leetcode
二叉树
从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树 迭代解法(官方实现)
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* buildTree(vector<int>& preorder, vector<int>& inorder) {
if (!preorder.size()) {
return nullptr;
}
TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(preorder[0]);
stack<TreeNode*> stk;
stk.push(root);
int inorderIndex = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < preorder.size(); ++i) {
int preorderVal = preorder[i];
TreeNode* node = stk.top();
if (node->val != inorder[inorderIndex]) {
node->left = new TreeNode(preorderVal);
stk.push(node->left);
}
else {
while (!stk.empty() && stk.top()->val == inorder[inorderIndex]) {
node = stk.top();
stk.pop();
++inorderIndex;
}
node->right = new TreeNode(preorderVal);
stk.push(node->right);
}
}
return root;
}
};
验证二叉搜索树
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
bool isValidBST(TreeNode* root) {
if (root==NULL){
return true;
}
stack<TreeNode*> st;
TreeNode* cur=root;
TreeNode* pre=NULL;
TreeNode* tmp=NULL;
st.push(root);
while (cur->left){
st.push(cur->left);
cur=cur->left;
}
while (!st.empty()){
cur=st.top();
st.pop();
if (pre!=NULL){
if (pre->val >= cur->val){
return false;
}
}
if(cur->right){
st.push(cur->right);
tmp=cur->right;
while (tmp->left){
st.push(tmp->left);
tmp=tmp->left;
}
if (tmp->val <= cur->val ){
return false;
}
pre=NULL;
continue;
}
pre=cur;
}
return true;
}
};
二叉搜索树中的插入操作
注意当插入值大于所有树节点的情况
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* insertIntoBST(TreeNode* root, int val) {
if (root==NULL){
TreeNode* new_node= new TreeNode(val);
return new_node;
}
stack<TreeNode*> st;
TreeNode* cur=root;
TreeNode* pre=NULL;
TreeNode* tmp=NULL;
st.push(root);
while (cur->left){
st.push(cur->left);
cur=cur->left;
}
while (!st.empty()){
cur=st.top();
st.pop();
if (pre==NULL){
if (val < cur->val){
TreeNode* new_node= new TreeNode(val);
cur->left=new_node;
return root;
}
}
else{
if (cur->left == pre){
if (val > pre->val && val < cur->val){
TreeNode* new_node= new TreeNode(val,pre,NULL);
cur->left=new_node;
return root;
}
}
else{
if (pre->right){
if (val > pre->val && val < cur->val){
TreeNode* new_node= new TreeNode(val);
cur->left=new_node;
return root;
}
}
else{
if (val > pre->val && val < cur->val){
TreeNode* new_node= new TreeNode(val);
pre->right=new_node;
return root;
}
}
}
}
if(cur->right){
st.push(cur->right);
tmp=cur->right;
while (tmp->left){
st.push(tmp->left);
tmp=tmp->left;
}
}
pre=cur;
}
TreeNode* new_node= new TreeNode(val);
cur->right=new_node;
return root;
}
};
链表
链表排序 (要求时间复杂度为 n l o g 2 n nlog_2n nlog2n)
leetcode 148.
