目录
1. Pattern: Sliding window,滑动窗口类型
3. Pattern: Fast & Slow pointers, 快慢指针类型
4. Pattern: Merge Intervals,区间合并类型
6. Pattern: In-place Reversal of a LinkedList,链表翻转
7. Pattern: Tree Breadth First Search,树上的BFS
8. Pattern: Tree Depth First Search,树上的DFS
10. Pattern: Subsets (backtracking),子集类型,一般都是使用多重DFS,一般用回溯来解
11. Pattern: Modified Binary Search,改造过的二分
12. Pattern: Top ‘K’ Elements,前K个系列
14. Pattern: 0/1 Knapsack (Dynamic Programming),0/1背包类型
15. Pattern: Topological Sort (Graph),拓扑排序类型
在之前的文章中,我们知道,刷Leetcode最有效的方式,是通过按题型刷来提高编程面试能力。在之前的文章里,不少小伙伴说好些题目和LeetCode对应不上。
所以咱们就来完善一下,我把Leetcode里面每个题型下的题目都给大家归类好,大家保存每个类型的链接后,直接可以去LC上面刷题。
给大家送一个福利,LeetCode慷慨给读者小伙伴们送出 15% off (优惠24刀)的年费折扣了。不需要等到一年一度的感恩节,也能享受到不错的折扣。平时有需要的小伙伴,可以使用这个链接: LeetCode Premium 通过链接购买年费会员才能享受折扣。LC的年费还是有很多好处的,可以按照频率刷题,看公司tag,还能看到不少问题的视频答案(新功能),锁住的题还有官方solutions等等。
之前的回答: LeetCode按照怎样的顺序来刷题比较好?
比如有最经典的sliding window模式,Two pointers模式,快慢指针模式,合并intervals模式,cyclic sort模式,in-place翻转链表模式,树上的BFS,树上的DFS,双Heaps模式,subsets模式,二分法变种,Top K模式,多路模式(K-ways),0/1背包,拓扑排序。
这个课程来自于educative,是一个美国的算法面试方面很出色的网课平台。

这门课程是一个算法总结提高的课程,它把算法面试中可能遇到的题分成了各种模式,每类题各个击破。
需要的小伙伴就去来一波吧!
他家最最出名的还是这门Grokking the System Design Interview, 但凡提到准备系统设计,这门课都上入门必推的:

以及OOD: Grokking the Object Oriented Design Interview
这门机器学习面试指南是这个系列最新的课程:

目前市面上机器学习面试相关的课程比较少,这门课程应该非常值得!
1. Pattern: Sliding window,滑动窗口类型
滑动窗口类型的题目经常是用来执行数组或是链表上某个区间(窗口)上的操作。比如找最长的全为1的子数组长度。滑动窗口一般从第一个元素开始,一直往右边一个一个元素挪动。当然了,根据题目要求,我们可能有固定窗口大小的情况,也有窗口的大小变化的情况。

该图中,我们的窗子不断往右一格一个移动
下面是一些我们用来判断我们可能需要上滑动窗口策略的方法:
- 这个问题的输入是一些线性结构:比如链表呀,数组啊,字符串啊之类的
- 让你去求最长/最短子字符串或是某些特定的长度要求
LeetCode滑动窗口类型问题list:
https://leetcode.com/list/5vexd9b3
具体题目:
https://leetcode.com/problems/permutation-in-string/
https://leetcode.com/problems/count-unique-characters-of-all-substrings-of-a-given-string/
https://leetcode.com/problems/fruit-into-baskets/
