程序注释题
import java.io.*;
public class ExamBuffereStream{
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{
InputStreamReader isr=new InputStreamReader(System. in);
BufferedReader br= new BufferedReader(isr);
OutputStream os=new FileOutputStream(". \\buffer. bin");
//以文件buffer.bin构造OutputStreamReader输出流对象os
OutputStreamWriter fout = new OutputStreamWriter(os);
//使用os构造OutputStream输出流对象bout(处理流)
BufferedWriter bout=new BufferedWriter(fout);
//使用bout构造BufferWriter输出流对象(处理流)
String str;
while(true) {
str=br.readLine(); //从键盘读取一行文本
if(str.equals("end"))
break;
bout. write(str); //将键盘读入的文本写入文件buffer.bin
bout.newLine(); //bout换行
}
bout. close();//关闭文件
InputStream is=new FileInputStream(".\\buffer. bin");
InputStreamReader fin = new InputStreamReader(is);
BufferedReader bin = new BufferedReader(fin);
while((str=bin.readLine())!=null) ...(7)
System.out.println(str);//从bin文件循环按行读取字符串,直到文件内容结束
bin. close();
}
}
class SuperClass{
int index=5;
public void printVal(){
System.out.println("SuperClass");
}
}
class SubClass extends SuperClass{
int index=2;
public void printVal(){
System.out.println("SubClass");
}
public void printVal(String name){
System.out.println(name+"SubClass");
}
public int getIndex(){
System.out.println("Sucess GetIndex");
return index;
}
}
public class Examplel{
public static void main(String[] args) {
SuperClass supc=new SuperClass();
SubClass subc=(SubClass)supc;
System.out.println(supc.index);
supc.printVal();
/*supc.printVal("supc");//A行 */
/*supc.getIndex();//B行*/
/*supc.printVal();//C行 */
subc.printVal("subc");
System.out.println(subc.index);
}
}
(1)上述程序运行结束后,请说明supc.index的值,supc.printVal()的打印结果,subc.printVal(“subc”)的打印结果,以及subc.index的值。(2分)
(2)上述程序的A、B、C行中,哪行注释(/·········/)删除后不会引起编译异常?如果发生编译异常,请分别解释原因?(3分)
(1)supc.index的值为5
supc.printVal()的打印结果为 SubClass
subc.printVal(“subc”)的打印结果为 subc:SubClass
subc.index的值为2
(2)删除C行注释后不会产生异常;
删除A行注释后会产生异常,因为SuperClass中没有方法printVal(String name),该方法只在子类中存在;
删除B行注释后会产生异常;因为SuperClass中没有方法getIndex(),该方法只在子类中存在;
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
import java.awt.*;
public class TestFrame{
public static void main(String args[]){
new MyFrame().load();
}
}
class MyFrame extends JFrame{
JButton b;
JTextField tf;
JLabel l;
public MyFrame(){
b = new JButton("ok");
tf = new JTextField(10);
l = new JLabel();
}
void load(){
JPanel p1 = new JPanel();
p1.add(tf);
p1.add(b);
b.addActionListener(new MyMonitor());//A行
add(p1,BorderLayout.NORTH);
l.setHorizontalAlignment(JLabel.HORIZONTAL);
JPanel p2 = new JPanel();
p2.add(l);
add(p2,BorderLayout.CENTER);
setBounds(400,300,200,120);
setVisible(true);
}
class MyMonitor implements ActionListener{
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e){
l.setText(tf.getText());
}
}
}
(1)该程序的功能是什么?(3分)
(2)该程序中A行的作用是什么?(2分)

import javax.awt.*;
mport javax.awt.event.*;
public class Test{
public static void main(String[]args){
new MyFrame();
}
}
class MyFrame extends JFrame{
JButton b= new JButton("Click me!");
public MyFrame(){
setLayout(new FlowLayout());
add(b);
b.addActionListener(new MyMonitor()) ;
setBounds(200,300,200,300);
setVisible(true);
this.setDefaultCloseOperation(DISPOSE_ON_CLOSE);
}
class MyMonitor implements ActionListener {
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
if (b.getText().equals("Click me!") )
b.setText("Click me again!");
else
b.setText(" Click me!");
}
}
}
导入包错误,应当使用javax.swing或修改为Frame.
