前面我介绍了z3求解器(SMT)和PuLP,前者可以求出指定约束条件下的可行解,后者可用于线性规划求解。链接:
z3求解器
https://blog.csdn.net/as604049322/article/details/120279521使用Python进行线性规划求解
https://blog.csdn.net/as604049322/article/details/120359951
今天我要介绍的是谷歌开发的用于解求解最优化问题的软件OR-Tools:
OR-Tools简介
它主要包含以下4个方面的求解器:
- 约束优化(Constraint Programming):用于计算可行解,与z3求解器的功能类似。
https://developers.google.cn/optimization/cp - 线性规划(Linear and Mixed-Integer Programming):与PuLP库的功能类似。
https://developers.google.cn/optimization/lp - 车辆路线图(Vehicle Routing):计算给定约束条件下最佳车辆路线的专用库。
https://developers.google.cn/optimization/routing - 网络流(Graph Algorithms):用于求解最大流量和最小成本流等问题。
https://developers.google.cn/optimization/flow
OR-Tools包含一部分z3求解器和PuLP的功能,安装它:
pip install ortools -U
我个人在安装过程中出现了:
ERROR: google-api-core 1.30.0 has requirement six>=1.13.0, but you'll have six 1.12.0 which is incompatible.
这需要升级six的版本再重新安装google-api-core:
pip install six -U
pip install google-api-core==1.30.0
所以在安装前,最好先升级six。
下面我们逐个看看这些求解器:
约束优化(CP)
约束编程,即constraint programming,简称CP。CP 是找到一个可行的解决方案,而不是找到一个最优的解决方案,它关注约束和变量,一般没有目标函数,即使有目标也仅仅是增加约束条件,将一大堆可能的解决方案缩小到一个更易于管理的子集。
入门示例
有三个变量xyz,取值范围0、1或2,约束为x ≠ y。求出可行解:
from ortools.sat.python import cp_model
# 声明模型
model = cp_model.CpModel()
# 创建变量,同时限制变量范围
x = model.NewIntVar(0, 2, 'x')
y = model.NewIntVar(0, 2, 'y')
z = model.NewIntVar(0, 2, 'z')
# 创建约束
model.Add(x != y)
# 调用规划求解器
solver = cp_model.CpSolver()
# 设置规划求解器的最长计算时间
# solver.parameters.max_time_in_seconds = 10
status = solver.Solve(model)
# 判断是否存在有效的解
if status == cp_model.OPTIMAL or status == cp_model.FEASIBLE:
print('x =', solver.Value(x), ', y =',
solver.Value(y), ', z =', solver.Value(z))
else:
print('未找到结果')
x = 1 , y = 0 , z = 0
如果某个程序运行时间过长,可以通过max_time_in_seconds参数设置最长计算时间。
在使用z3求解器时,默认情况下也只能获取一个可行解,为了获取多个解,我采用了不断添加约束不允许为上一个解,才获取到多个解(详见线性规划求解的最后面)。
那么ortools如何获取多个解呢?
答案是通过CpSolverSolutionCallback,下面我们继承CpSolverSolutionCallback编写处理每个结果的方法。
完整代码:
from ortools.sat.python import cp_model
class MyCpSolver(cp_model.CpSolverSolutionCallback):
def __init__(self, variables):
cp_model.CpSolverSolutionCallback.__init__(self)
self.__variables = variables
self.__data = []
def on_solution_callback(self):
self.__data.append([self.Value(v) for v in self.__variables])
def result(self):
return self.__data
# 声明模型
model = cp_model.CpModel()
# 创建变量,同时限制变量范围
x = model.NewIntVar(0, 2, 'x')
y = model.NewIntVar(0, 2, 'y')
z = model.NewIntVar(0, 2, 'z')
# 创建约束
model.Add(x != y)
# 调用规划求解器
solver = cp_model.CpSolver()
myCpSolver = MyCpSolver([x, y, z])
solver.parameters.enumerate_all_solutions = True
status = solver.Solve(model, myCpSolver)
data = myCpSolver.result()
print(solver.StatusName(status), f"共{
len(data)}个解:")
for x, y, z in data:
print(f"x={
x}, y={
y}, z={
z}")
OPTIMAL 共18个解:
x=1, y=0, z=0
x=2, y=0, z=0
x=2, y=0, z=1
x=1, y=0, z=1
x=2, y=1, z=1
x=2, y=1, z=0
x=2, y=1, z=2
x=2, y=0, z=2
x=1, y=0, z=2
x=0, y=1, z=2
x=0, y=1, z=1
x=0, y=2, z=1
x=0, y=2, z=2
x=1, y=2, z=2
x=1, y=2, z=1
x=1, y=2, z=0
x=0, y=2, z=0
x=0, y=1, z=0
如果我们需要在求解器计算出指定数量的解后终止,可以在on_solution_callback方法中调用StopSearch方法,例如在获取5个解后停止:
class MyCpSolver(cp_model.CpSolverSolutionCallback):
def __init__(self, variables):
cp_model.CpSolverSolutionCallback.__init__(self)
self.__variables = variables
self.__data = []
def on_solution_callback(self):
self.__data.append([self.Value(v) for v in self.__variables])
if len(self.__data) >= 5:
self.StopSearch()
def result(self):
return self.__data
密码拼图
给定数学方程:
CP
+ IS
+ FUN
--------
= TRUE
每个字母代表一个数字,希望计算出每个数字所代表的数字,例如:
23
+ 74
+ 968
--------
= 1065
不止一个可行解,现在需要找出所有的可行解。首先可以确定CIFT四个字母不能为零。
完整代码为:
from ortools.sat.python import cp_model
class MyCpSolver(cp_model.CpSolverSolutionCallback):
def __init__(self, variables):
cp_model.CpSolverSolutionCallback.__init__(self)
self.__variables = variables
self.__data = []
def on_solution_callback(self):
self.__data.append([self.Value(v) for v in self.__variables])
def result(self):
return self.__data
model = cp_model.CpModel()
letters = [model.NewIntVar(int(letter in "CIFT"), 9, letter)
for letter in "CPISFUNTRE"]
model.AddAllDifferent(letters)
# CP + IS + FUN = TRUE
c, p, i, s, f, u, n, t, r, e = letters
model.Add(c * 10 + p + i * 10 + s + f * 100 + u * 10 +
n == t * 1000 + r * 100 + u * 10 + e)
solver = cp_model.CpSolver()
myCpSolver = MyCpSolver(letters)
solver.parameters.enumerate_all_solutions = True
status = solver.Solve(model, myCpSolver)
data = myCpSolver.result()
print(f"status={
solver.StatusName(status)},conflicts={
solver.NumConflicts()},"
f"branches={
solver.NumBranches()},耗时:{
solver.WallTime():.4f}s,共{
len(data)}个解")
for x, (c, p, i, s, f, u, n, t, r, e) in enumerate(data, 1):
print(f"第{
x:0>2}解: {
c}{
p} + {
i}{
s} + {
f}{
u}{
n} = {
t}{
r}{
u}{
e}")
status=OPTIMAL,conflicts=179,branches=828,耗时:0.0101s,共72个解
第01解: 64 + 35 + 928 = 1027
第02解: 34 + 65 + 928 = 1027
第03解: 34 + 68 + 925 = 1027
第04解: 32 + 67 + 985 = 1084
......