冒泡 (超时)
public:
ListNode* sortList(ListNode* head) {
ListNode* end=NULL;
ListNode* cur=NULL;
ListNode* tmp=NULL;
ListNode* pre=NULL;
ListNode* next=NULL;
ListNode* fake1= new ListNode(0);
ListNode* fake2= new ListNode(0);
fake1->next=head;
while(fake1->next != NULL){
cur=fake1->next;
pre=fake1;
while(1){
next=cur->next;
if (next==NULL){
cur->next=end;
end=cur;
fake2->next=cur;
pre->next=NULL;
break;
}
else{
if (cur->val > next->val ){
pre->next=next;
tmp=next->next;
next->next=cur;
cur->next=tmp;
pre=next;
}else{
pre=cur;
cur=cur->next;
}
}
}
}
return fake2->next;
}
};
归并
可以用快慢链表找到中点
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* sortList(ListNode* head, int len=-1) {
ListNode* cur;
ListNode* tmp;
ListNode* new_head;
if (head==NULL){
return NULL;
}
if (len==-1){
cur=head;
len=1;
while(1) {
cur=cur->next;
if (cur==NULL){
break;
}else{
len+=1;
}
}
}
if(len==1){
return head;
}else{
cur=head;
int i=1;
int mid=round((float)len/(float)2);
while(cur!=NULL){
if(i==mid){
tmp=cur->next;
cur->next=NULL;
new_head=merge(sortList(head,i),sortList(tmp,len-i));
break;
}else{
cur=cur->next;
i+=1;
}
}
}
return new_head;
}
ListNode* merge(ListNode* a, ListNode* b){
ListNode* new_head=new ListNode(0);
ListNode* cur=new_head;
while (1){
if (a==NULL || b==NULL){
break;
}
if(a->val < b->val){
cur->next=a;
cur=a;
a=a->next;
}else{
cur->next=b;
cur=b;
b=b->next;
}
}
if (a!=NULL){
while(1){
if(a==NULL){
break;
}
cur->next=a;
cur=a;
a=a->next;
}
}else{
while(1){
if(b==NULL){
break;
}
cur->next=b;
cur=b;
b=b->next;
}
}
return new_head->next;
}
};
归并(非递归,效率待改进)
注意: 按照interval 划分之后,剩余的不足interval的部分,如果长度小于interval/2,说明这部分已经排好序;如果长度超过interval/2,则把这部分划分成interval/2 + x, 两部分合并排序。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* sortList(ListNode* head) {
if (!head){
return head;
}
ListNode* cur;
int len;
ListNode* next;
ListNode* tmp;
ListNode* pre;
ListNode* new_cur;
ListNode* new_start;
ListNode* new_end;
ListNode* slow;
ListNode* fast;
ListNode* fake=new ListNode(0);
int interval;
fake->next=head;
cur=head;
len=1;
while(1) {
cur=cur->next;
if (cur==NULL){
break;
}else{
len+=1;
}
}
for (interval=2; interval<=len; interval=interval*2){
cur=fake->next;
pre=fake;
while(cur){
// cout<<cur->val;
