了 the best search agent 后,the other search agents将试图更新他们的位置,以寻找the best search agent。
公式
D → = ∣ C → ⋅ X ∗ → ( t ) − X → ( t ) ∣ X → ( t + 1 ) = X ∗ → ( t ) − A → ⋅ D → \overrightarrow {D}=\vert\overrightarrow {C}·\overrightarrow {X^*}(t) - \overrightarrow {X}(t)\vert\\ \overrightarrow {X}(t+1) = \overrightarrow {X^*}(t) - \overrightarrow {A} · \overrightarrow {D} D=∣C⋅X∗(t)−X(t)∣X(t+1)=X∗(t)−A⋅D
- t 表示 the current iteration 当前迭代
- A → \overrightarrow {A} A、 C → \overrightarrow {C} C表示系数向量
- A → = 2 a → ⋅ r 1 → − a → \overrightarrow {A} = 2\overrightarrow {a} ·\overrightarrow {r_1} - \overrightarrow {a} A=2a⋅r1−a
- C → = 2 ⋅ r 2 → \overrightarrow {C} = 2·\overrightarrow {r_2} C=2⋅r2
- a → \overrightarrow{a} a 在搜索过程中,由2线性递减到0 a → = 2 − 2 t T m a x \overrightarrow{a} =2-\frac{2t}{T_{max}} a=2−Tmax2t
- t表示当前的迭代次数
- T m a x T_{max} Tmax为最大的迭代次数
- r 1 → \overrightarrow {r_1} r1 和 r 2 → \overrightarrow {r_2} r2 是满足[0,1]中的随机向量
- a → \overrightarrow{a} a 在搜索过程中,由2线性递减到0 a → = 2 − 2 t T m a x \overrightarrow{a} =2-\frac{2t}{T_{max}} a=2−Tmax2t
- X ∗ → ( t ) \overrightarrow {X^*}(t) X∗(t)表示目前为止最好的鲸鱼位置向量d
- X → \overrightarrow {X} X 表示当前鲸鱼的位置向量
- ∣ ∣ || ∣∣表示绝对值
如果有更加最优解, X ∗ X^* X∗会在每次迭代中更新
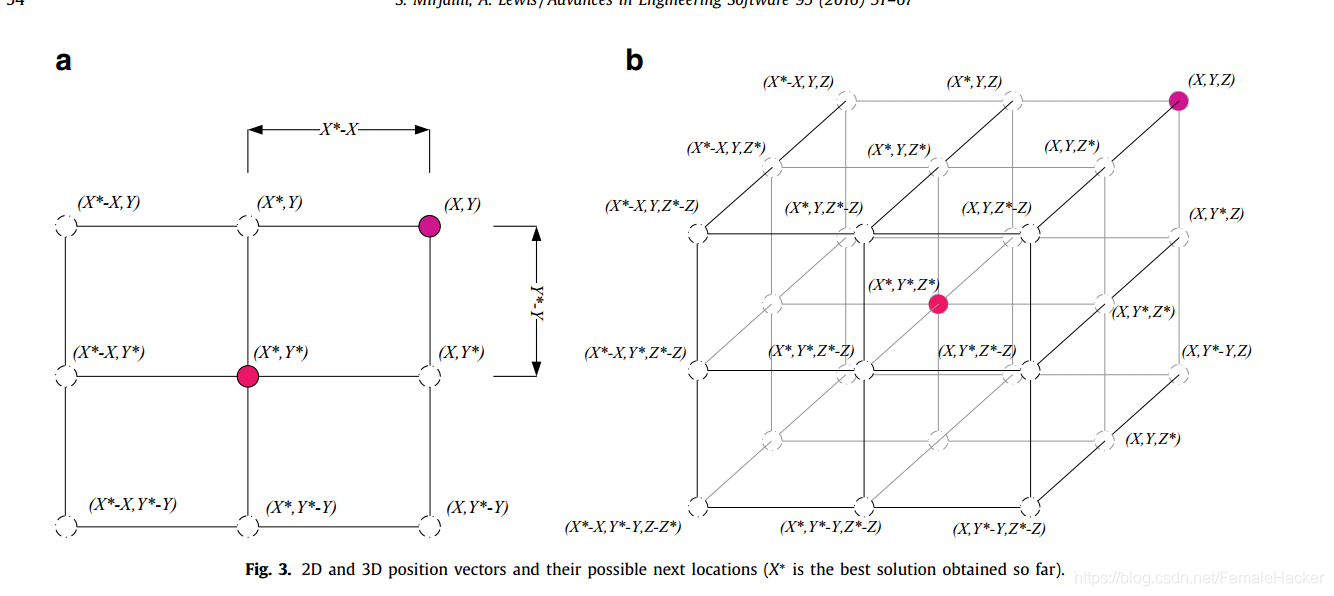
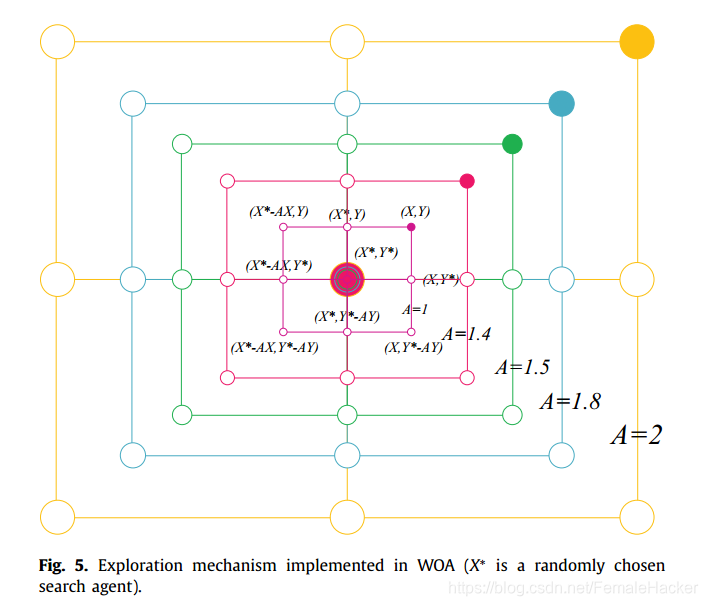