第72解: 65 + 32 + 987 = 1084
数学运算
二元一次方程
比如使用z3解二元一次方程:
x − y = 3 x-y = 3 x−y=3
3 x − 8 y = 4 3x-8y=4 3x−8y=4
from ortools.sat.python import cp_model
model = cp_model.CpModel()
x = model.NewIntVar(cp_model.INT32_MIN, cp_model.INT32_MAX, 'x')
y = model.NewIntVar(cp_model.INT32_MIN, cp_model.INT32_MAX, 'y')
model.Add(x-y == 3)
model.Add(3*x-8*y == 4)
solver = cp_model.CpSolver()
status = solver.Solve(model)
if status == cp_model.OPTIMAL or status == cp_model.FEASIBLE:
print('x =', solver.Value(x), ', y =', solver.Value(y))
x = 4 , y = 1
线性多项式约束
约束条件为:
x > 2 y < 10 x + 2 ∗ y = 7 x > 2 \\ y < 10 \\ x + 2 * y = 7 \\ x>2y<10x+2∗y=7
上述约束x和y都是整数:
from ortools.sat.python import cp_model
model = cp_model.CpModel()
x = model.NewIntVar(2, 7, 'x')
y = model.NewIntVar(0, 3, 'y')
model.Add(x + 2*y == 7)
solver = cp_model.CpSolver()
status = solver.Solve(model)
if status == cp_model.OPTIMAL or status == cp_model.FEASIBLE:
print('x =', solver.Value(x), ', y =', solver.Value(y))
x = 7 , y = 0
八皇后问题
有一个 8x8 的棋盘,希望往里放 8 个棋子(皇后),每个棋子所在的行、列、对角线都不能有另一个棋子。
下图中左图是满足条件的一种方法,又图是不满足条件的。八皇后问题就是期望找到满足这种要求的放棋子方式:
前面我已经演示了使用z3求解的解法,下面我们看看OR-Tools如何求解八皇后问题,完整代码如下:
import time
from ortools.sat.python import cp_model
class NQueenSolutionPrinter(cp_model.CpSolverSolutionCallback):
def __init__(self, queens):
cp_model.CpSolverSolutionCallback.__init__(self)
self.__queens = queens
self.__solution_count = 0
def solution_count(self):
return self.__solution_count
def on_solution_callback(self):
current_time = time.time()
self.__solution_count += 1
print(f" --------- {
self.solution_count()} ---------- ")
for queen in self.__queens:
for i in range(8):
if i == self.Value(queen):
print(end="Q ")
else:
print(end="* ")
print()
model = cp_model.CpModel()
# 每个皇后必须在不同的行中,记录每行对应的皇后对应的列位置
queens = [model.NewIntVar(0, 7, f'Q_{
i}') for i in range(8)]
# 每列最多一个皇后
model.AddAllDifferent(queens)
# 对角线约束
model.AddAllDifferent([queens[i] + i for i in range(8)])
model.AddAllDifferent([queens[i] - i for i in range(8)])
solver = cp_model.CpSolver()
solution_printer = NQueenSolutionPrinter(queens)
solver.parameters.enumerate_all_solutions = True
solver.Solve(model, solution_printer)
statistics=f"""
Statistics
conflicts : {
solver.NumConflicts()}
branches : {
solver.NumBranches()}
耗时 :{
solver.WallTime():.4f} s
共找到 : {
solution_printer.solution_count()}个解"""
print(statistics)
结果:
--------- 1 ---------
* * * * Q * * *
* * * * * * * Q
* * * Q * * * *
Q * * * * * * *
* * Q * * * * *
* * * * * Q * *
* Q * * * * * *
* * * * * * Q *
--------- 2 ---------
* * Q * * * * *
* * * * * * * Q
* * * Q * * * *
* * * * * * Q *
Q * * * * * * *
* * * * * Q * *
* Q * * * * * *
* * * * Q * * *
......
