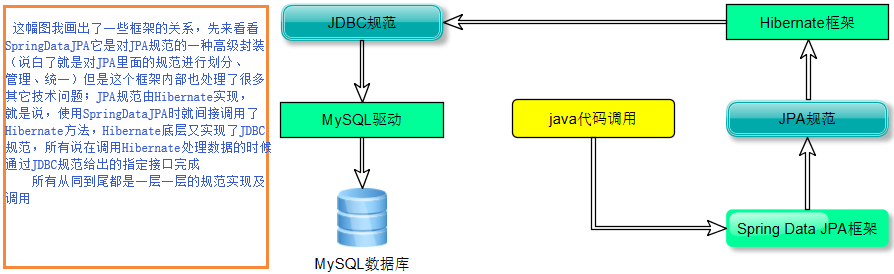
Spring Data JPA与JPA和hibernate三者关系
看三者框架中,JPA只是一种规范,内部都是由接口和抽象类构建的;hibernate它是我们最初使用的一套由ORM思想构建的成熟框架,但是这个框架内部又实现了一套JPA的规范(实现了JPA规范定义的接口),所有也可以称hibernate为JPA的一种实现方式我们使用JPA的API编程,意味着站在更高的角度上看待问题(面向接口编程);Spring Data JPA它是Spring家族提供的,对JPA规范有一套更高级的封装,是在JPA规范下专门用来进行数据持久化的解决方案。
Spring Data JPA与JPA和hibernate三者关系图
SpringDataJPA简单单表接口方法查询图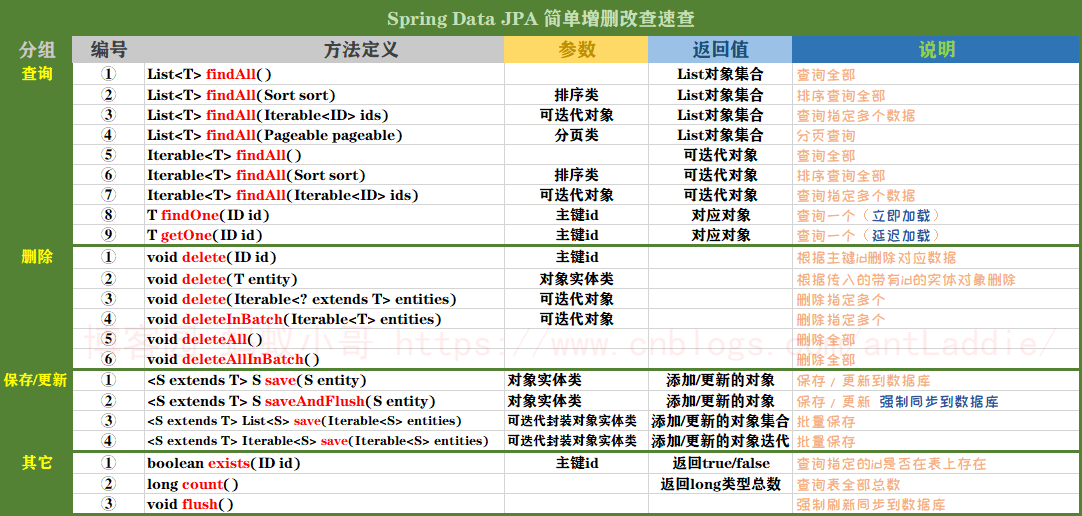
接口关系图

HelloWorld
sql
create database db_example;
drop table demo_user;
CREATE TABLE `demo_user` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`name` varchar(50) DEFAULT NULL,
`email` varchar(200) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
)
select * from demo_user;
controller
package com.example.demo.controller;
import com.example.demo.UserService.UserServiceImpl;
import com.example.demo.entity.User;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
@Controller
@RequestMapping(path = "/demo")
public class UserController {
@Autowired
private UserServiceImpl userServiceImpl;
@GetMapping(path = "/save")
public void saveUser( @RequestParam String name, @RequestParam String email ) {
User n = new User();
n.setName(name);
n.setEmail(email);
System.out.println(n);
userServiceImpl.saveUser(n);
}
@GetMapping(path = "/deleteById")
@ResponseBody
public void deleteById(Long id) {
userServiceImpl.deleteUser(id);
}
@GetMapping(path = "/deleteByUser")
@ResponseBody
public void deleteByUser(User user) {
userServiceImpl.deleteUser(user);
}
@GetMapping(path = "/update")
@ResponseBody
private User updateUser(Long id, String name){
User user = userServiceImpl.findUser(id);
user.setName(name);
userServiceImpl.updateUser(user);
return user;
}
@GetMapping(path = "/findOne")
@ResponseBody
public User getOneUser(Long id) {
return userServiceImpl.findUser(id);
}
@GetMapping(path = "/findAll")
@ResponseBody
public Iterable<User> getAllUser() {
return userServiceImpl.findAll();
}
}
service
package com.example.demo.UserService;
import com.example.demo.entity.User;
import java.util.List;
public interface UserService {
User saveUser(User user);
void deleteUser(User user);
void deleteUser(Long id);
User updateUser(User user);
User findUser(Long id);
Iterable<User> findAll();
}
package com.example.demo.UserService;
import com.example.demo.dao.UserRepository;
import com.example.demo.entity.User;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import java.util.List;
@Service
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
@Autowired
private UserRepository userRepository;
@Override
public User saveUser(User user) {
return userRepository.save(user);
}
@Override
public void deleteUser(User user) {
userRepository.delete(user);
}
@Override
public void deleteUser(Long id) {
userRepository.deleteById(id);
}
@Override
public User updateUser(User user) {
return userRepository.save(user);
}
@Override
public User findUser(Long id) {
return userRepository.findById(id).get();
}
@Override
public Iterable<User> findAll() {
System.out.println(userRepository.findAll());
return userRepository.findAll();
}
}
dao
JpaRepository比CrudRepository多了一个findAll??