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Person{
public static void main(String[] args) {
InputStreamReader isr=new InputStreamReader(System.in);
BufferedReader inputReader=new BufferedReader(isr);
String inputLine="";
System.out.println("请输入数字,每个数字之间用a分割");
try{
inputLine=inputReader.readLine();
}catch(Exception e){
}
String str[]=inputLine.split("a");
int strInt[]=new int[str.length];
for(int i=0;i<str.length;i++)
strInt[i]=Integer.parseInt(str[i]);//A行
Arrays.sort(strInt);//B行
for(int i=0;i<str.length;i++)
System.out.println(strInt[i]+",");
}
}
(1)A行和B行的含义是什么?(2分)
(2)简述上述程序实现的功能?(3分)
A行是利用Integer中的parseInt方法从字符串str[i]中解析出整形数据;
B行是将strInt数组中的整数进行排序。
上述程序的功能是:从控制台输入一组数字,每个数字之间用‘a’分隔,将输入的数据解析为整形数据,并将结果保留在数组中,将数组中 的数据排序后打印。
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
public class Test{
public static void main(string[]args){
Frame f=new Frame("Test");
Button b=new Button("Press Me!");
Monitor bh=new Monitor();
b.addActionListener(bh);
f.add(b,borderLayout.CENTER);
f.setVisible(true);
}
}
class Monitor implements ActionListener{
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e){
System.out.println("a button has been pressed");
}
}
缺少pack()方法,对象均看不到
public class Test{
public static void main(String[]args){
Dog d=new Dog();
System.out.println(d.name);
}
}
class Dog{
private int name;
Dog(){
name="Tom";
}
}
不能访问private数据

public class textscan{
public static void main(String[] args)throw Exception{
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
FileOutputStream outfile=new FileOutStream("test.txt");
OutputStreamWriter osw=new OutputStreamWriter(outfile);
BufferedWriter bw=new BufferedWriter(osw);
bw.write(sc.nextLine());
bw.close();
}
}
(1)描述改程序所实现的功能。
(2)main函数申明部分的throw Exception的作用及程序BufferedWriter流的作用?
从控制台读入一行字符串,写入test.txt文件
throw Exception的作用是传递异常(抛出异常),非彻底处理异常,而是把异常抛给了调用该方法的方法去处理。
BufferedWriter流的作用是将文本写入字符输出流,缓存各个字符,从而提供单个字符、数组和字符串的高效写入
import java.io.*;
public class Test{
public static void main(String[]args){
int i=0;
String Str[]={
"1","2","3"};
while(i<=3){
System.out.println(Str[i]);
i++;
}
}
}
正确答案:数组越界
public class Test{
public static void main(String[]args){
int j=3;
while(j==3){
System.out.println("j is"+j);
}
}
}
正确答案:死循环
public class Convert2{
public static void main(String[] args){
C1 c =new D1();
c.n=3.1415926;
c.m = 186;
c.f();
c.g();
____________________//A行
}
}
class C1{
int m;
double n;
void f(){
System.out.println("被子类继承的方法发()");
}
void g(){
System.out.println("你好,n="+n+" m=" +m);
}
}
class D1 extends C1{
int n = 12;
int w;
void g(){
System.out.println("子类重写方法g(),n="+n+" m="+m);
}
}
(1)请写出该程序的执行结果(3分)
(2)在A行空白处可以增加c.w=12;语句吗?为什么。(2分)
(1)输出的结果如下:
被子类继承的方法f()
子类重写方法g(),n=12 m=186
(2)不可以,上述型对象不能访问子类新增的成员变量。
public static void main(String[] args) {
final int MIN=25,MAX=40;
Scanner Scan=new Scanner(System.in); ...(1)
OutOfRangException problem=new OutOfRangException();
System.out.print("输入"+MIN+"至"+MAX+"之间的整数");
try {
int value=scan.nextInt();
if(value<MIN||value>MAX)
throw problem; ...(2)
}catch(OutOfRangException e) {
...(3)
System.out.println(e.toString());
}
System.out.println("主方法结束.");
}
}
class OutOfRangException extends Exception{
...(4)
OutOfRangException(){
super("输入数据超出范围!");
}
}
(1)定义一个scanner对象,使用in进行初始化
(2)抛出自定义异常
(3)捕获抛出的problem异常
(4)自定义一个异常类,类名为OutOfRangException
(5)使用键盘输入25到40之间的整数并在屏幕上显示,如果不在范围内则抛出异常,使用自定义的异常类
public class ex_4this{
public static void main(String[] args){
Cat cat1=new Cat("Tom");
Cat cat2=new Cat("Tom",30);
cat2.speak();
cat2.grow();
cat2.speak();
cat1.grewthis();
cat1.speak();
}
}
class Cat{
String name;
int weight;
int age=1;
public Cat(String name){
this.name=name;//A行
}
public Cat(String name,int weight){
this("jerry");//B行
this.weight=weight;
}
public void speak(){
System.out.println("my name is"+this.name+"and weight is"+this.weight+"kg");
}
public void grow(){
int weight=5;
this.weight++;//C行
System.out.println("My weight is"+weight+"kg");//D行
}
public Cat grewthis(){
weight++;
age++;
return this;
}
}
(1)写出程序运行结果
(2)分别解释程序A行和B行语句中this的用法?C行语句中的this.weight++改为weight++后,D行的输出结果为?
