1.软件版本
matlab2013b
2.本算法理论知识
传感器信息融合扩展卡尔曼滤波定位
步骤:
1.里程计位置估计
小车速度200mm/s(距离单位均按照mm来设计),里程计线速度误差0.01,旋转角速度误差0.1。
2.超声波卫星距离测量位置观测
一个超声波发生器作为卫星发射超声波信号,其在全局地图的坐标已知, 两个超声波接收器在小车上,获取两个距离值后计算出小车的位置和回转角度 (此部分模型如不理解请再讨论)。
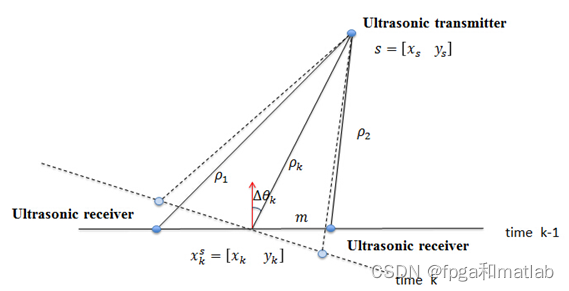
两个超声波接收器放在小车上,与小车heading方向垂直。小车的中心位置为两个接收器连线的中点。小车移动时计算小车的∆θ![]() 。小车的x,y计算方法为:
。小车的x,y计算方法为:
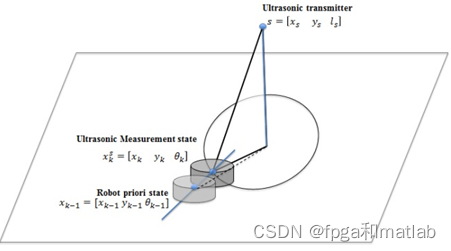
超声波测得的距离误差为±2![]() mm,卡尔曼滤波后得到新的小车位置.
mm,卡尔曼滤波后得到新的小车位置.
3.部分源码

function [x] = ExtKalman(u1)
% u1(x,y,th,dth) is got robot prior position
% u2(x,y,th) is U-SAT got robot position
persistent f P m e
%distance between the two wheel
b = 265;
m = 0;
%data robot prior position
x_p = u1(1);
y_p = u1(2);
theta_p = u1(3);
dtheta = u1(4);
%U-SAT data robot position
d_th_u = u1(5);
%U-SAT 1 sender position
x_s=00;
y_s=1000;
z_s=1000;
zk=0;
if isempty(f)
% f= 5;
x = [0 0 0]';
P = eye(3);
f=1;
else
% f= f-1;
x = [x_p y_p theta_p]'; % robot prior position
end
% Kalman filter
R =((-1)^m)*2; % measurement noise
m=m+1;
v = 0.02;
ds = 0.02; % get from the robot with time
xp=x+[ds*cos(theta_p+dtheta/2);ds*sin(theta_p+dtheta/2);dtheta];
da = ds/(2*b);
cos_th = cos(theta_p+dtheta/2);
sin_th = sin(theta_p+dtheta/2);
A = [1 0 -ds*sin_th;
0 1 ds*cos_th;
0 0 1];
F = [0.5*cos_th-da*sin_th 0.5*cos_th+da*sin_th;
0.5*sin_th+da*cos_th 0.5*sin_th-da*cos_th;
1/b -1/b];
G = [ 0.001*v 0 ;
0 0.002*v ];
Q= (F*G*F');
Pp = A*P*A'+Q;
h = sqrt((xp(1)-x_s)^2+(xp(2)-y_s)^2);
if d_th_u~=0
H = [(xp(1)-x_s)/h (xp(2)-y_s)/h 1];
else
H = [(xp(1)-x_s)/h (xp(2)-y_s)/h 0];
end
K = (Pp*H')/(H*Pp*H'+R);
x = xp+K*(zk-h);
P = Pp-K*H*Pp;
x_n = x(1);
y_n = x(2);
th_n = x(3);
4.仿真结论
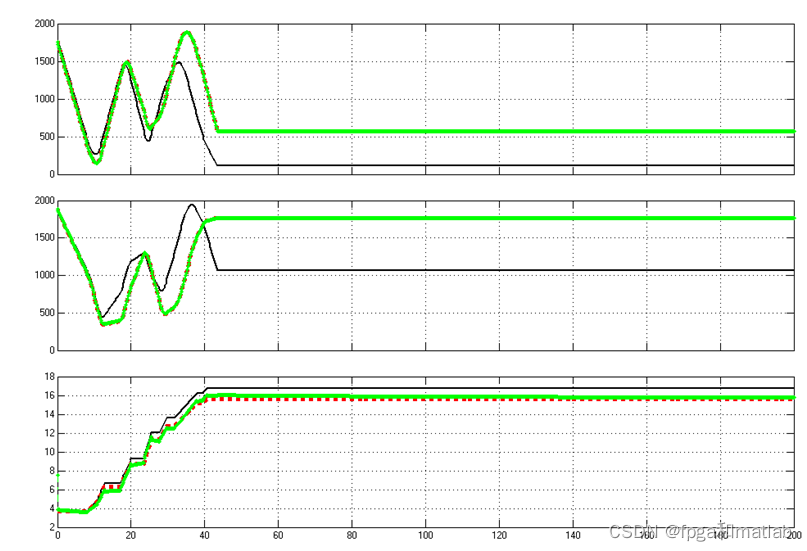
黑色为里程计定位结果
绿色为卡尔曼跟踪定位结果
红色为实际真实值
A25-11