--------- 92 ---------
* Q * * * * * *
* * * * * * Q *
* * Q * * * * *
* * * * * Q * *
* * * * * * * Q
* * * * Q * * *
Q * * * * * * *
* * * Q * * * *
Statistics
conflicts : 496
branches : 1994
耗时 :0.2352 s
共找到 : 92个解
可以看到ortools在很短的时间内已经计算出92个解。
解数独
有一个数独:
board = [
[0, 0, 0, 6, 0, 0, 0, 3, 0],
[5, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 6, 0, 0],
[0, 9, 0, 0, 0, 5, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 4, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 6],
[0, 0, 0, 4, 0, 3, 0, 0, 0],
[8, 0, 0, 0, 9, 0, 5, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 7, 0, 0, 0, 4, 0],
[0, 0, 5, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 8],
[0, 3, 0, 0, 0, 8, 0, 0, 0]
]
0表示还没有填值的空位,现在通过ortools求解它:
from ortools.sat.python import cp_model
model = cp_model.CpModel()
# 9x9 整数变量矩阵,数值范围1-9
X = [[model.NewIntVar(1, 9, 'x') for j in range(9)]
for i in range(9)]
# 每行每个数字最多出现一次
for i in range(9):
model.AddAllDifferent(X[i])
# 每列每个数字最多出现一次
for j in range(9):
model.AddAllDifferent([X[i][j] for i in range(9)])
# 每个 3x3 方格每个数字最多出现一次
for i0 in range(3):
for j0 in range(3):
constraint = [X[3*i0 + i][3*j0 + j]
for i in range(3) for j in range(3)]
model.AddAllDifferent(constraint)
def solveSudoku(board: list):
for i in range(9):
for j in range(9):
if board[i][j] == 0:
continue
model.Add(X[i][j] == board[i][j])
solver = cp_model.CpSolver()
status = solver.Solve(model)
if status != cp_model.OPTIMAL and status != cp_model.FEASIBLE:
print("无正确的解")
return
r = [[solver.Value(X[i][j]) for j in range(9)] for i in range(9)]
return r
solveSudoku(board)
结果:
[[7, 4, 1, 6, 2, 9, 8, 3, 5],
[5, 8, 2, 3, 4, 1, 6, 9, 7],
[3, 9, 6, 8, 7, 5, 4, 2, 1],
[9, 2, 4, 5, 1, 7, 3, 8, 6],
[6, 5, 7, 4, 8, 3, 2, 1, 9],
[8, 1, 3, 2, 9, 6, 5, 7, 4],
[1, 6, 8, 7, 5, 2, 9, 4, 3],
[2, 7, 5, 9, 3, 4, 1, 6, 8],
[4, 3, 9, 1, 6, 8, 7, 5, 2]]
护士排班问题
医院主管需要为四名护士制定为期三天的时间表,条件:
- 每天三班倒,每班8小时
- 每天的每个班次分配给一个护士,每个护士每天最多工作一个班次
- 每个护士在三天内至少被分配到两个班次
完整代码:
import math
from ortools.sat.python import cp_model
# 4个护士,3天,3个班次
num_nurses, num_shifts, num_days = 4, 3, 3
all_nurses, all_days, all_shifts = range(4), range(3), range(3)
model = cp_model.CpModel()
# 定义第n个护士第d天s班次是否被安排,1表示被分配
shifts = {
}
for n in all_nurses:
for d in all_days:
for s in all_shifts:
shifts[(n, d, s)] = model.NewBoolVar(f'n{
n}d{
d}s{
s}')
# 每天的每个班次分配给一个护士
for d in all_days:
for s in all_shifts:
model.Add(sum(shifts[(n, d, s)] for n in all_nurses) == 1)
# 每个护士每天最多工作一个班次
for n in all_nurses:
for d in all_days:
model.Add(sum(shifts[(n, d, s)] for s in all_shifts) <= 1)
# 从平均分配的角度看,计算每个护士应该被排班的班次次数
shifts_per_nurse = (num_shifts * num_days) / num_nurses
min_shifts_per_nurse = math.floor(shifts_per_nurse)
max_shifts_per_nurse = math.ceil(shifts_per_nurse)
# 每个护士在三天内至少被分配到两个班次
for n in all_nurses:
num_shifts_worked = [shifts[(n, d, s)]
for d in all_days for s in all_shifts]
model.Add(min_shifts_per_nurse <= sum(num_shifts_worked))
model.Add(sum(num_shifts_worked) <= max_shifts_per_nurse)
# 求解某个可行解
solver = cp_model.CpSolver()
status = solver.Solve(model)
if status == cp_model.OPTIMAL or status == cp_model.FEASIBLE:
for d in all_days:
print(f"第{
d+1}天")
for n in all_nurses:
is_working = False
for s in all_shifts:
if not solver.Value(shifts[(n, d, s)]):
continue
is_working = True
print(f'{
n}号护士,安排在第{
s}个班次')
if not is_working:
print(f'{
n}号护士,今天没有上班')
结果:
第1天
0号护士,今天没有上班
