目录
4、基于 HiddentHttpMethodFilter 的示例
一、RequestMapping 注解
1、使用说明
(1)源码:
@Target({ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Mapping
public @interface RequestMapping {
}(2)作用: 用于建立请求 URL 和处理请求方法之间的对应关系。
(3)出现位置:
- 类上:
请求 URL 的第一级访问目录。此处不写的话,就相当于应用的根目录。写的话需要以 / 开头。 它出现的目的是为了使我们的 URL可以按照模块化管理:
例如:
账户模块: /account/add /account/update /account/delete ...
订单模块: /order/add /order/update /order/delete
红色的部分就是把 RequsetMapping 写在类上,使我们的 URL 更加精细。
- 方法上:
请求 URL 的第二级访问目录。
(4)属性:
value:用于指定请求的 URL。它和 path 属性的作用是一样的。
method:用于指定请求的方式。
params:用于指定限制请求参数的条件。它支持简单的表达式。要求请求参数的 key 和 value 必须和配置的一模一样。 例如:params = {"moeny!=100"},表示请求参数中 money 不能是 100。
headers:用于指定限制请求消息头的条件。 注意: 以上四个属性只要出现 2 个或以上时,他们的关系是与的关系。
2、使用示例
(1)class 属性的示例
/**
* RequestMapping 注解出现的位置
* @Version 1.0
*/
@Controller("accountController")
@RequestMapping("/account")
public class AccountController {
@RequestMapping("/findAccount")
public String findAccount(){
System.out.println("查询了账户。。。。");
return "success";
}
}jsp 中的代码:
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%> <!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8">
<title>requestmapping 的使用</title>
</head>
<body>
<!-- 第一种访问方式 -->
<a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/account/findAccount">查询 账户</a> <br/>
<!--第二种访问方式 -->
<a href="account/findAccount">查询账户</a>
</body>
</html>注意:
当我们使用此种方式配置时,在 jsp 中第二种写法时,不要在访问 URL 前面加 / ,否则无法找到资源。
(2)method 属性的示例
控制器代码:
/**
* 保存账户
* @return
*/
@RequestMapping(value="/saveAccount",method=RequestMethod.POST)
public String saveAccount() {
System.out.println("保存了账户");
return "success";
}jsp 代码:
<!-- 请求方式的示例 -->
<a href="account/saveAccount">保存账户,get 请求</a>
<br/>
<form action="account/saveAccount" method="post">
<input type="submit" value="保存账户,post 请求">
</form>注意: 当使用 get 请求时,提示错误信息是 405,信息是方法不支持 get 方式请求
(3)params 属性的示例:
控制器的代码:
/**
* 删除账户
* @return
*/
@RequestMapping(value="/removeAccount",params= {"accountName","money=100"})
public String removeAccount() {
System.out.println("删除了账户");
return "success";
}jsp 中的代码:
<!-- 请求参数的示例 -->
<a href="account/removeAccount?accountName=aaa&money=100">删除账户, 金额 100</a>
<br/>
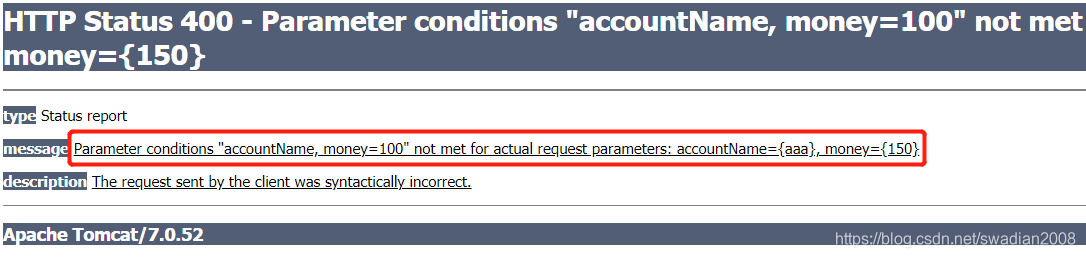
<a href="account/removeAccount?accountName=aaa&money=150">删除账户, 金额 150</a>注意: 当我们点击第一个超链接时,可以访问成功。 当我们点击第二个超链接时,无法访问。因为 params= {"accountName","money=100"} ,限制了 money=100 的条件
二、RequestParam注解
1、使用说明
作用: 把请求中指定名称的参数给控制器中的形参赋值。
属性: value:请求参数中的名称。 required:请求参数中是否必须提供此参数。
默认值:true。表示必须提供,如果不提供将报错。
2、使用示例
jsp
<!-- requestParams 注解的使用 -->
<a href="springmvc/useRequestParam?name=test">requestParam 注解</a>控制器中的代码:
/**
* requestParams 注解的使用
*
* @param username