https://leetcode.com/problems/minimum-number-of-k-consecutive-bit-flips/
https://leetcode.com/problems/longest-substring-without-repeating-characters/
https://leetcode.com/problems/substring-with-concatenation-of-all-words/
https://leetcode.com/problems/minimum-window-substring/
https://leetcode.com/problems/minimum-size-subarray-sum/
https://leetcode.com/problems/sliding-window-maximum/
https://leetcode.com/problems/longest-repeating-character-replacement/
2. Pattern: two points, 双指针类型
双指针是这样的模式:两个指针朝着左右方向移动(双指针分为同向双指针和异向双指针),直到他们有一个或是两个都满足某种条件。双指针通常用在排好序的数组或是链表中寻找对子。比如,你需要去比较数组中每个元素和其他元素的关系时,你就需要用到双指针了。
我们需要双指针的原因是:如果你只用一个指针的话,你得来回跑才能在数组中找到你需要的答案。这一个指针来来回回的过程就很耗时和浪费空间了 — 这是考虑算法的复杂度分析的时候的重要概念。虽然brute force一个指针的解法可能会奏效,但时间复杂度一般会是O(n²)。在很多情况下,双指针能帮助我们找到空间或是时间复杂度更低的解。
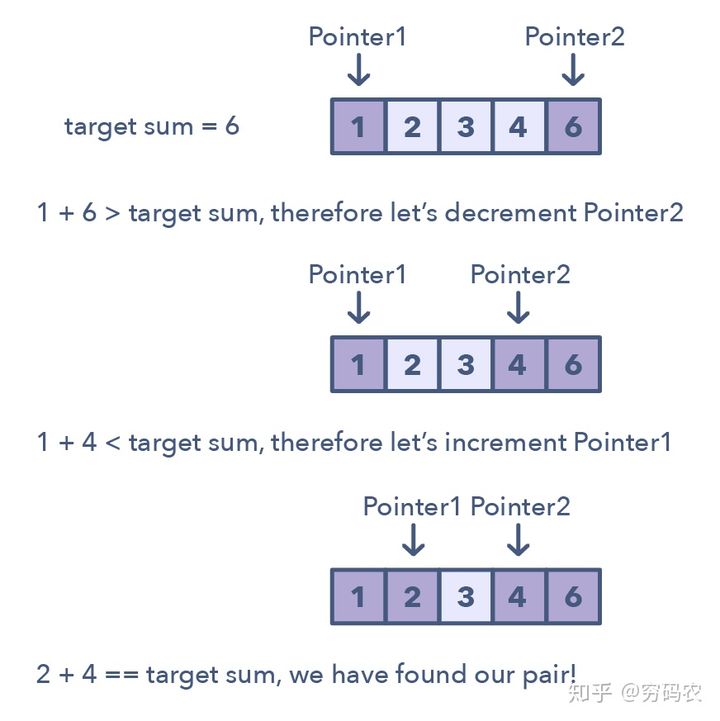
上图是说,我们在排好序的数组里面找是否有一对数加起来刚好等于目标和
识别使用双指针的招数:
- 一般来说,数组或是链表是排好序的,你得在里头找一些组合满足某种限制条件
- 这种组合可能是一对数,三个数,或是一个子数组
双指针类型经典题目合集:
https://leetcode.com/list/5vexz1vs
具体题目:
https://leetcode.com/problems/two-sum/
https://leetcode.com/problems/container-with-most-water/
https://leetcode.com/problems/3sum/
https://leetcode.com/problems/3sum-closest/
https://leetcode.com/problems/trapping-rain-water/
https://leetcode.com/problems/sort-colors/
https://leetcode.com/problems/minimum-window-substring/
https://leetcode.com/problems/remove-duplicates-from-sorted-list/
https://leetcode.com/problems/subarray-product-less-than-k/
https://leetcode.com/problems/backspace-string-compare/
https://leetcode.com/problems/squares-of-a-sorted-array/
3. Pattern: Fast & Slow pointers, 快慢指针类型
这种模式,有一个非常出门的名字,叫龟兔赛跑。咱们肯定都知道龟兔赛跑啦。但还是再解释一下快慢指针:这种算法的两个指针的在数组上(或是链表上,序列上)的移动速度不一样。还别说,这种方法在解决有环的链表和数组时特别有用。
通过控制指针不同的移动速度(比如在环形链表上),这种算法证明了他们肯定会相遇的。快的一个指针肯定会追上慢的一个(可以想象成跑道上面跑得快的人套圈跑得慢的人)。

上面这个图演示了快慢两个指针最终在5相遇了
咋知道需要用快慢指针模式勒?
- 问题需要处理环上的问题,比如环形链表和环形数组
- 当你需要知道链表的长度或是某个特别位置的信息的时候
那啥时候用快慢指针而不是上面的双指针呢?