1号护士,安排在第1个班次
2号护士,安排在第0个班次
3号护士,安排在第2个班次
第2天
0号护士,安排在第1个班次
1号护士,今天没有上班
2号护士,安排在第2个班次
3号护士,安排在第0个班次
第3天
0号护士,安排在第1个班次
1号护士,安排在第0个班次
2号护士,今天没有上班
3号护士,安排在第2个班次
如果我们需要获取多个解时:
class NursesPartialSolutionPrinter(cp_model.CpSolverSolutionCallback):
def __init__(self, limit):
cp_model.CpSolverSolutionCallback.__init__(self)
self._solution_count = 0
self._solution_limit = limit
def on_solution_callback(self):
self._solution_count += 1
print(f'-----------{
self._solution_count}-----------')
for d in all_days:
print(f"第{
d+1}天")
for n in all_nurses:
is_working = False
for s in all_shifts:
if not self.Value(shifts[(n, d, s)]):
continue
is_working = True
print(f'{
n}号护士,安排在第{
s}个班次')
if not is_working:
print(f'{
n}号护士,今天没有上班')
if self._solution_count >= self._solution_limit:
self.StopSearch()
def solution_count(self):
return self._solution_count
solver.parameters.linearization_level = 0
solver.parameters.enumerate_all_solutions = True
solution_printer = NursesPartialSolutionPrinter(limit=3)
solver.Solve(model, solution_printer)
statistics = f"""
Statistics
conflicts : {
solver.NumConflicts()}
branches : {
solver.NumBranches()}
耗时 :{
solver.WallTime():.4f} s
共找到 : {
solution_printer.solution_count()}个解"""
print(statistics)
-----------1-----------
第1天
0号护士,今天没有上班
1号护士,安排在第0个班次
2号护士,安排在第1个班次
3号护士,安排在第2个班次
第2天
0号护士,安排在第2个班次
1号护士,今天没有上班
2号护士,安排在第1个班次
3号护士,安排在第0个班次
第3天
0号护士,安排在第2个班次
1号护士,安排在第1个班次
2号护士,安排在第0个班次
3号护士,今天没有上班
-----------2-----------
第1天
0号护士,安排在第0个班次
1号护士,今天没有上班
2号护士,安排在第1个班次
3号护士,安排在第2个班次
第2天
0号护士,今天没有上班
1号护士,安排在第2个班次
2号护士,安排在第1个班次
3号护士,安排在第0个班次
第3天
0号护士,安排在第2个班次
1号护士,安排在第1个班次
2号护士,安排在第0个班次
3号护士,今天没有上班
-----------3-----------
第1天
0号护士,安排在第0个班次
1号护士,今天没有上班
2号护士,安排在第1个班次
3号护士,安排在第2个班次
第2天
0号护士,安排在第1个班次
1号护士,安排在第2个班次
2号护士,今天没有上班
3号护士,安排在第0个班次
第3天
0号护士,安排在第2个班次
1号护士,安排在第1个班次
2号护士,安排在第0个班次
3号护士,今天没有上班
Statistics
conflicts : 5
branches : 118
耗时 :0.0039 s
共找到 : 3个解
cp_model无法求解的问题
之前的z3求解器求解速度是远不如ortools,但是ortools的cp_model相对z3也有很多缺陷,例如只能创建整数变量,不支持非线性运算,缺少逻辑和依赖的api。这导致了一些z3能够解决的问题,ortools的cp_model却无法解决。例如:
- 非线性多项式约束
- 高中物理匀变速直线运动相关问题
- 安装依赖问题
- 逻辑题:谁是盗贼 和 煤矿事故
但cp_model不仅能求解整数约束问题还能求解整数规划问题:
在以下约束下:
x + 7 y ≤ 17.5 x ≤ 3.5 x ≥ 0 y ≥ 0 x + 7y ≤ 17.5 \\ x ≤ 3.5 \\ x ≥ 0 \\ y ≥ 0 \\ x+7y≤17.5x≤3.5x≥0y≥0
求x+10y的最大值:
from ortools.sat.python import cp_model
model = cp_model.CpModel()
x = model.NewIntVar(0, cp_model.INT32_MAX, 'x')
y = model.NewIntVar(0, cp_model.INT32_MAX, 'y')
# 定义约束条件
model.Add(x + 7 * y < 18)
model.Add(x < 4)
# 定义目标函数
model.Maximize(x + 10 * y)
solver = cp_model.CpSolver()
status = solver.Solve(model)
if status == cp_model.OPTIMAL or status == cp_model.FEASIBLE:
print(f'x={
solver.Value(x)}, '
f'y={
solver.Value(y)}, '
f'max(x+10y)={
solver.ObjectiveValue():.2f}')
else:
print('无解')
x=3, y=2, max(x+10y)=23.00
线性规划(LP)
线性规划,即 Linear optimization,用来计算一个问题的最佳解决方案,问题被建模为一组线性关系。 OR-Tools提供的求解LP问题的方法是MPSolver,链接:https://developers.google.cn/optimization/lp/mpsolver
入门示例
在以下约束下:
x + 2 y ≤ 14 3 x – y ≥ 0 x – y ≤ 2 x + 2y ≤ 14 \\ 3x – y ≥ 0 \\ x – y ≤2 \\ x+2y≤143x–y≥0x–y≤2
求3x+4y的最大值。
完整代码:
from ortools.linear_solver import pywraplp
# 创建默认的GLOP求解器
solver = pywraplp.Solver.CreateSolver('GLOP')
# 搜索时间限制为15秒
solver.set_time_limit(15)
x = solver.NumVar(0, solver.infinity(), 'x')
y = solver.NumVar(0, solver.infinity(), 'y')
# 定义约束条件
solver.Add(x + 2 * y <= 14.0)
solver.Add(3 * x - y >= 0.0)
solver.Add(x - y <= 2.0)
print('变量数量:', solver.NumVariables())
print('约束数量:', solver.NumConstraints())
# 定义目标函数
solver.Maximize(3 * x + 4 * y)
# 调用求解器
status = solver.Solve()
if status == pywraplp.Solver.OPTIMAL:
print(f'x={
x.solution_value():.2f}, '
f'y={
y.solution_value():.2f}, '
f'max(3x+4y)={
solver.Objective().Value():.2f}')
else:
print('无最优解')
变量数量: 2
约束数量: 3
x=6.00, y=4.00, max(3x+4y)=34.00
对于上述问题如果是整数约束,还可以使用上一节的CP库(CP-SAT 求解器要求所有的约束和目标必须是整数)来解决,代码如下:
from ortools.sat.python import cp_model
model = cp_model.CpModel()
x = model.NewIntVar(0, cp_model.INT32_MAX, 'x')
y = model.NewIntVar(0, cp_model.INT32_MAX, 'y')
# 定义约束条件
model.Add(x + 2 * y <= 14)
model.Add(3 * x - y >= 0)
model.Add(x - y <= 2)
# 定义目标函数
model.Maximize(3 * x + 4 * y)
solver = cp_model.CpSolver()
status = solver.Solve(model)
if status == cp_model.OPTIMAL or status == cp_model.FEASIBLE:
print(f'x={
solver.Value(x)}, '
f'y={
solver.Value(y)}, '
f'max(3x+4y)={
solver.ObjectiveValue()}')
else:
print('无解')
x=6, y=4, max(3x+4y)=34.0
MIP 求解器求解整数规划问题
LP求解器(例如上面使用的GLOP)变量结果是可以会得到非整数的,对于严格整数规划问题,除了使用CP-SAT 求解器外还可以使用MIP 求解器(例如SCIP)。
**示例1:**在以下约束下:
x + 7 y ≤ 17.5 x ≤ 3.5 x ≥ 0 y ≥ 0 x + 7y ≤ 17.5 \\ x ≤ 3.5 \\ x ≥ 0 \\ y ≥ 0 \\ x+7y≤17.5x≤3.5x≥0y≥0
求x+10y的最大值:
from ortools.linear_solver import pywraplp
# 创建SCIP求解器
solver = pywraplp.Solver.CreateSolver('SCIP')
# 搜索时间限制为15秒
solver.set_time_limit(15)
infinity = solver.infinity()
x = solver.IntVar(0, infinity, 'x')
y = solver.IntVar(0, infinity, 'y')
# 定义约束条件
solver.Add(x + 7 * y <= 17.5)
solver.Add(x <= 3.5)
print('变量数量:', solver.NumVariables())
print('约束数量:', solver.NumConstraints())
# 定义目标函数
solver.Maximize(x + 10 * y)
# 调用求解器
status = solver.Solve()
if status == pywraplp.Solver.OPTIMAL:
print(f'x={
x.solution_value():.2f}, '
f'y={
y.solution_value():.2f}, '
f'max(x+10y)={
solver.Objective().Value():.2f}')
else:
print('无最优解')
结果:
变量数量: 2
约束数量: 2
x=3.00, y=2.00, max(x+10y)=23.00
示例2:
在以下约束下:
5 x 1 + 7 x 2 + 9 x 3 + 2 x 4 + 1 x 5 ≤ 250 18 x 1 + 4 x 2 − 9 x 3 + 10 x 4 + 12 x 5 ≤ 285 4 x 1 + 7 x 2 + 3 x 3 + 8 x 4 + 5 x 5 ≤ 211 5 x 1 + 13 x 2 + 16 x 3 + 3 x 4 − 7 x 5 ≤ 315 \begin{aligned} &5 x_{1}+7 x_{2}+9 x_{3}+2 x_{4}+1 x_{5} \leq 250 \\ &18 x_{1}+4 x_{2}-9 x_{3}+10 x_{4}+12 x_{5} \leq 285 \\ &4 x_{1}+7 x_{2}+3 x_{3}+8 x_{4}+5 x_{5} \leq 211 \\ &5 x_{1}+13 x_{2}+16 x_{3}+3 x_{4}-7 x_{5} \leq 315 \end{aligned} 5x1+7x2+9x3+2x4+1x5≤25018x1+4x2−9x3+10x4+12x5≤2854x1+7x2+3x3+8x4+5x5≤2115x1+13x2+16x3+3x4−7x5≤315
求 7 x 1 + 8 x 2 + 2 x 3 + 9 x 4 + 6 x 5 7 x_{1}+8 x_{2}+2 x_{3}+9 x_{4}+6 x_{5} 7x1+8x2+2x3+9x4+6x5的最大值。
from ortools.linear_solver import pywraplp
# 创建默认的GLOP求解器
solver = pywraplp.Solver.CreateSolver('SCIP')
constraint_coeffs = [
[5, 7, 9, 2, 1],
[18, 4, -9, 10, 12],
[4, 7, 3, 8, 5],
[5, 13, 16, 3, -7],
]
bounds = [250, 285, 211, 315]
obj_coeffs = [7, 8, 2, 9, 6]
infinity = solver.infinity()
x = [solver.IntVar(0, infinity, f'x_{
i}') for i in range(5)]
for constraint_coeff, bound in zip(constraint_coeffs, bounds):
constraint = solver.RowConstraint(0, bound, '')
for xi, coeff in zip(x, constraint_coeff):
constraint.SetCoefficient(xi, coeff)
objective = solver.Objective()
for xi, obj_coeff in zip(x, obj_coeffs):
objective.SetCoefficient(xi, obj_coeff)
objective.SetMaximization()
status = solver.Solve()
if status == solver.OPTIMAL:
print("最大值:", objective.Value())
for xi in x:
print(xi.name(), ' = ', xi.solution_value())
