题目
1. 自定义注解,该注解用来描述,方法运行所需的时间上限(用long类型的数据表示时间,单位为ms),
然后,自定义注解处理器,
运行 加了运行时间上限注解的方法,判断 方法的运行时间,是否超出了注解中规定的时间上限,
如果超过,则返回true,未超过返回false
结果
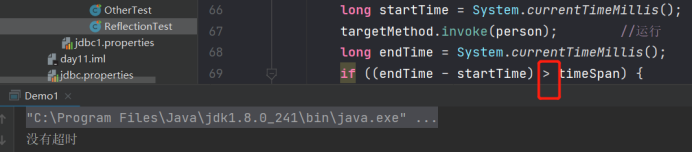
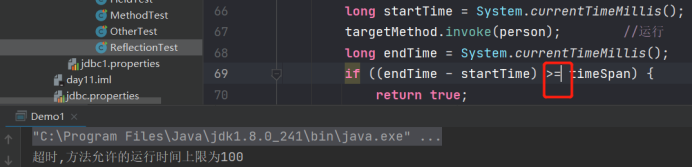
代码
package src;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target({
ElementType.METHOD})
@interface MethodRuntimeLimit {
long timeLimit();
}
class Person {
@MethodRuntimeLimit(timeLimit = 100)
public void method() {
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
class PersonFactory {
static Class Cls = Person.class;
public static boolean invokeMethod(Person person) throws NoSuchMethodException,
InvocationTargetException, IllegalAccessException {
Method targetMethod = Cls.getDeclaredMethod("method");
targetMethod.setAccessible(true);
long timeSpan = getTimeLimit(targetMethod);
if (timeSpan == -1) return false;
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
targetMethod.invoke(person);
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
if ((endTime - startTime) >= timeSpan) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
private static long getTimeLimit(Method targetMethod) throws NoSuchMethodException {
boolean annotationPresent = targetMethod.isAnnotationPresent(MethodRuntimeLimit.class);
if (!annotationPresent) return -1;
MethodRuntimeLimit annotation = targetMethod.getAnnotation(MethodRuntimeLimit.class);
long timeLimit = annotation.timeLimit();
return timeLimit;
}
}
public class Demo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Person person = new Person();
boolean isTimeOut = PersonFactory.invokeMethod(person);
if (isTimeOut) {
System.out.println("超时,方法允许的运行时间上限为100");
} else {
System.out.println("没有超时");
}
}
}