- 有些情形下,咱们不应该用双指针,比如我们在单链表上不能往回移动的时候。一个典型的需要用到快慢指针的模式的是当你需要去判断一个链表是否是回文的时候。
具体题目:
https://leetcode.com/problems/add-two-numbers/
https://leetcode.com/problems/remove-nth-node-from-end-of-list/
https://leetcode.com/problems/remove-duplicates-from-sorted-list/
https://leetcode.com/problems/linked-list-cycle/
https://leetcode.com/problems/linked-list-cycle-ii/
https://leetcode.com/problems/reorder-list/
https://leetcode.com/problems/sort-list/
https://leetcode.com/problems/remove-linked-list-elements/
https://leetcode.com/problems/palindrome-linked-list/
https://leetcode.com/problems/middle-of-the-linked-list/
4. Pattern: Merge Intervals,区间合并类型
区间合并模式是一个用来处理有区间重叠的很高效的技术。在设计到区间的很多问题中,通常咱们需要要么判断是否有重叠,要么合并区间,如果他们重叠的话。这个模式是这么起作用的:
给两个区间,一个是a,另外一个是b。别小看就两个区间,他们之间的关系能跑出来6种情况。详细的就看图啦。
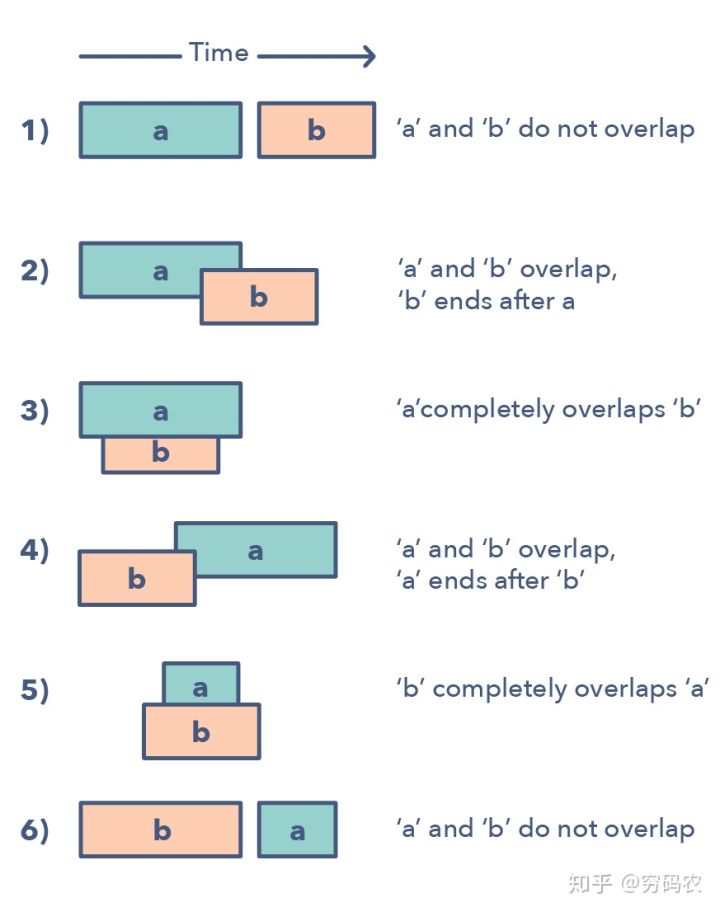
理解和识别这六种情况,灰常重要。因为这能帮你解决一大堆问题。这些问题从插入区间到优化区间合并都有。
怎么识别啥时候用合并区间模式呀?
- 当你需要产生一堆相互之间没有交集的区间的时候
- 当你听到重叠区间的时候
题目列表包含:
https://leetcode.com/problems/merge-intervals/
https://leetcode.com/problems/insert-interval/
https://leetcode.com/problems/non-overlapping-intervals/
https://leetcode.com/problems/minimum-number-of-arrows-to-burst-balloons/
https://leetcode.com/problems/task-scheduler/
https://leetcode.com/problems/interval-list-intersections/
LeetCode中国区:归类标签:数组
56. 合并区间 https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/merge-intervals/
57. 插入区间 https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/insert-interval
