目录
概览
- 了解各种数据类型在计算机中的表示方法
- 掌握C语言数据类型的位级表示及操作
问题
1、根据bits.c中的要求补全以下的函数:
int bitAnd(int x, int y) ;
int getByte(int x, int n) ;
int logicalShift(int x, int n) ;
int bitCount(int x) ;
int bang(int x) ;
int tmin(void) ;
int fitsBits(int x, int n);
int divpwr2(int x, int n) ;
int negate(int x) ;
int isPositive(int x) ;
int isLessOrEqual(int x, int y) ;
int ilog2(int x) ;
unsigned float_neg(unsigned uf) ;
unsigned float_twice(unsigned uf) ;
2、在Linux下测试以上函数是否正确,指令如下:
*编译:
./dlc bits.c*测试:
make btest
./btest实验环境:
- 计算机(Intel CPU)
- Ubuntu Linux操作系统
题解代码
1.由摩尔定律得,xy = not((not x)(not y))。
/*
* bitAnd - x&y using only ~ and |
* Example: bitAnd(6, 5) = 4
* Legal ops: ~ |
* Max ops: 8
* Rating: 1
*/
int bitAnd(int x, int y) {
return ~(~x | ~y);
}
- 2.右移再取低2字节,n<<3为字节乘数8得到需要右移位数
/*
* getByte - Extract byte n from word x
* Bytes numbered from 0 (LSB) to 3 (MSB)
* Examples: getByte(0x12345678,1) = 0x56
* Legal ops: ! ~ & ^ | + << >>
* Max ops: 6
* Rating: 2
*/
int getByte(int x, int n) {
//右移再取低2字节,n<<3为字节乘数8得到需要右移位数
return (x >> (n << 3)) & 0xff;
}
- 3.算数右移后再取低有效位
/*
* logicalShift - shift x to the right by n, using a logical shift
* Can assume that 0 <= n <= 31
* Examples: logicalShift(0x87654321,4) = 0x08765432
* Legal ops: ! ~ & ^ | + << >>
* Max ops: 20
* Rating: 3
*/
int logicalShift(int x, int n) {
//算数右移后再取低有效位
return (x >> n) & (~(1 << 31 >> n << 1));
}
4.将x不断偏移相加,逐渐把个位的1都加到最低位。
- 先用0x55555555(即01010101 01010101 01010101 01010101)取出x的奇数位,以及用x>>1取出偶数位且右对齐于最低位,2者相加得到的结果为:每隔两位此时的数,为该两位‘1’的个数。即32位和可分为每隔两位为一个数,共16个数(两位‘1’计数),各自存放原本该两位上‘1’的个数。
- 再用0x33333333(00110011 00110011 00110011 00110011)取出第2、4、6、8、10、12、14、16个两位‘1’计数组成的32位(每四位为一个数)为第1个加数,以及用x>>2取出第1、3、5、7、9、11、13、15个‘1’计数且右对齐于最低位组成的32位(每四位为一个数)为第2个加数,2者相加得到的结果为:每隔四位此时的数,为该四位‘1’的个数。即32位和可分为每隔四位为一个数,共8个数(四位‘1’计数),各自存放原本该四位上‘1’的个数。
- 再用0x0f0f0f0f(00001111 00001111 00001111 00001111)取出第2、4、6、8个四位‘1’计数组成的32位(每八位为一个数)为第1个加数,以及用x>>4取出第1、3、5、7个四位‘1’计数且右对齐于最低位组成的32位(每八位为一个数)为第2个加数,2者相加得到的结果为:每隔八位此时的数,为该八位‘1’的个数。即32位和可分为每隔八位为一个数,共4个数(八位‘1’计数),各自存放原本该八位上‘1’的个数。
- 再用0x00ff00ff(00000000 11111111 00000000 11111111)取出第2、4个八位‘1’计数组成的32位(每16位为一个数)为第1个加数,以及用x>>8取出第1、3个八位‘1’计数且右对齐于最低位组成的32位(每16位为一个数)为第2个加数,2者相加得到的结果为:每隔16位此时的数,为该16位‘1’的个数。即32位和可分为每隔16位为一个数,共2个数(16位‘1’计数),各自存放原本该16位上‘1’的个数。
