0 code test
// E.g. For 8 channels:
// Array Order : 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 etc. 16 etc...
// Sample Order: A0 B0 C0 D0 E0 F0 G0 H0 A1 B1 C2 etc. A2 etc...
// Output Order: A0 B0 C0 D0 E0 F0 G0 H0 A0+A1 B0+B1 C0+C2 etc. A0+A1+A2 etc...
#include <stdio.h>
typedef short din_t;
typedef short dout_t;
typedef int dacc_t;
#define CHANNELS 8
#define SAMPLES 4
#define N CHANNELS * SAMPLES
void array_io (dout_t d_o[N], din_t d_i[N]) {
int i, rem;
// Store accumulated data
static dacc_t acc[CHANNELS];//8 初始值是0
// Accumulate each channel
For_Loop: for (i=0;i<N;i++) {
rem=i%CHANNELS;//8个channel中第几个
acc[rem]= acc[rem] + d_i[i];//更新acc
d_o[i] = acc[rem];
}
}
默认是ram类型
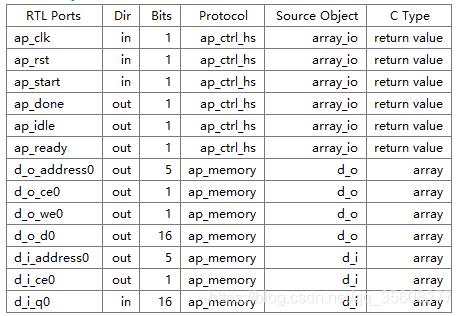
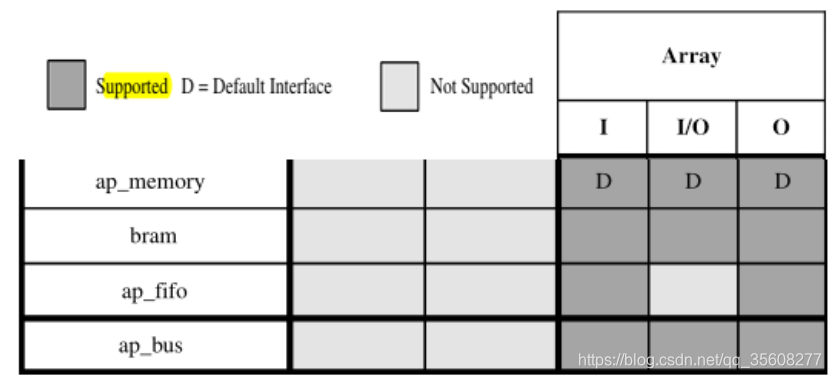
1 array 接口和存储
1.1 input array
input 作为resources,双口ram能够提高读入速度
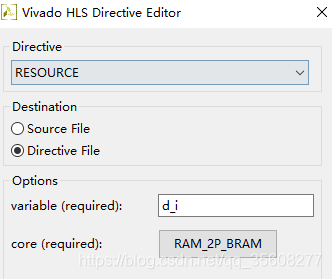
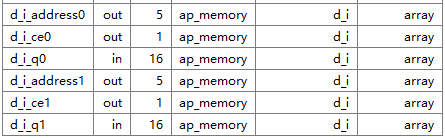
memory对应C类型为数组
同时读2次
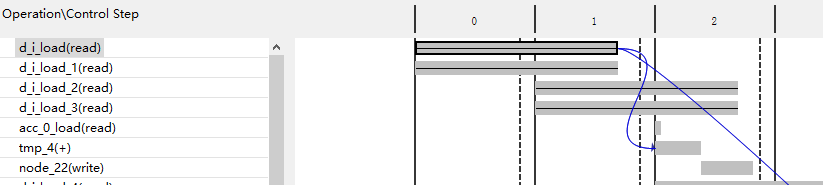
1.2 output array
是interface 选择fifo,输出是单口速度
