演示:
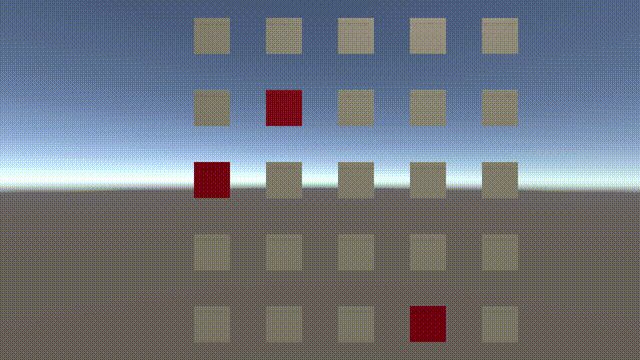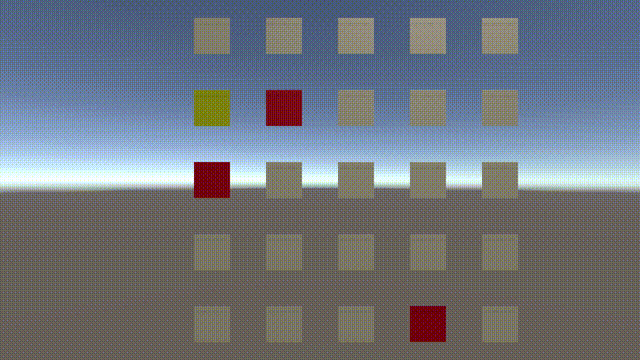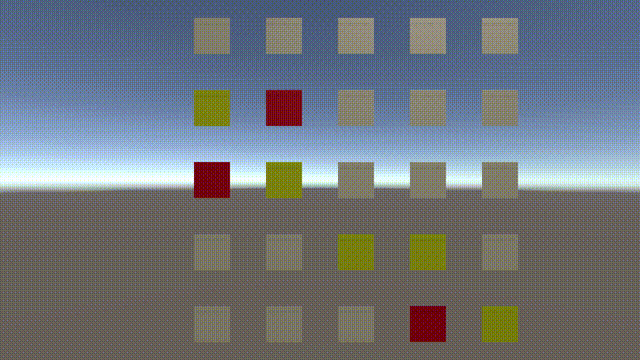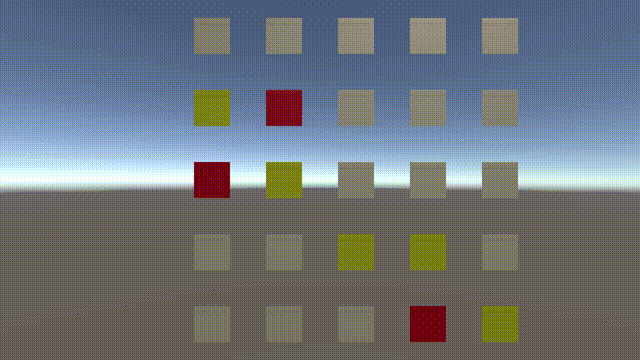
我们知道Unity中的Navigation只能实现3D场景的寻路,不能实现2D的寻路,常见的寻路算法有很多种,其中A星是项目中最常用的寻路方法。在项目中用到了A星,就简单总结一下吧。
原理:
最通俗的原理就是寻找周围的点。选出一个到终点最近的点,再从选出的点为起点寻找下一个点,直到到达目标点。
实现:
如何选出最近的点呢,我们就会利用曼哈顿街区算法公式寻找下一个点。

如下图:我们以黄色为起点,黄色的点周围有八个可以移动的点,移动的距离对角移动为1.4,直线移动为1。
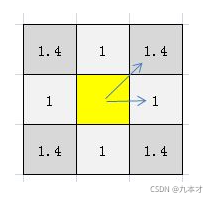
我们用f来代表寻路的总代价,g代表从开始点到下一个点的距离,h(此处用到麦哈顿街区算法)为从下一个点到目标点的距离。则f=g+h。
因此我们的格子类就基本完成了;
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using UnityEngine;
/// <summary>
/// 格子的类型
/// </summary>
public enum E_Node_Type {
Walk,
Stop
}
/// <summary>
/// 格子类
/// </summary>
public class AStarNode
{
//格子的坐标
public int x;
public int y;
//寻路消耗
public float f;
//起点距离
public float g;
//终点距离
public float h;
//父对象
public AStarNode father;
public E_Node_Type type;
public AStarNode( int x,int y,E_Node_Type type)
{
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
this.type = type;
}
}
接下来写寻路的控制器,经过分析,应该记录开始点周围的每一个点,经过计算后看看他是否是最近的点。这里我们就需要两个列表,一个列表记录格子周围的点。另一个列表我们要记录最近路径上的格子。另外我们还要一个二维数组来记录地图的信息。
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using UnityEngine;
/// <summary>
/// A星管理器
/// </summary>
public class AStarMgr : MonoBehaviour
{
public static AStarMgr Instance;
//地图的宽高
private int mapW;
private int mapeH;
//地图相关的所有的格子容器
public AStarNode[,] nodes;
//开启列表
private List<AStarNode> openList=new List<AStarNode>();
//关闭列表
private List<AStarNode> closeList=new List<AStarNode>();
private void Awake()
{
Instance = this;
}
/// <summary>
/// 初始化地图信息
/// </summary>
/// <param name="w"></param>
/// <param name="h"></param>
