ArrayList 源码解读
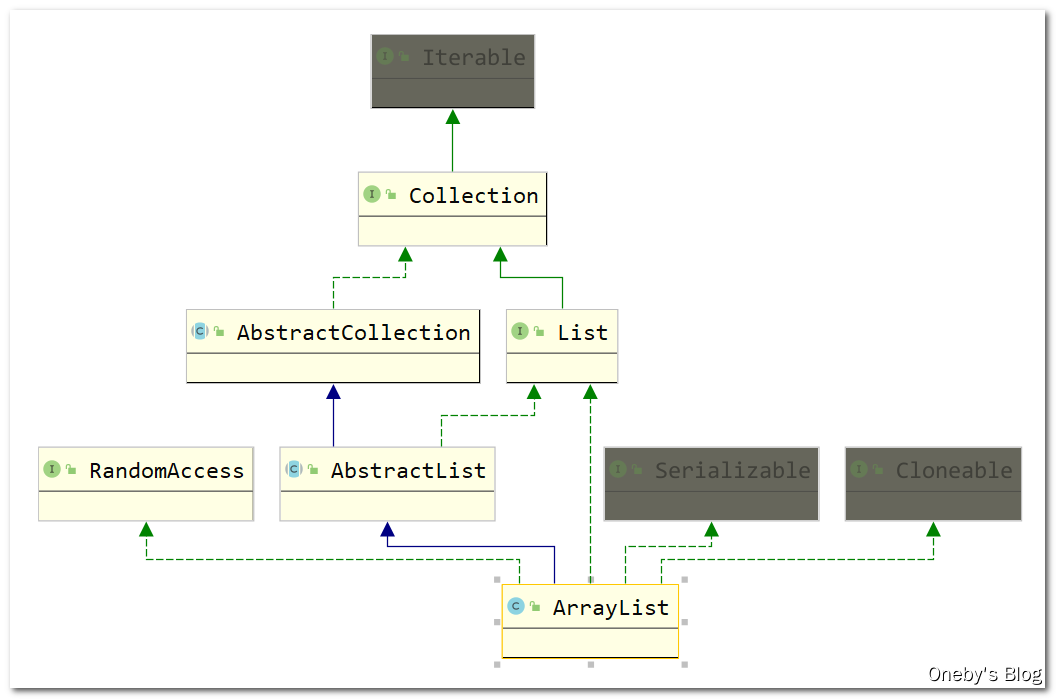
1、ArrayList 继承关系
ArrayList 继承树
ArrayList 继承了 AbstractList 抽象类,实现了 List 接口、RandomAccess 接口、Cloneable 接口、java.io.Serializable 接口
public class ArrayList<E> extends AbstractList<E>
implements List<E>, RandomAccess, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
{
1、List 接口
List接口的特点:
- 有序的集合,存储元素和取出元素的顺序是一致的
- 有索引,包含了一些带索引的方法
- 允许存储重复的元素
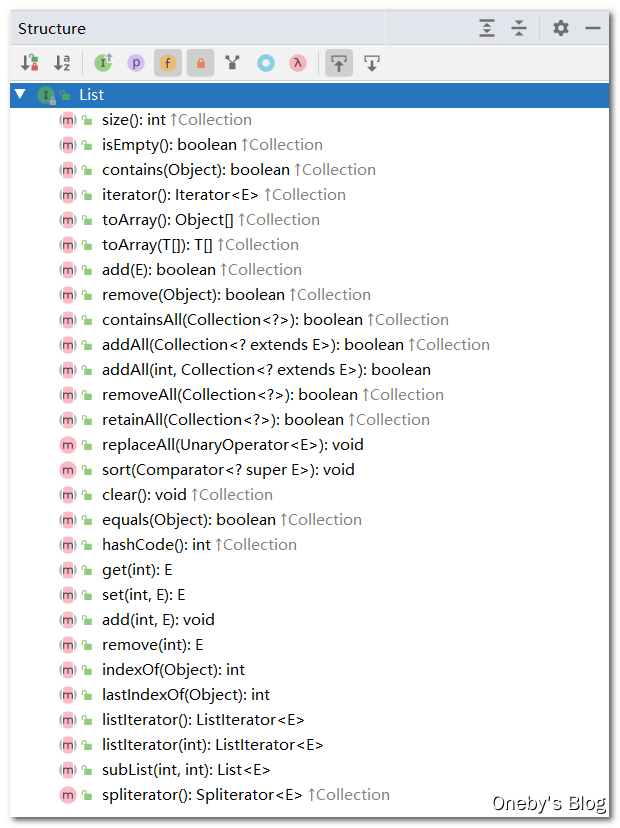
List 接口常用的方法
- 增:
add(Object obj) - 删:
remove(int index)/remove(Object obj) - 改:
set(int index, Object ele) - 查:
get(int index) - 插:
add(int index, Object ele) - 长度:
size() - 遍历:①
Iterator迭代器方式;② 增强for循环;③ 普通的循环
2、AbstractList 抽象类
在 AbstractList 抽象父类中:有些方法已经被赋予了具体的实现逻辑,比如 indexOf() 和 lastIndexOf() 方法;而有些方法则需要推迟到子类中去实现,比如 get()、set()、add()、remove() 等方法
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
*/
abstract public E get(int index);
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*
* <p>This implementation always throws an
* {@code UnsupportedOperationException}.
