文章目录
衡量单变量的相关性指标有很多,比如Pearson相关系数、Pearson卡方检验、Fisher得分、互信息等。
1 基本概念
详见:特征选择——互信息量
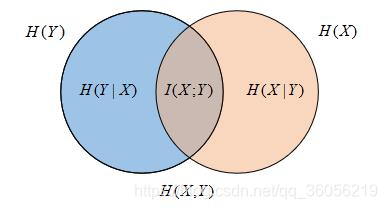
信息量

信息熵


条件熵

互信息量
在给出互信息定义前先看下这张关系图:

2 Python实现-特征选择过滤器
mutual_info_classif:离散目标变量的互信息
mutual_info_classif用于分类模型。基于互信息选择特征。互信息方法可以捕捉任何一种统计依赖,但是作为非参数方法,需要更多的样本进行准确的估计。
做特征选择时需要根据特征变量 X 和因变量 Y 的类型来选取合适的相关性指标,这里互信息适用于特征和因变量都是分类变量的情况。
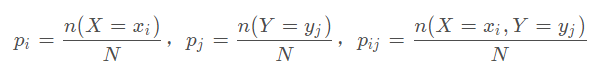
sklearn.feature_selection.mutual_info_classif(X, y,
discrete_features='auto',
n_neighbors=3,
copy=True,
random_state=None)[source]
参数说明如下:
扫描二维码关注公众号,回复:
13116924 查看本文章


Parameters
----------
X: array_like or sparse matrix, shape (n_samples, n_features)
Feature matrix.
特征矩阵。
y:array_like, shape (n_samples,)
Target vector.
标签向量。
discrete_features:{
‘auto’, bool, array_like}, default=‘auto’
如果为'auto',则将其分配给False(表示稠密)X,将其分配给True(表示稀疏)X。
如果是bool,则确定是考虑所有特征是离散特征还是连续特征。
如果是数组,则它应该是具有形状(n_features,)的布尔蒙版或具有离散特征索引的数组。
n_neighbors:int, default=3
用于连续变量的MI估计的邻居数;
较高的值会减少估计的方差,但可能会带来偏差。
copy:bool, default=True
是否复制给定的数据。如果设置为False,则初始数据将被覆盖。
random_state:int, RandomState instance or None, optional, default None
确定随机数生成,以将小噪声添加到连续变量中以删除重复值。
在多个函数调用之间传递int以获得可重复的结果。
Returns
-------
mi:ndarray, shape (n_features,)
每个功能和目标之间的估计相互信息。
import numpy as np
from sklearn.feature_selection import mutual_info_classif
def predict(a, b):
""" Compute the test statistic
Args:
a (array-like): Variable 1
b (array-like): Variable 2
Returns:
float: test statistic
"""
a = np.array(a).reshape((-1, 1))
b = np.array(b).reshape((-1, 1))
return (mutual_info_classif(a, b.reshape((-1,)),random_state=123)+mutual_info_classif(b, a.reshape((-1,)),random_state=123))/2
a=np.random.randint(1,3,5) # array([1, 1, 1, 2, 1])
b=np.random.randint(1,3,5) # array([1, 2, 2, 1, 2])
predict(a,a) # array([1.5])
predict(b,b) # array([0.78333333])
# predict(a,b) # =predict(b,a)=array([0.3])
mutual_info_regression:连续目标变量的互信息
mutual_info_regression用于回归模型,估计一个连续目标变量的互信息。基于互信息选择特征。互信息用于度量 X 和 Y 共享的信息:度量知道这两个变量其中一个,对另一个不确定度减少的程度。
两个随机变量之间的互信息(MI)是非负值,用于衡量变量之间的依存关系。值越高说明两个变量越相近。
该函数依赖于非参数方法,该方法基于k-邻近邻居距离的熵估计。
sklearn.feature_selection.mutual_info_regression(X, y,
discrete_features='auto',
n_neighbors=3,
copy=True,
random_state=None)
参数说明:
Parameters
----------
X:array_like or sparse matrix, shape (n_samples, n_features)
Feature matrix.
特征矩阵。
y:array_like, shape (n_samples,)
Target vector.
标签向量。
discrete_features:{
'auto', bool, array_like}, default ‘auto’
如果为'auto',则将其分配给False(表示稠密)X,将其分配给True(表示稀疏)X。
如果是bool,则确定是考虑所有特征是离散特征还是连续特征。
如果是数组,则它应该是具有形状(n_features,)的布尔蒙版或具有离散特征索引的数组。
n_neighbors: int, default=3
用于连续变量的MI估计的邻居数;
较高的值会减少估计的方差,但可能会带来偏差。
copy: bool, default=True
是否复制给定的数据。如果设置为False,则初始数据将被覆盖。
random_state: int, RandomState instance or None, optional, default None
确定随机数生成,以将小噪声添加到连续变量中以删除重复值。
在多个函数调用之间传递int以获得可重复的结果。
Returns
-------
mi: ndarray, shape (n_features,)
每个特征和标签之间的估计相互信息。
import numpy as np
from sklearn.feature_selection import mutual_info_regression
def predict(a, b):
""" Compute the test statistic
Args:
a (array-like): Variable 1
b (array-like): Variable 2
Returns:
float: test statistic
"""
a = np.array(a).reshape((-1, 1))
b = np.array(b).reshape((-1, 1))
return (mutual_info_regression(a, b.reshape((-1,))) + mutual_info_regression(b, a.reshape((-1,))))/2
a=np.random.uniform(5,10,size=20)
b=np.random.uniform(5,10,size=20)
predict(a,a) # array([1.71440632])
predict(b,b) # array([1.71440632])
predict(a,b) # =predict(b,a)=array([0.])