(1)my name is jerry and weight is 30kg
my weight is 5kg
my name is jerry and weight is 31kg
my name is Tom and weight is 1kg
(2)A行语句中this的用法:区别同名的成员变量与局部变量,B行语句中this的用法:调用本类的public Cat(String name){···}构造方法
my weight is 6kg
import java.io.*
public class FileTest{
public static void main(String[] args)throws IOException{
InputStream is = new FileInputStream("c:\\offline_FtnInfo.txt");
InputStreamReader in = new InputStreamReader(is);
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(in);
String str;
int c = 0;
while((str = br.readLine())!=null){
System.out.println(str);
}
}
}
(1)该程序的功能是什么?(3分)
(2)该程序中使用了哪些流,指出哪些流是节点流,那些流是处理流(2分)
(1)将c:\offline_FtnInfo.txt的内容显示在控制台上。
(2)程序中使用了FileInputStream、InputStreamReader、BufferedReader等流,其中InputStreamReader、BufferedReader是处理流。
import java.awt.BorderLayout;
import jaba.awt.event.*
import javax.swing.*;
public class Ex8_10_UseButtonEvent{
public static void main(String[]args){
JFrame frm = new Jframe("理解事件处理“);
frm.setLayout(null);
JButton btn = new JButton("click me");
frm.getContentPane().add(btn);
ButtonHandler btnHandler = new ButtonHandler();
btn.addActionListener(btnHandler); //A行
btn.setBounds(100,50,110,30);
frm.setBounds(400,200,400,200);
frm.setVisible(true); //B行
}
}
class ButtonHandler implements ActionListenner{
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e){
System.out.println("clicked me");
}
}
(1)该程序实现的功能是什么(4分)
(2)若要实现点击“click me”按钮,按钮上的文本内容变为“clicked me”,则actionPerformed()方法该如何实现?(4分)
(1)产生一个窗体,在窗体上有一个按钮,点击按钮后,控制台输出“click me”
(2)JButton jb=(JButton)e.getSource();
jb.setText(“clicked me”);
public class Ex_superUse{
static int n = 10; //A行
public static void main(String[]args){
SubClass sc1 = new SubClass(n);
SubClass sc2 = new SubClass();
}
}
class SuperClass{
private int n;
SuperClass(){
//B行
System.out.println("SuperClass()");
}
SuperClass(int n){
System.out.println("SuperClass("+n+")");
this.n = n;
}
}
class SubClass extends SuperClass{
private int n;
SubClass(int n){
System.out.println("SubClass("+n+")");
this.n = n;
}
SubClass(){
System.out.println("SubClass()");
}
}
(1)写出上述程序的运行结果
(2)A行中static关键字是什么含义,可否去掉static关键字,为什么?
正确答案
(1)SuperClass()
SubClass(10)
SuperClass()
SubClass()
(2)不能,main方法是类方法,不能调用实例变量
public class TestFile{
public static void main(Stringp[]args) throws IOException{
InputStream is = new FileInputStream(arges[0]);
InputStreamReader in = new InputStreamReader(is);
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(in);
String str;
int c = 0;
while((str = br.readLine()!=null){
System.out.println(str);
}
}
}
(1)该程序的功能是什么?
(2)请用符合规定的Java文件名命名该文件。
(3)上述程序中FileInputStream是节点流还是处理流
(1)该程序的功能是从控制台输入一个文件名,并将给文件内容输出到控制台。
(2)TestFile.java
(3)上述程序中FileInputStream是节点流
public class CatchException{
public static void main(String args[]){
int a,b,c;
a = 9;
b = 0;
try{
c = a/b;
System.out.println(a+"/"+b+"="+c);
}catch(ArithmeticException e){
//A行
System.out.println("出现被0除的异常情况");
}catch(Exception e){
//B行
System.out.println("异常类型为"+e);
}finally{
System.out.println("除数="+a);
System.out,println("被除数="+b);
}
}
}
(1)写出上述程序运行结果
(2)A行中的异常类型可以与B行中的异常类型交换吗?请解释原因
(1) 出现被0除的异常情况 除数 = 9 被除数=0
(2)不可以,父类应该在子类的后面。
import java.io.*
public class Example3{
public static void main(String[]args){
InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(System.in);
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(isr);
FileWriter fout = new FileWriter(".\\buffer.txt");
BufferedWriter bout = new BufferedWriter(fout);
String str;
while(true){
str = br.readLine();
if(str.equals("end"))
break;
bout.write(str);
bout newLine();
}
bout.close();
FileReader fin = new FileReader(".\\buffer.txt");
BufferedReader bin = new BufferedReader(fin);
while(str = bin.readLine()!=null)
System.out.println(str);
bin.close();
}
}
(1)以上程序是否需要进行异常处理?如果需要,说明如何进行异常处理才能使程序正常运行
(2)简述上述程序实现的功能
(1)需要异常处理。要么在main函数后面增加throwsIOException进行异常声明,要么在main函数中利用try-catch-finally语句进行异常处理
(2)将用户从控制台输入的字符串写到文件buffer.txt中,直到用户输入end为止。最后,读取文本文件buffer中的数据,并将其按行打印出来
问答题
1.什么是类变量和类方法?简述类变量和实例变量的区别,以及类方法与实例方法的区别?
