rpc调用,有多种序列化的方式,通用如json,mongodb使用的bson;java方面的,比如Java默认的序列化,比如hessian;还有跨语言的,比如thrift、protocolbuf。thrift和pb的好处是序列化后size比较小,但是缺点是得生成java代码,这个挺鸡肋的,所以不管二者运行时效率有多高,开发效率相对比较低的。像hessian,是有一些在用,但是感觉不如pb那样强大。所以也一直在寻找运行效率与开发效率兼得的序列化方式。偶尔在网上看到protostuff,觉得找到了一直在找的这种序列化方式。
protostuff简介
protobuf的一个缺点是需要数据结构的预编译过程,首先要编写.proto格式的配置文件,再通过protobuf提供的工具生成各种语言响应的代码。由于java具有反射和动态代码生成的能力,这个预编译过程不是必须的,可以在代码执行时来实现。有protostuff已经实现了这个功能。
protostuff效率
- Ser Time+Deser Time (ns)
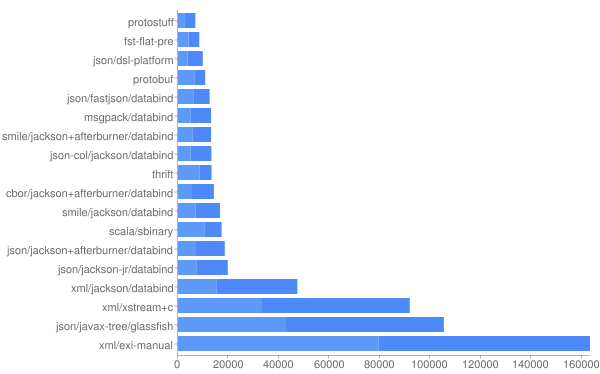
- Size, Compressed size [light] in bytes
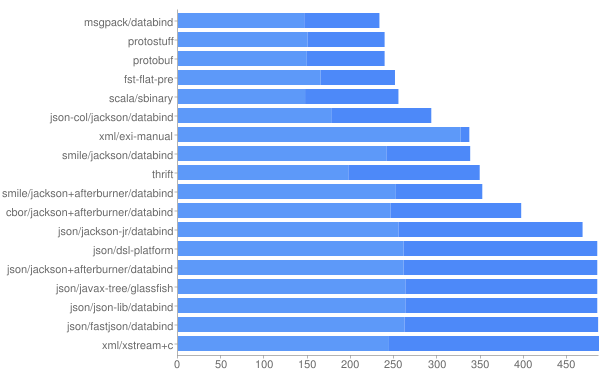
使用
pom依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>com.dyuproject.protostuff</groupId>
<artifactId>protostuff-core</artifactId>
<version>1.0.8</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.dyuproject.protostuff</groupId>
<artifactId>protostuff-runtime</artifactId>
<version>1.0.8</version>
</dependency>工具类
public class SerializationUtil {
private static Map<Class<?>, Schema<?>> cachedSchema = new ConcurrentHashMap<Class<?>, Schema<?>>();
private static Objenesis objenesis = new ObjenesisStd(true);
private static <T> Schema<T> getSchema(Class<T> clazz) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Schema<T> schema = (Schema<T>) cachedSchema.get(clazz);
if (schema == null) {
schema = RuntimeSchema.getSchema(clazz);
if (schema != null) {
cachedSchema.put(clazz, schema);
}
}
return schema;
}
/**
* 序列化
*
* @param obj
* @return
*/
public static <T> byte[] serializer(T obj) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Class<T> clazz = (Class<T>) obj.getClass();
LinkedBuffer buffer = LinkedBuffer.allocate(LinkedBuffer.DEFAULT_BUFFER_SIZE);
try {
Schema<T> schema = getSchema(clazz);
return ProtostuffIOUtil.toByteArray(obj, schema, buffer);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new IllegalStateException(e.getMessage(), e);
} finally {
buffer.clear();
}
}
/**
* 反序列化
*
* @param data
* @param clazz
* @return
*/
public static <T> T deserializer(byte[] data, Class<T> clazz) {
try {
T obj = objenesis.newInstance(clazz);
Schema<T> schema = getSchema(clazz);
ProtostuffIOUtil.mergeFrom(data, obj, schema);
return obj;
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new IllegalStateException(e.getMessage(), e);
}
}
}基于netty的rpc
- NettyServer
public class NettyServer {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(NettyServer.class);
private int ioThreadNum;
//内核为此套接口排队的最大连接个数,对于给定的监听套接口,内核要维护两个队列,未链接队列和已连接队列大小总和最大值
private int backlog;
private int port;
private Channel channel;
private EventLoopGroup bossGroup;
private EventLoopGroup workerGroup;
public NettyServer(int ioThreadNum, int backlog, int port) {
this.ioThreadNum = ioThreadNum;
this.backlog = backlog;
this.port = port;
}
public void start() throws InterruptedException {
bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(this.ioThreadNum);
final Map<String,Object> demoService = new HashMap<String, Object>();
demoService.put("com.codecraft.service.HelloService", new HelloServiceImpl());
ServerBootstrap serverBootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
serverBootstrap.group(bossGroup, workerGroup)
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, backlog)
//注意是childOption
.childOption(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, true)
.childOption(ChannelOption.TCP_NODELAY, true)
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel socketChannel) throws Exception {