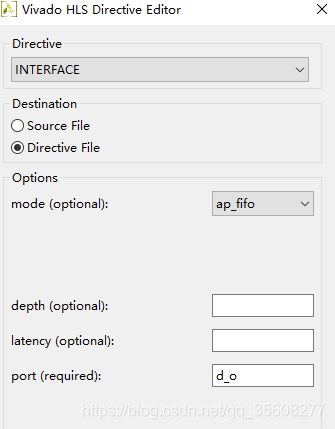
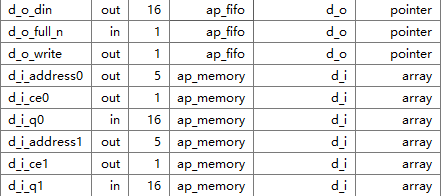
fifo对应的是指针
2 数组优化
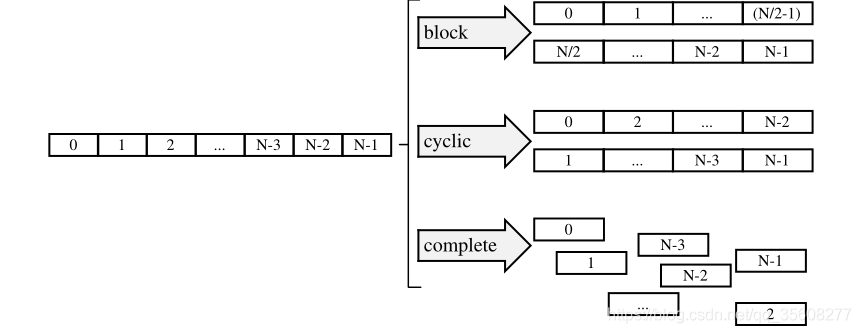
2.1 #pragma HLS ARRAY_PARTITION
数组分割可以提高吞吐量,因为通常数组是使用bram存储,最多有两个读数据口,会受到限制,因此通过数组分割操作,增加多个ram,提高吞吐量。
#pragma HLS array_partition variable=<name> <type> factor=<int> dim=<int>
< type >:
cyclic: 将原数组中元素循环放在cyclic个数组中
block: 将原数组中元素按顺序放在cyclic个数组中
complete:将原数组中元素放在单个寄存器中
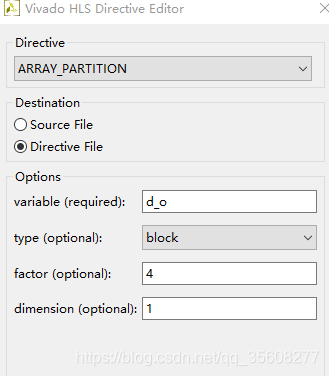
#pragma HLS ARRAY_PARTITION variable=d_o block factor=4 dim=1
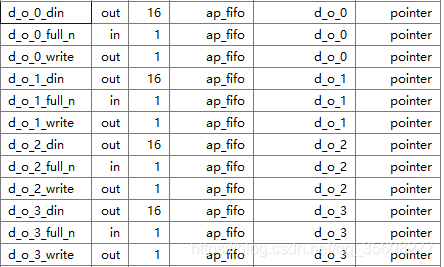
- 有多个小内存或多个寄存器,而不是一个大内存。
- 有效地增加了用于存储的读写端口数量。
- 可以潜在地提高设计的吞吐量。
- 需要更多的内存实例或寄存器。
dim:
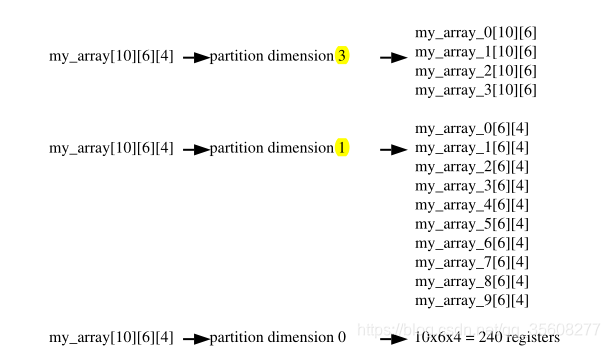
二维数组AB[6][4]
#pragma HLS array_partition variable=AB block factor=2 dim=2
分成2个 [6][2]
2.2 #pragma ARRAY_PARTITION variable=d_i complete dim=1
3 使用 AXI4-Stream 最优选择
#pragma HLS INTERFACE axis
C类型为指针
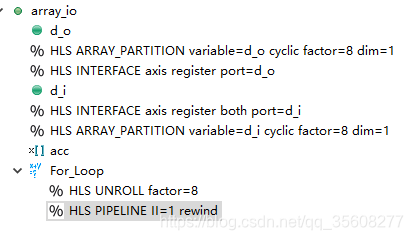
3.1 pragma HLS unroll
将循环按照factor个数并行,循环范围缩小到循环长度/factor。能够增加数据获取和吞吐量
unroll是针对整个循环的迭代次数优化。
#pragma HLS unroll factor=<N> region skip_exit_check
- region:有这个参数,只展开region内的for
- skip_exit_check:用在factor=?未指定
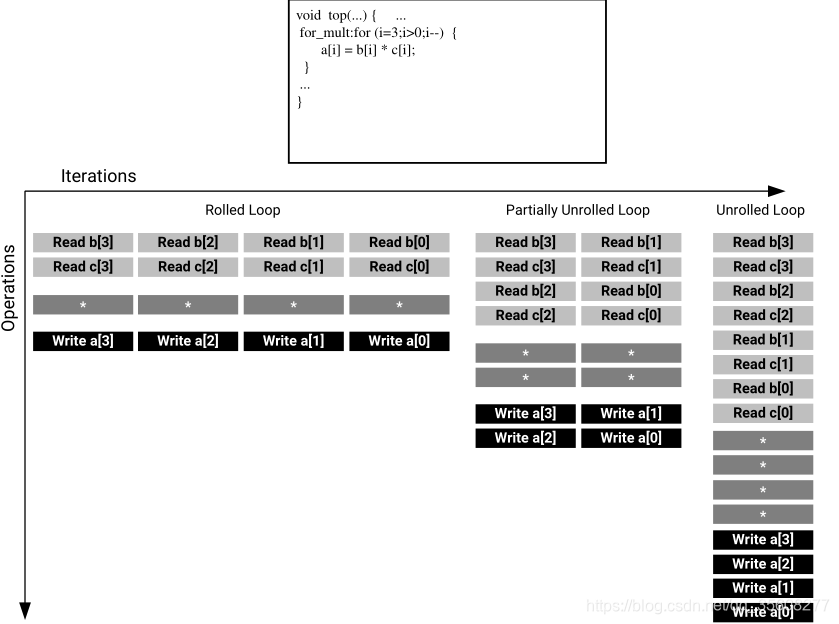
eg
factor分割
for(int i = 0; i < X; i++) {
pragma HLS unroll factor=2
a[i] = b[i] + c[i];
}
两个两个的取数,每组第一个是第一部分,每组第2个是第2部分
for(int i = 0; i < X; i += 2) {
a[i] = b[i] + c[i];
if (i+1 >= X) break;
a[i+1] = b[i+1] + c[i+1];
}
eg
不展开loop1
void foo(int data_in[N], int scale, int data_out1[N], int data_out2[N]) {
int temp1[N];
loop_1: for(int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
#pragma HLS unroll region
temp1[i] = data_in[i] * scale;
loop_2: for(int j = 0; j < N; j++) {
data_out1[j] = temp1[j] * 123;
}
loop_3: for(int k = 0; k < N; k++) {
data_out2[k] = temp1[k] * 456;
}
}
}
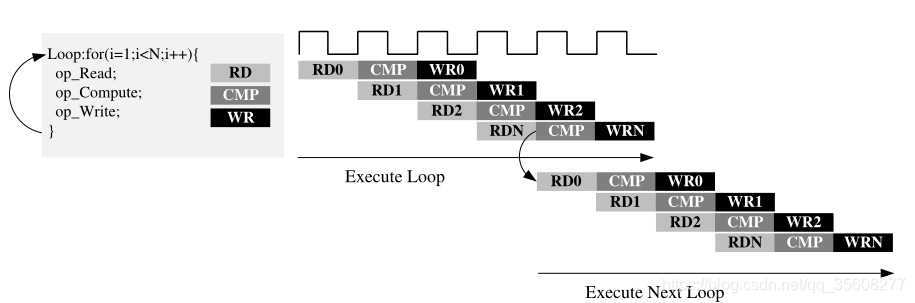
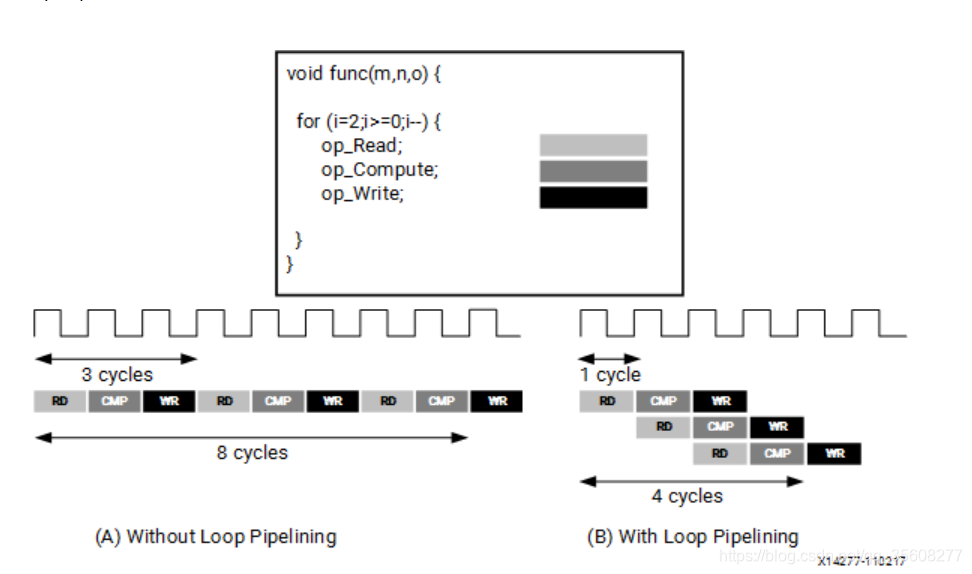
3.2 pragma HLS pipeline
流水,降低启动间隔initiation interval(N个时钟),每N个时钟开始一个新的循环。默认是1。
pipeline是针对一次循环的内部去优化。
#pragma HLS pipeline II=<int> enable_flush rewind
enable_flush:当pineline中的数据有效为低时,将暂停
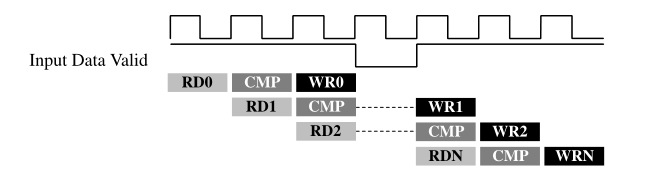
rewind: 在只有一个循环的结构中开始时执行一次,使得下一次迭代能够连续