类变量是指用static关键字修饰的成员变量;
类方法是指用static关键字修饰的成员方法;
类变量与类方法既可以使用类名直接调用,也可以通过实例对象调用;
实例变量与实例方法只能通过实例对象调用。
2.类方法与实例方法有什么区别?类方法能调用实例方法吗?
被static修饰的成员方法称为类方法,没有被static修饰的方法为实例方法。
类方法与类变量都依赖类而非对象,可以不创建对象直接通过类来调用访问,类方法不能调用实例方法.
3.分别说明final关键字可以修饰的成分有哪些?这些成分被该关键字修饰后都分别具有哪些特性?
final可以修饰类,此类不能派生子类
final可以修饰变量,常量,只能初始赋值;
final可以修饰方法,此方法不能被重写
4.解释类变量,类方法与实例变量和方法的区别
类变量,类方法被static修饰,普通变量和方法没有;
类变量,类方法可以被类名和实例对象直接调用,普通变量和方法只能被实例对象调用;
类变量,类方法属于整个类,只有一个空间内存,储存数据,普通变量和方法每个变量都有属于自己的空间内存
类方法内只能使用类变量,普通方法可以使用类变量和普通变量
类方法内不能使用this,普通方法可以使用this
5.简述线程5种状态及其含义。
新建状态(New):线程对象被创建后,就进入了新建状态。例如,Thread thread = new Thread()。
就绪状态(Runnable):也被称为“可执行状态”。线程对象被创建后,其他线程调用了该对象的start()方法,从而来启动该线程,例如,threa.start()。处于就绪状态下的线程,随时可能被CPU调度执行。
运行状态(Running):线程获取CPU权限进行执行。需要注意的是,线程只能从就绪状态进入到运行状态。
阻塞状态(Blocked):阻塞状态是线程因为某种原因放弃CPU使用权,暂时停止运行。直到线程进入就绪状态,才有机会转到运行状态
死亡状态(Dead):线程执行完了或者因异常退出了run()方法,该线程结束生命周期。
6.简述编写GUI编程中容器与布局的概念及其常用的组件。
容器:是用来组织或容纳其他组件和容器的特殊组件,是用容器类(Container类)创建的对象。
布局:负责管理组件在容器中的排放顺序。
常用的组件:按钮(JButton)、单选按钮(JRadioButton)、复选按钮(JCheckBox)、标签(JLabel)、文本域(JTextField)、列表(JList)、组合框(JComboBox)、菜单(JMenu)等。
窗体底端
7简述Java如何实现多态性(包括静态多态与动态多态)。
静态多态通过方法重载实现
动态多态通过方法覆盖和上转型实现
8类方法与实例方法有什么区别?类方法能调用实例方法吗?
类方法是被static修饰的成员方法(1分)
没有被static修饰的成员方法是实例方法(1分)
类方法可以不需要重建实例对象,直接通过类名调用(1分)
类方法不能调用实例方法(1分)
9Java提供实现Runnable接口或继承Thread类两种方法实现线程,请简述如何通过继承Thread类来实现多线称。
(1)创建一个类继承(extend)Thread类,定义线程的构造方法;
(2)用需在此线程中执行的代码覆盖Thread类的run()方法;
(3)用关键字new创建所定义的线程类的一个实例化对象;
(4)调用该对象的start()方法启动线程。
10.Java多态性包括静态多态与动态多态,简述这两种多态的实现机制。
多态性包括静态多态和动态多态两种。
静态多态性主要通过方法重载实现,它们根据参数表(类型以及个数)区别语义和执行的功能
动态多态性是指定义在一个类层次的不同类中的重写函数,他们具有相同的函数原型,需要根据指针指向的对象所在类来区别语义。其实现需要具备两个条件:(1)子类继承父类,并重写父类方法;(2)父类引用指向子类对象
11.简述Java的事件处理机制。
用户点击特定组件时,会触发特定事件,用户必须实现处理该事件的监听器接口,并通过实现监听器接口中的方法完成时事件处理,最后需要调用事件源中的addXxxListener方法来注册监听器。
12.简述抽象类和接口的定义?抽象类和接口在具体使用过程中与具体类有哪些区别?