cur=cur->next;
}
// cout<<endl;
cur=fake->next;
while (true){
slow=cur;
fast=cur;
int i=0;
int j=0;
while (true){
if(fast->next&& fast->next->next && i+2<interval){
fast=fast->next->next;
slow=slow->next;
i+=2;
j+=1;
}else{
if (fast->next && i+1 < interval){
fast=fast->next;
// cout<<"shift one"<<endl;
i+=1;
}
// cout<<"slow"<<slow->val<<"fast"<<fast->val<<endl;
break;
}
}
if(i!=interval-1){
if (i> (interval/2-1)){
while (j< (interval/2-1)){
slow=slow->next;
j=j+1;
}
}else{
tmp=NULL;
break;
}
}
tmp=slow->next;
slow->next=NULL;
next=fast->next;
fast->next=NULL;
// if (cur && tmp ){
// cout<<"left"<<cur->val<<"right"<<tmp->val<<endl;
// }
if (cur && tmp){
merge(cur,tmp,new_start,new_end);
// cout<<"merge"<<"new_start"<<new_start->val<<"end"<<new_end->val<<endl;
pre->next=new_start;
new_end->next=next;
}
if(i== (interval-1) && next ){
cur=next;
// cout<<"next"<<next->val<<endl;
pre=new_end;
}else{
// cout<<"break"<<endl;
break;
}
}
}
interval=interval/2;
if (interval!=len){
// cout<<"pre"<<pre->val<<"cur"<<cur->val<<endl;
if(tmp){
// cout<<"tmp";
pre->next=NULL;
merge(fake->next,new_start,new_start,new_end);
fake->next=new_start;
}else{
pre->next=NULL;
merge(fake->next,cur,new_start,new_end);
fake->next=new_start;
}
}
return fake->next;
}
void merge(ListNode* a, ListNode* b, ListNode* &new_start,ListNode* &new_end){
ListNode* A;
ListNode* B;
A=a;
B=b;
// cout<<"a";
while(A){
if(A){
// cout<<A->val;
A=A->next;
}
}
cout<<"b";
while(B){
if(B){
// cout<<B->val;
B=B->next;
}
}
cout<<endl;
ListNode* new_head=new ListNode(0);
ListNode* cur=new_head;
while (1){
if (a==NULL || b==NULL){
break;
}
if(a->val < b->val){
cur->next=a;
cur=a;
a=a->next;
}else{
cur->next=b;
cur=b;
b=b->next;
}
}
if (a!=NULL){
while(1){
cur->next=a;
cur=a;
if(a->next == NULL){
new_end=a;
break;
}else{
a=a->next;
}
}
}else{
while(1){
cur->next=b;
cur=b;
if(b->next == NULL){
new_end=b;
break;
}else{
b=b->next;
}
}
}
new_start=new_head->next;
}
};
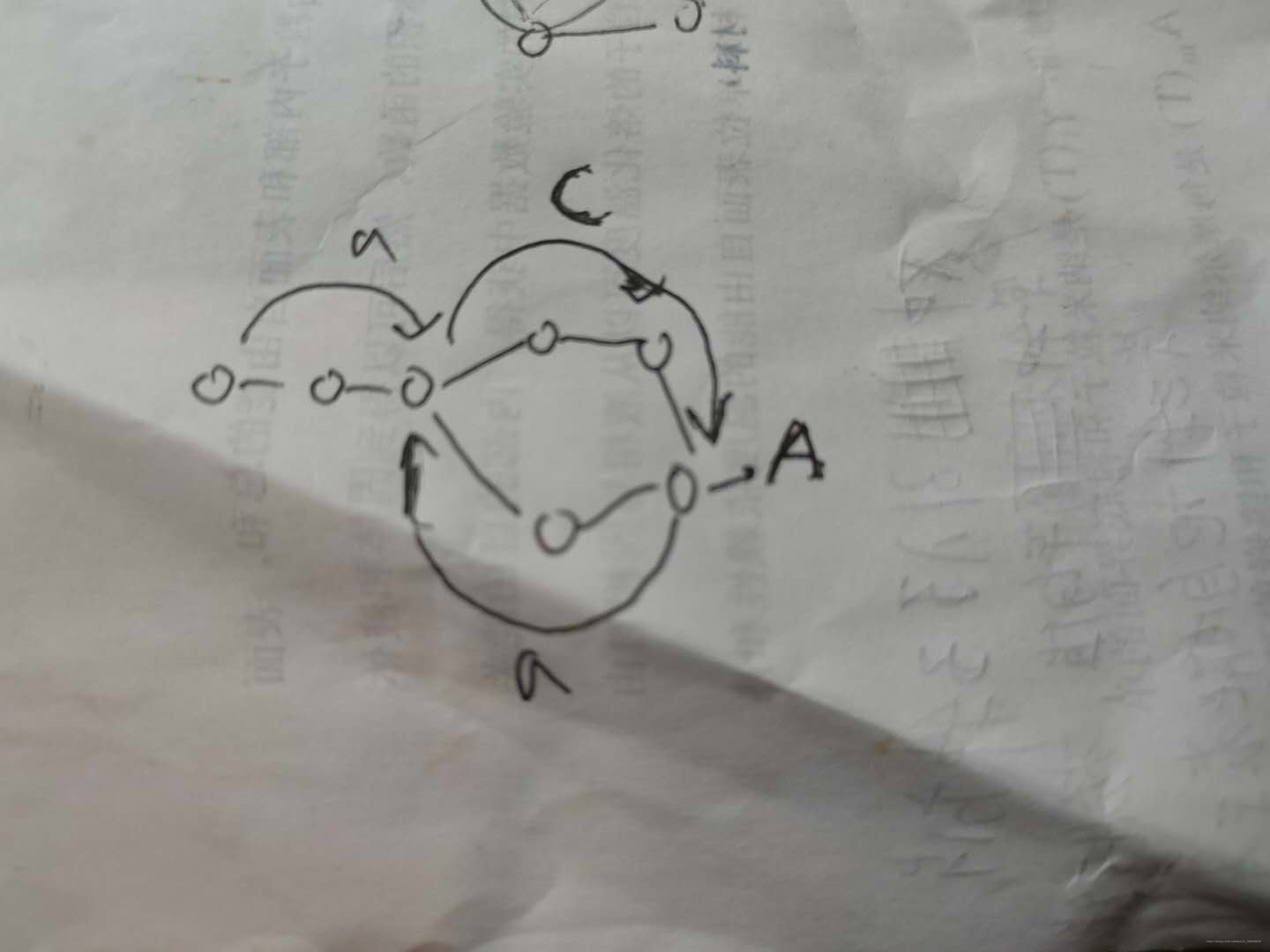
环形链表 II
给定一个链表,返回链表开始入环的第一个节点。 如果链表无环,则返回 null
思路: A是第一次相遇的节点。之后令slow=head, fast=A 且两者的步长都为1,则相遇点为入环点。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode *detectCycle(ListNode *head) {
if (!head){
return NULL;
}
ListNode* slow;
