一、Series
Series是一种类似于一维数组的对象,由数据及与之相关的标签组成。
https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/reference/series.html
1、Series的创建
1.1 使用列表或者np.array来创建
1.1.1 默认数值索引
> import numpy as np
> import pandas as pd
> array= np.array([1, 3, 5, 7, np.NaN])
> series = pd.Series(array)
> print(series)
0 1.0
1 3.0
2 5.0
3 7.0
4 NaN
dtype: float64
> print(pd.Series([2, 4, 6, 8, np.NaN]))
0 2.0
1 4.0
2 6.0
3 8.0
4 NaN
dtype: float64
1.1.2 自定义索引
> series_index = pd.Series([0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5],index=['a', 'b', 'c', 'd',
> 'e', 'f']) print(series_index)
a 0
b 1
c 2
d 3
e 4
f 5
dtype: int64``
1.2 使用字典来创建
> dict = {
'a':10, 'b':20, 'c':30.0, 'd':40, 'e':50, 'f':60} s =
> pd.Series(dict)
a 0
b 1
c 2
d 3
e 4
f 5
dtype: float64
2、使用
2.1、获取数值
2.1.1、通过索引获取数值
> dict = {
'a':10, 'b':20, 'c':30.0, 'd':40, 'e':50, 'f':60}
> s = pd.Series(dict)
> print(s['a'], s['f'])
10.0 60.0
2.1.2、通过切片来获取
> s[0:len(s):2]
a 10.0
c 30.0
e 50.0
dtype: float64
2.2 判断Series是否包含索引
> print('a' in s)
> print('z' in s)
True
False
2.2 属性
2.2.1
> print(s.index)
> print('-'*66)
> print(s.array)
> print('-'*66)
> print(s.values)
> print('-'*66)
> print(s.dtype)
> print('-'*66)
> print(s.shape)
> print('-'*66)
> print(s.size)
Index(['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e', 'f'], dtype='object')
------------------------------------------------------------------
<PandasArray>
[10.0, 20.0, 30.0, 40.0, 50.0, 60.0]
Length: 6, dtype: float64
------------------------------------------------------------------
[10. 20. 30. 40. 50. 60.]
------------------------------------------------------------------
float64
------------------------------------------------------------------
(6,)
------------------------------------------------------------------
6
> dict = {
'a':10, 'b':20, 'c':30.0, 'd':40, 'e':50, 'f':np.NaN}
> s = pd.Series(dict) print(s.hasnans)
True
> s.name = 'my_Series'
> s.index.name = 'my_Series_Index'
> print(s)
my_Series_Index
a 10.0
b 20.0
c 30.0
d 40.0
e 50.0
f NaN
Name: my_Series, dtype: float64
2.3 notes
可以使用s.str 来对转化为字符串从而使用字符串的方法
二、DataFrame
1、DataFrame的创建
DataFrame是一个表格型的数据结构,它含有一组有序的列,每列可以是不同的值类型(数值、字符串、布尔值等)。DataFrame既 有行索引也有列索引,它可以被看做由Series组成的字典(共用同一个索引)。跟其他类似的数据结构相比( 如R的data.frame),DataFrame数据是以一个或多个二维块存放的(而不是列表、字典或别的一维数据结构)。有关中 面向行和面向列的操作基本.上是平衡的。
https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/reference/frame.html
1.1 使用等长列表或Numpy数组组成的字典:
列名:[数据],
列名:[数据],
列名:[数据]
> data= {
> 'province':['shanxi', 'shanxi', 'beijing', 'shanghai', 'sichuan', 'jiangsu'],
> 'year':[2016, 2017, 2018, 2019, 2020, 2021],
> 'pop':[2.0, 2.5, 4.0, 7.0, 6.0, 7.0] }
> frame = pd.DataFrame(data,columns=['year','province','pop'])
> frame
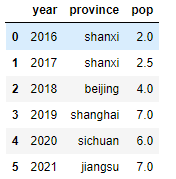

frame = pd.DataFrame(data, columns=['year','province','pop', 'debt'], index = ['one', 'two', 'three', 'four', 'five', 'six'])
frame
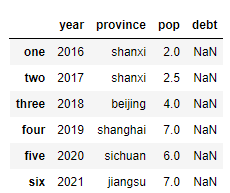
notes:datafrme相当于具有相同索引的Series的组合,每一个列都是Series。如下frame[‘year’]的属性名和类型
> type(frame['year'])
pandas.core.series.Series
> frame['year']
one 2016
two 2017
three 2018
four 2019
five 2020
six 2021
Name: year, dtype: int64
1.2 字典套字典的形式创建:
{
列名:{行名:数据,行名:数据},
列名:{行名:数据,行名:数据},
列名:{行名:数据,行名:数据}
}
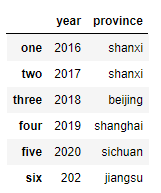
data2 = {
'year':{
'one':2016, 'two':2017, 'three':2018, 'four':2019, 'five':2020, 'six':202},
'province':{
'one':'shanxi', 'two':'shanxi', 'three':'beijing', 'four':'shanghai', 'five':'sichuan', 'six':'jiangsu'}}
frame = pd.DataFrame(data2)
frame
2、使用
2.1、获取数值
2.1.1 通过列名获取Series
frame['year']
one 2016
two 2017
three 2018
four 2019
five 2020
six 202
Name: year, dtype: int64
2.1.2 通过索引切片获得每个Series下的值
frame[:4]
year province
one 2016 shanxi
two 2017 shanxi
three 2018 beijing
four 2019 shanghai
2.1.3 获取指定数据
> frame['year']['one']
2016

2.2 属性
> print(frame.index)
> print('-'*60)
> print(frame.values)
> print('-'*60)
> print(frame.columns)
> print('-'*60)
> print(frame.size)
> print('-'*60)
> print(frame.shape)
> print('-'*60)
Index(['one', 'two', 'three', 'four', 'five', 'six'], dtype='object')
------------------------------------------------------------
[[2016 'shanxi']
[2017 'shanxi']
[2018 'beijing']
[2019 'shanghai']
[2020 'sichuan']
[202 'jiangsu']]
------------------------------------------------------------
Index(['year', 'province'], dtype='object')
------------------------------------------------------------
12
------------------------------------------------------------
(6, 2)
> print(frame.keys())
Index(['year', 'province'], dtype='object')
>for column_name,column_series in frame.items():
print(column_name)
print(column_series)
year
one 2016
two 2017
three 2018
four 2019
five 2020
six 202
Name: year, dtype: int64
province
one shanxi
two shanxi
three beijing
four shanghai
five sichuan
six jiangsu
Name: province, dtype: object
2.3 loc,iloc
https://www.jianshu.com/p/d6a9845a0a34