抽象类需要使用关键字abstract修饰,抽象类中可能包含抽象方法,也可能不包含抽象方法;
接口通过inerface修饰,接口中的成员变量默认为public static final(常量),接口中的成员方法都是抽象方法;
抽象类和接口不能直接实例化,必须新建一个具体类来继承抽象类并实现抽象类中所有的抽象方法,或者实现接口并实现接口中的所有抽象方法,然后才能新建对象,进而调用其中的成员函数和成员变量。
13.画出线程生命周期图,并注明每种状态之间的转换条件
①调用start()方法
②运行yield()方法
③获得CPU
④资源缺少,sleep()方法,wait()方法等
⑤获得资源,睡眠时间到,notify()方法
⑥线程结束,stop()方法,destory()方法.
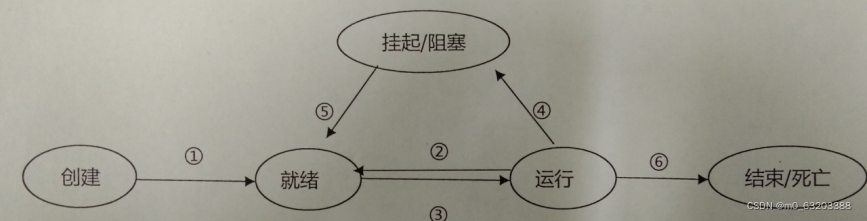 新建状态(New):线程对象被创建后,就进入了新建状态。
新建状态(New):线程对象被创建后,就进入了新建状态。
就绪状态(Runnable):也被称为“可执行状态”。线程对象被创建后,其他线程调用了该对象的start()方法,从而来启动该线程。处于就绪状态下的线程,随时可能被CPU调度执行。
运行状态(Running):线程获取CPU权限进行执行。需要注意的是,线程只能从就绪状态进入到运行状态。
阻塞状态(Blocked):阻塞状态是线程因为某种原因放弃CPU使用权,暂时停止运行。直到线程进入就绪状态,才有机会转到运行状态
死亡状态(Dead):线程执行完了或者因异常退出了run()方法,该线程结束生命周期。
14.Java提供实现Runnable接口或继承Thread类两种方法实现线程,请简述如何通过实现Runnable接口来实现多线程。
(1)创建一个类实现(implements)Runnable接口;
(2)用需在此线程中执行的代码覆盖Thread类的run()方法;
(3)在类中定义一个Thread类对象;
(4)应用Thread类的构造函数Thread(Runnable target)实例化(2)所定义的对象;
(5)调用该对象的start()方法启动线程加粗样式
15.简述this关键字的使用场合。
关键字this代表实例对象自身,有以下几种使用情况:
(1)在类的成员方法中,通过this来访问实例对象的成员变量或调用成员方法;
(2)在类的成员方法中,区分成员变量和局部变量;
(3)在类的成员方法中,使用this返回实例对象本身的引用;
(4)在类的构造方法中,使用this调用该类的其他构造方法。
窗体底端
计算题
编写程序,要求显示一个300*100像素的窗口,窗口中包含三个按钮和一个标签(如下图所示)。当点击第一个按钮时,窗口标签中显示“button1 is pressed”;当点击第二个按钮时,窗口标签中显示“button2 is pressed”;当点击第三个按钮时,窗口标签中显示“button3 is pressed”.
