目录
分类
行布局
多列布局
圣杯布局
双飞翼布局
行布局
<!doctype html>
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content" content="text/html" charset="utf-8"/>
<style>
body{
margin:0;padding:0;color:#fff;text-align:center;
}
.header{
width:800px;height:50px;background:#333;margin:0 auto;
line-height:50px;position:fixed;
}
.banner{
width:800px;height:300px;background:#30a457;margin:0 auto;
padding-top:50px;
}
.container{
width:800px;height:1000px;background:#39F;
margin:0 auto;
}
.foot{
width:800px;height:300px;background:#9C3;
margin:0 auto;line-height:100px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="header">这是页面的头部</div>
<div class="banner">这是页面的banner图</div>
<div class="container">这是页面内容</div>
<div class="foot">这是页面尾部</div>
</body>
</html>
展示:

列布局
两列布局
<!document html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8"/>
<title>css演示</title>
<style type="text/css">
body{
margin:0;padding:0;color:#fff;
}
.pre{
width:90%;height:1000px;margin:0 auto;
}
.left{
width:60%;height:1000px;background:#0F0;float:left;
}
.right{
width:40%;height:1000px;background:#969;float:right;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="pre">
<div class="left">这是页面的左侧</div>
<div class="right">这是页面右侧</div>
</div>
</body>
<html>
展示

三列布局
<!document html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8"/>
<title>css演示</title>
<style type="text/css">
body{
margin:0;padding:0;color:#fff;
}
.pre{
width:100%;height:1000px;margin:0 auto;
}
.left{
width:30%;height:1000px;background:#0F0;float:left;
}
.middle{
width:20%;height:1000px;background:#F6C;float:right;
}
.right{
width:50%;height:1000px;background:#969;float:left;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="pre">
<div class="left">这是页面的左侧</div>
<div class="middle">这是页面中间</div>
<div class="right">这是页面右侧</div>
</div>
</body>
<html>
展示:

混合布局
将上述两种布局混合使用
圣杯布局

并且,中间栏要在浏览器中优先展示渲染
允许任意列的高度最高
<!document html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8"/>
<title>css演示</title>
<style type="text/css">
*{
margin:0;padding:0;
}
body{
min-width:700px;color:#fff;
}
.pre{
width:100%;margin:0 auto;
padding:0 220px 0 200px;
}
.header,.foot{
float:left;
width:100%;
background:#ddd;
height:40px;
line-height:40px;
text-align:center;
}
.left{
width:200px;background:#0F0;
margin-left:-100%;left:-200px;
}
.middle{
width:100%;background:#F6C;
}
.right{
width:200px;background:#969;
margin-left:-220px;right:-220px;
}
.right,.middle,.left{
position:relative;
float:left;
min-height:300px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="header">
<h4>header</h4>
</div>
<div class="pre">
<div class="middle">
<h4>middle</h4>
<p>这是页面中间这是页面中间这是页面中间这是页面中间这是页面中间这是页面中间这是页面中间这是页面中间这是页面中间这是页面中间这是页面中间这是页面中间这是页面中间
</div>
<div class="left">
<h4>left</h4>
<p>这是页面的左侧
</div>
<div class="right">
<h4>right</h4>
<p>这是页面右侧
</div>
</div>
<div class="foot">
<h4>这是页面尾部</h4>
</div>
</body>
<html>
展示:

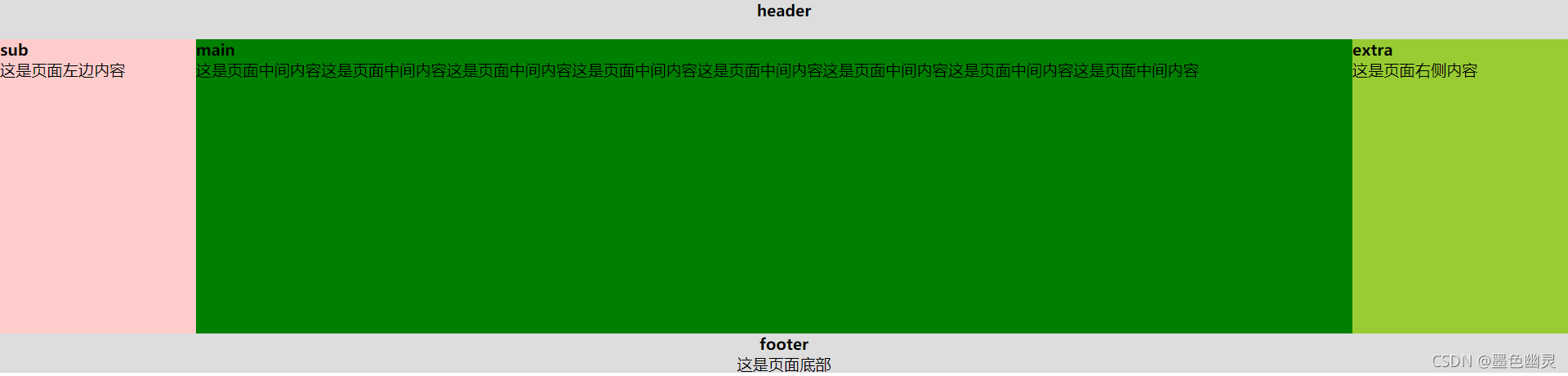
双飞翼布局
<!document html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8"/>
<title>css演示</title>
<style type="text/css">
*{
margin:0;padding:0;
}
.body{
min-width:700px;
}
.header,.footer{
height:40px;
width:100%;
background:#ddd;
text-align:center;
float:left;
}
.sub,.main,.extra{
float:left;
min-height:300px;
}
.main{
width:100%;
}
.main-inner{
margin-left:200px;margin-right:220px;
background:green;
min-height:300px;
}
.sub{
width:200px;
background:#FCC;
margin-left:-100%;
}
.extra{
width:220px;
background:#9C3;
margin-left:-220px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="header">
<h4>header</h4>
</div>
<div class="main">
<div class="main-inner">
<h4>main</h4>
<p>这是页面中间内容这是页面中间内容这是页面中间内容这是页面中间内容这是页面中间内容这是页面中间内容这是页面中间内容这是页面中间内容</p>
</div>
</div>
<div class="sub">
<h4>sub</h4>
<p>这是页面左边内容</p>
</div>
<div class="extra">
<h4>extra</h4>
<p>这是页面右侧内容</p>
</div>
<div class="footer">
<h4>footer</h4>
<p>这是页面底部</p>
</div>
</body>
<html>
展示:
javaScript基础
组成
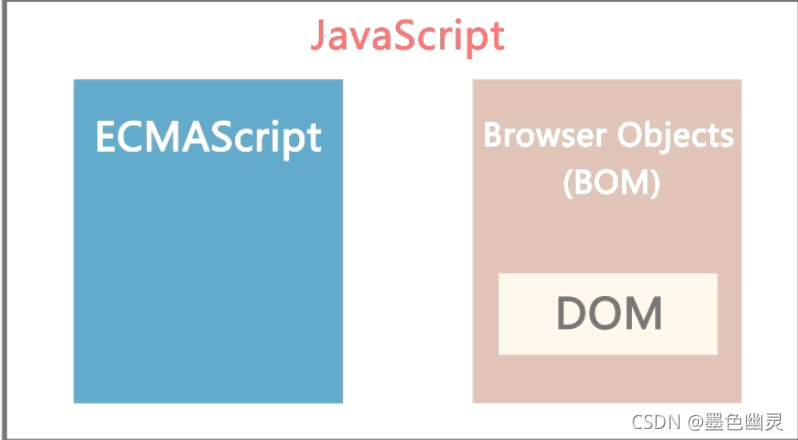
ECMAScript:语法
Brower Objects(DOM、BOM):特性
基础
注释:// /**/
区分大小写,分号结束
标识符:变量、函数、属性的名字,或函数参数
变量为松散类型:可以用来保存任何类型的数据
变量声明
<!document html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8"/>
<title>css演示</title>
<style type="text/css">
<script>
//声明用户名变量
var name = "张飞";
//声明多个变量
var id = "10086",age = 18;
</script>
</style>
</body>
<html>
说明:省略var声明的变量为全局变量(不推荐使用)
操作符
逻辑操作符
<!document html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8"/>
<title>js演示</title>
</head>
<body>
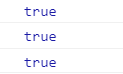
<script>
var num1 = 12,
num2 = 13,
num3 = 45,
num4 = 45;
console.log(num1 < num2);
console.log(num1 < num2 && num3 == num4);
console.log(num1 < num2 || num3 > num4);
</script>
</body>
</html>
结果(在浏览器控制台)
注意:
有一个操作数不是布尔类型,逻辑与操作就不一定返回值:
如果第一个操作数隐式类型转换后为true,则返回第二个操作数
如果第一个操作数隐式类型转换后为false,则返回第一个操作数
<script>
var num1 = 12,
n = null,
m;
console.log(n && 3); //返回null
console.log(22*"abc" && 3) //返回NAN
console.log(m && true); //undefined
</script>
逻辑或
说明:在有一个操作数不是布尔值的情况,逻辑或操作就不一定返回值,此时遵循以下规则
如果第一个操作数隐式类型转换后为true,则返回第一个操作数
如果第一个操作数隐式类型转换后为false,则返回第二个操作数
如果两个操作数是null,返回null
如果两个操作数是NaN,返回NaN
如果两个操作数是undefined,则返回undefined
<script>
console.log('' || 88 || true);// 88
console.log('' || 0 || "abc"); // abc
console.log('' || 0 || false); // false
console.log('' || 0 || true); // true
</script>
逻辑非
只返回true或false
<script>
console.log(!0);//true
console.log(!99);//false
console.log(!null);//true
</script>
js数据类型
检测数据类型:
typeof
<script>
console.log(typeof(18));//number
console.log(typeof("abc"));//string
console.log(typeof(null));//object
console.log(typeof(undefined));//undefined
console.log(typeof(NaN));//number
console.log(typeof(true));//boolean
</script>
Number
表示整数和浮点数
NaN:即非数值(Not A Number),是一个特殊的数值,任何涉及NaN的操作,返回都是NaN,NaN与任何值都不相等,包括NaN本身
isNaN(n)
用于检测n是否是非数值
console.log(isNaN("abc"));//true
console.log(isNaN(15));//false
注意:isNaN()在接收到一个值,先尝试转换为数值,再做运算
如:
console.log(isNaN("12"));//false
类型转换:Number(),parseInt(),parseFloat()
Number()可以用于任何数据类型
parseInt()和parseFloat()则专门用于把字符串转换成数据
console.log(typeof Number("21"));//Number 将字符串转成了Number类型
console.log(Number("marry"));//NsN
console.log(parseInt("321"));//321
console.log(parseInt("44"));//44
console.log(typeof parseInt("7665"));//number
console.log(parseInt("78.890"));//78
console.log(parseFloat("655.455"));//655.455
parseInt()会忽略字符串前面的空格,直至找到第一个非空格字符
parseInt()转换空字符串返回NaN
parseInt()这个函数提供第二个参数:转换时使用的基数(多少进制)
console.log(parseInt("56px"));//56
console.log(parseInt("0xf"))//15
console.log(parseInt("0xf",16));//15 意义同上
parseFloat:从第一个字符开始解析每一个字符,直至遇见一个无效的浮点数字符为止
除了第一个小数点有效外,parseFloat()与parseInt()第二个区别在于它始终都会忽略前导的零
string
字符串
//转换方法
console.log(String(NaN));
console.log("ab".toString());
boolean
布尔类型,true和fals
除0之外的数字,转换为布尔型都为true
除“”之外的所有字符,转换为布尔型都为true
null和undefined转换为布尔型为false
console.log(Boolean(0));//false
console.log(Boolean("as "));//true
console.log(Boolean(null));//false
console.log(Boolean(NaN));//false
表达式,操作符
将同类型的数据(常量、变量、函数等)用运算符号按一定规则连接起来的有意义的式子称为表达式
算数操作符
+ - * / %
递增
a++ , ++a , a-- ,–a
赋值操作符
=, +=, -= ,*= ,/=
var n = "hello";
n += "world";
console.log(n);//helloworld
比较操作符
>, < ,>=, <= ,==, === ,!= ,!===
==:相等,只比较值是否相等
===:相等,比较值的同时比较数据烈性是否相等
!=:比较值是否不相等
!===:不相等,比较值的同时比较数据类型是否不相等
var x = '10',
y = 10;
console.log(x == y);//true
console.log(x === y);//false
console.log(x != y);//false
console.log(x !== y);//true
三元操作符

条件语句
if语句
用法与java大致相同
<!document html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8"/>
<title>js演示</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
var x = 10;
if(x < 19){
alert("您还没有成年.");
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
结果:

alert() 函数:网页中出现警报窗口
prompt() : 弹出输入框
<!document html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8"/>
<title>js演示</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
var age = prompt("请输入您的年龄");
console.log(age);
if(age < 18){
alert("您还未成年");
}else{
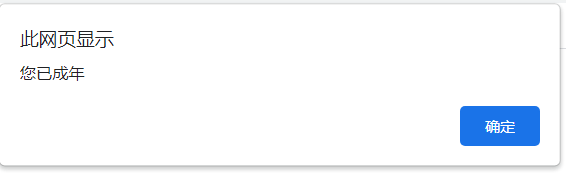
alert("您已成年");
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
展示:

switch语句
获取星期:new Date.getDay(),返回0-6(0为星期天)
向浏览器输出内容 :document.write(“内容”)
var day = new Date().getDay();
switch(day){
case 0:
document.write("今天是星期日")
break;
case 1:
document.write("星期一");
break;
case 2:
document.write("星期二");
break;
default:
document.write("其它");
break;
}
结果:
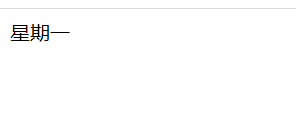
for循环
for(var i = 0;i < 5;i++){
document.write(i + "<br>");
}
结果:

do while() while
同java,不列
break continue
同java,不列
函数

<!document html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8"/>
<title>js演示</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
//函数的声明
function myFun(name){
alert(name);
}
myFun("张飞");
</script>
>
</body>
</html>
结果:

arguments
ECMAScript中的参数在内部用一个数组来表示
在函数体内通过arguments对象来访问这个数组参数
arguments对象只是与数组类似,并不是数组实例
[]语法访问每一个元素
length属性确定传递参数的个数
<script>
//函数的声明
function myFun(){
console.log(arguments.length);
console.log(arguments[0]);
}
myFun("张飞","cck");
</script>
结果:

数组
<!document html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8"/>
<title>js演示</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
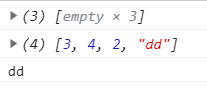
var nums = new Array(3);
console.log(nums);
var nums2 = new Array(3,4,2,"dd");
console.log(nums2);
console.log(nums2[3]);
</script>
</body>
</html>
结果:
数组长度
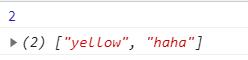
var array = [2,"yellow","haha"];
console.log(array.length);//3
数组的栈方法
push()
把它的参数顺序添加到arrayObject的尾部分
返回值:把指定的值添加到数组后的新长度
<script>
var array = [2,"yellow","haha"];
array.push("newObject");
console.log(array);
array.push("newOne","newTwo");//可以添加多个
console.log(array);
</script>
结果:

unshift()
将元素加到前面
var array = [2,"yellow","haha"];
array.unshift("newObject");
console.log(array);
结果:

shift()
删除第一个元素,返回被删除的元素
<script>
var array = [2,"yellow","haha"];
console.log(array.shift());
console.log(array);
</script>
结果:
pop()
删除末尾
var array = [2,"yellow","haha"];
console.log(array.pop());
console.log(array);
结果:
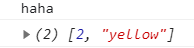
数组的转换
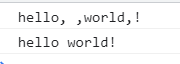
join()
var test = ['hello',' ','world','!'];
console.log(test.join());//会有逗号隔开
console.log(test.join(""));
结果
reverse()
反转数组
<script>
var nums = [1,2,3,4,5];
console.log(nums.reverse());
</script>
结果:

sort()
排序
<!document html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8"/>
<title>js演示</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
var nums = [1,54,23,211,512,9,43];
console.log(nums.sort());
/* 降序排列 */
console.log(nums.sort(function(a,b) {
return b-a;}));
/* 升序排列 */
console.log(nums.sort(function(a,b) {
return a-b;}));
</script>
</body>
</html>
结果:

concat()
用于连接两个或多个数组
<!document html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8"/>
<title>js演示</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
var nums = [1,54,23];
var nums2 = [3,32,1];
var nums3 = [5,56,54];
var nums4;
nums4 = nums.concat(nums2,nums3);
console.log(nums4);
</script>
</body>
</html>
结果

slice()从已有的数组返回选定的元素
参数:
start:起始位置(必需)
end:结束位置(可选)
如没指定end,则截取到结束
如slice()方法中有一个负数,则用数组长度加上该数确定相应位置
<script>
var nums = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9];
var test = nums.slice(0,4);
console.log(test);
</script>
结果:

splice()
删除,插入,替换
splice(index,count)
删除从index开始的若干个值
count是要删除的项目数,如果为0,则不删除,不设置则删除index开始的所有值
<script>
var nums = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9];
var test = nums.splice(0,4);
console.log(nums);
</script>
结果:

插入
splice(index,0,item1,…)
<script>
var nums = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9];
var test = nums.splice(1,0,"m","n");
console.log(nums);
</script>
结果

替换
splice(index,count,item1,…)
<script>
var nums = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9];
var test = nums.splice(1,2,"m","n");
console.log(nums);
</script>
结果:

查找
indexOf()
<script>
var nums = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9];
var r = nums.indexOf(4,0)//从第0位置开始找,找不到返回-1
console.log(r);
</script>
结果为3,即第三个位置
lastIndexOf()
从末尾开始查找
<script>
var nums = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9];
var r = nums.lastIndexOf(4)//从第0位置开始找,找不到返回-1
console.log(r);
</script>
结果同上
String
查找方法
charAt()
<script>
var nums = "helloworld";
console.log(nums[1]);//e
console.log(nums.charAt(1));//e
</script>
indexOf()/lastIndexOf()
<script>
var nums = "helloworld";
console.log(nums.indexOf('l'));//2
console.log(nums.lastIndexOf('l'));//8 从结尾开始读取,取最后一位
</script>
截取方法
slice()
<script>
var nums = "helloworld";
console.log(nums.slice(0,5));//hello
</script>
subString()
用法跟slice()一样,区别在于,参数为负数时,自动转为0
substr(start,len)
截取子字符串
start:必需,指定字符串开始位置
len:表示截取的字符总数
start为负,将此值与字符串的长度相加
当len为负,返回空字符串
<script>
var nums = "helloworld";
console.log(nums.substr(2,3));//llo
</script>
分割
split(separator)
separator:分隔符
把一个字符串分割成字符串数组
<script>
var nums = "this is a pencial";
console.log(nums.split(' '));
</script>
结果:

取代
replace(‘原有’,‘新值’)
<script>
var nums = "this is a pencial";
console.log(nums.replace('i','-'));//只替换一个,且不改变nums
</script>
结果:

大小写转换
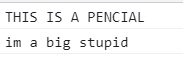
toUpperCase、toLowerCase
<script>
var nums = "this is a pencial";
console.log(nums.toUpperCase());
var s2 = "Im A biG StuPid";
console.log(s2.toLowerCase());
</script>
结果: