文章目录
1.前言
在Linux内核中经常会见到container_of这个宏,通过某一个成员变量的地址获取这个结构体的地址,比如在一个工作队列中获取一个结构体的地址,watchdog_work为plat_data的一个成员变量
static void work_func(struct work_struct *work)
{
struct plat_data *data = container_of(work, struct plat_data, watchdog_work);
}
2.结构体变量在结构体的地址偏移
从结构体首地址开始,每一个结构体变量对于结构体的首地址有一个固定的地址偏移,当结构体的首地址为0时,此时结构体中各个成员变量的地址就是相对于结构体首地址的偏移
代码示例:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct s{
int age;
int id;
char *name;
};
int main()
{
//地址
printf("&s =%p\n",(struct s*)0);
printf("&age =%p\n",&((struct s*)0)->age);
printf("&id =%p\n",&((struct s*)0)->id);
printf("&name=%p\n",&((struct s*)0)->name);
return 0;
}
结果:
&s =(nil)
&age =(nil)
&id =0x4
&name=0x80
3.以空指针进行调用
#include <stdio.h>
struct ST
{
int i; // 0
int j; // 4
char c; // 8
};
void func(struct ST* pst)
{
int* pi = &(pst->i); // 0
int* pj = &(pst->j); // 4
char* pc = &(pst->c); // 8
printf("pst = %p\n", pst);
printf("pi = %p\n", pi);
printf("pj = %p\n", pj);
printf("pc = %p\n", pc);
}
int main()
{
struct ST s = {
0};
func(&s);
func(NULL);
return 0;
}

func调用空指针并没有导致程序崩溃,这说明编译器并没有访问这段内存,而是获取这段内存的地址,Linux内核中的offset宏就是利用这一思想
4.offsetof宏
#define offsetof(TYPE, MEMBER) ((size_t) &((TYPE *)0)->MEMBER)
其中MEMBER为结构体成员变量,TYPE为结构体的类型,从而获取MEMBER成员变量在TYPE结构体类型中的偏移位置
5.{()}是什么语法
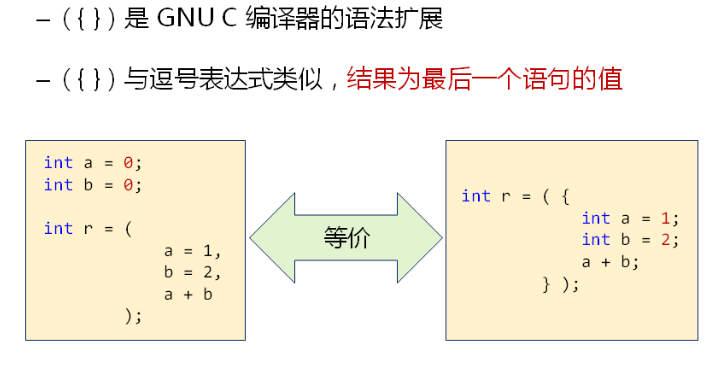
代码:
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int r = ({
int a = 1;
int b = 2;
a + b;
});
printf("r=%d\n",r);
return 0;
}
结果
r = 3
6.typeof关键字
typeof是GNU C编译器特有的关键字,只在编译器有效,用来获取变量的类型
int i = 100
typeof(i) j = 100;//int j =100
const type(i)* p = &j; //const int* p = &j
代码:
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int i = 100;
typeof(i) j = 100;//int j =100
printf("sizeof(j)=%d\n",sizeof(j));
printf("j=%d\n",j);
return 0;
}
结果:
sizeof(j)=4
j=100
7.最后的原理

所以,可以得到p的地址为,结构体成员变量的地址值(pc)=结构体的地址值§+结构体成员变量的地址值偏移值(offset)
pc = p + offset
struct ST* p = (struct ST*)((char*)pc-offset);//转换为char*类型方便指针运算,一次只偏移一个字节
8.container_of原理剖析
1 #ifndef container_of
2 #define container_of(ptr, type, member) ({
\
3 const typeof(((type*)0)->member)* __mptr = (ptr); \
4 (type*)((char*)__mptr - offsetof(type, member));
})
5 #endif
container_of三个参数为:
- ptr:结构体内成员member的地址
- type:结构体类型
- member:结构体变量
程序示例:
#include <stdio.h>
#define offsetof(TYPE, MEMBER) ((size_t) &((TYPE *)0)->MEMBER)
#define container_of(ptr, type, member) ({
\
const typeof( ((type *)0)->member ) *__mptr = (ptr); \
(type *)( (char *)__mptr - offsetof(type,member) );
})
struct s
{
int id;
char sex;
int age;
};
int main(void)
{
struct s s1 = {
4,'S',6};
printf("&s1 = %p\n", &s1);
printf("&s1.sex = %p\n", &s1.sex);
printf("offsetof(struct s,sex)= %ld\n",offsetof(struct s,sex));
printf("&s1 = %p\n", container_of(&s1.sex, struct s, sex));
printf("&s1 = %p\n", (struct s*)((char *)&s1.sex-offsetof(struct s,sex)));
printf("s1->id=%d\n",(struct s*)((char *)&s1.sex-offsetof(struct s,sex))->id);
return 0;
}
结果为:
&s1 = 0x7ffe5da751ec