package com.example.demo.dao;
import com.example.demo.entity.User;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
import org.springframework.data.repository.CrudRepository;
//泛型为操作的bean类型 主键类型
public interface UserRepository extends JpaRepository<User, Long> {
}
entity
不需要构造方法吗?为什么?
package com.example.demo.entity;
import javax.persistence.*;
@Entity
@Table(name="demo_user")
public class User {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy=GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Long id;
@Column(name="name" )
private String username;
private String email;
public Long getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Long id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.username = name;
}
public String getEmail() {
return email;
}
public void setEmail(String email) {
this.email = email;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User{" +
"id=" + id +
", username='" + username + '\'' +
", email='" + email + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
application.yml
spring:
datasource:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://39.99.164.237:3306/db_example?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai
username: root
password: 123456
# jpa:
# hibernate:
# ddl-auto: update
# show-sql: true
或者application.properties
# 通用数据源配置
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://39.99.164.237:3306/db_example
spring.datasource.username=root
spring.datasource.password=123456
# JPA 相关配置 配置自动建表 ????
#spring.jpa.database-platform=org.hibernate.dialect.MySQL5InnoDBDialect
#spring.jpa.show-sql=true
#spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto=update # !注意不要用create
# ddl-auto区别
#
# ddl-auto:create:每次运行该程序,没有表格会新建表格,表内有数据会清空。
# ddl-auto:create-drop:每次程序结束的时候会清空表。
# ddl-auto:update:每次运行程序,没有表格会新建表格,表内有数据不会清空,只会更新。
# ddl-auto:validate:运行程序会校验数据与数据库的字段类型是否相同,不同会报错
测试
http://localhost:8080/demo/save?name=lisi&[email protected]
http://localhost:8080/demo/findAll
http://localhost:8080/demo/findOne?id=12
常见注解
@query
@Transactional
@Temporal
数据库的字段类型有date、time、datetime
而Temporal注解的作用就是帮Java的Date类型进行格式化,一共有三种注解值:
第一种:@Temporal(TemporalType.DATE)——>实体类会封装成日期“yyyy-MM-dd”的 Date类型。
第二种:@Temporal(TemporalType.TIME)——>实体类会封装成时间“hh-MM-ss”的 Date类型。
第三种:@Temporal(TemporalType.TIMESTAMP)——>实体类会封装成完整的时间“yyyy-MM-dd hh:MM:ss”的 Date类型。
注解方式有两种:
写在字段上:
@Temporal(TemporalType.TIMESTAMP)
private Date birthday;
写在 getXxx方法上:
@Temporal(TemporalType.DATE)
@Column(name = "birthday", length = 10)
public Date getBirthday() {
return this.birthday;
}
@Entity
应用于实体类,表明该实体类被JPA管理,将映射到指定的数据库表
@Id
应用于实体类的属性或者属性对应的getter方法,表示该属性映射为数据库表的主键
@GerneratedValue
于@Id一同使用,表示主键的生成策略,通过strategy属性指定。
JPA提供的生成策略有:
- AUTO — JPA自动选择合适的策略,是默认选项
- IDENTITY — 采用数据库ID自增长的方式来生成主键值,Oracle不支持这种方式;
- SEQUENCE — 通过序列产生主键,通过@SequenceGenerator注解指定序列名,MySql不支持这种方式;
- TABLE — 采用表生成方式来生成主键值,这种方式比较通用,但是效率低
Repository常用方法使用规范
| 关键字 | 方法命名 | sql where字句 |
|---|---|---|
| And | findByNameAndPwd | where name= ? and pwd =? |
| Or | findByNameOrSex | where name= ? or sex=? |
| Is,Equals | findById,findByIdEquals | where id= ? |
| Between | findByIdBetween | where id between ? and ? |
| LessThan | findByIdLessThan | where id < ? |
| LessThanEquals | findByIdLessThanEquals | where id <= ? |
| GreaterThan | findByIdGreaterThan | where id > ? |
| GreaterThanEquals | findByIdGreaterThanEquals | where id > = ? |
| After | findByIdAfter | where id > ? |
| Before | findByIdBefore | where id < ? |
| IsNull | findByNameIsNull | where name is null |
| isNotNull,NotNull | findByNameNotNull | where name is not null |
| Like | findByNameLike | where name like ? |
| NotLike | findByNameNotLike | where name not like ? |
| StartingWith | findByNameStartingWith | where name like ‘?%’ |
| EndingWith | findByNameEndingWith | where name like ‘%?’ |
| Containing | findByNameContaining | where name like ‘%?%’ |
| OrderBy | findByIdOrderByXDesc | where id=? order by x desc |
| Not | findByNameNot | where name <> ? |
| In | findByIdIn(Collection<?> c) | where id in (?) |
| NotIn | findByIdNotIn(Collection<?> c) | where id not in (?) |
| True | findByAaaTue | where aaa = true |
| False | findByAaaFalse | where aaa = false |
| IgnoreCase | findByNameIgnoreCase | where UPPER(name)=UPPER(?) |