435. 无重叠区间 https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/non-overlapping-intervals/
452. 用最少数量的箭引爆气球 https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/minimum-number-of-arrows-to-burst-balloons
621. 任务调度器 https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/task-scheduler
986. 区间列表的交集 https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/interval-list-intersections
5. Pattern: Cyclic Sort,循环排序
这种模式讲述的是一直很好玩的方法:可以用来处理数组中的数值限定在一定的区间的问题。这种模式一个个遍历数组中的元素,如果当前这个数它不在其应该在的位置的话,咱们就把它和它应该在的那个位置上的数交换一下。你可以尝试将该数放到其正确的位置上,但这复杂度就会是O(n^2)。这样的话,可能就不是最优解了。因此循环排序的优势就体现出来了。
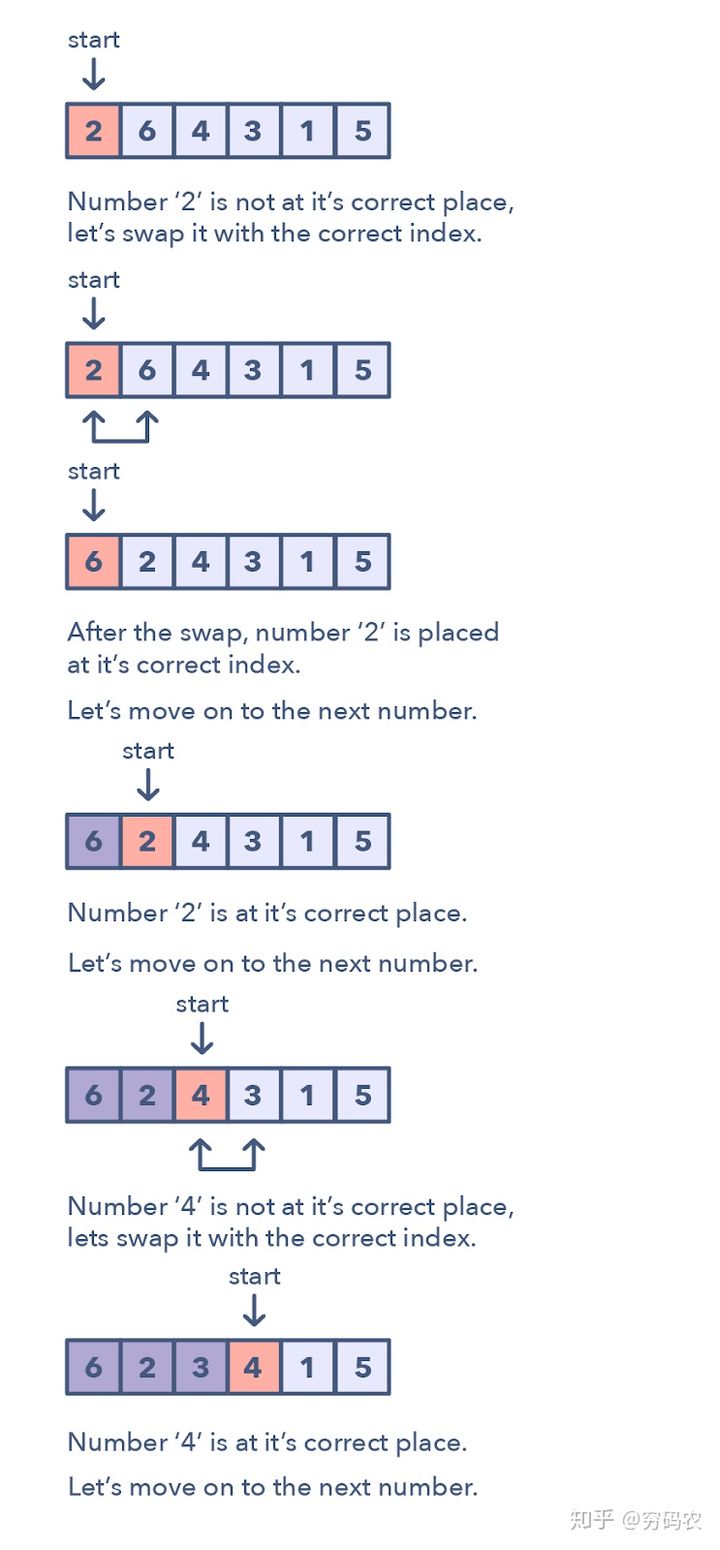
咋鉴别这种模式?
- 这些问题一般设计到排序好的数组,而且数值一般满足于一定的区间
- 如果问题让你需要在排好序/翻转过的数组中,寻找丢失的/重复的/最小的元素
列表包含题目:
https://leetcode.com/problems/missing-number/
https://leetcode.com/problems/find-the-duplicate-number/
中文版:268. 丢失的数字 https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/missing-number/
287. 寻找重复数 https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/find-the-duplicate-number/
6. Pattern: In-place Reversal of a LinkedList,链表翻转
在众多问题中,题目可能需要你去翻转链表中某一段的节点。通常,要求都是你得原地翻转,就是重复使用这些已经建好的节点,而不使用额外的空间。这个时候,原地翻转模式就要发挥威力了。
这种模式每次就翻转一个节点。一般需要用到多个变量,一个变量指向头结点(下图中的current),另外一个(previous)则指向咱们刚刚处理完的那个节点。在这种固定步长的方式下,你需要先将当前节点(current)指向前一个节点(previous),再移动到下一个。同时,你需要将previous总是更新到你刚刚新鲜处理完的节点,以保证正确性。
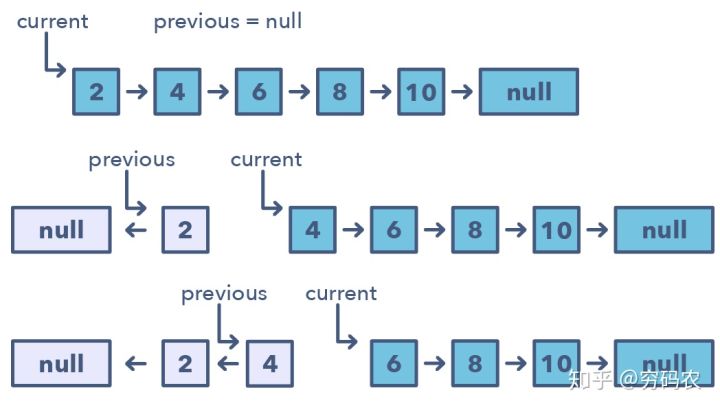
咱们怎么去甄别这种模式呢?