* @return
*/
@RequestMapping("/useRequestParam")
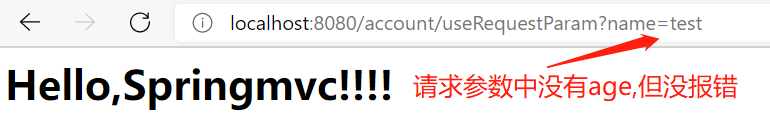
public String useRequestParam(@RequestParam("name") String username, @RequestParam(value = "age", required = false) Integer age) {
System.out.println(username + "," + age);
return "success";
}运行结果:
三、RequestBody注解
1、使用说明
作用: 用于获取请求体内容。直接使用得到是 key=value&key=value...结构的数据。 get 请求方式不适用。
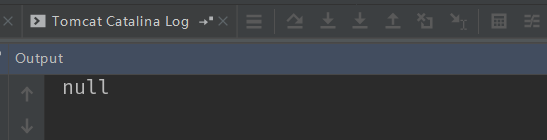
属性: required:是否必须有请求体。默认值是:true。当取值为 true 时,get 请求方式会报错。如果取值为 false,get 请求得到是 null。
2、使用示例
post 请求 jsp 代码:
<!-- request body 注解 -->
<form action="springmvc/useRequestBody" method="post">
用户名称:<input type="text" name="username" ><br/>
用户密码:<input type="password" name="password" ><br/>
用户年龄:<input type="text" name="age" ><br/>
<input type="submit" value="保存">
</form>get 请求 jsp 代码:
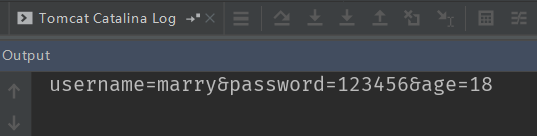
<a href="springmvc/useRequestBody?body=test">requestBody 注解 get 请求</a>控制器代码:
/**
* RequestBody 注解
* @return
*/
@RequestMapping("/useRequestBody")
public String useRequestBody(@RequestBody(required=false) String body){
System.out.println(body);
return "success";
}post 请求运行结果:
get 请求运行结果:
四、PathVaribale注解
1、使用说明
作用: 用于绑定 url 中的占位符。例如:请求 url 中 /delete/{id},这个{id}就是 url 占位符。 url 支持占位符是 spring3.0 之后加入的。是 springmvc 支持 rest 风格 URL 的一个重要标志。
属性: value:用于指定 url 中占位符名称。 required:是否必须提供占位符。
2、使用示例
jsp代码:
<!-- PathVariable 注解 -->
<a href="springmvc/usePathVariable/100">pathVariable 注解</a>控制器代码:
/**
* PathVariable 注解
*
* @return
*/
@RequestMapping("/usePathVariable/{id}")
public String usePathVariable(@PathVariable("id") Integer id) {
System.out.println(id);
return "success";
}运行结果:

3、REST 风格 URL
(1)什么是 rest
REST(英文:Representational State Transfer,简称 REST)描述了一个架构样式的网络系统,比如 web 应用程序。它首次出现在 2000 年 Roy Fielding 的博士论文中,他是 HTTP 规范的主要编写者之一。在目前主流的三种 Web 服务交互方案中,REST 相比于 SOAP(Simple Object Access protocol,简单对象访问协议)以及 XML-RPC 更加简单明了,无论是对 URL 的处理还是对 Payload 的编码,REST 都倾向于用更加简单轻量的方法设计和实现。值得注意的是 REST 并没有一个明确的标准,而更像是一种设计的风格。它本身并没有什么实用性,其核心价值在于如何设计出符合 REST 风格的网络接口。
(2)restful 的优点
它结构清晰、符合标准、易于理解、扩展方便,所以正得到越来越多网站的采用。
(3)restful 的特性
资源(Resources):网络上的一个实体,或者说是网络上的一个具体信息。 它可以是一段文本、一张图片、一首歌曲、一种服务,总之就是一个具体的存在。可以用一个 URI(统一资源定位符)指向它,每种资源对应一个特定的 URI 。要获取这个资源,访问它的 URI 就可以,因此 URI 即为每一个资源的独一无二的识别符。
表现层(Representation):把资源具体呈现出来的形式,叫做它的表现层(Representation)。
比如,文本可以用 txt 格式表现,也可以用 HTML 格式、XML 格式、JSON 格式表现,甚至可以采用二进制格式。
状态转化(State Transfer):每发出一个请求,就代表了客户端和服务器的一次交互过程。 HTTP 协议,是一个无状态协议,即所有的状态都保存在服务器端。因此,如果客户端想要操作服务器,必须通过某种手段,让服务器端发生“状态转化”(State Transfer)。而这种转化是建立在表现层之上的,所以就是“表现层状态转化”。
具体说,就是 HTTP 协议里面,四个表示操作方式的动词:GET 、POST 、PUT、DELETE。它们分别对应四种基本操作:
- GET 用来获取资源
- POST 用来新建资源
- PUT 用来更新资源
