1.模拟实现简易版shell
1.1 模拟思路
模拟实现如下图shell模型:
- 用
while(1)死循环实现总体框架,在一个命令执行完以后可继续执行下一个命令。用ctrl+c进行退出。 - 如上图:我们的shell需要展示
当前用户、主机、当前目录、等命令行提示符。 - 需要能够
获取命令行。 - 需要能够
解析执行命令行。 建立一个子进程(fork),让子进程执行解析出来的命令,即使子进程执行出现问题不会使整个myshell崩掉。- 将解析出来的命令
替换子进程(execvp)。 - 父进程等待子进程退出(wait)。
1.2 模拟代码
1 #include<stdio.h>
2 #include<unistd.h>
3 #include<string.h>
4 #include<sys/wait.h>
5 #include<stdlib.h>
6
7 #define SIZE 128
8
9 int main()
10 {
11 while(1) //注释1
12 {
13 printf("[myshell@VM-8-16-centos shell]$ ");//注释2
14 char str[SIZE]={
0};
15
16 fgets(str,SIZE,stdin); //注释3
17 str[strlen(str)-1]='\0'; //注释4
18
19 char *arg[SIZE]={
0};
20
21 arg[0]=strtok(str," "); //注释5
22
23 int i=1;
24
25 do //注释6
26 {
27 arg[i]=strtok(NULL," ");
28 if(!arg[i])
29 {
30 break;
31 }
32 i++;
33 }while(1);
34
35 pid_t id=fork();//注释7
36 if(id<0)
37 {
38 perror("fork error!");
39 }
40 if(id==0)
41 {
42 execvp(arg[0],arg);//注释8
43
44 printf("comman not error!");
45 exit(1);
46 }
47
48 int st;
49 waitpid(id,&st,0);//注释9
50
51 printf("state is:%d \n",(st>>8)&0xff);//注释10
52 }
53
54 return 0;
55 }
1.3 运行展示
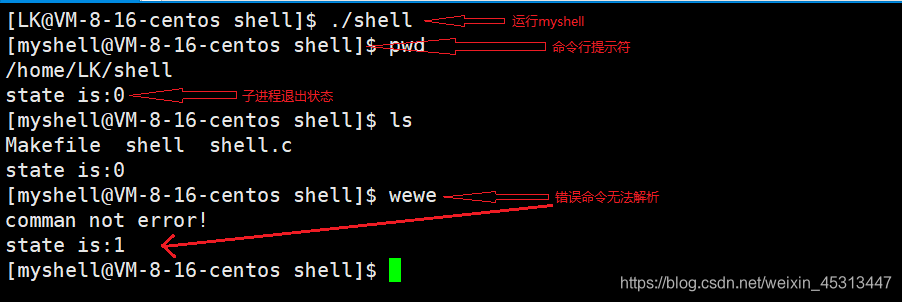
1.4 注释详解
-
注释1:整个程序在while(1)死循环中执行。可以在一条命令执行完以后执行别的命令。
-
注释2:命令行提示符。
-
注释3:从标准输入获取字符串。
获得一个字符串,放到缓冲区; 这个缓冲区有多大; 从哪种流方式获得。
char *fgets(char *s,int size,FILE * stream)。 -
注释4:str[strlen(str)-1]=’\0’,
str 中存储的字符串最终是‘\n\0’形式结尾,导致在解析的时候,arg[i] 最后会解析一个 ‘\n’的命令,最终会导致命令解析错误,故str[strlen(str)-1]=’\0’将‘\n'替换成了’\0'。 -
注释5:保存解析出来的第一个命令,为后面
execvp(arg[0],arg)做准备,arg[0]就是int execvp(const char *file, char *const argv[]);中的const char *file。 -
注释6:
strtok(NULL," ")用strtok函数对字符串以空格进行切割。 -
注释7:创建子进程,让子进程执行解析出来的命令。
-
注释8:进程替换,
int execvp(const char *file, char *const argv[]);
进程替换详解link -
注释9:父进程等待子进程执行完退出waitpid。进程等待详解link
-
注释10:获得子进程退出码。