socketChannel.pipeline()
.addLast(new RpcDecoder(RpcRequest.class))
.addLast(new RpcEncoder(RpcResponse.class))
.addLast(new ServerRpcHandler(demoService));
}
});
channel = serverBootstrap.bind("127.0.0.1",port).sync().channel();
logger.info("NettyRPC server listening on port "+ port + " and ready for connections...");
Runtime.getRuntime().addShutdownHook(new Thread(){
@Override
public void run(){
//do shutdown staff
}
});
}
public void stop() {
if (null == channel) {
throw new ServerStopException();
}
bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();
workerGroup.shutdownGracefully();
channel.closeFuture().syncUninterruptibly();
bossGroup = null;
workerGroup = null;
channel = null;
}
}- ServerRpcHandler
public class ServerRpcHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<RpcRequest> {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(ServerRpcHandler.class);
private final Map<String, Object> serviceMapping;
public ServerRpcHandler(Map<String, Object> serviceMapping) {
this.serviceMapping = serviceMapping;
}
@Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext channelHandlerContext, RpcRequest rpcRequest) throws Exception {
RpcResponse response = new RpcResponse();
response.setTraceId(rpcRequest.getTraceId());
try {
logger.info("server handle request:{}",rpcRequest);
Object result = handle(rpcRequest);
response.setResult(result);
} catch (Throwable t) {
response.setError(t);
}
channelHandlerContext.writeAndFlush(response);
}
private Object handle(RpcRequest request) throws Throwable {
String className = request.getClassName();
Object serviceBean = serviceMapping.get(className);
Class<?> serviceClass = serviceBean.getClass();
String methodName = request.getMethodName();
Class<?>[] parameterTypes = request.getParameterTypes();
Object[] parameters = request.getParameters();
FastClass serviceFastClass = FastClass.create(serviceClass);
FastMethod serviceFastMethod = serviceFastClass.getMethod(methodName, parameterTypes);
return serviceFastMethod.invoke(serviceBean, parameters);
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) {
logger.error(cause.getMessage(), cause);
RpcResponse response = new RpcResponse();
if(cause instanceof ServerException){
response.setTraceId(((ServerException) cause).getTraceId());
}
response.setError(cause);
ctx.writeAndFlush(response);
}
}- NettyClient
public class NettyClient implements IClient {
private EventLoopGroup workerGroup;
private Channel channel;
private int workerGroupThreads;
private ClientRpcHandler clientRpcHandler;
private final Optional<Pair<Long,TimeUnit>> NO_TIMEOUT = Optional.<Pair<Long,TimeUnit>>absent();
public NettyClient(int workerGroupThreads) {
this.workerGroupThreads = workerGroupThreads;
}
public void connect(InetSocketAddress socketAddress) {
workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(workerGroupThreads);
clientRpcHandler = new ClientRpcHandler();
Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap();
bootstrap
.group(workerGroup)
.channel(NioSocketChannel.class)
.option(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, true)
.option(ChannelOption.TCP_NODELAY, true)
.handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ch.pipeline()
.addLast(new RpcDecoder(RpcResponse.class))
.addLast(new RpcEncoder(RpcRequest.class))
.addLast(clientRpcHandler);
}
});
channel = bootstrap.connect(socketAddress.getAddress().getHostAddress(), socketAddress.getPort())