print("耗时:", solver.wall_time(),
",迭代次数:", solver.iterations(),
",branch-and-bound nodes:", solver.nodes())
else:
print('无最优解')
结果:
最大值: 259.99999999999966
x_0 = 8.0
x_1 = 21.0
x_2 = 0.0
x_3 = 2.0
x_4 = 3.0
耗时: 17 ,迭代次数: 71 ,branch-and-bound nodes: 7
斯蒂格勒的饮食问题
斯蒂格勒饮食法要求营养素必须达到的最低标准:
| 营养素 | 每日摄入量 |
|---|---|
| 卡路里(Calories) | 3000卡路里 |
| 蛋白质(Protein) | 70克 |
| 钙(Calcium) | 0.8克 |
| 铁(Iron) | 12毫克 |
| 维生素 A(Vitamin A) | 5000国际单位 |
| 硫胺素(Thiamine, Vitamin B1) | 1.8毫克 |
| 核黄素(Riboflavin, Vitamin B2) | 2.7毫克 |
| 烟酸(Niacin) | 18毫克 |
| 抗坏血酸(Ascorbic Acid, Vitamin C) | 75毫克 |
下表是每种食品的价格和以及一美元购买后所包含的营养素(前9行):
| 日用品 | 单位 | 价格 | 卡路里(千卡) | 蛋白质(克) | 钙(克) | 铁(毫克) | 维生素 A (KIU) | 硫胺素(毫克) | 核黄素(mg) | 烟酸(毫克) | 抗坏血酸(毫克) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 小麦粉 | 10磅 | 36 | 44.7 | 1411 | 2 | 365 | 0 | 55.4 | 33.3 | 441 | 0 |
| 通心粉 | 1磅 | 14.1 | 11.6 | 418 | 0.7 | 54 | 0 | 3.2 | 1.9 | 68 | 0 |
| 小麦谷类 | 28盎司 | 24.2 | 11.8 | 377 | 14.4 | 175 | 0 | 14.4 | 8.8 | 114 | 0 |
| 玉米片 | 8盎司 | 7.1 | 11.4 | 252 | 0.1 | 56 | 0 | 13.5 | 2.3 | 68 | 0 |
| 玉米粉 | 1磅 | 4.6 | 36.0 | 897 | 1.7 | 99 | 30.9 | 17.4 | 7.9 | 106 | 0 |
| 玉米粒 | 24盎司 | 8.5 | 28.6 | 680 | 0.8 | 80 | 0 | 10.6 | 1.6 | 110 | 0 |
| 米饭 | 1磅 | 7.5 | 21.2 | 460 | 0.6 | 41 | 0 | 2 | 4.8 | 60 | 0 |
| 燕麦片 | 1磅 | 7.1 | 25.3 | 907 | 5.1 | 341 | 0 | 37.1 | 8.9 | 64 | 0 |
| 白面包(浓缩) | 1磅 | 7.9 | 15.0 | 488 | 2.5 | 115 | 0 | 13.8 | 8.5 | 126 | 0 |
由于所有的营养素都已经被价格标准化,我们的目标只是简单地最小化食物的总量。
下面我使用pandas辅助计算,首先准备好数据:
from ortools.linear_solver import pywraplp
import pandas as pd
# 最低营养素需求
nutrients = [
['Calories (kcal)', 3],
['Protein (g)', 70],
['Calcium (g)', 0.8],
['Iron (mg)', 12],
['Vitamin A (KIU)', 5],
['Vitamin B1 (mg)', 1.8],
['Vitamin B2 (mg)', 2.7],
['Niacin (mg)', 18],
['Vitamin C (mg)', 75],
]
# 每种食品的价格、重量、价格和所包含的营养素
data = [
['Wheat Flour (Enriched)', '10 lb.', 36, 44.7,
1411, 2, 365, 0, 55.4, 33.3, 441, 0],
['Macaroni', '1 lb.', 14.1, 11.6, 418, 0.7, 54, 0, 3.2, 1.9, 68, 0],
['Wheat Cereal (Enriched)', '28 oz.', 24.2, 11.8,
377, 14.4, 175, 0, 14.4, 8.8, 114, 0],
['Corn Flakes', '8 oz.', 7.1, 11.4, 252, 0.1, 56, 0, 13.5, 2.3, 68, 0],
[
'Corn Meal', '1 lb.', 4.6, 36.0, 897, 1.7, 99, 30.9, 17.4, 7.9, 106,
0
],
[
'Hominy Grits', '24 oz.', 8.5, 28.6, 680, 0.8, 80, 0, 10.6, 1.6,
110, 0
],
['Rice', '1 lb.', 7.5, 21.2, 460, 0.6, 41, 0, 2, 4.8, 60, 0],
['Rolled Oats', '1 lb.', 7.1, 25.3, 907, 5.1, 341, 0, 37.1, 8.9, 64, 0],
[
'White Bread (Enriched)', '1 lb.', 7.9, 15.0, 488, 2.5, 115, 0,
13.8, 8.5, 126, 0
],
[
'Whole Wheat Bread', '1 lb.', 9.1, 12.2, 484, 2.7, 125, 0, 13.9,
6.4, 160, 0
],
['Rye Bread', '1 lb.', 9.1, 12.4, 439, 1.1, 82, 0, 9.9, 3, 66, 0],
['Pound Cake', '1 lb.', 24.8, 8.0, 130, 0.4, 31, 18.9, 2.8, 3, 17, 0],
['Soda Crackers', '1 lb.', 15.1, 12.5, 288, 0.5, 50, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
['Milk', '1 qt.', 11, 6.1, 310, 10.5, 18, 16.8, 4, 16, 7, 177],
[
'Evaporated Milk (can)', '14.5 oz.', 6.7, 8.4, 422, 15.1, 9, 26, 3,
23.5, 11, 60
],
['Butter', '1 lb.', 30.8, 10.8, 9, 0.2, 3, 44.2, 0, 0.2, 2, 0],
['Oleomargarine', '1 lb.', 16.1, 20.6, 17, 0.6, 6, 55.8, 0.2, 0, 0, 0],
['Eggs', '1 doz.', 32.6, 2.9, 238, 1.0, 52, 18.6, 2.8, 6.5, 1, 0],
[
'Cheese (Cheddar)', '1 lb.', 24.2, 7.4, 448, 16.4, 19, 28.1, 0.8,
10.3, 4, 0
],
['Cream', '1/2 pt.', 14.1, 3.5, 49, 1.7, 3, 16.9, 0.6, 2.5, 0, 17],
[
'Peanut Butter', '1 lb.', 17.9, 15.7, 661, 1.0, 48, 0, 9.6, 8.1,