*
* @throws UnsupportedOperationException {@inheritDoc}
* @throws ClassCastException {@inheritDoc}
* @throws NullPointerException {@inheritDoc}
* @throws IllegalArgumentException {@inheritDoc}
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public E set(int index, E element) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*
* <p>This implementation always throws an
* {@code UnsupportedOperationException}.
*
* @throws UnsupportedOperationException {@inheritDoc}
* @throws ClassCastException {@inheritDoc}
* @throws NullPointerException {@inheritDoc}
* @throws IllegalArgumentException {@inheritDoc}
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public void add(int index, E element) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*
* <p>This implementation always throws an
* {@code UnsupportedOperationException}.
*
* @throws UnsupportedOperationException {@inheritDoc}
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public E remove(int index) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
// Search Operations
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*
* <p>This implementation first gets a list iterator (with
* {@code listIterator()}). Then, it iterates over the list until the
* specified element is found or the end of the list is reached.
*
* @throws ClassCastException {@inheritDoc}
* @throws NullPointerException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public int indexOf(Object o) {
ListIterator<E> it = listIterator();
if (o==null) {
while (it.hasNext())
if (it.next()==null)
return it.previousIndex();
} else {
while (it.hasNext())
if (o.equals(it.next()))
return it.previousIndex();
}
return -1;
}
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*
* <p>This implementation first gets a list iterator that points to the end
* of the list (with {@code listIterator(size())}). Then, it iterates
* backwards over the list until the specified element is found, or the
* beginning of the list is reached.
*
* @throws ClassCastException {@inheritDoc}
* @throws NullPointerException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public int lastIndexOf(Object o) {
ListIterator<E> it = listIterator(size());
if (o==null) {
while (it.hasPrevious())
if (it.previous()==null)
return it.nextIndex();
} else {
while (it.hasPrevious())
if (o.equals(it.previous()))
return it.nextIndex();
}
return -1;
}
3、RandomAccess 接口
RandomAccess 这个接口很有趣,里面并没有定义任何方法规范,是个空接口。RandomAccess 接口是一个标志接口(Marker),只要 List 集合实现这个接口,就能支持快速随机访问(类似于数组那样根据索引下标进行访问)
public interface RandomAccess {
}
4、Cloneable 接口
Cloneable 这个借口也是个空接口(标志接口),我们要使用一个对象的 clone()方法,必须实现 Cloneable 接口,这个接口没有任何实现,跟 RandomAccess一样是一种标志性接口,如果不实现 Cloneable 接口,会抛出 CloneNotSupportedException 异常
其实吧,并不是 Cloneable 借口没有对应的方法规范,而是 JDK 编写者觉得所有对象都应该有 clone() 这种行为规范,于是将这种共同的行为规范提取到 Object 类中去了~
public interface Cloneable {
}
5、java.io.Serializable 接口
哇塞塞,又是一个标志性接口,Serializable 接口是启用其序列化功能的接口。实现 java.io.Serializable 接口的类是可序列化的。没有实现此接口的类将不能使它们的任意状态被序列化或逆序列化。
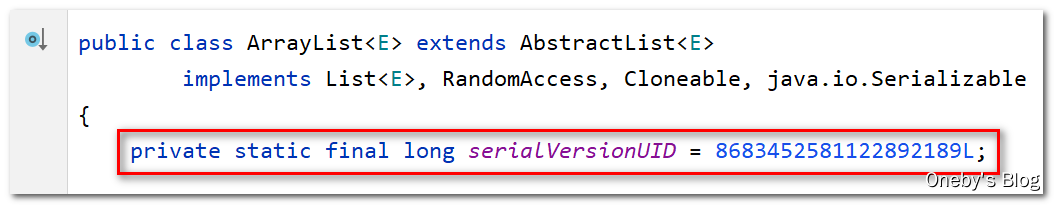
实现 java.io.Serializable 这个接口是为序列化,serialVersionUID 用来表明实现序列化类的不同版本间的兼容性。如果你修改了此类,要修改此值。
public interface Serializable {
}
我们可以在 ArrayList 的源码中看到此 serialVersionUID
2、ArrayList 的初始容量
ArrayList 的空参构造方法
注释说:Constructs an empty list with an initial capacity of ten.,即构造一个初始容量为 10 的 ArrayList
/**
* Constructs an empty list with an initial capacity of ten.
*/
public ArrayList() {
this.elementData = DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
}
构造器中的字段
elementData 就是用来存放实际数据的数组,可以看到这是一个 Object[] 类型的数组,也就是说什么类型的数据也能往这个数组里面放,因为 Object 类是所有类的顶级父类。字段使用 transient 关键字修饰,表示在类的实例对象的序列化处理过程中会被忽略
DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA 是个空数组啊,为啥构造器的注释写写着构造了一个初始容量为 10 的数组,别着急,往下看
来看看 elementData 字段上面的注释:The capacity of the ArrayList is the length of this array buffer. Any empty ArrayList with elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA will be expanded to DEFAULT_CAPACITY when the first element is added.,当第一个元素被添加时,数组容量将被扩充到 10
/**
* Default initial capacity.
*/
private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10;
/**
* Shared empty array instance used for empty instances.
*/
private static final Object[] EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {
};
/**
* Shared empty array instance used for default sized empty instances. We
* distinguish this from EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA to know how much to inflate when
* first element is added.
*/
private static final Object[] DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {
};
/**
* The array buffer into which the elements of the ArrayList are stored.
* The capacity of the ArrayList is the length of this array buffer. Any
* empty ArrayList with elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA
* will be expanded to DEFAULT_CAPACITY when the first element is added.
*/
transient Object[] elementData; // non-private to simplify nested class access
/**
* The size of the ArrayList (the number of elements it contains).
*
* @serial
*/
private int size;
3、ArrayList#add() 方法
添加元素的方法:boolean add(E e) 方法
方法注释:Appends the specified element to the end of this list,即将一个指定的元素添加到 ArrayList 集合的尾部;并返回是否添加成功
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1) 实现 ArrayList 的扩容
elementData[size++] = e 负责将元素添加到 ArrayList 集合尾部,并将集合元素个数 size 加 1
/**
* Appends the specified element to the end of this list.
*
* @param e element to be appended to this list
* @return <tt>true</tt> (as specified by {@link Collection#add})
*/
public boolean add(E e) {
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!
elementData[size++] = e;
return true;
}
扩容方法:ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1) 方法
形参为 minCapacity,也就是刚才的 size + 1,表示 ArrayList 所需的最小容量
这里有个很重要的判断:我们在构造器初始化时,将 this.elementData 赋值为 DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA,因此 if (elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) 判断成立(即 elementData 数组为空数组),所以就会执行 minCapacity = Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity) 方法。第一次执行 add() 方法,集合元素个数 size = 0,因此 minCapacity =DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10。这就是上面所讲的当第一个元素被添加时,数组容量将被扩充到 10
接下来便执行 ensureExplicitCapacity(minCapacity) 方法将数组容量扩充到 10
private void ensureCapacityInternal(int minCapacity) {
if (elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) {
minCapacity = Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity);
}
ensureExplicitCapacity(minCapacity);
}
扩容方法:ensureExplicitCapacity(minCapacity) 方法
首先执行 modCount++ 标记 ArrayList 已经被修改过了
if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0):如果 ArrayList 所需容量已经超过 ArrayList 实际容量,则需要执行 grow(minCapacity) 方法进行扩容
private void ensureExplicitCapacity(int minCapacity) {
modCount++;
// overflow-conscious code
if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0)
grow(minCapacity);
}
关于 modCount 变量
modCount 变量是在抽象父类 AbstractList 中定义的变量,用于标识集合是否被修改过(The number of times this list has been structurally modified.)
