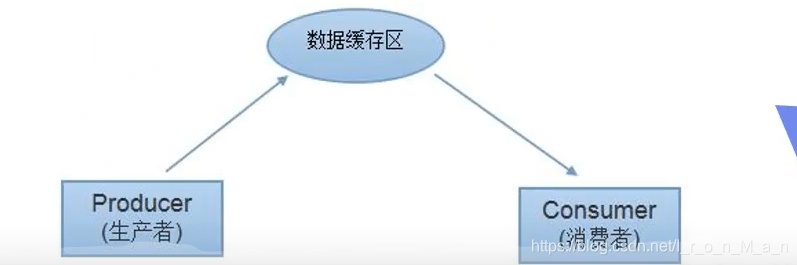
应用:生产者和消费者问题
- 假设仓库中只能存放一件产品,生产者将生产出来的产品放入仓库﹐消费者将仓库中产品取走消费.
- 如果仓库中没有产品﹐则生产者将产品放入仓库,否则停止生产并等待,直到仓库中的产品被消费者取走为止.
- 如果仓库中放有产品﹐则消费者可以将产品取走消费﹐否则停止消费并等待,直到仓库中再次放入产品为止.
分析
这是一个线程同步问题,生产者和消费者共享同一个资源,并且生产者和消费者之间相互依赖,互为条件.
- 对于生产者﹐没有生产产品之前,要通知消费者等待﹒而生产了产品之后,又需要马上通知消费者消费
- 对于消费者﹐在消费之后﹐要通知生产者已经结束消费,需要生产新的产品以供消费.
- 在生产者消费者问题中,仅有synchronized是不够的:synchronized 可阻止并发更新同一个共享资源,实现了同步,但synchronized不能用来实现不同线程之间的消息传递(通信)。
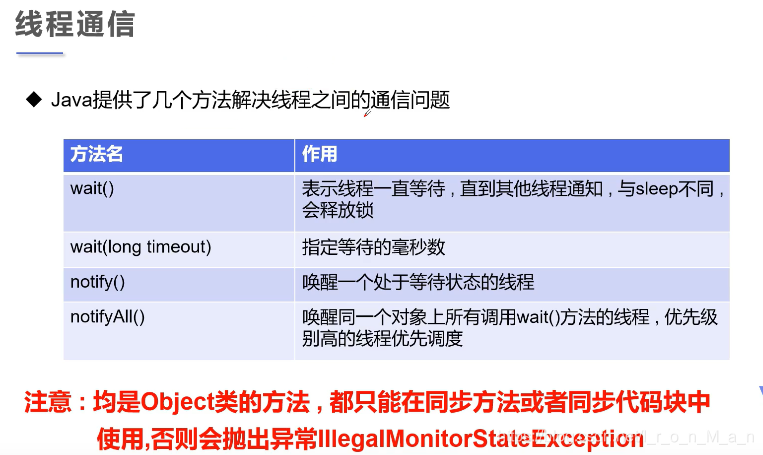
java提供了几个方法解决线程之间的通信问题
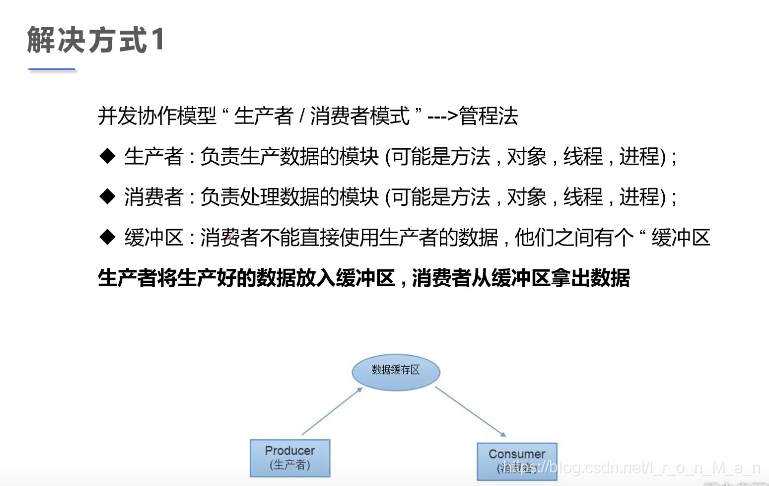
解决方式1
管程法
示例:
package Multithreading.生产者消费者问题;
// 测试:生产者消费者模型-->利用缓冲区解决:管程法
public class TestPC01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SynContainer container = new SynContainer();
new Producer(container).start();
new Consumer(container).start();
}
}
// 生产者
class Producer extends Thread {
SynContainer container;
public Producer(SynContainer container) {
this.container = container;
}
// 生产
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 1; i < 100; i++) {
try {
container.push(new Chicken(i));
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("生产了" + i + "只鸡");
}
}
}
// 消费者
class Consumer extends Thread {
SynContainer container;
public Consumer(SynContainer container) {
this.container = container;
}
// 消费
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
try {
System.out.println("消费了-->" + container.pop().id + "只鸡");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
// 产品
class Chicken {
int id;
public Chicken(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
}
// 缓冲区
class SynContainer {
// 需要一个容器大小
Chicken[] chickens = new Chicken[10];
// 容器计数器
int count = 0;
// 生产者放入产品
public synchronized void push(Chicken chicken) throws InterruptedException {
// 如果容器满了,就需要等待消费者消费
if (count == chickens.length) {
// 通知生产者,生产等待
this.wait();
}
//如果没有满,我们就需要丢入产品
chickens[count] = chicken;
count++;
// 可以通知消费者消费了
this.notifyAll();
}
// 消费者消费产品
public synchronized Chicken pop() throws InterruptedException {
// 判断能否消费
if (count == 0) {
// 等待生产者生产,消费者等待
this.wait();
}
// 如果可以消费
count--;
Chicken chicken = chickens[count];
// 吃完了,通知生产者生产
this.notifyAll();
return chicken;
}
}
运行结果:

解决方式2
信号灯法

示例:
package Multithreading.生产者消费者问题;
// 测试生产者消费问题:信号灯法,标志位
public class TestPC02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
TV tv = new TV();
new Player(tv).start();
new Watcher(tv).start();
}
}
// 生产者-->演员
class Player extends Thread {
TV tv;
public Player(TV tv) {
this.tv = tv;
}
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
if (i % 2 == 0) {
try {
tv.play("快乐大本营播放中");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
} else {
try {
tv.play("广告播放中");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
// 消费者-->观众
class Watcher extends Thread {
TV tv;
public Watcher(TV tv) {
this.tv = tv;
}
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
try {
tv.watch();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
// 产品-->节目
class TV {
// 演员表演,关注等待
// 观众观看,演员等待
String voice;// 表演的节目
boolean flag = true;
// 演员表演
public synchronized void play(String voice) throws InterruptedException {
if (!flag) {
this.wait();
}
System.out.println("演员表演了: " + voice);
// 通知观众观看
this.notifyAll();
this.voice = voice;
this.flag = !this.flag;
}
// 观众观看
public synchronized void watch() throws InterruptedException {
if (flag) {
this.wait();
}
System.out.println("观看了: " + voice);
// 通知演员表演
this.notifyAll();
this.flag = !this.flag;
}
}