471, 0
],
['Mayonnaise', '1/2 pt.', 16.7, 8.6, 18, 0.2, 8, 2.7, 0.4, 0.5, 0, 0],
['Crisco', '1 lb.', 20.3, 20.1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
['Lard', '1 lb.', 9.8, 41.7, 0, 0, 0, 0.2, 0, 0.5, 5, 0],
[
'Sirloin Steak', '1 lb.', 39.6, 2.9, 166, 0.1, 34, 0.2, 2.1, 2.9,
69, 0
],
['Round Steak', '1 lb.', 36.4, 2.2, 214, 0.1, 32, 0.4, 2.5, 2.4, 87, 0],
['Rib Roast', '1 lb.', 29.2, 3.4, 213, 0.1, 33, 0, 0, 2, 0, 0],
['Chuck Roast', '1 lb.', 22.6, 3.6, 309, 0.2, 46, 0.4, 1, 4, 120, 0],
['Plate', '1 lb.', 14.6, 8.5, 404, 0.2, 62, 0, 0.9, 0, 0, 0],
[
'Liver (Beef)', '1 lb.', 26.8, 2.2, 333, 0.2, 139, 169.2, 6.4, 50.8,
316, 525
],
['Leg of Lamb', '1 lb.', 27.6, 3.1, 245, 0.1, 20, 0, 2.8, 3.9, 86, 0],
[
'Lamb Chops (Rib)', '1 lb.', 36.6, 3.3, 140, 0.1, 15, 0, 1.7, 2.7,
54, 0
],
['Pork Chops', '1 lb.', 30.7, 3.5, 196, 0.2, 30, 0, 17.4, 2.7, 60, 0],
[
'Pork Loin Roast', '1 lb.', 24.2, 4.4, 249, 0.3, 37, 0, 18.2, 3.6,
79, 0
],
['Bacon', '1 lb.', 25.6, 10.4, 152, 0.2, 23, 0, 1.8, 1.8, 71, 0],
['Ham, smoked', '1 lb.', 27.4, 6.7, 212, 0.2, 31, 0, 9.9, 3.3, 50, 0],
['Salt Pork', '1 lb.', 16, 18.8, 164, 0.1, 26, 0, 1.4, 1.8, 0, 0],
[
'Roasting Chicken', '1 lb.', 30.3, 1.8, 184, 0.1, 30, 0.1, 0.9, 1.8,
68, 46
],
['Veal Cutlets', '1 lb.', 42.3, 1.7, 156, 0.1, 24, 0, 1.4, 2.4, 57, 0],
[
'Salmon, Pink (can)', '16 oz.', 13, 5.8, 705, 6.8, 45, 3.5, 1, 4.9,
209, 0
],
['Apples', '1 lb.', 4.4, 5.8, 27, 0.5, 36, 7.3, 3.6, 2.7, 5, 544],
['Bananas', '1 lb.', 6.1, 4.9, 60, 0.4, 30, 17.4, 2.5, 3.5, 28, 498],
['Lemons', '1 doz.', 26, 1.0, 21, 0.5, 14, 0, 0.5, 0, 4, 952],
['Oranges', '1 doz.', 30.9, 2.2, 40, 1.1, 18, 11.1, 3.6, 1.3, 10, 1998],
['Green Beans', '1 lb.', 7.1, 2.4, 138, 3.7, 80, 69, 4.3, 5.8, 37, 862],
['Cabbage', '1 lb.', 3.7, 2.6, 125, 4.0, 36, 7.2, 9, 4.5, 26, 5369],
['Carrots', '1 bunch', 4.7, 2.7, 73, 2.8, 43, 188.5, 6.1, 4.3, 89, 608],
['Celery', '1 stalk', 7.3, 0.9, 51, 3.0, 23, 0.9, 1.4, 1.4, 9, 313],
['Lettuce', '1 head', 8.2, 0.4, 27, 1.1, 22, 112.4, 1.8, 3.4, 11, 449],
['Onions', '1 lb.', 3.6, 5.8, 166, 3.8, 59, 16.6, 4.7, 5.9, 21, 1184],
[
'Potatoes', '15 lb.', 34, 14.3, 336, 1.8, 118, 6.7, 29.4, 7.1, 198,
2522
],
['Spinach', '1 lb.', 8.1, 1.1, 106, 0, 138, 918.4, 5.7, 13.8, 33, 2755],
[
'Sweet Potatoes', '1 lb.', 5.1, 9.6, 138, 2.7, 54, 290.7, 8.4, 5.4,
83, 1912
],
[
'Peaches (can)', 'No. 2 1/2', 16.8, 3.7, 20, 0.4, 10, 21.5, 0.5, 1,
31, 196
],
[
'Pears (can)', 'No. 2 1/2', 20.4, 3.0, 8, 0.3, 8, 0.8, 0.8, 0.8, 5,
81
],
[
'Pineapple (can)', 'No. 2 1/2', 21.3, 2.4, 16, 0.4, 8, 2, 2.8, 0.8,
7, 399
],
[
'Asparagus (can)', 'No. 2', 27.7, 0.4, 33, 0.3, 12, 16.3, 1.4, 2.1,
17, 272
],
[
'Green Beans (can)', 'No. 2', 10, 1.0, 54, 2, 65, 53.9, 1.6, 4.3,
32, 431
],
[
'Pork and Beans (can)', '16 oz.', 7.1, 7.5, 364, 4, 134, 3.5, 8.3,
7.7, 56, 0
],
['Corn (can)', 'No. 2', 10.4, 5.2, 136, 0.2, 16, 12, 1.6, 2.7, 42, 218],
[
'Peas (can)', 'No. 2', 13.8, 2.3, 136, 0.6, 45, 34.9, 4.9, 2.5, 37,
370
],
[
'Tomatoes (can)', 'No. 2', 8.6, 1.3, 63, 0.7, 38, 53.2, 3.4, 2.5,
36, 1253
],
[
'Tomato Soup (can)', '10 1/2 oz.', 7.6, 1.6, 71, 0.6, 43, 57.9, 3.5,
2.4, 67, 862
],
[
'Peaches, Dried', '1 lb.', 15.7, 8.5, 87, 1.7, 173, 86.8, 1.2, 4.3,
55, 57
],
[
'Prunes, Dried', '1 lb.', 9, 12.8, 99, 2.5, 154, 85.7, 3.9, 4.3, 65,
257
],
[
'Raisins, Dried', '15 oz.', 9.4, 13.5, 104, 2.5, 136, 4.5, 6.3, 1.4,
24, 136
],
[
