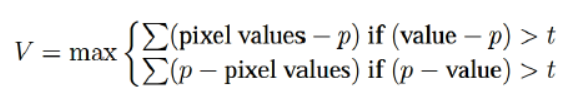目录
1 背景说明
- ORB特征在OpenCV (以下代码已OpenCV4.5.1为例)中有两种评分方式 FAST_SCORE 和 HARRIS_SCORE
- ORB_SLAM3中ORB特征的计算,使用的是FAST_SCORE
先来看官方介绍
1.1 函数原型
//出处:\opencv\sources\modules\features2d\doc\feature_detection_and_description.rst
// 或者:...\modules\features2d\include\opencv2\features2d.hpp
ORB::ORB(int nfeatures = 500, float scaleFactor = 1.2f, int nlevels = 8, int edgeThreshold = 31, int firstLevel = 0, int WTA_K=2, int scoreType=ORB::HARRIS_SCORE, int patchSize=31)
- The default HARRIS_SCORE means that Harris algorithm is used to rank features (the score is written to ``KeyPoint::score`` and is used to retain best ``nfeatures`` features);
- 默认的HARRIS_SCORE意味着使用Harris算法对特征进行排名(分数写入到' ' KeyPoint::score ' ',用于保留最好的' ' nfeatures ' '特征);
- FAST_SCORE is alternative value of the parameter that produces slightly less stable keypoints, but it is a little faster to compute.
- FAST_SCORE是参数的替代值,它产生的关键点稍微不那么稳定,但计算起来更快一些。
2 评分算法
2.1 FAST评分算法
参考论文: Features from Accelerated Segment Test (FAST)
判断以特征点p为中心的一个邻域(如3x3或5x5)内,如16个点与中心差值的绝对值总和(公式中用V表示得分,t表示阈值
- (ORB_SLAM3中使用的阈值t =7,对应变量minThFAST))
原文:The score function is defined as:“The sum of the absolute difference between the pixels in the contiguous arc and the centre pixel”.
- 得分函数定义为:“相邻弧线像素与中心像素之间的绝对差之和”。

2.1.1 源码:
//引用:...\modules\features2d\include\opencv2\features2d\features2d.hpp
//出处:...\modules\features2d\src\fast.cpp
// 部分片段
template<int patternSize>
void FAST_t(InputArray _img, std::vector<KeyPoint>& keypoints, int threshold, bool nonmax_suppression)
{
...
const uchar* prev = buf[(i - 4 + 3)%3];
const uchar* pprev = buf[(i - 5 + 3)%3];
cornerpos = cpbuf[(i - 4 + 3)%3] + 1; // cornerpos[-1] is used to store a value
ncorners = cornerpos[-1];
for( k = 0; k < ncorners; k++ )
{
j = cornerpos[k];
int score = prev[j];
if( !nonmax_suppression ||
(score > prev[j+1] && score > prev[j-1] &&
score > pprev[j-1] && score > pprev[j] && score > pprev[j+1] &&
score > curr[j-1] && score > curr[j] && score > curr[j+1]) )
{
keypoints.push_back(KeyPoint((float)j, (float)(i-1), 7.f, -1, (float)score));
}
}
}
}2.2 Harris评分算法
参考论文: 1988年 Harris大佬的文章 A COMBINED CORNER AND EDGE DETECTOR
参考链接:Harris角点算法
2.2.1 说明:
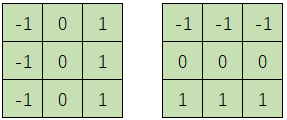
Harris角点原理来源于人对角点的感性判断,即图像在各个方向灰度有明显变化。算法的核心是利用局部窗口在图像上进行移动判断灰度发生较大的变化,所以此窗口用于计算图像的灰度变化为:如下图[-1,0,1;-1,0,1;-1,0,1][-1,-1,-1;0,0,0;1,1,1]。在各个方向上移动这个特征的小窗口,如下图3中窗口内区域的灰度发生了较大的变化,那么就认为在窗口内遇到了角点。如图1中,窗口内图像的灰度没有发生变化,那么窗口内就不存在角点;如果窗口在某一个方向移动时,窗口内图像的灰度发生了较大的变化,而在另一些方向上没有发生变化,那么,窗口内的图像可能就是一条直线的线段。
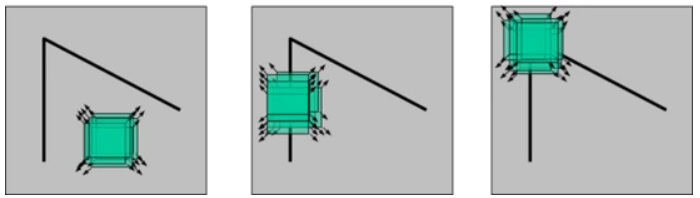
根据算法思想,构建数学模型,计算移动窗口的的灰度差值。
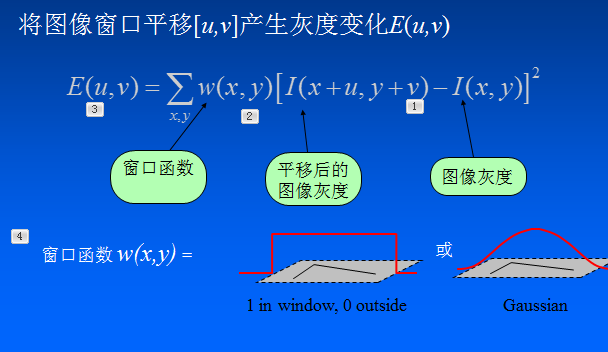
2.2.2 角点响应函数R:

M为梯度的协方差矩阵
2.2.3 源码:
//出处: ...\modules\features2d\src\orb.cpp
HarrisResponses(const Mat& img, const std::vector<Rect>& layerinfo,
std::vector<KeyPoint>& pts, int blockSize, float harris_k)
{
CV_Assert( img.type() == CV_8UC1 && blockSize*blockSize <= 2048 );
size_t ptidx, ptsize = pts.size();
const uchar* ptr00 = img.ptr<uchar>();
int step = (int)(img.step/img.elemSize1());
int r = blockSize/2;
float scale = 1.f/((1 << 2) * blockSize * 255.f);
float scale_sq_sq = scale * scale * scale * scale;
AutoBuffer<int> ofsbuf(blockSize*blockSize);
int* ofs = ofsbuf.data();
for( int i = 0; i < blockSize; i++ )
for( int j = 0; j < blockSize; j++ )
ofs[i*blockSize + j] = (int)(i*step + j);
for( ptidx = 0; ptidx < ptsize; ptidx++ )
{
int x0 = cvRound(pts[ptidx].pt.x);
int y0 = cvRound(pts[ptidx].pt.y);
int z = pts[ptidx].octave;
const uchar* ptr0 = ptr00 + (y0 - r + layerinfo[z].y)*step + x0 - r + layerinfo[z].x;
int a = 0, b = 0, c = 0;
for( int k = 0; k < blockSize*blockSize; k++ )
{
const uchar* ptr = ptr0 + ofs[k];
int Ix = (ptr[1] - ptr[-1])*2 + (ptr[-step+1] - ptr[-step-1]) + (ptr[step+1] - ptr[step-1]);
int Iy = (ptr[step] - ptr[-step])*2 + (ptr[step-1] - ptr[-step-1]) + (ptr[step+1] - ptr[-step+1]);
a += Ix*Ix;
b += Iy*Iy;
c += Ix*Iy;
}
pts[ptidx].response = ((float)a * b - (float)c * c -
harris_k * ((float)a + b) * ((float)a + b))*scale_sq_sq;
}
}