- 如果你被问到需要去翻转链表,要求不能使用额外空间的时候
经典题目列表:
https://leetcode.com/list/5ve5dgd5
列表包含题目:
https://leetcode.com/problems/swap-nodes-in-pairs/
https://leetcode.com/problems/reverse-nodes-in-k-group/
https://leetcode.com/problems/rotate-list/
https://leetcode.com/problems/reverse-linked-list-ii/
https://leetcode.com/problems/reverse-linked-list/
https://leetcode.com/problems/odd-even-linked-list/
7. Pattern: Tree Breadth First Search,树上的BFS
这种模式基于宽搜(Breadth First Search (BFS)),适用于需要遍历一颗树。借助于队列数据结构,从而能保证树的节点按照他们的层数打印出来。打印完当前层所有元素,才能执行到下一层。所有这种需要遍历树且需要一层一层遍历的问题,都能用这种模式高效解决。
这种树上的BFS模式是通过把根节点加到队列中,然后不断遍历直到队列为空。每一次循环中,我们都会把队头结点拿出来(remove),然后对其进行必要的操作。在删除每个节点的同时,其孩子节点,都会被加到队列中。
识别树上的BFS模式:
- 如果你被问到去遍历树,需要按层操作的方式(也称作层序遍历)
经典题目列表:
https://leetcode.com/list/5ve57tn2
列表包含题目:
https://leetcode.com/problems/binary-tree-level-order-traversal/
https://leetcode.com/problems/binary-tree-zigzag-level-order-traversal/
https://leetcode.com/problems/binary-tree-level-order-traversal-ii/
https://leetcode.com/problems/minimum-depth-of-binary-tree/
https://leetcode.com/problems/populating-next-right-pointers-in-each-node/
https://leetcode.com/problems/populating-next-right-pointers-in-each-node-ii/
https://leetcode.com/problems/binary-tree-right-side-view/
https://leetcode.com/problems/number-of-islands/
https://leetcode.com/problems/average-of-levels-in-binary-tree/
https://leetcode.com/problems/all-nodes-distance-k-in-binary-tree/
8. Pattern: Tree Depth First Search,树上的DFS
树形DFS基于深搜(Depth First Search (DFS))技术来实现树的遍历。
咱们可以用递归(或是显示栈,如果你想用迭代方式的话)来记录遍历过程中访问过的父节点。
该模式的运行方式是从根节点开始,如果该节点不是叶子节点,我们需要干三件事:
- 需要区别我们是先处理根节点(pre-order,前序),处理孩子节点之间处理根节点(in-order,中序),还是处理完所有孩子再处理根节点(post-order,后序)。
- 递归处理当前节点的左右孩子。
识别树形DFS:
- 你需要按前中后序的DFS方式遍历树
- 如果该问题的解一般离叶子节点比较近。
经典题目列表:
https://leetcode.com/list/5ve5llac
列表包含题目:
https://leetcode.com/problems/path-sum/
https://leetcode.com/problems/path-sum-ii/
https://leetcode.com/problems/binary-tree-maximum-path-sum/
https://leetcode.com/problems/implement-trie-prefix-tree/
https://leetcode.com/problems/word-search-ii/
https://leetcode.com/problems/invert-binary-tree/
https://leetcode.com/problems/kth-smallest-element-in-a-bst/
https://leetcode.com/problems/lowest-common-ancestor-of-a-binary-search-tree/
https://leetcode.com/problems/lowest-common-ancestor-of-a-binary-tree/