public void InItMapInfo(int w,int h)
{
this.mapeH = h;
this.mapW = w;
nodes = new AStarNode[w,h];
for (int i = 0; i < w; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < h; j++)
{
AStarNode node = new AStarNode(i, j, Random.Range(0, 100) < 20 ? E_Node_Type.Stop : E_Node_Type.Walk);
nodes[i, j] = node;
}
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 寻路的方法
/// </summary>
/// <param name="startPos"></param>
/// <param name="endPos"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
public List<AStarNode>FindPath(Vector2 startPos,Vector2 endPos)
{
//判断起始点是不是在地图的范围内
if (startPos.x < 0 || startPos.x >= mapW
|| startPos.y < 0 || startPos.y >= mapeH
|| endPos.x < 0 || endPos.x >= mapW
|| endPos.y < 0 || endPos.y >= mapeH
)
return null;
//判断起始点是不是不能通行的点
AStarNode start = nodes[(int)startPos.x, (int)startPos.y];
AStarNode end = nodes[(int)endPos.x, (int)endPos.y];
if (start.type == E_Node_Type.Stop || end.type == E_Node_Type.Stop)
return null;
closeList.Clear();
openList.Clear();
//开始点放入关闭列表中
start.father = null;
start.f = 0;
start.g = 0;
start.h = 0;
closeList.Add(start);
while (true)
{
//周围的点
FindNearlyToOpenList(start.x - 1, start.y - 1, 1.4f, start, end);
FindNearlyToOpenList(start.x, start.y - 1, 1.4f, start, end);
FindNearlyToOpenList(start.x + 1, start.y - 1, 1.4f, start, end);
FindNearlyToOpenList(start.x - 1, start.y, 1.4f, start, end);
FindNearlyToOpenList(start.x + 1, start.y, 1.4f, start, end);
FindNearlyToOpenList(start.x - 1, start.y + 1, 1.4f, start, end);
FindNearlyToOpenList(start.x, start.y + 1, 1.4f, start, end);
FindNearlyToOpenList(start.x + 1, start.y + 1, 1.4f, start, end);
if (openList.Count == 0)
return null;
//排序选出最小的点
openList.Sort(SortOpenList);