.syncUninterruptibly()
.channel();
}
public RpcResponse syncSend(RpcRequest request) throws InterruptedException {
System.out.println("send request:"+request);
channel.writeAndFlush(request).sync();
return clientRpcHandler.send(request,NO_TIMEOUT);
}
public RpcResponse asyncSend(RpcRequest request,TimeUnit timeUnit,long timeout) throws InterruptedException {
channel.writeAndFlush(request);
return clientRpcHandler.send(request, Optional.of(Pair.of(timeout,timeUnit)));
}
public InetSocketAddress getRemoteAddress() {
SocketAddress remoteAddress = channel.remoteAddress();
if (!(remoteAddress instanceof InetSocketAddress)) {
throw new RuntimeException("Get remote address error, should be InetSocketAddress");
}
return (InetSocketAddress) remoteAddress;
}
public void close() {
if (null == channel) {
throw new ClientCloseException();
}
workerGroup.shutdownGracefully();
channel.closeFuture().syncUninterruptibly();
workerGroup = null;
channel = null;
}
}- ClientRpcHandler
@ChannelHandler.Sharable
public class ClientRpcHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<RpcResponse> {
//用blocking queue主要是用阻塞的功能,省的自己加锁
private final ConcurrentHashMap<String, BlockingQueue<RpcResponse>> responseMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<String, BlockingQueue<RpcResponse>>();
//messageReceived
@Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, RpcResponse rpcResponse) throws Exception {
System.out.println("receive response:"+rpcResponse);
BlockingQueue<RpcResponse> queue = responseMap.get(rpcResponse.getTraceId());
queue.add(rpcResponse);
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {
super.exceptionCaught(ctx, cause);
cause.printStackTrace();
}
public RpcResponse send(RpcRequest request,Optional<Pair<Long,TimeUnit>> timeout) throws InterruptedException {
responseMap.putIfAbsent(request.getTraceId(), new LinkedBlockingQueue<RpcResponse>(1));
RpcResponse response = null;
try {
BlockingQueue<RpcResponse> queue = responseMap.get(request.getTraceId());
if(timeout == null || !timeout.isPresent()){
response = queue.take();
}else{
response = queue.poll(timeout.get().getKey(),timeout.get().getValue());
}
} finally {
responseMap.remove(request.getTraceId());
}
return response;
}
}- decoder
public class RpcDecoder extends ByteToMessageDecoder {
private Class<?> genericClass;
public RpcDecoder(Class<?> genericClass) {
this.genericClass = genericClass;
}
@Override
protected void decode(ChannelHandlerContext channelHandlerContext, ByteBuf byteBuf, List<Object> list) throws Exception {
if (byteBuf.readableBytes() < 4) {
return;
}
byteBuf.markReaderIndex();
int dataLength = byteBuf.readInt();
if (dataLength < 0) {
channelHandlerContext.close();
}
if (byteBuf.readableBytes() < dataLength) {
byteBuf.resetReaderIndex();
}
byte[] data = new byte[dataLength];
byteBuf.readBytes(data);
Object obj = SerializationUtil.deserializer(data, genericClass);
list.add(obj);
}
}- encoder
public class RpcEncoder extends MessageToByteEncoder {
private Class<?> genericClass;
public RpcEncoder(Class<?> genericClass) {
this.genericClass = genericClass;
}
@Override
protected void encode(ChannelHandlerContext channelHandlerContext, Object obj, ByteBuf byteBuf) throws Exception {
if (genericClass.isInstance(obj)) {
byte[] data = SerializationUtil.serializer(obj);
byteBuf.writeInt(data.length);
byteBuf.writeBytes(data);
}
}
}