import java.awt.*;
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
public class TestFrame{
public static void main (String[] args){
//TODD Auto-generated method stub
new MyFrame().load();
}
}
class MyFrame extends JFrame{
JButton btn1,btn2,btn3;
Jlabel lab;
public MyFrame (){
btn1 = new JButton("button1");
btn2 = new JButton("button2");
btn3 = new JButton("button3");
lab = new JLabel("button1 is pressed");
}
void load(){
this.setLayout(new FlowLayout());
lab.setSize(300,50);
this.add(lab);
this.add(btn1);
this.add(btn2);
this.add(btn3);
btn1.addActionListener(new MyMonitor());
btn2.addActionListener(new MyMonitor());
btn3.addActionListener(new MyMonitor());
this.setBounds(200,300,250,100);
this. setVisible(true);
}
class MyMonitor implements ActionListener{
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e){
JButton b = (JButton)e.getSource();
lab.setText(" "+b.getText()+"is pressed");
}
}
}
创建一个复数类complex,进行数学运算,复数具有如下格式:
RealPart+ImaginaryRart*I,其中,I为-1的平方根
要求如下:
①利用浮点类型的变量表示该类的私有数据,且提供两个构造方法:一个为无参的构造方法(要求吧复数的实部和虚部均初始化为0);另一个用于对该类对象进行指定值初始化
②提供量复数相加的运算方法
③按格式“(a,b)”打印所得复数的结果,其中a为实部,b为虚部
class Complex{
float realPart;
float imaginPart;
public Complex(){
realPart=0;
imaginPart=0;
}
public Complex(float a,float b){
realPart =a;
imaginPart=b;
}
void sub(Complex c1){
realPart+=c1.realPart;
imaginPart+=c1.imaginPart;
System.out.println("("+realPart+","+imaginPart+")");
}
}
编写一个有关多态的程序。
功能要求:
(1)定义一个名为Number的类和名为INumber的接口,前者实现后者;
(2)INmuber接口中至少两个名字相同的max()方法,其中,一个支持返回2个整型数中的较大者,另一个支持返回2个双精度浮点中的较大者;
(3)在Number类中实现每一个max()方法。
(4)要求写出测试该功能的Exam2类(该包含main()方法)。
public interface INumber
{
abstract int max(int a,int b);
abstract double max(double a,double b);
}
public class Number implements INumber
{
public int max (int a ,int b) {
return a>b?a:b;}
public double max(double a ,double b){
return a>b?a:b;}
}
public class Exam2 {
public static void main(String[]args)
{
Number testa= new Number();
System.out.println(testa.min(5,4));
System.out.println(testa.min(11.9,20.87));
}
}
import java.io.*
public class Example3{
public static void main(String[]args){
InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(System.in);
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(isr);
FileWriter fout = new FileWriter(".\\buffer.txt");
BufferedWriter bout = new BufferedWriter(fout);
String str;
while(true){
str = br.readLine();
if(str.equals("end"))
break;
bout.write(str);
bout newLine();
}
bout.close();
FileReader fin = new FileReader(".\\buffer.txt");
BufferedReader bin = new BufferedReader(fin);
while(str = bin.readLine()!=null)
System.out.println(str);
bin.close();
}
}
(1)以上程序是否需要进行异常处理?如果需要,说明如何进行异常处理才能使程序正常运行
(2)简述上述程序实现的功能
(1)需要异常处理。要么在main函数后面增加throwsIOException进行异常声明,要么在main函数中利用try-catch-finally语句进行异常处理
(2)将用户从控制台输入的字符串写到文件buffer.txt中,直到用户输入end为止。最后,读取文本文件buffer中的数据,并将其按行打印出来
创建一个Fraction类执行分数运算,要求如下:
1.包含两个double类型的私有成员变量,f1(分子),f2(分母);
2.提供两个构造函数,一个是无参构造函数(初始化分子分母为1.0),另外一个构造函数Fraction(double f1, double f2),用来初始化f1和f2;
3.提供浮点数的形式输出分数的方法printF1;
4.提供以a/b的形式输出人数的方法printF2;
5.提供两个分数相加add,减subtract,乘multiply,除divide的公有方法;
6.编写Fraction的子类FractionSub,重写父类的无参构造函数,初始化分子为2,分母为3,并以a/b形式输出分数。
7.编写测试类FractionTest测试分数类中的各公有方法,测试FractionSub类中的无参构造函数。
class Fraction{
double f1;
double f2;
public Fraction() {
f1=1.0;
f2=1.0;
}
public Fraction(double f1, double f2) {
this.f1=f1;
this.f2=f2;
}
public void printF1() {
System.out.println("Printing the fraction in the form of the float number:" +f1/f2);
}
public void printF2() {
System.out.println("Printing the fraction in the a/b form:"+f1+"/"+f2);
}
public Fraction add(Fraction anotherF1) {
double numerator=this.f1*anotherF1.f2+this.f2*anotherF1.f1;
double denominator=this.f2*anotherF1.f2;