扩容方法:grow(minCapacity) 方法
关键在这一个右移操作上:oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1),这个操作会将当前数组的容量扩容为之前的 1.5 倍
接着进行一系列的安全检查后,执行 elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity) 方法将原来数组中的元素拷贝到数组中
/**
* Increases the capacity to ensure that it can hold at least the
* number of elements specified by the minimum capacity argument.
*
* @param minCapacity the desired minimum capacity
*/
private void grow(int minCapacity) {
// overflow-conscious code
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1);
if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)
newCapacity = minCapacity;
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
// minCapacity is usually close to size, so this is a win:
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
}
private static int hugeCapacity(int minCapacity) {
if (minCapacity < 0) // overflow
throw new OutOfMemoryError();
return (minCapacity > MAX_ARRAY_SIZE) ?
Integer.MAX_VALUE :
MAX_ARRAY_SIZE;
}
4、ArrayList#get() 方法
获取指定索引处的元素:E get(int index) 方法
首先执行 rangeCheck(index) 方法进行安全检查,然后直接从数组指定索引元素处取值并返回
/**
* Returns the element at the specified position in this list.
*
* @param index index of the element to return
* @return the element at the specified position in this list
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public E get(int index) {
rangeCheck(index);
return elementData(index);
}
边界检查:rangeCheck(int index) 方法
若超边界,则直接抛异常,够狠啊
/**
* Checks if the given index is in range. If not, throws an appropriate
* runtime exception. This method does *not* check if the index is
* negative: It is always used immediately prior to an array access,
* which throws an ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException if index is negative.
*/
private void rangeCheck(int index) {
if (index >= size)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index));
}
5、ArrayList#remove() 方法
删除指定索引处的元素:E remove(int index) 方法
首先还是执行 rangeCheck(index) 进行边界检查
执行 modCount++ 指令标记集合已经被修改过了
执行 E oldValue = elementData(index) 方法取出指定索引处的元素
执行 System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index, numMoved) 方法,将数组后面的元素往前面移,实现覆盖删除的效果(index 索引处的元素被覆盖)
执行 elementData[--size] = null,将 elementData[size] 元素设置为 null,让 GC 回收掉 elementData[size] 元素指向的对象;同时 size 执行减 1 操作,集合元素个数减 1
最后将被删除的元素返回
/**
* Removes the element at the specified position in this list.
* Shifts any subsequent elements to the left (subtracts one from their
* indices).
*
* @param index the index of the element to be removed
* @return the element that was removed from the list
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public E remove(int index) {
rangeCheck(index);
modCount++;
E oldValue = elementData(index);
int numMoved = size - index - 1;
if (numMoved > 0)
System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index,
numMoved);
elementData[--size] = null; // clear to let GC do its work
return oldValue;
}
6、ArrayList#set() 方法
设置指定索引处元素的值:E set(int index, E element) 方法
首先还是执行 rangeCheck(index) 进行边界检查,然后修改 index 索引处元素的值
/**
* Replaces the element at the specified position in this list with
* the specified element.
*
* @param index index of the element to replace
* @param element element to be stored at the specified position
* @return the element previously at the specified position
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public E set(int index, E element) {
rangeCheck(index);
E oldValue = elementData(index);
elementData[index] = element;
return oldValue;
}
// Positional Access Operations
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
E elementData(int index) {
return (E) elementData[index];
}
7、ArrayList#indexOf() 方法
获取元素的索引:int indexOf(Object o) 方法
这里分为两种情况:o == null 和 o != null。当 o == null,判断相等使用 elementData[i]==null 进行判断;当 o != null,判断相等使用 o.equals(elementData[i]) 进行判断
/**
* Returns the index of the first occurrence of the specified element
* in this list, or -1 if this list does not contain the element.