下图说明了上述公式背后的原理。a search agent 的位置(X,Y)可以根据当前最佳记录的位置进行更新 ( X ∗ , Y ∗ ) (X^*,Y^*) (X∗,Y∗)。Different places around the best agent can be achieved with respect to the current position by adjusting the value of A → \overrightarrow {A} A、 C → \overrightarrow {C} C vectors.
Bubble-net attcking method
Two procedures including shrinking encircling and spiraling updating are designed to mathematically model the bubble-net attacking behaviour.
【设计了收缩包围和螺旋更新两种方法对泡网攻击行为进行数学建模】
shrinking encircling(包围猎物)
该过程通过在迭代过程中降低 a → \overrightarrow {a} a值来实现。
将 A → \overrightarrow {A} A限制为[-1,1],search agent的新位置另一定义为 the agent的当前位置和 the best agent的位置之间的任何位置。
spiraling updating(狩猎行为)
这种方法首先计算位于(X,Y)的鲸鱼和位于 ( X ∗ , Y ∗ ) (X^*,Y^*) (X∗,Y∗)的猎物之间的距离,然后在鲸鱼和猎物的位置之间建立一个螺旋方程来模拟座头鲸的螺旋形运动。
公式
X → ( t + 1 ) = D ′ → ⋅ e b l ⋅ cos ( 2 π l ) X ∗ → ( t ) \overrightarrow {X}(t+1) = \overrightarrow {D^{\prime}}· e^{bl}·\cos(2\pi l)\overrightarrow {X^*}(t) X(t+1)=D′⋅ebl⋅cos(2πl)X∗(t)
- D ′ → = ∣ X ∗ → ( t ) − X → ( t ) ∣ \overrightarrow {D^{\prime}}=\vert\overrightarrow {X^*}(t) - \overrightarrow {X}(t)\vert D′=∣X∗(t)−X(t)∣表示第i个search agent 到目标的距离
- b是个常数,定义了对数螺旋的形状
- l是均匀分布的随机向量[-1,1]
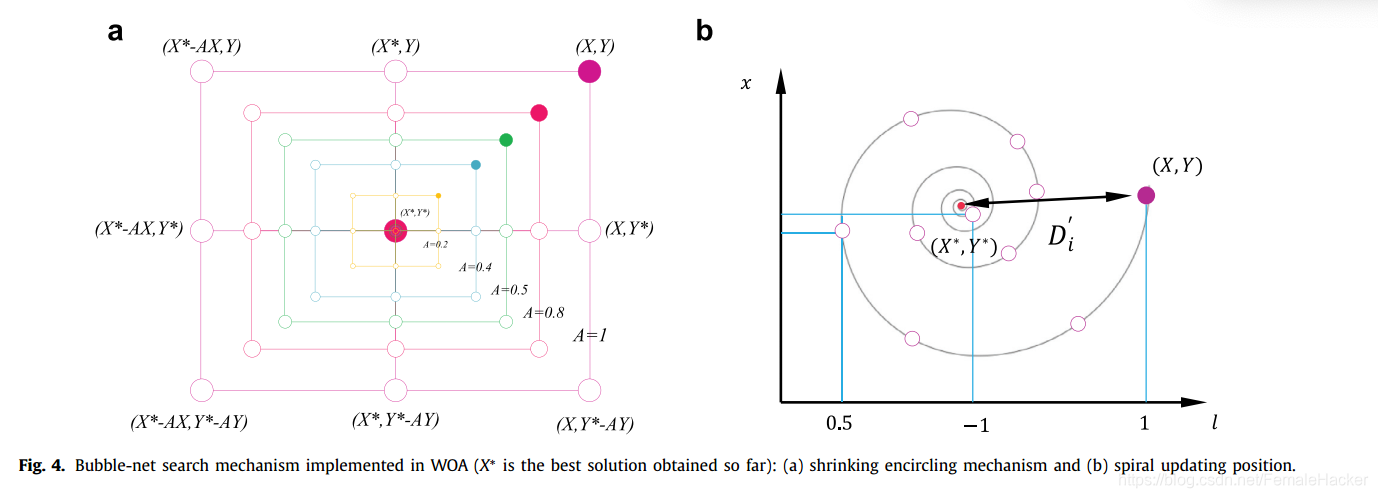
座头鲸会在一个缩小的圈内同时沿着一个螺旋形的路径绕着猎物游来游去。为模拟这种同时发生的行为,我们假设50%的可能性在收缩环绕机制和螺旋模型之间进行选择,以便在优化过程中更新鲸鱼的位置。
