一、函数参考
1、Primal-dual算法
Primal-dual algorithm是一种用于解决特殊类型的变分问题的算法(即找到一个函数来最小化一些泛函)。
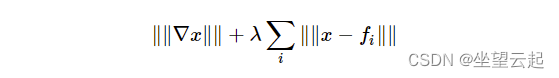
特别是由于图像去噪可以看作是变分问题,因此可以使用原始对偶算法进行去噪,这正是该算法所实现的。
cv::denoise_TVL1 (const std::vector< Mat > &observations, Mat &result, double lambda=1.0, int niters=30)| observations | 该数组应包含要恢复的图像的一个或多个噪声版本。 |
| result | 这里将存储去噪图像。 无需预先分配存储空间,必要时会自动分配。 |
| lambda | 对应于上述公式中的 λ。 当它被放大时,平滑(模糊)的图像比细节(但可能有更多噪点)的图像更受欢迎。 粗略地说,随着它变小,结果会更加模糊,但会去除更多的异常值。 |
| niters | 算法将运行的迭代次数。 当然,越多的迭代越好,但是这个说法很难量化细化,所以就使用默认值,如果结果不好就增加它。 |
2、非局部均值去噪算法
使用非局部均值去噪算法,该方法基于一个简单的原理:将像素的颜色替换为相似像素颜色的平均值。 但是与给定像素最相似的像素根本没有理由靠近。 因此,扫描图像的大部分以寻找真正类似于想要去噪的像素的所有像素是合法的。执行图像去噪,并进行了多种计算优化。 噪声预期为高斯白噪声。
cv::cuda::fastNlMeansDenoising (InputArray src, OutputArray dst, float h, int search_window=21, int block_size=7, Stream &stream=Stream::Null())
cv::fastNlMeansDenoising (InputArray src, OutputArray dst, float h=3, int templateWindowSize=7, int searchWindowSize=21)
cv::fastNlMeansDenoising (InputArray src, OutputArray dst, const std::vector< float > &h, int templateWindowSize=7, int searchWindowSize=21, int normType=NORM_L2)针对彩色图像的 fastNlMeansDenoising 函数。
cv::cuda::fastNlMeansDenoisingColored (InputArray src, OutputArray dst, float h_luminance, float photo_render, int search_window=21, int block_size=7, Stream &stream=Stream::Null())
cv::fastNlMeansDenoisingColored (InputArray src, OutputArray dst, float h=3, float hColor=3, int templateWindowSize=7, int searchWindowSize=21)
针对图像序列的 fastNlMeansDenoising 函数。
cv::fastNlMeansDenoisingColoredMulti (InputArrayOfArrays srcImgs, OutputArray dst, int imgToDenoiseIndex, int temporalWindowSize, float h=3, float hColor=3, int templateWindowSize=7, int searchWindowSize=21)
cv::fastNlMeansDenoisingMulti (InputArrayOfArrays srcImgs, OutputArray dst, int imgToDenoiseIndex, int temporalWindowSize, float h=3, int templateWindowSize=7, int searchWindowSize=21)
cv::fastNlMeansDenoisingMulti (InputArrayOfArrays srcImgs, OutputArray dst, int imgToDenoiseIndex, int temporalWindowSize, const std::vector< float > &h, int templateWindowSize=7, int searchWindowSize=21, int normType=NORM_L2)执行纯非局部方法去噪,没有任何简化,因此速度不快。
cv::cuda::nonLocalMeans (InputArray src, OutputArray dst, float h, int search_window=21, int block_size=7, int borderMode=BORDER_DEFAULT, Stream &stream=Stream::Null())三、OpenCV源码
1、源码路径
opencv\modules\photo\src\denoise_tvl1.cpp2、源码代码
#include "precomp.hpp"
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#define ABSCLIP(val,threshold) MIN(MAX((val),-(threshold)),(threshold))
namespace cv{
class AddFloatToCharScaled{
public:
AddFloatToCharScaled(double scale):_scale(scale){}
inline double operator()(double a,uchar b){
return a+_scale*((double)b);