* More formally, returns the lowest index <tt>i</tt> such that
* <tt>(o==null ? get(i)==null : o.equals(get(i)))</tt>,
* or -1 if there is no such index.
*/
public int indexOf(Object o) {
if (o == null) {
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
if (elementData[i]==null)
return i;
} else {
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
if (o.equals(elementData[i]))
return i;
}
return -1;
}
8、ArrayList 迭代器
迭代器:Iterator 迭代器接口
迭代器是一种设计模式,它是一个对象,它可以遍历并选择序列中的对象,而开发人员不需要了解该序列的底层结构。迭代器通常被称为“轻量级”对象,因为创建它的代价小
Java中的Iterator功能比较简单,并且只能单向移动
- 使用
hasNext()检查序列中是否还有元素。 - 使用
next()获得序列中的下一个元素。 - 使用
remove()将迭代器新返回的元素删除。
public interface Iterator<E> {
/**
* Returns {@code true} if the iteration has more elements.
* (In other words, returns {@code true} if {@link #next} would
* return an element rather than throwing an exception.)
*
* @return {@code true} if the iteration has more elements
*/
boolean hasNext();
/**
* Returns the next element in the iteration.
*
* @return the next element in the iteration
* @throws NoSuchElementException if the iteration has no more elements
*/
E next();
/**
* Removes from the underlying collection the last element returned
* by this iterator (optional operation). This method can be called
* only once per call to {@link #next}. The behavior of an iterator
* is unspecified if the underlying collection is modified while the
* iteration is in progress in any way other than by calling this
* method.
*
* @implSpec
* The default implementation throws an instance of
* {@link UnsupportedOperationException} and performs no other action.
*
* @throws UnsupportedOperationException if the {@code remove}
* operation is not supported by this iterator
*
* @throws IllegalStateException if the {@code next} method has not
* yet been called, or the {@code remove} method has already
* been called after the last call to the {@code next}
* method
*/
default void remove() {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("remove");
}
/**
* Performs the given action for each remaining element until all elements
* have been processed or the action throws an exception. Actions are
* performed in the order of iteration, if that order is specified.
* Exceptions thrown by the action are relayed to the caller.
*
* @implSpec
* <p>The default implementation behaves as if:
* <pre>{@code
* while (hasNext())
* action.accept(next());
* }</pre>
*
* @param action The action to be performed for each element
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified action is null
* @since 1.8
*/
default void forEachRemaining(Consumer<? super E> action) {
Objects.requireNonNull(action);
while (hasNext())
action.accept(next());
}
}
ArrayList 内部类:Itr 迭代器类
Iterator是Java迭代器最简单的实现,在 ArrayList 类中找到 Itr 类,该类实现了 Iterator 接口,并重写了其中的方法
Itr 中的字段
cursor:下一个元素的索引lastRet:最近一次返回的元素的索引expectedModCount:期望的修改计数器
/**
* An optimized version of AbstractList.Itr
*/
private class Itr implements Iterator<E> {
int cursor; // index of next element to return
int lastRet = -1; // index of last element returned; -1 if no such
int expectedModCount = modCount;
boolean hasNext() 方法
如果下一个元素的索引 == 集合元素个数,则说明已经没有下一个元素了,那么 hasNext() 的条件为 cursor != size
public boolean hasNext() {
return cursor != size;
}
E next() 方法
首先通过 checkForComodification() 方法检查集合是否已经被更改(modCount != expectedModCount),若已经被更改,则抛出 ConcurrentModificationException 异常。接着还有一些 Guard Safe 语句,就不多赘述
最后将游标 cursor 右移,准备访问下一个元素,将待访问的元素(elementData[i])返回,并将最近一次访问过的元素索引设置为 i(lastRet = i)
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public E next() {
checkForComodification();
int i = cursor;
if (i >= size)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
Object[] elementData = ArrayList.this.elementData;
if (i >= elementData.length)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
cursor = i + 1;
return (E) elementData[lastRet = i];
}
final void checkForComodification() {
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
remove() 方法
Guard Safe:判断 lastRet(最近一次访问过的元素索引)是否存在,以及判断集合是够被修改过,若有上述情况,则抛出相应的异常
因为 Itr 类是 ArrayList 的内部类,通过 ArrayList.this.remove(lastRet) 这种方式调用当前 ArrayList 对象的 remove() 方法,实现删除操作