- DELETE 用来删除资源
(4)restful 的示例:
- /account/1 HTTP GET : 得到 id = 1 的 account
- /account/1 HTTP DELETE: 删除 id = 1 的 account
- /account/1 HTTP PUT: 更新 id = 1 的 account
- /account HTTP POST: 新增 account
4、基于 HiddentHttpMethodFilter 的示例
作用: 由于浏览器 form 表单只支持 GET 与 POST 请求,而 DELETE、PUT 等 method 并不支持,Spring3.0 添加了一个过滤器,可以将浏览器请求改为指定的请求方式,发送给我们的控制器方法,使得支持 GET、POST、PUT 与 DELETE 请求。
使用方法:
- 第一步:在 web.xml 中配置该过滤器。 HiddenHttpMethodFilter
- 第二步:请求方式必须使用 post 请求。
- 第三步:按照要求提供 _method 请求参数,该参数的取值就是我们需要的请求方式。
web.xml 中配置过滤器
<!--配置HiddenHttpMethodFilter-->
<!--
配置 org.springframework.web.filter.HiddenHttpMethodFilter: 可以把 POST 请求转为 DELETE 或 PUT 请求
-->
<filter>
<filter-name>HiddenHttpMethodFilter</filter-name>
<filter-class>org.springframework.web.filter.HiddenHttpMethodFilter</filter-class>
</filter>
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>HiddenHttpMethodFilter</filter-name>
<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
</filter-mapping>jsp中示例代码:
<!-- 保存 -->
<form action="account/testRestPOST" method="post">
用户名称:<input type="text" name="username"><br/>
<input type="hidden" name="_method" value="POST">
<input type="submit" value="保存">
</form>
<hr/>
<!-- 更新 -->
<form action="account/testRestPUT/1" method="post">
用户名称:<input type="text" name="username"><br/>
<input type="hidden" name="_method" value="PUT">
<input type="submit" value="更新"></form>
<hr/>
<!-- 删除 -->
<form action="account/testRestDELETE/1" method="post">
<input type="hidden" name="_method" value="DELETE">
<input type="submit" value="删除">
</form>
<hr/>
<!-- 查询一个 -->
<form action="account/testRestGET/1" method="post">
<input type="hidden" name="_method" value="GET">
<input type="submit" value="查询">
</form>控制器中示例代码
/**
* post 请求:保存
*
* @return
*/
@RequestMapping(value = "/testRestPOST", method = RequestMethod.POST)
public String testRestfulURLPOST(String username) {
System.out.println("rest post , " + username);
return "success";
}
/**
* put 请求:更新
*
* @return
*/
@RequestMapping(value = "/testRestPUT/{id}", method = RequestMethod.PUT)
public String testRestfulURLPUT(@PathVariable("id") Integer id, String username) {
System.out.println("rest put , " + id + "," + username);
return "success";
}
/**
* post 请求:删除
*
* @return
*/
@RequestMapping(value = "/testRestDELETE/{id}", method = RequestMethod.DELETE)
public String testRestfulURLDELETE(@PathVariable("id") Integer id) {
System.out.println("rest delete , " + id);
return "success";
}
/**
* post 请求:查询
*
* @return
*/
@RequestMapping(value = "/testRestGET/{id}", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String testRestfulURLGET(@PathVariable("id") Integer id) {