&s1.sex = 0x7ffe5da751f0
offsetof(struct s,sex)= 4
&s1 = 0x7ffe5da751ec
&s1 = 0x7ffe5da751ec
s1->id=4
将上面示例展开为:
#define container_of(ptr, type, member)
({
const typeof( ((type *)0)->member ) *__mptr = (ptr);
(type *)( (char *)__mptr - offsetof(type,member) );
})
container_of(&s1.sex, struct s, sex)
const typeof( ((struct s*)0)->sex) *__mptr = (&s1.sex); //
(struct s *)( (char *)&s1.sex - offsetof(type,member)
上面的mptr为s1.sex的地址,(struct s *)( (char *)&s1.sex - offsetof(type,member)的值为s1的地址值,(struct s*)((char *)&s1.sex-offsetof(struct s,sex))->id的值为4,我们在Linux内核编程中,传给某个函数的参数是某个结构体的成员变量,在这个函数中可能还会用到此结构体的其它成员变量,这个时候通过宏变量container_of ,找到结构体的首地址,然后就可以访问其它成员变量了。
9.const typeof(((type*)0)->member)* __mptr = (ptr)的作用
const typeof(((type*)0)->member)* __mptr = (ptr);代码的作用就是做类型检查
改写contain_of宏为
#ifndef container_of
#define container_of_new(ptr, type, member) ({
\
(type*)((char*)__mptr - offsetof(type, member));
})
#endif
代码:
#include <stdio.h>
#define offsetof(TYPE, MEMBER) ((size_t) &((TYPE *)0)->MEMBER)
#ifndef container_of
#define container_of_new(ptr, type, member) ((type*)((char*)ptr - offsetof(type, member)))
#endif
struct ST{
char c;
int i;
int j;
};
int main()
{
struct ST s = {
0 };
char* pc = &s.c;
int e = 0;
int* pe = &e;
struct ST* pst = container_of_new(pe, struct ST, c);
printf("&s = %p\n", &s);
printf("pst = %p\n", pst);
return 0;
}
结果:
&s = 00CFFC28
pst = 00CFFC08
可以看到,计算结果是错误的,不改写contain_of时,代码为:
#include <stdio.h>
#ifndef offsetof
#define offsetof(TYPE, MEMBER) ((size_t)&((TYPE*)0)->MEMBER)
#endif
#ifndef container_of
#define container_of(ptr, type, member) ({
\
const typeof(((type*)0)->member)* __mptr = (ptr); \
(type*)((char*)__mptr - offsetof(type, member)); })
#endif
#ifndef container_of_new
#define container_of_new(ptr, type, member) ((type*)((char*)(ptr) - offsetof(type, member)))
#endif
struct ST
{
int i; // 0
int j; // 4
char c; // 8
};
int main()
{
struct ST s = {
0 };
char* pc = &s.c;
int e = 0;
int* pe = &e;
struct ST* pst = container_of(pe, struct ST, c);
printf("&s = %p\n", &s);
printf("pst = %p\n", pst);
return 0;
}
结果:
&s = 0x7ffea13f27d4
pst = 0x7ffea13f27c8
main.c: In function ‘main’:
main.c:9:52: warning: initialization of ‘const char *’ from incompatible pointer type ‘int *’ [-Wincompatible-pointer-types]
9 | const typeof(((type*)0)->member)* __mptr = (ptr); \
| ^
main.c:31:22: note: in expansion of macro ‘container_of’
31 | struct ST* pst = container_of(pe, struct ST, c);
| ^~~~~~~~~~~~
main.c:9:52: note: (near initialization for ‘pst’)
9 | const typeof(((type*)0)->member)* __mptr = (ptr); \
| ^
main.c:31:22: note: in expansion of macro ‘container_of’
31 | struct ST* pst = container_of(pe, struct ST, c);
| ^~~~~~~~~~~~
这时候会报类型不兼容的警告,使用const typeof(((type*)0)->member)* __mptr = (ptr);编译器首先将0转换为type类型的指针,再通过typeof获取到member数据成员的类型,使用ptr来对其进行初始化,如果传入的类型一致不会报警告,当传入的类型不一样时会报编译警告
小结
- ({})与逗号表达式类似,结果为最后一个语句的值
- typeof只在编译器有效,用于得到变量的类型
- container_of使用({})进行类型安全检查