基于EFcore 采用DBFirst模式 实现DBContext依赖注入
1.SQL Server创建数据库
创建一个名为Example的数据库,并含有UserInfo、Contacts数据表
UserInfo字段:
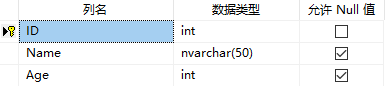
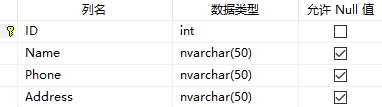
Contacts字段:
2.VS引入Nuget程序包
可以在程序包管理控制台 手动键入命令行安装Nuget包:
install-package microsoft.entityframeworkcore
install-package microsoft.entityframeworkcore.sqlserver
install-package mircosoft.entityframeworkcore.tools
3.Scaffold-DbContext框架生成Model
Scaffold-DBContext “server=.;database=Example;uid=sa;pwd=sa123456” microsoft.entityframeworkcore.sqlserver -outputDir Models
命令行说明:

框架Build Succeed后,自动生成数据库实体类与DbContext类
UserInfo:
namespace WebApplication24.Models
{
public partial class UserInfo
{
public int Id {
get; set; }
public string Name {
get; set; }
public int? Age {
get; set; }
}
}
Contact:
namespace WebApplication24.Models
{
public partial class Contact
{
public int Id {
get; set; }
public string Name {
get; set; }
public string Phone {
get; set; }
public string Address {
get; set; }
}
}
ExampleContext:
namespace WebApplication24.Models
{
public partial class ExampleContext : DbContext
{
public ExampleContext()
{
}
public ExampleContext(DbContextOptions<ExampleContext> options)
: base(options)
{
}
public virtual DbSet<Contact> Contacts {
get; set; }
public virtual DbSet<UserInfo> UserInfos {
get; set; }
protected override void OnModelCreating(ModelBuilder modelBuilder)
{
modelBuilder.HasAnnotation("Relational:Collation", "Chinese_PRC_CI_AS");
modelBuilder.Entity<Contact>(entity =>
{
entity.Property(e => e.Id)
.ValueGeneratedNever()
.HasColumnName("ID");
entity.Property(e => e.Address).HasMaxLength(50);
entity.Property(e => e.Name).HasMaxLength(50);
entity.Property(e => e.Phone).HasMaxLength(50);
});
modelBuilder.Entity<UserInfo>(entity =>
{
entity.ToTable("UserInfo");
entity.Property(e => e.Id)
.ValueGeneratedNever()
.HasColumnName("ID");
entity.Property(e => e.Name).HasMaxLength(50);
});
OnModelCreatingPartial(modelBuilder);
}
partial void OnModelCreatingPartial(ModelBuilder modelBuilder);
}
}
4.依赖注入DBContext
Startup类中依赖注入
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
services.AddControllersWithViews();
services.AddDbContext<ExampleContext>(options => {
options.UseSqlServer(Configuration.GetConnectionString("defaultConnection"));
});
}
appsettings.json中加入连接字符串
"ConnectionStrings": {
"defaultConnection": "server=.;database=example;uid=sa;pwd=sa123456"
}
AddDbContext解释摘要:
摘要:
// Registers the given context as a service in the Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection.IServiceCollection.
// Use this method when using dependency injection in your application, such as
// with ASP.NET Core. For applications that don't use dependency injection, consider
// creating Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.DbContext instances directly with its
// constructor. The Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.DbContext.OnConfiguring(Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.DbContextOptionsBuilder)
// method can then be overridden to configure a connection string and other options.
// For more information on how to use this method, see the Entity Framework Core
// documentation at https://aka.ms/efdocs. For more information on using dependency
// injection, see https://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkId=526890.
5.DBContext构造函数注入
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Logging;
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Diagnostics;
using System.Linq;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using WebApplication24.Models;
namespace WebApplication24.Controllers
{
public class HomeController : Controller
{
private readonly ILogger<HomeController> _logger;
private readonly ExampleContext _db;
public HomeController(ILogger<HomeController> logger,ExampleContext exampleContext)
{
_logger = logger;
_db = exampleContext;
}
public IActionResult Index()
{
var query = _db.UserInfos.Find(1);
return View();
}
}
}