System.out.println("rest get , " + id);
return "success";
}执行结果

五、RequestHeader注解
1、使用说明
作用: 用于获取请求消息头。
属性: value:提供消息头名称 required:是否必须有此消息头
- 注:在实际开发中一般不怎么用。
2、使用示例
jsp中代码
<!-- RequestHeader 注解 -->
<a href="springmvc/useRequestHeader">获取请求消息头</a>控制器中代码:
/**
* RequestHeader 注解 * @param user * @return
*/
@RequestMapping("/useRequestHeader")
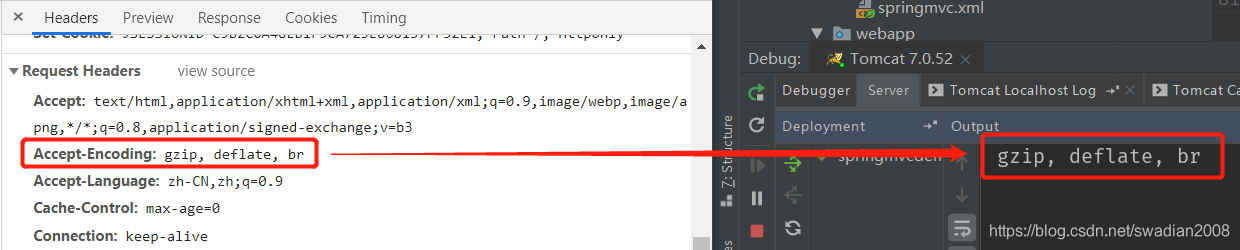
public String useRequestHeader(@RequestHeader(value = "Accept-Encoding", required = false) String requestHeader) {
System.out.println(requestHeader);
return "success";
}执行结果:
六、CookieValue注解
1、使用说明
作用: 用于把指定 cookie 名称的值传入控制器方法参数。
属性: value:指定 cookie 的名称。 required:是否必须有此 cookie。
2、使用示例
jsp中代码:
<!-- CookieValue 注解 -->
<a href="springmvc/useCookieValue">绑定 cookie 的值</a>控制器中的代码:
/**
* Cookie 注解注解 * @param user * @return
*/
@RequestMapping("/useCookieValue")
public String useCookieValue(@CookieValue(value = "JSESSIONID", required = false) String cookieValue) {
System.out.println(cookieValue);
return "success";
}执行结果:

七、SessionAttribute注解
1、使用说明
作用: 用于多次执行控制器方法间的参数共享。
属性: value:用于指定存入的属性名称 type:用于指定存入的数据类型。
2、使用示例
jsp中的代码:
<!-- SessionAttribute 注解的使用 -->
<a href="account/testPut">存入 SessionAttribute</a>
<hr/>
<a href="account/testGet">取出 SessionAttribute</a>
<hr/>
<a href="account/testClean">清除 SessionAttribute</a>控制器中的代码:
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.ui.Model;
import org.springframework.ui.ModelMap;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.SessionAttributes;
import org.springframework.web.bind.support.SessionStatus;
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/account")
@SessionAttributes(value = {"username", "password"}, types = {Integer.class})
public class AccountController {
/**
* 把数据存入 SessionAttribute
*
* @param model
* @return Model 是 spring 提供的一个接口,该接口有一个实现类 ExtendedModelMap
* 该类继承了 ModelMap,而 ModelMap 就是 LinkedHashMap 子类
*/
@RequestMapping("/testPut")
public String testPut(Model model) {
model.addAttribute("username", "泰斯特");
model.addAttribute("password", "123456");
model.addAttribute("age", 31);
//跳转之前将数据保存到 username、password 和 age 中,因为注解 @SessionAttribute 中有这几个参数
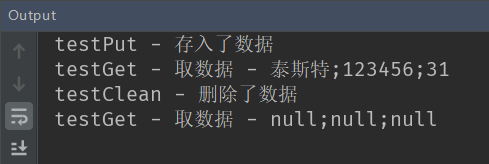
System.out.println("testPut - 存入了数据");
return "success";
}
@RequestMapping("/testGet")
public String testGet(ModelMap model) {
System.out.println("testGet - 取数据 - " + model.get("username") + ";" + model.get("password") + ";" + model.get("age"));
return "success";
}
@RequestMapping("/testClean")
public String complete(SessionStatus sessionStatus) {
sessionStatus.setComplete();
System.out.println("testClean - 删除了数据");
return "success";
}
}运行结果: