文章目录
噪声模型
图像噪声主要来源于图像的获取和传输过程。
(1)图像传感器的工作情况受各种因素的影响,如图像获取中的环境条件和传感元器件自身的质量。例如,当使用CCD摄像机获取图像时,光照强度和传感器的温度是生成图像中产生大量噪声的主要因素。
(2)图像在传输过程中主要由于所用传输信道被干扰而受到噪声污染。比如,通过无线网络传输的图像可能会因为光或其他大气因素的干扰被污染。
1 噪声种类
1 .1 高斯噪声
高斯噪声是理论研究中最常见的噪声。一般而言,对一个抗噪系统而言高斯噪声是最恶劣的噪声,设计系统时只要能够抵抗高斯噪声,那么系统性能就有保证。
高斯噪声也是现实生活中极为常见的。根据中心极限定理,在自然界中,一些现象受到许多相互独立的随机因素的影响,如果每个因素所产生的影响都很微小,那么总的影响可以看作是服从正态分布的。
高斯随机变量z的概率密度函数由下式给出:

其中,z表示灰度值,u表示z的平局值或期望。
1.2 瑞利噪声
当一个随机二维向量的两个分量呈独立的、有着相同的方差的正态分布时,这个向量的模呈瑞利分布。服从这种分布的噪声即瑞利噪声,其概率密度函数由下式给出

概率密度的均值为:

方差为:

1.3 伽玛噪声
服从伽玛分布的噪声为伽玛噪声,伽玛分布由形状参数和尺度参数控制。其概率密度函数由下式给出:

其密度的均值和方差由

给出。
1.4 指数噪声
指数噪声的概率密度函数可由下式给出:

其中,
</span><span class="katex-html"><span class="base"><span class="strut" style="height: 0.64444em; vertical-align: 0em;"></span><span class="mord mathdefault">a</span><span class="mord cjk_fallback">></span><span class="mord">0</span></span></span></span></span>。概率密度函数的期望值和方差是<br> <img src="https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/20201019141415982.png#pic_center" alt="在这里插入图片描述"></p>
注意
指数分布的概率密度函数是当
</span><span class="katex-html"><span class="base"><span class="strut" style="height: 0.69444em; vertical-align: 0em;"></span><span class="mord mathdefault">b</span><span class="mspace" style="margin-right: 0.277778em;"></span><span class="mrel">=</span><span class="mspace" style="margin-right: 0.277778em;"></span></span><span class="base"><span class="strut" style="height: 0.64444em; vertical-align: 0em;"></span><span class="mord">1</span></span></span></span></span>时伽玛概率密度分布的特殊情况。</p>
1.5 均匀分布噪声
均匀分布噪声的概率密度可由下式给出:

概率密度函数的期望值和方差可由下式给出:

1.6 脉冲噪声(椒盐噪声)
(双极)脉冲噪声的概率密度函数可由下式给出:

如果
以上介绍的各种噪声可以用于对实际当中的图像退化建模。在一幅图像中,高斯噪声的产生源于电子电路噪声和由低照明或高温带来的传感器噪声。瑞利密度分布在图像范围内特征化噪声现象时非常有用。指数密度分布和伽玛密度分布在激光成像中有一些应用。椒盐噪声主要表现在成像中的短暂停留,例如错误的开关操作。均匀分布是实践中出现得最少的噪声,但可以根据均匀噪声产生其他噪声。
2 用MATLAB绘制噪声的概率密度图
noise_product.m
function Y = show_noise_pdf(type,x,a,b)
% show_noise_pdf显示不同噪声的概率密度函数
% type:字符串,取值随噪声种类而定
% 高斯噪声:gaussian,参数为(x,y),默认值为(0,10)
% 瑞利噪声: rayleigh,参数为x,默认值为30
% 伽马噪声: gamma,参数为(x,y),默认值为(2,10)
% 指数噪声: exp,参数为x,默认值为15
% 均匀分布: uniform,参数为(x.y),默认值为(-20,20)
% 椒盐噪声: salt & pepper:强度为x,默认值为0.02
% example
% Y=show_noise_pdf('gamma',2,5,x);
% plot(x,Y);
% 设置默认噪声类型
if nargin==1
type='gaussian';
end
% 开始处理
switch lower(type)
case 'gaussian' % 高斯噪声
if nargin<4
b=10;
end
if nargin<3
a=0;
end
Y=normpdf(x,a,b); % 正态分布概率密度函数
case 'uniform' % 均匀分布
if nargin<4
b=20;
end
if nargin<3
a=-20
end
Y=unifpdf(x,a,b);
case 'salt & pepper' % 椒盐噪声
Y=zeros(size(x));
Y(1)=0.5;
Y(end)=0.5;
case 'rayleigh' % 瑞利噪声
if nargin<3
a=30;
end
Y=raylpdf(x,a);
case 'exp' % 指数噪声
if nargin<3
a=15;
end
Y=exppdf(x,a);
case 'gamma' % 伽马噪声
if nargin<4
b=10;
end
if nargin<3
a=2;
end
Y=gampdf(x,a,b);
otherwise
error('Unkown distribution type')
end
end
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
show_noise_pdf.m
clc;clear
x=-4:0.1:4;
subplot(321)
Y1=show_noise_pdf('gaussian',x,0,1);
plot(x,Y1)
title('高斯')
subplot(322)
Y2=show_noise_pdf('uniform',x,-3,3);
plot(x,Y2)
title('均匀')
subplot(323)
Y3=show_noise_pdf('salt & pepper',x);
plot(x,Y3)
title('椒盐')
subplot(324)
Y4=show_noise_pdf('rayleigh',x,1);
plot(x,Y4)
title('瑞利')
subplot(325)
Y5=show_noise_pdf('exp',x,1);
plot(x,Y5)
title('指数')
subplot(326)
Y6=show_noise_pdf('gamma',x,2,5);
plot(x,Y6)
title('伽马')
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26

3 为图像添加噪声
add_noise.m
function IJ = add_noise(I,type,x,y)
% add_noise函数用于产生各种噪声
% I:输入图形矩阵,为灰度图像
% type:字符串,取值随噪声种类而定
% 高斯噪声:gaussian,参数为(x,y),默认值为(0,10)
% 瑞利噪声: rayleigh,参数为x,默认值为30
% 伽马噪声: gamma,参数为(x,y),默认值为(2,10)
% 指数噪声: exp,参数为x,默认值为15
% 均匀分布: uniform,参数为(x.y),默认值为(-20,20)
% 椒盐噪声: salt & pepper:强度为x,默认值为0.02
% IJ:添加噪声后的图像
% 预处理
if ndims(I)>=3
I=rgb2gray(I);
end
[M,N]=size(I); % 输入图像的大小
% 设置默认噪声类型
if nargin==1
type='gaussian';
end
% 开始处理
switch lower(type)
case 'gaussian' % 高斯噪声
if nargin<4
y=10;
end
if nargin<3
x=0;
end
% 产生高斯分布随机数
R=normrnd(x,y,M,N);
IJ=double(I)+R;
IJ=uint8(round(IJ));
case 'uniform' % 均匀分布
if nargin<4
y=20;
end
if nargin<3
x=-20;
end
% 产生均匀分布随机数
R=unifrnd(x,y,M,N);
IJ=double(I)+R;
IJ=uint8(round(IJ));
case 'salt & pepper' % 椒盐噪声
IJ=imnoise(I,'salt & pepper',x);
if nargin<3
x=0.02;
end
a1=rand(M,N)<x;
a2=rand(M,N)<x;
IJ=I;
IJ(a1)=0;
IJ(a2)=255;
case 'rayleigh' % 瑞利噪声
if nargin<3
x=30;
end
R=raylrnd(x,M,N);
IJ=double(I)+R;
IJ=uint8(round(IJ));
case 'exp' % 指数噪声
if nargin<3
x=15;
end
R=exprnd(x,M,N);
IJ=double(I)+R;
IJ=uint8(round(IJ));
case 'gamma' % 伽马噪声
if nargin<4
y=10;
end
if nargin<3
x=2;
end
R=gamrnd(x,y,M,N);
IJ=double(I)+R;
IJ=uint8(round(IJ));
otherwise
error('Unkown distribution type')
end
end
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
原图:
clc;clear
close all
x=uint8(zeros(256)+120);
imshow(x)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4

3.1 添加高斯噪声
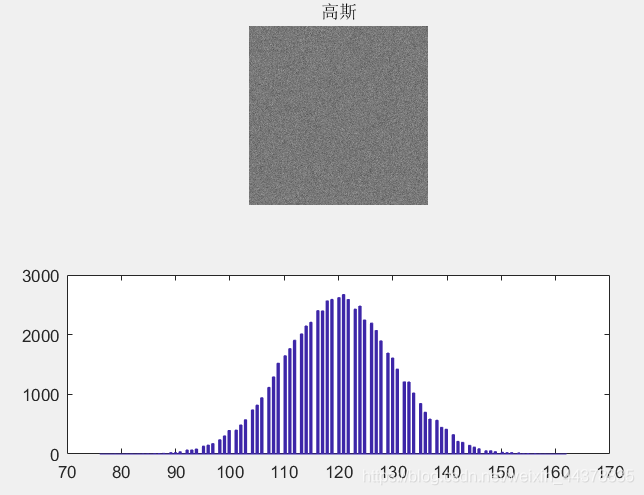
Y1=add_noise(x,'gaussian',0,10);
subplot(2,1,1)
imshow(Y1)
title('高斯')
subplot(2,1,2)
hist(double(Y1(:)),200);
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
3.2 添加均匀噪声
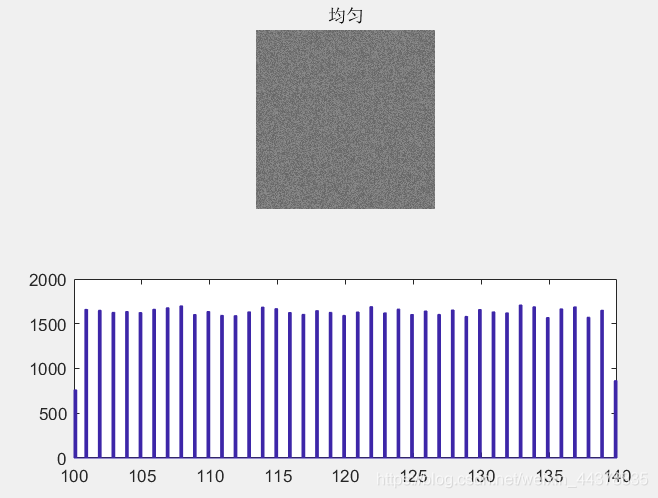
Y2=add_noise(x,'uniform',-20,20);
subplot(2,1,1)
imshow(Y2)
title('均匀')
subplot(2,1,2)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
3.3 添加椒盐噪声
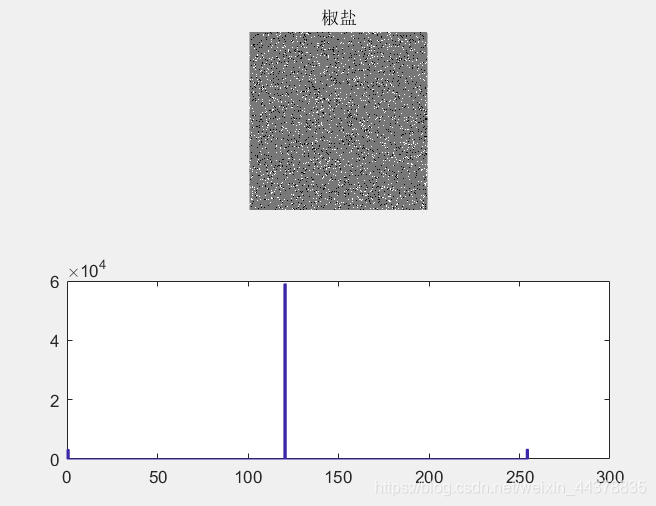
Y3=add_noise(x,'salt & pepper',0.05);
subplot(2,1,1)
imshow(Y3)
title('椒盐')
subplot(2,1,2)
hist(double(Y3(:)),200);
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
3.4 添加瑞利噪声
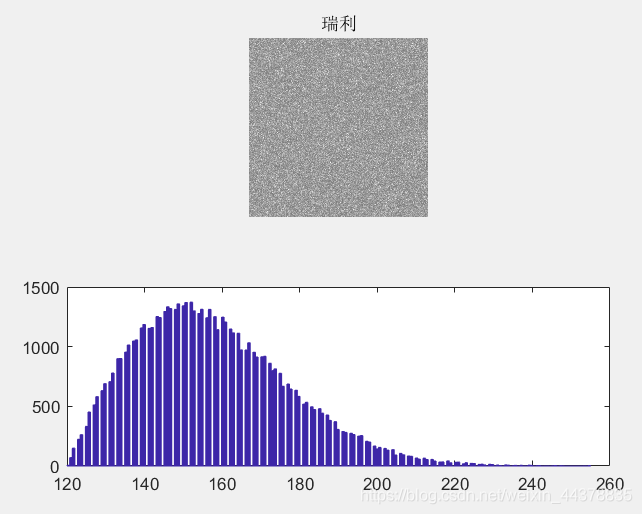
Y4=add_noise(x,'rayleigh',30);
subplot(2,1,1)
imshow(Y4)
title('瑞利')
subplot(2,1,2)
hist(double(Y4(:)),200);
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
3.5 添加指数噪声
Y5=add_noise(x,'exp',15);
subplot(2,1,1)
imshow(Y5)
title('指数')
subplot(2,1,2)
hist(double(Y5(:)),200);
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6

3.6 添加伽马噪声
Y6=add_noise(x,'gamma',2,10);
subplot(2,1,1)
imshow(Y6)
title('伽马')
subplot(2,1,2)
hist(double(Y6(:)),100);
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6

Reference