- 再用0x0000ffff(00000000 00000000 11111111 11111111)取出第2个16位‘1’计数第1个加数,以及用x>>16取出第16位‘1’计数且右对齐于最低位为第2个加数,2者相加得到的结果为为‘1’的个数。
int bitCount(int x) {
int a, b, c, d, e;//偏移量
a = 0x55 + (0x55 << 8);
a = a + (a << 16);//0x55555555(0101 0101……)
b = 0x33 + (0x33 << 8);
b = b + (b << 16);//0x33333333(0011 0011……)
c = 0xF + (0xF << 8);
c = c + (c << 16);//0x0f0f0f0f(0000 1111……)
d = 0xFF + (0xFF << 16);//0x00ff00ff(0000 0000 1111 1111……)
e = 0xFF + (0xFF << 8);//0x0000ffff(0000 0000 0000 0000 1111 1111……)
x = (x & a) + ((x >> 1) & a);//相邻2位加到低位
x = (x & b) + ((x >> 2) & b);//相邻4位加到低位
x = (x & c) + ((x >> 4) & c);//相邻8位加到低位
x = (x & d) + ((x >> 8) & d);//相邻16位加到低位
x = (x & e) + ((x >> 16) & e);//相邻32位加到低位
return x;
}
5.只有0取负相加后符号位依旧是0
/*
* bang - Compute !x without using !
* Examples: bang(3) = 0, bang(0) = 1
* Legal ops: ~ & ^ | + << >>
* Max ops: 12
* Rating: 4
*/
int bang(int x) {
//只有0取负相加后符号位依旧是0
return ((x | (~x + 1)) >> 31) + 1;
}
6.0x80000000最小
/*
* tmin - return minimum two's complement integer
* Legal ops: ! ~ & ^ | + << >>
* Max ops: 4
* Rating: 1
*/
int tmin(void) {
return 1 << 31;//0x80000000最小
}
7.先用m = 32 – n存偏移量。左右移m和原数相同为同一数就位数够。判题系统的问题所以额外去除32位的情况,~32 + 1 + n == n-32
/*
* fitsBits - return 1 if x can be represented as an
* n-bit, two's complement integer.
* 1 <= n <= 32
* Examples: fitsBits(5,3) = 0, fitsBits(-4,3) = 1
* Legal ops: ! ~ & ^ | + << >>
* Max ops: 15
* Rating: 2
*/
int fitsBits(int x, int n)
{
int m = 32 + (~n + 1);//32-n
//左右移和原数相同为同一数就位数够
//判题系统的问题所以额外去除32位的情况,~32 + 1 + n=n-32
return !(x ^ ((x << m) >> m))& !!(~32 + 1 + n);
}
7. (x >> 31 & ~(1 << 31 >> 31 << n)为偏移量,保证向偶数进位,再算数右移为除法.
/*
* divpwr2 - Compute x/(2^n), for 0 <= n <= 30
* Round toward zero
* Examples: divpwr2(15,1) = 7, divpwr2(-33,4) = -2
* Legal ops: ! ~ & ^ | + << >>
* Max ops: 15
* Rating: 2
*/
int divpwr2(int x, int n) {
//(x >> 31 & ~(1 << 31 >> 31 << n)为偏移量保证向偶数进位,再算数右移为除法
return ((x >> 31 & ~(1 << 31 >> 31 << n)) + x) >> n;
}
8.取负和补码计算类似。
/*
* negate - return -x
* Example: negate(1) = -1.
* Legal ops: ! ~ & ^ | + << >>
* Max ops: 5
* Rating: 2
*/
int negate(int x) {
return ~x + 1;
}
9. 符号位为0且不为0为正数
/*
* isPositive - return 1 if x > 0, return 0 otherwise
* Example: isPositive(-1) = 0.