cursor = lastRet:因为是删除元素,不是访问元素,因此 cursor 无需移动,原地踏步即可
lastRet = -1:上除了上次访问的元素,那么上次访问的元素索引就没有啦,需要将 lastRet 设置为 -1
expectedModCount = modCount:删除了集合中的元素,modCount 会减 1,需要更新 expectedModCount 的值,否则下次操作时会抛出 ConcurrentModificationException 异常
public void remove() {
if (lastRet < 0)
throw new IllegalStateException();
checkForComodification();
try {
ArrayList.this.remove(lastRet);
cursor = lastRet;
lastRet = -1;
expectedModCount = modCount;
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
forEachRemaining(Consumer<? super E> consumer) 方法
若没有其他线程争抢,那么执行 while (i != size && modCount == expectedModCount) 循环将会从 i 处遍历至集合尾部,并将集合元素传入消费者的 accept() 方法中进行消费
cursor = i 和 lastRet = i - 1:更新游标信息和上一次访问的元素索引信息
最后执行 checkForComodification() 方法查看是否出现了并发修改异常
@Override
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public void forEachRemaining(Consumer<? super E> consumer) {
Objects.requireNonNull(consumer);
final int size = ArrayList.this.size;
int i = cursor;
if (i >= size) {
return;
}
final Object[] elementData = ArrayList.this.elementData;
if (i >= elementData.length) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
while (i != size && modCount == expectedModCount) {
consumer.accept((E) elementData[i++]);
}
// update once at end of iteration to reduce heap write traffic
cursor = i;
lastRet = i - 1;
checkForComodification();
}
Consumer 接口
Consumer 是一个函数式接口,void accept(T t) 方法负责消费一个对象
@FunctionalInterface
public interface Consumer<T> {
/**
* Performs this operation on the given argument.
*
* @param t the input argument
*/
void accept(T t);
/**
* Returns a composed {@code Consumer} that performs, in sequence, this
* operation followed by the {@code after} operation. If performing either
* operation throws an exception, it is relayed to the caller of the
* composed operation. If performing this operation throws an exception,
* the {@code after} operation will not be performed.
*
* @param after the operation to perform after this operation
* @return a composed {@code Consumer} that performs in sequence this
* operation followed by the {@code after} operation
* @throws NullPointerException if {@code after} is null
*/
default Consumer<T> andThen(Consumer<? super T> after) {
Objects.requireNonNull(after);
return (T t) -> {
accept(t); after.accept(t); };
}
}
List 集合专用迭代器:ListIterator 接口
boolean hasPrevious():是否存在前一个元素
E previous():返回前一个元素
int nextIndex():下一个元素的索引
int previousIndex():前一个元素的索引
set(E e):设置元素的值
add(E e):添加元素
public interface ListIterator<E> extends Iterator<E> {
// Query Operations
/**
* Returns {@code true} if this list iterator has more elements when
* traversing the list in the forward direction. (In other words,
* returns {@code true} if {@link #next} would return an element rather
* than throwing an exception.)
*
* @return {@code true} if the list iterator has more elements when
* traversing the list in the forward direction
*/
boolean hasNext();
/**
* Returns the next element in the list and advances the cursor position.
* This method may be called repeatedly to iterate through the list,
* or intermixed with calls to {@link #previous} to go back and forth.
* (Note that alternating calls to {@code next} and {@code previous}
* will return the same element repeatedly.)
*
* @return the next element in the list
* @throws NoSuchElementException if the iteration has no next element
*/
E next();
/**
* Returns {@code true} if this list iterator has more elements when
* traversing the list in the reverse direction. (In other words,
* returns {@code true} if {@link #previous} would return an element
* rather than throwing an exception.)
*
* @return {@code true} if the list iterator has more elements when
* traversing the list in the reverse direction
*/
boolean hasPrevious();
/**
* Returns the previous element in the list and moves the cursor
* position backwards. This method may be called repeatedly to
* iterate through the list backwards, or intermixed with calls to
* {@link #next} to go back and forth. (Note that alternating calls
* to {@code next} and {@code previous} will return the same
* element repeatedly.)