return new Fraction(numerator,denominator);
}
public Fraction subtract(Fraction anotherF1) {
return add(new Fraction(-1.0*anotherF1.f1,anotherF1.f2));
}
public Fraction multiply(Fraction anotherF1) {
return new Fraction(this.f1*anotherF1.f1,this.f2*anotherF1.f2);
}
public Fraction divide(Fraction anotherF1) {
return new Fraction(this.f1*anotherF1.f2,this.f2*anotherF1.f1);
}
}
class FractionSub extends Fraction{
public FractionSub() {
super(2.0,3.0);
}
}
public class FractionTest{
public static void main(String[]args) {
Fraction frac1=new Fraction();
Fraction frac2=new Fraction(2.0,1.0);
frac1.printF1();
frac1.printF2();
frac2.printF1();
frac2.printF2();
frac1.add(frac2).printF1();
frac1.subtract(frac2).printF1();
frac1.multiply(frac2).printF1();
frac1.divide(frac2).printF1();
}
}
编写一个名为Exmal类,至少包含一个chat()方法,可以实现如下功能
(1)接收来自键盘输入的一句英语(不包含标点符号,各单词间勇敢空格分隔);
(2)单词能立刻逆序回显在屏幕上,并等待输入下一句;
(3)当输入end时结束循环。
效果示例:
Input:My name is White
RevEcho: White is name my
Input:I am a student
RevEcho:student a am I
Input:end
public class Exam1 {
public static void chat()
{
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
While(!text.equals("end")){
System.out.print("Input:");
String text=sc.nextLine();
String str[]= text.replace(':',' ').text.splites("");
System.out.println();
for(int i =str.length-1;i>0;i--)
System.out.println("RevEcho:"+str[i]+"");
}
}
}
定义一个点类(Point)类,该类用来表示三维空间总中的点,该类的要求如下:
①可以生成具有特定坐标的点对象
②可以提供设置三个点坐标的方法
③提供可以获取三个点坐标的方法
④提供可以计算该“点”距原点(0,0,0)距离的方法
class Point{
double x;
double y;
double z;
public Point(){
x=0;
y=0;
z=0;
}
public Point(double x,double y,double z){
this.x=x;
this.y=y;
this.z=z;
}
public void setpoint(double x,double y,double z){
this.x=x;
this.y=y;
this.z=z;
}
public double getx(){
return x;
}
public double gety(){
return y;
}
public double getz(){
return z;
}
public double distant(Point p){
double d=Math.sqrt(p.x*p.x+p.y*p.y+p.z*p.z);
System.out.println("d="+d);
return d;
}
创建一个复数类Complex,复数具有如下格式:RealPart+ImaginaryRart*i,其中,i为-1的平方根。要求如下
(1)包括两个私有成员变量RealPart、ImaginaruPart,分别保存复数的实部和虚部。
(2)提供两个构造方法,public Complex()和public Complex(double a,double b).前者用于将复数的实部和虚部初始化为0,后者用于将复数的实部与虚部分别初始化为a、b.
(3)实现复数相减的运算方法 sub(Complex c)
class Complex{
float realPart;
float imaginPart;
public Complex(){
realPart = 0;
imaginPart = 0;
}
public Complex(float a,float b){
realPart = a;
imaginPart = b;
}
void sub(Complex c1){
realPart-=c1.realPart;
imaginPart-=c1.imaginPart;
}
}
输入一段字符串,统计其中有多少个单词(单词用空格隔开),并输出所有由6个字母组成的单词
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
public class Wordnum{
public static void main(String [] args)throws Exception{
String lineBuffer;
BufferedRead br=new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
while (null !=(lineBuffer=br.readline())){
String words[]=LineBuffer.split(" ");
System.out.println("单词个数为:"+words.length);
for(int i=0,i<words.length;i++){
< p="">
if(words[i].length()==5)
System.out.peintln("长度为5的单词为:”+words[i]);
}
}
}
}
编程实现,从控制台上输入一批数据,以end结束,求这批数据的最大值。
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Test{
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
String number = "";
int max = 0;
do{
number = sc.next();
try{
max = Integer.parseInt(number)>=max?Integer.parseInt(number):max;
}
catch(java.lang.NumberFormatException e){
System.out.println("非法输入");
}
}while(!number.toString().toLowerCase().equals("end"));
System.out.println("Max="+max);
}
}
设计一个多线程程序,一个线程完成打印1到1000之间的所有偶数之和;另一个线程完成打印100到1000之间的三位水仙花数。三位水仙花数的定义如下:假设一个数A的个位、十位与百位分别是X、Y、Z如果A=XXX+YYY+ZZZ,则称A是水仙花数。
public class ThreadExam{
public static void main(String[]args){
Thread th1=new Thread(new Runnable(){
public void run(){
int sum=0;
for(int i=0;i<1000;i+=2)
sum+=i;
System.out.println("sum"+sum);
}