ListNode* fast;
ListNode* A;
slow=head;
fast=head;
while(true){
if (fast->next && fast->next->next){
fast=fast->next->next;
slow=slow->next;
if (fast==slow){
A=fast;
break;
}
}
else{
return NULL;
}
}
slow=head;
fast=A;
while(true){
if (slow==fast){
return slow;
}
slow=slow->next;
fast=fast->next;
}
}
};
栈和队列
设计一个支持 push ,pop ,top 操作,并能在常数时间内检索到最小元素的栈。
思路:辅助栈 记录当前最小元素
class MinStack {
public:
/** initialize your data structure here. */
stack<int> stack_a;
stack<int> stack_b;
MinStack() {
stack_a.push(2147483647);
stack_b.push(2147483647);
}
void push(int x) {
stack_a.push(x);
int m=stack_b.top();
if (x<m){
stack_b.push(x);
}else{
stack_b.push(m);
}
}
void pop() {
stack_a.pop();
stack_b.pop();
}
int top() {
return stack_a.top();
}
int getMin() {
return stack_b.top();
}
};
/**
* Your MinStack object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MinStack* obj = new MinStack();
* obj->push(x);
* obj->pop();
* int param_3 = obj->top();
* int param_4 = obj->getMin();
*/
逆波兰表达式求值
根据 逆波兰表示法,求表达式的值。
有效的运算符包括 +, -, *, / 。每个运算对象可以是整数,也可以是另一个逆波兰表达式。
class Solution {
public:
int evalRPN(vector<string>& tokens) {
stack<int> st;
int a;
int b;
for(auto i = tokens.begin(); i != tokens.end (); ++i){
auto s=*i;
stringstream sin(s);
int tmp;
if (sin>>tmp){
st.push(tmp);
}else{
switch(s.c_str()[0]){
case '+':
b=st.top();
st.pop();
a=st.top();
st.pop();
tmp=a+b;
st.push(tmp);
break;
case '-':
b=st.top();
st.pop();
a=st.top();
st.pop();
tmp=a-b;
st.push(tmp);
break;
case '*':
b=st.top();
st.pop();
a=st.top();
st.pop();
tmp=a*b;
st.push(tmp);
break;
case '/':
b=st.top();
st.pop();
a=st.top();
st.pop();
tmp=a/b;
st.push(tmp);
break;
}
}
}
return st.top();
}
};
根据一般表达式生成逆波兰表达式
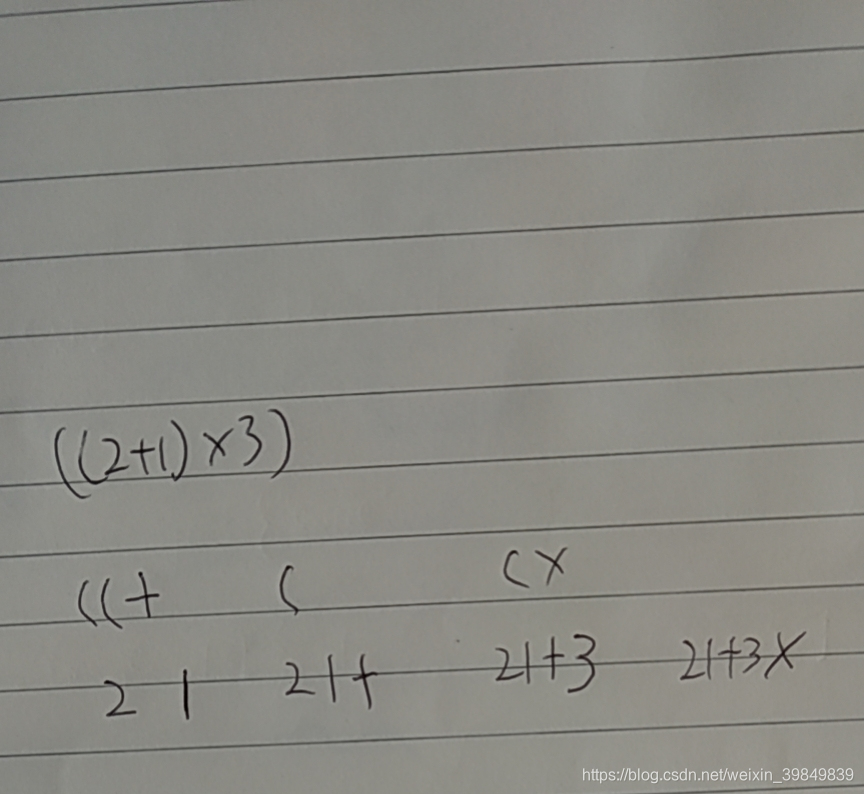
字符串解码
输入:s = “3[a2[c]]”
输出:“accaccacc”
思路:总共有三个栈,times用来记录复制的倍数,digits用来记录字母,而priors用来记录字母相对应优先级;
每一次复制时把优先级相同的字母拼接起来作为要复制的单元。
利用stringstream进行倍数的提取和识别。
class Solution {
public:
string decodeString(string s) {
stack<int> times;
stack<string> digits;
stack<int> priors;
int prior=0;
int tmp_prior;
string cur;
int time;
stringstream global_sin;
for (int i = 0; i < s.size(); i++){
cur=string(1,s[i]);
stringstream sin(cur);
if(sin>>time){
// times.push(time);
// prior=prior+1;
global_sin<<cur;
continue;
}else if (s[i]=='['){
// cout<<"[ "<<cur<<endl;
global_sin>>time;
global_sin.clear();
times.push(time);
prior=prior+1;
continue;
}
else if(s[i]!=']'){
// cout<<"digit "<<cur<<endl;
digits.push(cur);
priors.push(prior);
continue;
}else {
// cout<<"] "<<cur<<endl;
time=times.top();
times.pop();
string tmp_result=string();
string result=string();
while(!digits.empty()){
cur=digits.top();
tmp_prior=priors.top();
if (tmp_prior==prior){
// cout<<"prior"<<prior<<endl;
tmp_result.insert(0,cur);
// cout<<"append"<<cur<<endl;
digits.pop();
priors.pop();
// cout<<"pop"<<endl;
// cout<<"tmp_result"<<tmp_result<<endl;
}else{
// cout<<"break"<<endl;
break;
}
}
cout<<"tmp_result"<<tmp_result<<endl;
for (int j=0; j<time; j++){
result.append(string(tmp_result));
}
digits.push(result);
prior=prior-1;
priors.push(prior);
}
}
string final_result=string();
while(!digits.empty()){
final_result.insert(0,digits.top());
digits.pop();
}
return final_result;
}
};
岛屿数量
给你一个由 ‘1’(陆地)和 ‘0’(水)组成的的二维网格,请你计算网格中岛屿的数量。岛屿总是被水包围,并且每座岛屿只能由水平方向或竖直方向上相邻的陆地连接形成。此外,你可以假设该网格的四条边均被水包围。
注意: 可以直接用grid记录节点是否被访问,节点入栈之后把其在grid中的值马上设为‘0’。
class Solution {
public:
int numIslands(vector<vector<char>>& grid) {
if (grid.empty()){
return 0;
}
int countRow=grid.size();
int countCol=grid[0].size();
int count=0;
queue<pair<int,int>> que;
// vector<vector<int> > indicator(countRow,vector<int>(countCol,0));
for (int r=0; r<countRow; r++){
for (int c=0; c<countCol; c++){
if (grid[r][c]== '1'){
que.push({
r, c});
grid[r][c]='0';
while(!que.empty()){
auto tmp=que.front();
que.pop();
int r_t=tmp.first;
int c_t=tmp.second;
// indicator[r_t][c_t]=1;
if ( r_t>0 && grid[r_t-1][c_t]=='1'){
que.push({
r_t-1, c_t});
grid[r_t-1][c_t]='0';
}
if ( r_t < countRow-1 && grid[r_t+1][c_t]=='1'){
que.push({
r_t+1, c_t});
grid[r_t+1][c_t]='0';
}
if ( c_t > 0 && grid[r_t][c_t-1]=='1'){
que.push({
r_t, c_t-1});
grid[r_t][c_t-1]='0';
}
if ( c_t < countCol-1 && grid[r_t][c_t+1]=='1'){
que.push({
r_t, c_t+1});
grid[r_t][c_t+1]='0';
}
}
count+=1;
}
}
}
return count;
}
};
柱状图中最大的矩形
给定 n 个非负整数,用来表示柱状图中各个柱子的高度。每个柱子彼此相邻,且宽度为 1 。求在该柱状图中,能够勾勒出来的矩形的最大面积。
思路:前向和后向两个单调栈。如果当前高度大于栈顶高度,则入栈。,否则不断弹出直到当前高度大于栈顶高度。
class Solution {
public:
int largestRectangleArea(vector<int>& heights) {