*
* @return the previous element in the list
* @throws NoSuchElementException if the iteration has no previous
* element
*/
E previous();
/**
* Returns the index of the element that would be returned by a
* subsequent call to {@link #next}. (Returns list size if the list
* iterator is at the end of the list.)
*
* @return the index of the element that would be returned by a
* subsequent call to {@code next}, or list size if the list
* iterator is at the end of the list
*/
int nextIndex();
/**
* Returns the index of the element that would be returned by a
* subsequent call to {@link #previous}. (Returns -1 if the list
* iterator is at the beginning of the list.)
*
* @return the index of the element that would be returned by a
* subsequent call to {@code previous}, or -1 if the list
* iterator is at the beginning of the list
*/
int previousIndex();
// Modification Operations
/**
* Removes from the list the last element that was returned by {@link
* #next} or {@link #previous} (optional operation). This call can
* only be made once per call to {@code next} or {@code previous}.
* It can be made only if {@link #add} has not been
* called after the last call to {@code next} or {@code previous}.
*
* @throws UnsupportedOperationException if the {@code remove}
* operation is not supported by this list iterator
* @throws IllegalStateException if neither {@code next} nor
* {@code previous} have been called, or {@code remove} or
* {@code add} have been called after the last call to
* {@code next} or {@code previous}
*/
void remove();
/**
* Replaces the last element returned by {@link #next} or
* {@link #previous} with the specified element (optional operation).
* This call can be made only if neither {@link #remove} nor {@link
* #add} have been called after the last call to {@code next} or
* {@code previous}.
*
* @param e the element with which to replace the last element returned by
* {@code next} or {@code previous}
* @throws UnsupportedOperationException if the {@code set} operation
* is not supported by this list iterator
* @throws ClassCastException if the class of the specified element
* prevents it from being added to this list
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if some aspect of the specified
* element prevents it from being added to this list
* @throws IllegalStateException if neither {@code next} nor
* {@code previous} have been called, or {@code remove} or
* {@code add} have been called after the last call to
* {@code next} or {@code previous}
*/
void set(E e);
/**
* Inserts the specified element into the list (optional operation).
* The element is inserted immediately before the element that
* would be returned by {@link #next}, if any, and after the element
* that would be returned by {@link #previous}, if any. (If the
* list contains no elements, the new element becomes the sole element
* on the list.) The new element is inserted before the implicit
* cursor: a subsequent call to {@code next} would be unaffected, and a
* subsequent call to {@code previous} would return the new element.
* (This call increases by one the value that would be returned by a
* call to {@code nextIndex} or {@code previousIndex}.)
*
* @param e the element to insert
* @throws UnsupportedOperationException if the {@code add} method is
* not supported by this list iterator
* @throws ClassCastException if the class of the specified element
* prevents it from being added to this list
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if some aspect of this element
* prevents it from being added to this list
*/
void add(E e);
}
ArrayList 的内部类:ListItr 迭代器类
ListItr 类继承了 Itr 类,并实现了 ListIterator 接口,它可以从两个方向遍历 List,也可以从 List 中插入和删除元素。
至于源码方面和 Itr 类的设计思想很相似,这里就不展开赘述了,一看便能看懂
private class ListItr extends Itr implements ListIterator<E> {
ListItr(int index) {
super();
cursor = index;
}
public boolean hasPrevious() {
return cursor != 0;
}
public int nextIndex() {
return cursor;
}
public int previousIndex() {
return cursor - 1;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public E previous() {
checkForComodification();
int i = cursor - 1;
if (i < 0)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
Object[] elementData = ArrayList.this.elementData;
if (i >= elementData.length)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
cursor = i;
return (E) elementData[lastRet = i];
}
public void set(E e) {
if (lastRet < 0)
throw new IllegalStateException();
checkForComodification();
try {
ArrayList.this.set(lastRet, e);
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
public void add(E e) {
checkForComodification();
try {
int i = cursor;
ArrayList.this.add(i, e);
cursor = i + 1;
lastRet = -1;
expectedModCount = modCount;
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
}