});
Thread th2=new Thread(new Runnable(){
public void run(){
for(int i=100;i<1000;i++){
String tempStr=Integer.toString(i);
int x=Integer.parseInt(tempStr.substring(0,1));
int y=Integer.parseInt(tempStr.substring(1,2));
int z=Integer.parseInt(tempStr.substring(2,3));
if(i==x*x*x+y*y*y+z*z*z)
System.out.println("The flower number:"+i);
}
}
});
th1.start();
th2.start();
}
}
设计一个多线程程序,一个线程完成s=1+2+…+10000,另一个线程计算m=100!,主线程输出s与m的计算结果。
有两个线程,其中主线程计算s,另外一个线程计算m。
public class Test extends Thread{
static long s,m = 1;
public static void main(String[] args){
Test t1 = new Test();
t1.start();
for(int i = 1;i<10000;i++){
< p="">
s+=i;
}
System.out.println("s =" +s);
System.out.println("m =" +m);
}
public void run(){
for(int j = 1;j<=100;j++){
< p="">
m*=j;
}
}
}
通过自己定义一个“点”(Point)类用来表示三维空间中的点(有三个坐标)。完成下面的设计要求:(10分)
(1)可以生成具有特定坐标的点对象。
(2)提供可以设置三个坐标值的方法。
(3)在这个类中提供可以计算该“点”原点距离平方和的方法。
(4)在这个类中提供可以计算该“点”距空间任意一点距离平方和的方法。
class Point{
double x,y,z;
Point(double _x,double _y,double _z){
//构造方法(2分)
x=_x; y=_y; z=_z;
}
void setX(double _x){
//设置方法(2分)
x=_x;
}
double getDistance(Point p){
//计算方法(2分)
return (x-p.x)*(x-p.x)+(y-p.y)*(y-p.y)+(z-p.z)*(z-p.z);
}
}
public class TestPoint{
//测试方法(2分)
public static void main(String[] args) {
Point p=new Point(1.0,2.0,3.0);//对象说明(2分)
Point p1=new Point(0.0,0.0,0.0);
System.out.println(p.getDistance(p1));
p.setX(5.0);
System.out.println(p.getDistance(new Point(1.0,1.0,1.0)));
}
}
在控制台输入一个整数,编写一个程序计算该整数的的各位数字之和。
如: 输入:123456
输出:各位数字之和为1+2+3+4+5+6=21
(1.2分)
import java.util.*;
public class Test1{
public static void main(String[]args){
String str = " ";
System.out.println("请输入一个整数");
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
str = " " +sc.nextInt();
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0;i <= str.length();i++){
int temp = Integer.parseInt(str.charAt(i)+" ");
sum += temp;
}
System.out.println(str+"的各位数之和为:"+sum);
}
在一个窗体对象(Frame)(800600)中添加一个Panel对象(400300)。使用线程控制其从上到下以动画方式进入窗体中。
提示:重点考虑程序的结构控制,对于其中的代码尽可能实现。(20分)
(1)考虑线程的使用;
(2)考虑控制结构的正确使用;
(3)考虑包的引入方式;
(4)考虑异常处理方式;
import java.awt.*;//引入包(2分)
import java.awt.event.*;
public class Test {
static int px,py;
public static void main(String args[]) {
MyFrame fr=new MyFrame(100,100,600,600,Color.green);
MyPanel p=new MyPanel();
p.setBounds(100,50,400,400);
p.setBackground(Color.red);
fr.setBackground(new Color(255,255,255));
fr.addWindowListener( new WindowAdapter(){
//事件处理(4分[匿名类])
public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e){
System.exit(0);
}
});
fr.add(p);//添加对象(2分)
fr.setVisible(true);//对象可见(2分)
for(py=0;py<400;py+=20){
< p="""""""">
p.setBounds(100,py,400,400);
p.run();//方法调用,
}
}
}
class MyFrame extends Frame{
static int id=0;
MyFrame(int x,int y,int w,int h,Color color){
super("MyFrame");
setBackground(color);
setLayout(null);
setBounds(x,y,w,h);
}
}
class MyPanel extends Panel implements Runnable{
public void run(){
try{
Thread.sleep(100);
}catch(InterruptedException e){
return;
}
}
}
创建一个复数类Complex,复数具有如下格式:RealPart + ImaginaryRart*i,其中,i为-1的平方根。要求如下:
(1)包括两个私有成员变量RealPart、ImaginaryRart,分别保存复数的实部和虚部。
(2)提供两个构造方法,public Complex()和public Complex(double a,double b)。前者用于将复数的实部和虚部初始化为0,后者用于将复数的实部与虚部分别初始化为a,b.
(3)实现复数相加的运算方法add(Complex c)。
(4)将该类定义在myMath包中。
package my Math;
public class Complex{
private int ReadPart;
private int ImaginaryPart ;
public Complex(){
this.ReadPart = 0;
this.ImaginaryPart = 0;
}
public Complex(double a,double b){
this.ReadPart = (int)(a);
this.ImaginaryPart = (int)(b);
}
public void add(Complex c){
System.out.println((this.ReadPart+c.ReadPart) +"+"+(this.ImaginaryPart+c.ImaginaryPart)+"i");
}
public static void main(String[] args){
Complex c = new Complex(3,4);
c.add(new Complex(1,1));
}
}