X → ( t + 1 ) = { X → ( t + 1 ) = X ∗ → ( t ) − A → ⋅ D → , i f p < 0.5 D ′ → ⋅ e b l ⋅ cos ( 2 π l ) X ∗ → ( t ) , i f p ≥ 0.5 \overrightarrow {X}(t+1) =\begin{cases} \overrightarrow {X}(t+1) = \overrightarrow {X^*}(t) - \overrightarrow {A} · \overrightarrow {D}, & if p < 0.5\\ \overrightarrow {D^{\prime}}· e^{bl}·\cos(2\pi l)\overrightarrow {X^*}(t), & if p \geq 0.5\end{cases} X(t+1)={
X(t+1)=X∗(t)−A⋅D,D′⋅ebl⋅cos(2πl)X∗(t),ifp<0.5ifp≥0.5
- p 是[0,1]之间的随机数
Search for prey(搜索猎物)
除了气泡网法,座头鲸还会随机寻找猎物。
in contrast to the exploitation phase,我们在exploration阶段根据随机选择的search agent 而不是目前找到的 the best search agent 来更新 search agent 的位置。
D → = ∣ C → ⋅ X r a n d → − X → ( t ) ∣ X → ( t + 1 ) = X r a n d → − A → ⋅ D → \overrightarrow {D}=\vert\overrightarrow {C}·\overrightarrow {X_{rand}} - \overrightarrow {X}(t)\vert \\ \overrightarrow {X}(t+1) = \overrightarrow {X_{rand}}- \overrightarrow {A} · \overrightarrow {D} D=∣C⋅Xrand−X(t)∣X(t+1)=Xrand−A⋅D
- X r a n d → \overrightarrow {X_{rand}} Xrand是随机选择的鲸鱼位置向量
算法设定当 A≥1时,随机选择一个搜索代理,根据随机选择的鲸鱼位置来更新其他鲸鱼的位置,迫使鲸鱼偏离猎物,借此找到一个更合适的猎物,这样可以加强算法的勘探能力使 WOA 算法能够进行全局搜索。
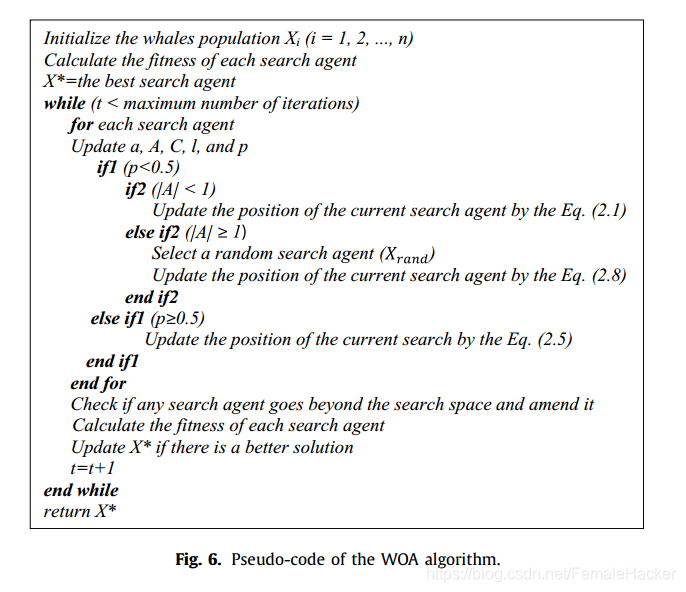
算法流程
【1】WOA算法从一组随机解开始。在每次迭代中,搜索代理根据随机选择的搜索代理或目前获得的最佳解决方案更新它们的位置。
【2】将a参数从2降到0,分别用于exploration和exploitation。