* Legal ops: ! ~ & ^ | + << >>
* Max ops: 8
* Rating: 3
*/
int isPositive(int x) {
return !(x >> 31) & !!x; //符号位为0且不为0
}
10.考虑溢出问题,要单独判断异号问题。y正x负返回1,x正y负返回0,同号作差。
/*
* isLessOrEqual - if x <= y then return 1, else return 0
* Example: isLessOrEqual(4,5) = 1.
* Legal ops: ! ~ & ^ | + << >>
* Max ops: 24
* Rating: 3
*/
int isLessOrEqual(int x, int y) {
int t = ~x + 1 + y;//y-x
//y正x负返回1,x正y负返回0,同号作差
return ((!(y >> 31)) & (x >> 31)) | ((~((y >> 31) ^ (x >> 31))) & !(t >> 31));
}
11.即求最高位位数+1,通过偏移把最高位后面的位都改为1,利用上面1计数得到最高位数。
/*
* ilog2 - return floor(log base 2 of x), where x > 0
* Example: ilog2(16) = 4
* Legal ops: ! ~ & ^ | + << >>
* Max ops: 90
* Rating: 4
*/
int ilog2(int x) {
int a, b, c, d, e;
//把最高位后面的位都改为1
x |= x >> 1;
x |= x >> 2;
x |= x >> 4;
x |= x >> 8;
x |= x >> 16;
//用上面数1法,数到的1为位数
a = 0x55 + (0x55 << 8);
a = a + (a << 16);
b = 0x33 + (0x33 << 8);
b = b + (b << 16);
c = 0xF + (0xF << 8);
c = c + (c << 16);
d = 0xFF + (0xFF << 16);
e = 0xFF + (0xFF << 8);
x = (x & a) + ((x >> 1) & a);
x = (x & b) + ((x >> 2) & b);
x = (x & c) + ((x >> 4) & c);
x = (x & d) + ((x >> 8) & d);
x = (x & e) + ((x >> 16) & e);
return x+~0;//+1
}
12.特殊情况为阶码全1且位数不全为0,为NaN,直接返回原参数,否则符号位取反就行。
/*
* float_neg - Return bit-level equivalent of expression -f for
* floating point argument f.
* Both the argument and result are passed as unsigned int's, but
* they are to be interpreted as the bit-level representations of
* single-precision floating point values.
* When argument is NaN, return argument.
* Legal ops: Any integer/unsigned operations incl. ||, &&. also if, while
* Max ops: 10
* Rating: 2
*/
unsigned float_neg(unsigned uf) {
unsigned e = uf & 0x7f800000; //获得 阶码
unsigned f = uf & 0x007fffff; //获得尾数
if (e == 0x7f800000 && f)
return uf;//阶码全为1且尾数不全为0为NaN,返回参数
return uf ^ 0x80000000; //符号位取反
}
13.(1)0直接返回
(2)最小数0x80000000取正会溢出是特殊情况,直接返回结果。
(3)其他为一般情况:
①如果负数取正获得x绝对值。
②通过不断右移x值(temp备份x)直到为0获得位数(右移次数)。
③位数大于24的会截断,需要考虑向偶数进位。
/*
* float_i2f - Return bit-level equivalent of expression (float) x
* Result is returned as unsigned int, but
* it is to be interpreted as the bit-level representation of a
* single-precision floating point values.
* Legal ops: Any integer/unsigned operations incl. ||, &&. also if, while
* Max ops: 30
* Rating: 4
*/
unsigned float_i2f(int x) {
unsigned s = x & 0x80000000; //获得符号位
unsigned t;//舍弃最高位
int m = 0;//位数
int temp;//x副本
if (!x) //为0直接返回
return x;
else if (x == 0x80000000)//最小数取负会越界
return 0xCF000000;
else if (s)
x = ~x + 1;//如果为负绝对值
temp = x;
for (; temp; m++)
temp >>= 1;//右移
if (m > 24) {
s += x >> (m - 24) & 0x007fffff;//加尾数
t = 0x3 << (m - 25);//舍弃最高位
if ((x & (~(-1 << (m - 24)))) > (t / 3) || (x & t) == t) {
s++;//向偶数进位
}
}
else
s += x << (24 - m) & 0x007fffff;//加尾数
s += (m + 126) << 23; //加入阶码
return s;
}
14.阶码全1为NaN和inf,以及uf==0直接返回uf。阶码为全0为非规格化数,经计算其翻倍结果绝对值刚好为左移1位。其他一般情况阶码加1就行。
/*
* float_twice - Return bit-level equivalent of expression 2*f for
* floating point argument f.
* Both the argument and result are passed as unsigned int's, but
* they are to be interpreted as the bit-level representation of
* single-precision floating point values.
* When argument is NaN, return argument
* Legal ops: Any integer/unsigned operations incl. ||, &&. also if, while
* Max ops: 30
* Rating: 4
*/
unsigned float_twice(unsigned uf) {
unsigned s = uf & 0x80000000;//符号
unsigned e = uf & 0x7f800000;//阶码
if ((e == 0x7f800000) || !uf)
return uf;//NaN inf 0
else if (!e)//如果阶码全0
return (uf << 1) + s;
return uf += 0x00800000;//非特殊情况阶码加1
}
判题结果如下,全部通过,代码无误。(图1)
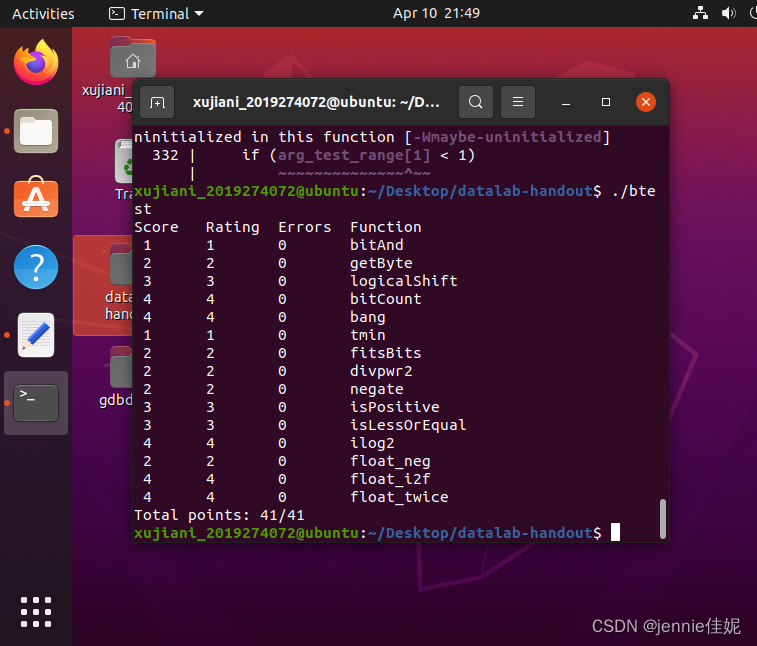
图表 1 判题结果
总结与体会
通过本次实验,我进一步加深了关于计算机内部数据表示的认识。对不同数据类型的数据在计算机内部的存放方式,不同数据类型之间的转换有了更深刻的认识。
同时也了解通过位操作实现部分功能的方法,如取负、比较大小。如移位操作可实现简单乘除,要进一步实现向偶数进位可通过加入偏移量实现。&按位与操作可起到掩码作用。通过多次的偏移、移位和加法操作可实现将各位上的1相加。同时也尝试了实现关于int和float的转换过程,尤其截取中向偶数进位过程的实现。
在该次过程中,我也认识到重视极端数值的重要性。只有考虑了极端情况的代码,才是比较具备健壮性的。