}
private:
double _scale;
};
using std::transform;
void denoise_TVL1(const std::vector<Mat>& observations,Mat& result, double lambda, int niters){
CV_Assert(observations.size()>0 && niters>0 && lambda>0);
const double L2 = 8.0, tau = 0.02, sigma = 1./(L2*tau), theta = 1.0;
double clambda = (double)lambda;
double s=0;
const int workdepth = CV_64F;
int i, x, y, rows=observations[0].rows, cols=observations[0].cols,count;
for(i=1;i<(int)observations.size();i++){
CV_Assert(observations[i].rows==rows && observations[i].cols==cols);
}
Mat X, P = Mat::zeros(rows, cols, CV_MAKETYPE(workdepth, 2));
observations[0].convertTo(X, workdepth, 1./255);
std::vector< Mat_<double> > Rs(observations.size());
for(count=0;count<(int)Rs.size();count++){
Rs[count]=Mat::zeros(rows,cols,workdepth);
}
for( i = 0; i < niters; i++ )
{
double currsigma = i == 0 ? 1 + sigma : sigma;
// P_ = P + sigma*nabla(X)
// P(x,y) = P_(x,y)/max(||P(x,y)||,1)
for( y = 0; y < rows; y++ )
{
const double* x_curr = X.ptr<double>(y);
const double* x_next = X.ptr<double>(std::min(y+1, rows-1));
Point2d* p_curr = P.ptr<Point2d>(y);
double dx, dy, m;
for( x = 0; x < cols-1; x++ )
{
dx = (x_curr[x+1] - x_curr[x])*currsigma + p_curr[x].x;
dy = (x_next[x] - x_curr[x])*currsigma + p_curr[x].y;
m = 1.0/std::max(std::sqrt(dx*dx + dy*dy), 1.0);
p_curr[x].x = dx*m;
p_curr[x].y = dy*m;
}
dy = (x_next[x] - x_curr[x])*currsigma + p_curr[x].y;
m = 1.0/std::max(std::abs(dy), 1.0);
p_curr[x].x = 0.0;
p_curr[x].y = dy*m;
}
//Rs = clip(Rs + sigma*(X-imgs), -clambda, clambda)
for(count=0;count<(int)Rs.size();count++){
transform<MatIterator_<double>,MatConstIterator_<uchar>,MatIterator_<double>,AddFloatToCharScaled>(
Rs[count].begin(),Rs[count].end(),observations[count].begin<uchar>(),
Rs[count].begin(),AddFloatToCharScaled(-sigma/255.0));
Rs[count]+=sigma*X;
min(Rs[count],clambda,Rs[count]);
max(Rs[count],-clambda,Rs[count]);
}
for( y = 0; y < rows; y++ )
{
double* x_curr = X.ptr<double>(y);
const Point2d* p_curr = P.ptr<Point2d>(y);
const Point2d* p_prev = P.ptr<Point2d>(std::max(y - 1, 0));
// X1 = X + tau*(-nablaT(P))
x = 0;
s=0.0;
for(count=0;count<(int)Rs.size();count++){
s=s+Rs[count](y,x);
}
double x_new = x_curr[x] + tau*(p_curr[x].y - p_prev[x].y)-tau*s;
// X = X2 + theta*(X2 - X)
x_curr[x] = x_new + theta*(x_new - x_curr[x]);
for(x = 1; x < cols; x++ )
{
s=0.0;
for(count=0;count<(int)Rs.size();count++){
s+=Rs[count](y,x);
}
// X1 = X + tau*(-nablaT(P))
x_new = x_curr[x] + tau*(p_curr[x].x - p_curr[x-1].x + p_curr[x].y - p_prev[x].y)-tau*s;
// X = X2 + theta*(X2 - X)
x_curr[x] = x_new + theta*(x_new - x_curr[x]);
}
}
}
result.create(X.rows,X.cols,CV_8U);
X.convertTo(result, CV_8U, 255);
}
}
四、效果图像示例