【3】随机代理选择当 ∣ A ∣ > 1 \vert A\vert >1 ∣A∣>1,而最好的解决方案是选 ∣ A ∣ < 1 \vert A\vert <1 ∣A∣<1更新的位置搜索代理。
【4】根据p的值,WOA可以在螺旋或圆周运动之间切换。
【5】最后,通过满足一个中指准则==(一般是达到最大迭代次数)==来终止WOA算法
i f p < 0.5 if p < 0.5 ifp<0.5
i f ∣ A ∣ < 1 if \vert A\vert <1 if∣A∣<1
X → ( t + 1 ) = X ∗ → ( t ) − A → ⋅ ∣ C → ⋅ X ∗ → ( t ) − X → ( t ) ∣ \overrightarrow {X}(t+1) =\overrightarrow {X^*}(t) - \overrightarrow {A} · \vert\overrightarrow {C}·\overrightarrow {X^*}(t) - \overrightarrow {X}(t)\vert X(t+1)=X∗(t)−A⋅∣C⋅X∗(t)−X(t)∣
else
X → ( t + 1 ) = X r a n d → − A → ⋅ ∣ C → ⋅ X r a n d → − X → ( t ) ∣ \overrightarrow {X}(t+1) = \overrightarrow {X_{rand}}- \overrightarrow {A} · \vert\overrightarrow {C}·\overrightarrow {X_{rand}} - \overrightarrow {X}(t)\vert X(t+1)=Xrand−A⋅∣C⋅Xrand−X(t)∣
else
X → ( t + 1 ) = D ′ → ⋅ e b l ⋅ cos ( 2 π l ) X ∗ → ( t ) \overrightarrow {X}(t+1) = \overrightarrow {D^{\prime}}· e^{bl}·\cos(2\pi l)\overrightarrow {X^*}(t) X(t+1)=D′⋅ebl⋅cos(2πl)X∗(t)
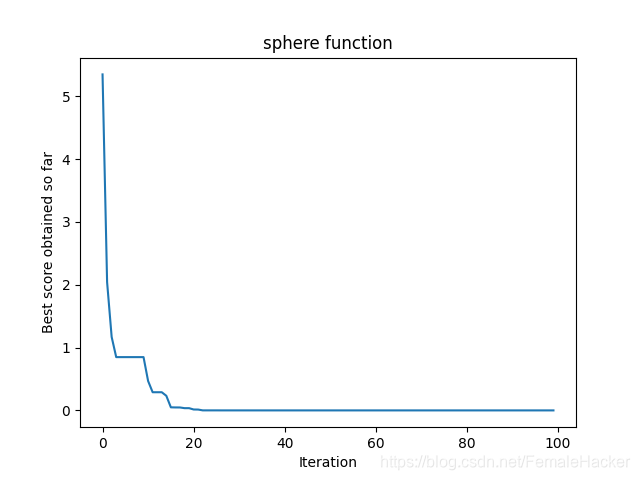
算法结果示例
参考文献
[1]Seyedali Mirjalili,Andrew Lewis. The Whale Optimization Algorithm[J]. Advances in Engineering Software,2016,95.
[2]Sai, Li , and F. Huajing . “A WOA-based algorithm for parameter optimization of support vector regression and its application to condition prognostics.” Control Conference 2017:7345-7350.