//放入关闭列表,然后从开启列表中移除
closeList.Add(openList[0]);
//找到这个点,进行下一次寻路
start = openList[0];
openList.RemoveAt(0);
if (start == end)
{
//结束
List<AStarNode> path = new List<AStarNode>();
path.Add(end);
while (end.father != null)
{
path.Add(end.father);
end = end.father;
}
path.Reverse();
return path;
}
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 排序函数
/// </summary>
/// <param name="a"></param>
/// <param name="b"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
private int SortOpenList(AStarNode a,AStarNode b)
{
if (a.f > b.f)
return 1;
else if (a.f == b.f)
return 1;
else
return -1;
}
/// <summary>
/// 临近的点放入开启列表
/// </summary>
/// <param name="x"></param>
/// <param name="y"></param>
private void FindNearlyToOpenList(int x,int y,float g,AStarNode father, AStarNode end)
{
if (x < 0 || x >= mapW || y < 0 || y >= mapeH)
return;
AStarNode node = nodes[x, y];
if (node == null||node.type==E_Node_Type.Stop
||closeList.Contains(node)
||openList.Contains(node)
)
return;
//计算f值 f=g+h;
node.father = father;
node.g = father.g + g;
node.h = Mathf.Abs(end.x - node.x) + Mathf.Abs(end.y - node.y);
node.f = node.g + node.h;
openList.Add(node);
}
}
以上的代码就完成了A星算法的核心内容。下边为测试代码:
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using UnityEngine;
public class TestAStar : MonoBehaviour
{
public int beginX = -3;
public int beginY = 5;
public int offsetX = 2;
public int offsetY = 2;
public int mapW = 5;
public int mapH = 5;
private Vector2 beginPos = Vector2.right * -1;
private Vector2 endPos = Vector2.right * -1;
public Material red;
public Material yellow;
private Dictionary<string, GameObject> cubes = new Dictionary<string, GameObject>();
void Start()
{
AStarMgr.Instance.InItMapInfo(mapW, mapW);
for (int i = 0; i < mapW; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < mapH; j++)
{
GameObject obj = GameObject.CreatePrimitive(PrimitiveType.Cube);
obj.transform.position = new Vector3(beginX + i * offsetX, beginY + j * offsetY, 0);
obj.name = i + "_" + j;
cubes.Add(obj.name, obj);
AStarNode node = AStarMgr.Instance.nodes[i, j];
if (node.type == E_Node_Type.Stop)
{
obj.GetComponent<MeshRenderer>().material = red;
}
}
}
}
// Update is called once per frame
void Update()
{
if (Input.GetMouseButtonDown(0))
{
RaycastHit hit;
Ray ray = Camera.main.ScreenPointToRay(Input.mousePosition);
if (Physics.Raycast(ray, out hit, 1000))
{
if (beginPos == Vector2.right * -1)
{
string[] strs = hit.collider.gameObject.name.Split('_');
beginPos = new Vector2(int.Parse(strs[0]), int.Parse(strs[1]));
hit.collider.gameObject.GetComponent<MeshRenderer>().material = yellow;
}
else
{
string[] strs = hit.collider.gameObject.name.Split('_');
endPos = new Vector2(int.Parse(strs[0]), int.Parse(strs[1]));
Debug.Log(endPos);
List<AStarNode> list = AStarMgr.Instance.FindPath(beginPos, endPos);
Debug.Log(list.Count);
if (list != null)
{
for (int i = 0; i < list.Count; i++)
{
Debug.Log(list[i]);
cubes[list[i].x + "_" + list[i].y].GetComponent<MeshRenderer>().material = yellow;
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
以上为A星寻路算法的核心理念,在用到商业项目中肯定要对算法进行封装。那下边就介绍一个已经封装完善的A星算法插件:
A* Pathfinding Project
下载免费版:点击更多信息-点击download就可以下载免费版。
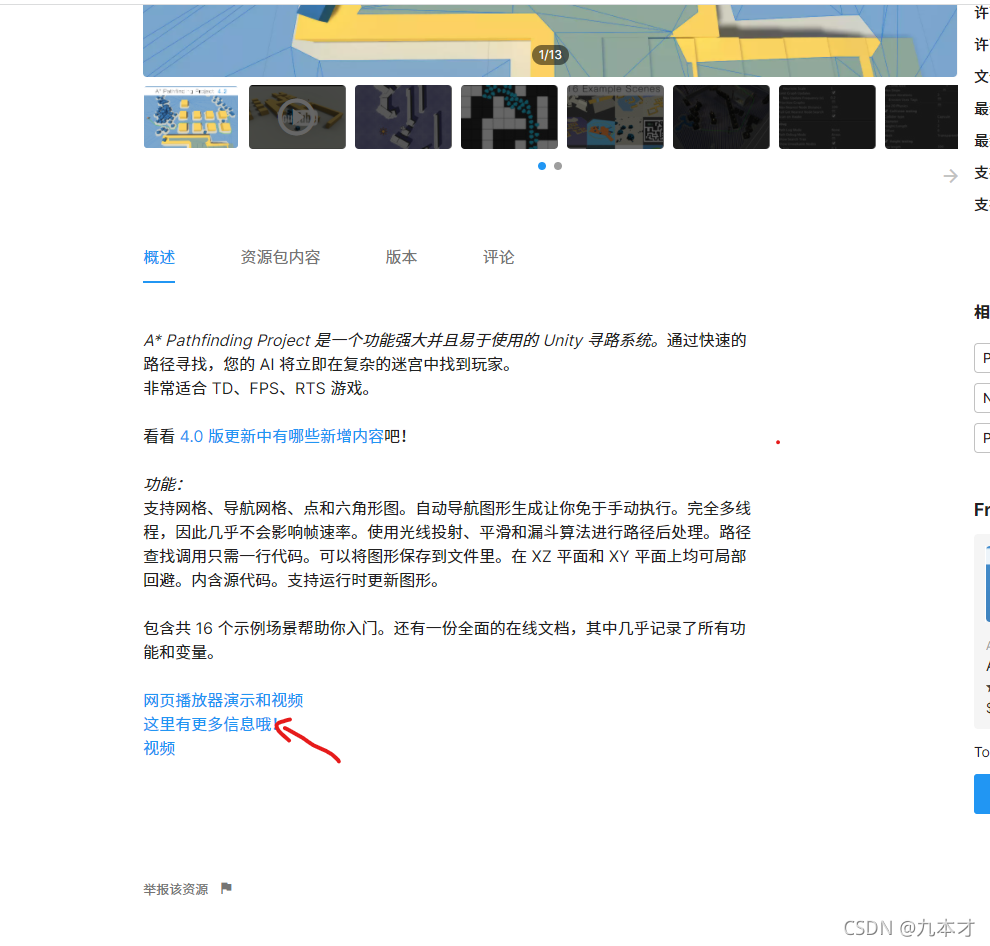
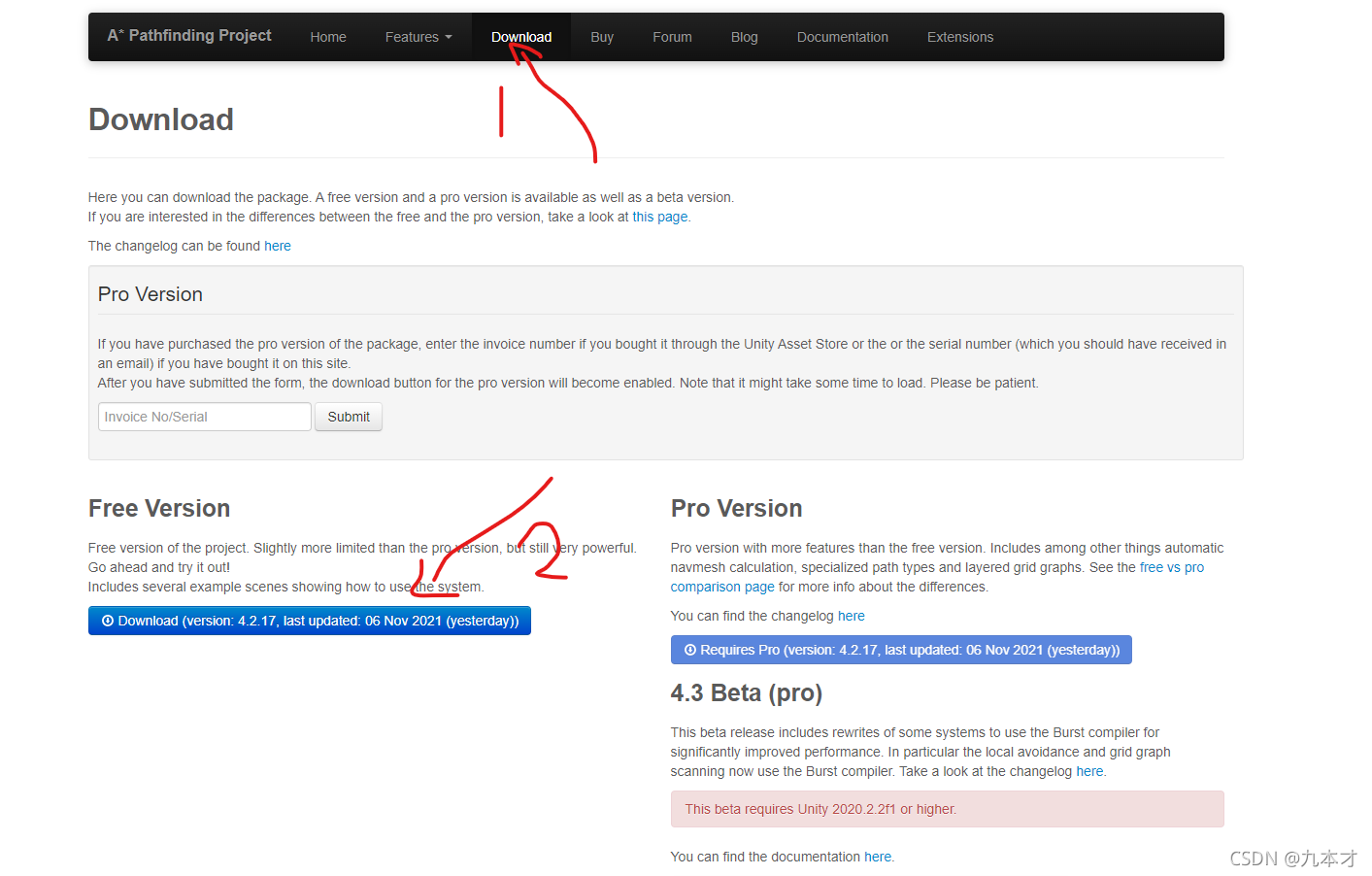
使用方法看这个视频吧:
 https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1D4411N7FZ
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1D4411N7FZ