https://leetcode.com/problems/serialize-and-deserialize-binary-tree/
https://leetcode.com/problems/path-sum-iii/
https://leetcode.com/problems/diameter-of-binary-tree/
https://leetcode.com/problems/subtree-of-another-tree/
https://leetcode.com/problems/merge-two-binary-trees/
https://leetcode.com/problems/maximum-binary-tree/
https://leetcode.com/problems/maximum-width-of-binary-tree/
https://leetcode.com/problems/validate-binary-search-tree/
https://leetcode.com/problems/same-tree/
https://leetcode.com/problems/maximum-depth-of-binary-tree/
https://leetcode.com/problems/construct-binary-tree-from-preorder-and-inorder-traversal/
9. Pattern: Two Heaps,双堆类型
很多问题中,我们被告知,我们拿到一大把可以分成两队的数字。为了解决这个问题,我们感兴趣的是,怎么把数字分成两半?使得:小的数字都放在一起,大的放在另外一半。双堆模式就能高效解决此类问题。
正如名字所示,该模式用到了两个堆,是不是很难猜?一个最小堆用来找最小元素;一个最大堆,拿到最大元素。这种模式将一半的元素放在最大堆中,这样你可以从这一堆中秒找到最大元素。同理,把剩下一半丢到最小堆中,O(1)时间找到他们中的最小元素。通过这样的方式,这一大堆元素的中位数就可以从两个堆的堆顶拿到数字,从而计算出来。
判断双堆模式的秘诀:
- 这种模式在优先队列,计划安排问题(Scheduling)中有奇效
- 如果问题让你找一组数中的最大/最小/中位数
- 有时候,这种模式在涉及到二叉树数据结构时也特别有用
经典题目列表:
https://leetcode.com/list/5ve5idmi
列表包含题目:
https://leetcode.com/problems/find-median-from-data-stream/
https://leetcode.com/problems/sliding-window-median/
https://leetcode.com/problems/ipo/
10. Pattern: Subsets (backtracking),子集类型,一般都是使用多重DFS,一般用回溯来解
超级多的编程面试问题都会涉及到排列和组合问题。子集问题模式讲的是用BFS来处理这些问题。
这个模式是这样的:
给一组数字 [1, 5, 3]
- 我们从空集开始:[[]]
- 把第一个数(1),加到之前已经存在的集合中:[[], [1]];
- 把第二个数(5),加到之前的集合中得到:[[], [1], [5], [1,5]];
- 再加第三个数(3),则有:[[], [1], [5], [1,5], [3], [1,3], [5,3], [1,5,3]].
该模式的详细步骤如下:
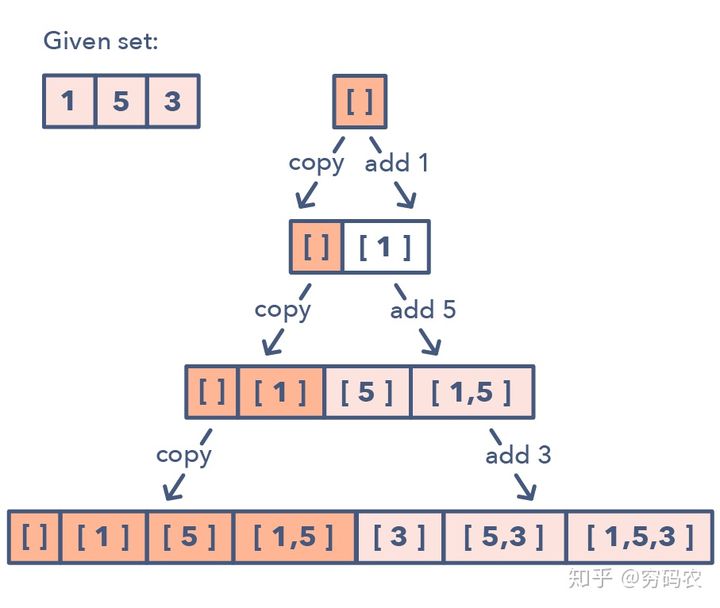
如果判断这种子集模式:
- 问题需要咱们去找数字的组合或是排列
经典题目列表:
https://leetcode.com/list/5ve5tmog
列表包含题目:
https://leetcode.com/problems/letter-combinations-of-a-phone-number/
https://leetcode.com/problems/generate-parentheses/
https://leetcode.com/problems/sudoku-solver/
https://leetcode.com/problems/combination-sum/
https://leetcode.com/problems/combination-sum-ii/
https://leetcode.com/problems/permutations/
https://leetcode.com/problems/permutations-ii/
https://leetcode.com/problems/n-queens/
https://leetcode.com/problems/combinations/
https://leetcode.com/problems/subsets/
https://leetcode.com/problems/subsets-ii/
https://leetcode.com/problems/palindrome-partitioning/
https://leetcode.com/problems/combination-sum-iii/
https://leetcode.com/problems/target-sum/
https://leetcode.com/problems/letter-case-permutation/
11. Pattern: Modified Binary Search,改造过的二分
当你需要解决的问题的输入是排好序的数组,链表,或是排好序的矩阵,要求咱们寻找某些特定元素。这个时候的不二选择就是二分搜索。这种模式是一种超级牛的用二分来解决问题的方式。
对于一组满足上升排列的数集来说,这种模式的步骤是这样的:
- 首先,算出左右端点的中点。最简单的方式是这样的:middle = (start + end) / 2。但这种计算方式有不小的概率会出现整数越界。因此一般都推荐另外这种写法:middle = start + (end — start) / 2
- 如果要找的目标改好和中点所在的数值相等,我们返回中点的下标就行
- 如果目标不等的话:我们就有两种移动方式了
- 如果目标比中点在的值小(key < arr[middle]):将下一步搜索空间放到左边(end = middle - 1)
- 如果比中点的值大,则继续在右边搜索,丢弃左边:left = middle + 1
图示该过程的话,如下图所示:
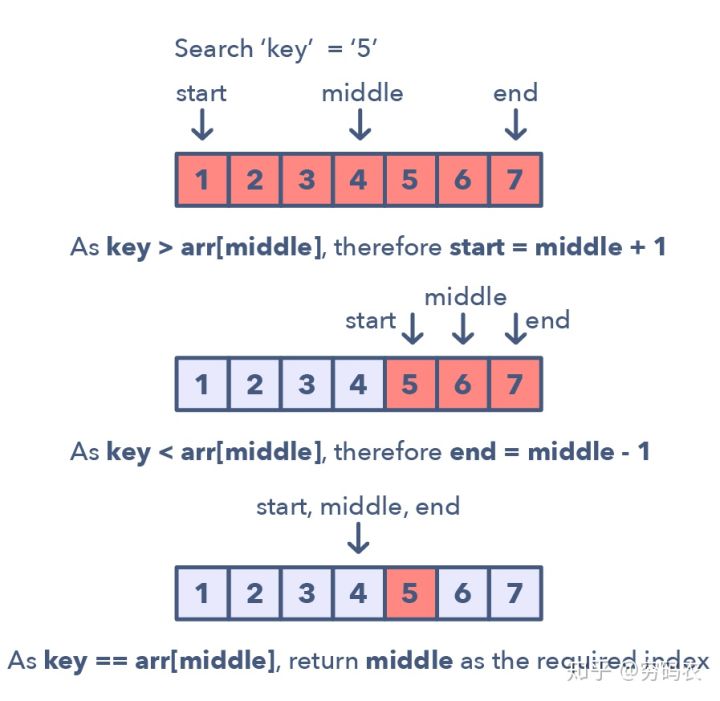
经典题目列表:
https://leetcode.com/list/5ve5355j
列表包含题目:
https://leetcode.com/problems/peak-index-in-a-mountain-array/
https://leetcode.com/problems/search-in-rotated-sorted-array/
https://leetcode.com/problems/search-a-2d-matrix/
https://leetcode.com/problems/search-in-rotated-sorted-array-ii/
https://leetcode.com/problems/find-minimum-in-rotated-sorted-array/
https://leetcode.com/problems/find-peak-element/
https://leetcode.com/problems/count-of-range-sum/
https://leetcode.com/problems/find-smallest-letter-greater-than-target/
https://leetcode.com/problems/binary-search/
12. Pattern: Top ‘K’ Elements,前K个系列
任何让我们求解最大/最小/最频繁的K个元素的题,都遵循这种模式。
用来记录这种前K类型的最佳数据结构就是堆了(译者注:在Java中,改了个名,叫优先队列(PriorityQueue))。这种模式借助堆来解决很多这种前K个数值的问题。
这个模式是这样的:
- 根据题目要求,将K个元素插入到最小堆或是最大堆。
- 遍历剩下的还没访问的元素,如果当前出来到的这个元素比堆顶元素大,那咱们把堆顶元素先删除,再加当前元素进去。

注意这种模式下,咱们不需要去排序数组,因为堆具有这种良好的局部有序性,这对咱们需要解决问题就够了。
识别最大K个元素模式:
- 如果你需要求最大/最小/最频繁的前K个元素
- 如果你需要通过排序去找一个特定的数
经典题目列表:
https://leetcode.com/list/5ve5qchr
列表包含题目:
https://leetcode.com/problems/find-k-closest-elements/
https://leetcode.com/problems/reorganize-string/
https://leetcode.com/problems/maximum-frequency-stack/
https://leetcode.com/problems/k-closest-points-to-origin/
https://leetcode.com/problems/kth-largest-element-in-an-array/
https://leetcode.com/problems/kth-smallest-element-in-a-bst/
https://leetcode.com/problems/top-k-frequent-elements/
https://leetcode.com/problems/sort-characters-by-frequency/
https://leetcode.com/problems/course-schedule-iii/
13. Pattern: K-way merge,多路归并
K路归并能帮咱们解决那些涉及到多组排好序的数组的问题。
每当你的输入是K个排好序的数组,你就可以用堆来高效顺序遍历其中所有数组的所有元素。你可以将每个数组中最小的一个元素加入到最小堆中,从而得到全局最小值。当我们拿到这个全局最小值之后,再从该元素所在的数组里取出其后面紧挨着的元素,加入堆。如此往复直到处理完所有的元素。

该模式是这样的运行的:
- 把每个数组中的第一个元素都加入最小堆中
- 取出堆顶元素(全局最小),将该元素放入排好序的结果集合里面
- 将刚取出的元素所在的数组里面的下一个元素加入堆
- 重复步骤2,3,直到处理完所有数字
识别K路归并:
- 该问题的输入是排好序的数组,链表或是矩阵