vector<int> forward;
vector<int> backward;
stack<pair<int,int>> st;
st.push(make_pair(INT_MIN,-1));
int len=heights.size();
forward.resize(len,-1);
backward.resize(len,len);
int cur;
int top;
int pos;
int result=0;
for(int i=0;i<len;i++){
cur=heights[i];
while(true){
top=st.top().first;
pos=st.top().second;
if (cur>top){
forward[i]=pos;
st.push(make_pair(cur,i));
break;
}else{
st.pop();
}
}
}
st.pop();
st.push(make_pair(INT_MIN,len));
for(int i=len-1;i>=0;i--){
cur=heights[i];
while(true){
top=st.top().first;
pos=st.top().second;
if (cur>top){
backward[i]=pos;
st.push(make_pair(cur,i));
break;
}else{
st.pop();
}
}
}
for(int k=0;k<len;k++){
int tmp=heights[k]*(backward[k]-forward[k]-1);
if (tmp>result){
result=tmp;
}
}
return result;
}
};
矩阵
给定一个由 0 和 1 组成的矩阵,找出每个元素到最近的 0 的距离。两个相邻元素间的距离为 1 。
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> updateMatrix(vector<vector<int>>& matrix) {
int row=matrix.size();
int col=matrix[0].size();
int cur_len=0;
int tmp_len=0;
int dis=1;
vector<vector<int> > result(row,vector<int>(col,-1));
queue<pair<int,int>> que;
for(int i=0;i<row;i++){
for(int j=0;j<col;j++){
if (matrix[i][j]==0){
que.push(make_pair(i,j));
result[i][j]=0;
cur_len+=1;
}
}
}
while(!que.empty()){
auto cur=que.front();
auto cur_row=cur.first;
auto cur_col=cur.second;
// cout<<"cur"<<"row"<<cur_row<<"col"<<cur_col<<endl;
que.pop();
if (cur_row>0 && result[cur_row-1][cur_col]==-1){
que.push(make_pair(cur_row-1,cur_col));
// cout<<"row"<<cur_row-1<<"col"<<cur_col<<endl;
result[cur_row-1][cur_col]=dis;
tmp_len+=1;
}
if(cur_row<row-1 && result[cur_row+1][cur_col]==-1){
que.push(make_pair(cur_row+1,cur_col));
// cout<<"row"<<cur_row+1<<"col"<<cur_col<<endl;
result[cur_row+1][cur_col]=dis;
tmp_len+=1;
}
if(cur_col>0 && result[cur_row][cur_col-1]==-1){
que.push(make_pair(cur_row,cur_col-1));
// cout<<"row"<<cur_row<<"col"<<cur_col-1<<endl;
result[cur_row][cur_col-1]=dis;
tmp_len+=1;
}
if(cur_col<col-1 && result[cur_row][cur_col+1]==-1){
que.push(make_pair(cur_row,cur_col+1));
// cout<<"row"<<cur_row<<"col"<<cur_col+1<<endl;
result[cur_row][cur_col+1]=dis;
tmp_len+=1;
}
cur_len-=1;
if(cur_len==0){
cur_len=tmp_len;
tmp_len=0;
dis+=1;
}
}
return result;
}
};