目录
1、快速排序复习
基本思想:
1、在当前的排序序列中任意选取一个元素,把该元素称为基准元素或支点,把下雨等于基准元素的所有元素都移动到基准元素的前面,把大于基准元素的所有元素都移到基准元素的后面,这样使得基准元素所处的位置 恰好就是排序的最终位置,并且把当前参加排序的序列分为前后两个序列。
2、上述的过程称为一趟快速排序,即快速排序的一次划分
3、接下来分别对这两个子序列重复上述的排序操作(如果子序列长度大于1的话),直到所有元素都被移动到排序后他们应处的最终位置上。
效率之所以高:每一次元素的移动都是跳跃的,不会像冒泡排序只能在相邻元素之间进行,元素移动的间隔较大,因此总的比较和移动次数减少
具体步骤:
1、假设序列a,设置两个变量i、j.分别指向首元素和尾元素,设定i指向的首元素为基准元素
2、反复执行i++,直到i指向的元素>=基准元素,或者i指向尾部
3、反复执行j–,直到指向的元素<基准元素,或者j指向头部
4、若此时i<j,将i和j指向的元素进行交换。(大的元素在后面)
5、完成第一次交换后,重复执行步骤1、2,直到i>=j位置
6、此时i>=j,然后将基准元素与j指向的元素交换位置,至此完成了原序列的第一次划分
7、接下来分别对基准元素前后的子序列中长度大于1的子序列重复执行上述操作。
步骤分析:
对于每个子序列的操作又是一次划分,因此这个算法具有递归性质。
每次划分过程的基准元素仍可设定为子序列的第一个元素
#include<iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
//快速排序
void Quicksort(vector<int>& a, int s, int t)
{
int i, j;
if (s < t)
{
//【1】设置两个变量i、j.分别指向首元素和尾元素,设定i指向的首元素为基准元素
i = s;
j = t + 1;
while (1)
{
do i++;
while (!(a[s] <= a[i] || i == t)); //【2】重复i++操作,直到i指向的元素>=基准元素,或者i指向尾部
do j--;
while (!(a[s] >= a[j] || j == s)); //【3】反复执行j--,直到指向的元素<基准元素,或者j指向头部
if (i < j) //【5】若此时i<j,将i和j指向的元素进行交换。(大的元素在后面)
{
swap(a[j], a[i]);
}
else break; //【5】完成第一次交换后,重复执行步骤1、2,直到i>=j位置
}
//【6】此时i>=j,然后将基准元素与j指向的元素交换位置,至此完成了原序列的第一次划分
swap(a[s], a[j]);
//【7】接下来分别对基准元素前后的子序列中长度大于1的子序列重复执行上述操作。
Quicksort(a, s, j - 1); //前半序列
Quicksort(a, j + 1, t); //后半序列
}
}
void show_sort_result(vector<int> a, int k)
{
for (int f = 0;f < k;f++)
{
cout << a[f] << " ";
}
printf("\n");
}
int main()
{
vector<int> a = {
98,76,109,34,67,190,80,12,14,89,1 };
printf("快速排序\n");
Quicksort(a,0,a.size() - 1);
show_sort_result(a, a.size() - 1);
return 0;
}
2、链表部分复习
链表定义
struct ListNode {
int val;
ListNode *next;
ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {
}
ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {
}
ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {
}
};
203. 移除链表元素
不使用虚拟头节点
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* removeElements(ListNode* head, int val) {
//删除头节点
while(head != nullptr && head->val == val)
{
ListNode* temp = head;
head = head->next;
delete(temp);
}
//删除非头节点
ListNode* cur = head;
while(cur != nullptr && cur->next != nullptr)
{
if(cur->next->val == val)
{
ListNode* temp = cur->next;
cur->next = cur->next->next;
delete(temp);
}
else
{
cur = cur->next;
}
}
return head;
}
};
使用虚拟头节点:
注意如果使用指针的话,没有delete dummy会造成内存泄漏。
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* removeElements(ListNode* head, int val) {
ListNode* dummyHead = new ListNode(0);
dummyHead->next = head;
ListNode* cur = dummyHead;
while(cur->next != nullptr)
{
if(cur->next->val == val)
{
ListNode* temp = cur->next;
cur->next = cur->next->next;
delete temp;
}
else
{
cur = cur->next;
}
}
ListNode* ret = dummyHead->next;
delete dummyHead;
return ret;
}
};
707. 设计链表
注意虚拟头节点的使用。
class MyLinkedList {
public:
//定义链表的结构体
struct ListNode {
int val;
ListNode* next;
ListNode(int val) : val(val) , next(nullptr) {
}
};
private:
//定义链表的虚拟头节点
ListNode* _dummyHead;
int _size;
public:
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
MyLinkedList() {
_dummyHead = new ListNode(0);
_size = 0; //记录链表中已经存在的元素个数
}
/** Get the value of the index-th node in the linked list. If the index is invalid, return -1. */
int get(int index) {
if(index < 0 || index > _size -1)
return -1;
ListNode* cur = _dummyHead->next;
while(index--){
cur = cur->next;
}
return (cur->val);
}
/** Add a node of value val before the first element of the linked list. After the insertion, the new node will be the first node of the linked list. */
void addAtHead(int val) {
ListNode* newNode = new ListNode(val);
newNode->next = _dummyHead->next;
_dummyHead->next = newNode;
_size++;
}
/** Append a node of value val to the last element of the linked list. */
void addAtTail(int val) {
ListNode* newNode = new ListNode(val);
ListNode* cur = _dummyHead; //注意cur从_dummy开始,防止链表一开始为空
while(cur->next != nullptr){
cur = cur->next;
}
//此时cur->next为空
cur->next = newNode;
_size++;
}
/** Add a node of value val before the index-th node in the linked list. If index equals to the length of linked list, the node will be appended to the end of linked list. If index is greater than the length, the node will not be inserted. */
void addAtIndex(int index, int val) {
if(index > _size) return ;
if(index < 0)
{
addAtHead(val);
return ;
}
ListNode* newNode = new ListNode(val);
ListNode* cur = _dummyHead;
while(index--){
cur = cur->next;
}
newNode->next = cur->next;
cur->next = newNode;
_size++;
}
/** Delete the index-th node in the linked list, if the index is valid. */
void deleteAtIndex(int index) {
if(index >= _size || index < 0)
{
return ;
}
ListNode* cur = _dummyHead;
while(index--)
cur = cur->next;
ListNode* temp = cur->next;
cur->next = cur->next->next;
delete temp;
_size--;
}
};
/**
* Your MyLinkedList object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MyLinkedList* obj = new MyLinkedList();
* int param_1 = obj->get(index);
* obj->addAtHead(val);
* obj->addAtTail(val);
* obj->addAtIndex(index,val);
* obj->deleteAtIndex(index);
*/
206. 反转链表
注意while循环的条件以及最后返回的是pre。
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) {
ListNode* cur = head;
ListNode* pre = nullptr;
while(cur != nullptr)
{
ListNode* temp = cur->next;
cur->next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = temp;
}
return pre;
}
};
142.环形链表 II
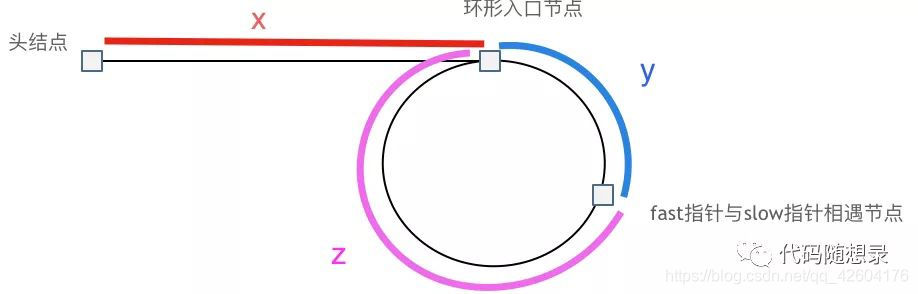
数学推导:
相遇时:
slow走过节点数:x+y
fast走过节点数:x+y+n(y+z)
并且有:
(x+y)*2 = x+y+n(y+z)
当n= 1时,x = z:
即:
从头节点出发一个指针,从相遇节点也出发一个指针,这两个指针每次只走一个节点,那么当这两个指针相遇的时候就是环形入口的节点了。
class Solution {
public:
ListNode *detectCycle(ListNode *head) {
ListNode* fast = head;
ListNode* slow = head;
while(fast != nullptr && fast->next != nullptr)
{
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
//快慢指针相遇
if(fast == slow)
{
ListNode* index1 = fast;
ListNode* index2 = head;
while(index1 != index2)
{
index1 = index1->next;
index2 = index2->next;
}
return index2;
}
}
return nullptr;
}
};
3、二分法复习
二分法变种对于不完全有序的还需要再刷刷
4、哈希法复习
242. 有效的字母异位词
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/valid-anagram/
349. 两个数组的交集,注意set的使用,还是不太熟悉
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/intersection-of-two-arrays/
202. 快乐数
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/happy-number/
1. 两数之和,注意map的使用,不是很熟悉,要熟悉map的insert操作
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/two-sum/submissions/
454. 四数相加 II ,注意count加上的是该值上所有的频次。
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/4sum-ii/submissions/
383. 赎金信,注意在map中加哪个减哪个。如果ransomNote中出现了magazine不存在的字母,则失败。
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/ransom-note/
5、双指针复习
15. 三数之和
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/3sum/
需要注意三个地方:
1、第一次去重,在外层for循环中,如果遇到相同的相邻元素continue
2、第二次去重,每一次找到一次三元组后也要进行一次去重,直到不再符合left < right
3、找到一个答案后,双指针同时收缩
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> threeSum(vector<int>& nums) {
sort(nums.begin(),nums.end());
vector<vector<int>> result;
for(int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++)
{
if(nums[i] > 0) break;
//第一次去重,在外层for循环中,如果遇到相同的相邻元素continue
if(i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i-1]) continue;
int left = i + 1;
int right = nums.size() - 1;
while(left < right) //不能取=
{
int tmp_sum = nums[i] + nums[left] + nums[right];
if(tmp_sum > 0) right--;
else if(tmp_sum < 0) left++;
else {
result.emplace_back(vector<int>{
nums[i],nums[left],nums[right]});
//第二次去重,每一次找到一次三元组后也要进行一次去重,直到不再符合left < right
while(left < right && nums[right - 1] == nums[right]) right--;
while(left < right && nums[left] == nums[left + 1]) left++;
//找到一个答案后,双指针同时收缩
left++;
right--;
}
}
}
return result;
}
};
18. 四数之和
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/4sum/
需要注意地方:
分为3重嵌套,比上一题多了一层循环。所以在最外层也多一个去重。
剪枝操作时错误的,不可以剪枝。
三数之和:
for{
剪枝;
去重;
while(再去重);
}
四数之和:
for
{
去重;
for{
去重;
while(再去重);
}
}
27. 移除元素
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/remove-element/
重点在于fast每时每刻都在往后走(无论该元素是否==val),如果不等于的话slow也需要走。nums【fast】=val的时候slow不走,fast走。
接着到下一个 nums【fast】!=val时,将指向的元素向前移动。
class Solution {
public:
int removeElement(vector<int>& nums, int val) {
int slow = 0;
for(int fast = 0; fast < nums.size(); fast++)
{
if(nums[fast] != val)
{
nums[slow] = nums[fast];
slow++;
}
}
return slow;
}
};
344. 反转字符串,简单,双指针从两侧往中间靠拢,并随时swap
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/reverse-string/
剑指 Offer 05. 替换空格
先计算扩充后大小,然后从后向前替换空格。数组填充类题均是这样做。
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/ti-huan-kong-ge-lcof/
class Solution {
public:
string replaceSpace(string s) {
int count = 0; //记录空格数
int old_size = s.size();
for(int i = 0; i < old_size; i++)
{
if(s[i] == ' ') count++;
}
//扩充s
s.resize(old_size + count * 2);
int new_size = s.size();
//定义两个指针,指向两个位置
int new_index = new_size - 1;
int old_index = old_size - 1;
while(old_index < new_index)
{
if(s[old_index] != ' ')
{
s[new_index] = s[old_index];
}
else
{
s[new_index] = '0';
new_index--;
s[new_index] = '2';
new_index--;
s[new_index] = '%';
}
new_index--;
old_index--;
}
return s;
}
};
151. 翻转字符串里的单词
,这一题还得多做几遍。。
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/reverse-words-in-a-string/
这一题对空格的处理操作更加繁琐一点;
思路:
1、移除多余空格
2、将整个字符串反转
3、将每个单词反转
如:
“the sky is blue” => “the sky is blue” => “eulb si yks eht” => “blue is sky the”
1、去除多余空格,使用双指针
void removeExtraSpaces(string& s)
{
//定义快慢指针
int slow = 0;
int fast = 0;
//去除字符串前面的空格
while(s.size() > 0 && fast < s.size() && s[fast] == ' ') fast++;
//去除字符串中间的荣誉空格
while(fast < s.size())
{
if(fast > 1 && s[fast] == ' ' && s[fast - 1] == ' ')
{
fast++;
continue;
}
else
{
s[slow] = s[fast];
slow++;
fast++;
}
}
//去除字符串末尾的空格,并重新设置字符串大小
if(slow > 1 && s[slow - 1] == ' ')
{
s.resize(slow - 1);
}
else
{
s.resize(slow);
}
}
2、反转字符串,使用双指针
void reverse(string& s,int left,int right)
{
while(left <= right)
{
swap(s[left],s[right]);
left++;
right--;
}
}
3、将字符串中的每个单词反转
string reverseWords(string s) {
removeExtraSpaces(s);
reverse(s,0,s.size() - 1);
int fast = 0;
int slow = 0;
while(fast < s.size())
{
//如果遍历到字符串中间一个单词结束
if(s[fast] == ' ')
{
reverse(s,slow,fast - 1);
//跳过空格
slow = fast + 1;
}
//如果遍历到最后一个单词结束(此时没有空格)
if(fast == s.size() -1)
{
reverse(s,slow,fast);
}
fast++;
}
return s;
}