- 如果问题让咱们合并多个排好序的集合,或是需要找这些集合中最小的元素
经典题目列表:
https://leetcode.com/list/5ve5kkbd
列表包含题目:
https://leetcode.com/problems/merge-two-sorted-lists/
https://leetcode.com/problems/merge-k-sorted-lists/
https://leetcode.com/problems/find-k-pairs-with-smallest-sums/
https://leetcode.com/problems/kth-smallest-element-in-a-sorted-matrix/
https://leetcode.com/problems/smallest-range-covering-elements-from-k-lists/
14. Pattern: 0/1 Knapsack (Dynamic Programming),0/1背包类型
经典题目列表:
https://leetcode.com/list/5ve5zu13
列表包含题目:
https://leetcode.com/problems/combination-sum-iv/
https://leetcode.com/problems/partition-equal-subset-sum/
https://leetcode.com/problems/palindromic-substrings/
https://leetcode.com/problems/number-of-longest-increasing-subsequence/
https://leetcode.com/problems/partition-to-k-equal-sum-subsets/
https://leetcode.com/problems/counting-bits/
https://leetcode.com/problems/longest-palindromic-substring/
https://leetcode.com/problems/maximum-subarray/
https://leetcode.com/problems/jump-game/
https://leetcode.com/problems/unique-paths/
https://leetcode.com/problems/climbing-stairs/
https://leetcode.com/problems/decode-ways/
https://leetcode.com/problems/best-time-to-buy-and-sell-stock/
https://leetcode.com/problems/word-break/
https://leetcode.com/problems/maximum-product-subarray/
https://leetcode.com/problems/house-robber/
https://leetcode.com/problems/house-robber-ii/
https://leetcode.com/problems/longest-increasing-subsequence/
https://leetcode.com/problems/range-sum-query-immutable/
https://leetcode.com/problems/best-time-to-buy-and-sell-stock-with-cooldown/
https://leetcode.com/problems/coin-change/
15. Pattern: Topological Sort (Graph),拓扑排序类型
拓扑排序模式用来寻找一种线性的顺序,这些元素之间具有依懒性。比如,如果事件B依赖于事件A,那A在拓扑排序顺序中排在B的前面。
这种模式定义了一种简单方式来理解拓扑排序这种技术。
这种模式是这样奏效的:
- 初始化
a) 借助于HashMap将图保存成邻接表形式。
b) 找到所有的起点,用HashMap来帮助记录每个节点的入度 - 创建图,找到每个节点的入度
a) 利用输入,把图建好,然后遍历一下图,将入度信息记录在HashMap中 - 找所有的起点
a) 所有入度为0的节点,都是有效的起点,而且我们讲他们都加入到一个队列中 - 排序
a) 对每个起点,执行以下步骤
—i) 把它加到结果的顺序中
— ii)将其在图中的孩子节点取到
— iii)将其孩子的入度减少1
— iv)如果孩子的入度变为0,则改孩子节点成为起点,将其加入队列中
b) 重复(a)过程,直到起点队列为空。

拓扑排序模式识别:
- 待解决的问题需要处理无环图
- 你需要以一种有序的秩序更新输入元素
- 需要处理的输入遵循某种特定的顺序
经典题目列表:
https://leetcode.com/list/5ve54wz1
列表包含题目:
https://leetcode.com/problems/course-schedule/
https://leetcode.com/problems/course-schedule-ii/
https://leetcode.com/problems/minimum-height-trees/
编辑于 01-06