'Peas, Dried', '1 lb.', 7.9, 20.0, 1367, 4.2, 345, 2.9, 28.7, 18.4,
162, 0
],
[
'Lima Beans, Dried', '1 lb.', 8.9, 17.4, 1055, 3.7, 459, 5.1, 26.9,
38.2, 93, 0
],
[
'Navy Beans, Dried', '1 lb.', 5.9, 26.9, 1691, 11.4, 792, 0, 38.4,
24.6, 217, 0
],
['Coffee', '1 lb.', 22.4, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 4, 5.1, 50, 0],
['Tea', '1/4 lb.', 17.4, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 2.3, 42, 0],
['Cocoa', '8 oz.', 8.6, 8.7, 237, 3, 72, 0, 2, 11.9, 40, 0],
['Chocolate', '8 oz.', 16.2, 8.0, 77, 1.3, 39, 0, 0.9, 3.4, 14, 0],
['Sugar', '10 lb.', 51.7, 34.9, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
['Corn Syrup', '24 oz.', 13.7, 14.7, 0, 0.5, 74, 0, 0, 0, 5, 0],
['Molasses', '18 oz.', 13.6, 9.0, 0, 10.3, 244, 0, 1.9, 7.5, 146, 0],
[
'Strawberry Preserves', '1 lb.', 20.5, 6.4, 11, 0.4, 7, 0.2, 0.2,
0.4, 3, 0
],
]
nutrients = pd.DataFrame(nutrients, columns=["name", "min_need"]).set_index("name")
display(nutrients)
columns = ["Commodity", "Unit",
"1939 price (cents)", "Calories (kcal)", "Protein (g)", "Calcium (g)",
"Iron (mg)", "Vitamin A (KIU)", "Vitamin B1 (mg)", "Vitamin B2 (mg)",
"Niacin (mg)", "Vitamin C (mg)"]
data = pd.DataFrame(data, columns=columns)
data.head()
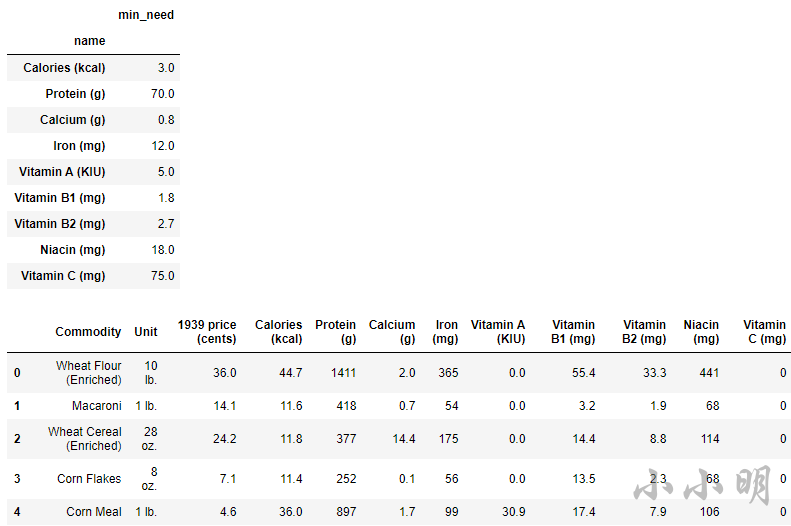
首先创建求解器并申明变量:
# 创建默认的GLOP求解器
solver = pywraplp.Solver.CreateSolver('GLOP')
# 每种食物的消费(美元)
foods = [solver.NumVar(0.0, solver.infinity(), item)
for item in data.Commodity.values]
print("食物种类数:", solver.NumVariables())
食物种类数: 77
下面添加约束并设置目标函数:
constraints = data.iloc[:, 3:].multiply(foods, axis="index").sum()
for constraint, min_nutrients in zip(constraints.values, nutrients.min_need.values):
solver.Add(constraint >= min_nutrients)
print('变量数量:', solver.NumVariables())
print('约束数量:', solver.NumConstraints())
# 定义目标函数
solver.Minimize(solver.Sum(foods))
另一种添加的约束的方法:
# 添加约束 for column in data.columns[3:]: constraint = solver.Constraint( nutrients.at[column, "min_need"], solver.infinity()) for item, food in zip(data[column].astype("float").values, foods): constraint.SetCoefficient(food, item) print('变量数量:', solver.NumVariables()) print('约束数量:', solver.NumConstraints()) # 定义目标函数 objective = solver.Objective() for food in foods: objective.SetCoefficient(food, 1) objective.SetMinimization()与上述代码的最终效果一致。
变量数量: 77
约束数量: 9
下面调用求解器并整理一下结果:
# 调用求解器
status = solver.Solve()
status={
solver.OPTIMAL:"最优解",solver.FEASIBLE:"可行解"}.get(status)
if status is not None:
print(status)
else:
print("无解")
最优解
整理一下结果(每年对指定食品的消费):
result = [(food.name(), food.solution_value()*365)
for food in foods if food.solution_value() != 0]
result = pd.DataFrame(result, columns=["Commodity", "price_per_year"])
print(result)
Commodity price_per_year
0 Wheat Flour (Enriched) 10.774458
1 Liver (Beef) 0.690783
2 Cabbage 4.093269
3 Spinach 1.827796
4 Navy Beans, Dried 22.275426
整理其他结果:
print("一年的最少消费(美元):", result.price_per_year.sum(),
solver.Objective().Value()*365)
curr_nutrient = data.loc[data.Commodity.isin(result.Commodity)].iloc[:, 3:].multiply(
result.price_per_year.values, axis="index").sum()/365
nutrients["curr_nutrient"] = curr_nutrient
print(nutrients)
print(f'耗时:{
solver.wall_time()} ms,迭代次数{
solver.iterations()}')
一年的最少消费(美元): 39.66173154546625 39.66173154546625
min_need curr_nutrient
name
Calories (kcal) 3.0 3.000000
Protein (g) 70.0 147.413535
Calcium (g) 0.8 0.800000
Iron (mg) 12.0 60.466922
Vitamin A (KIU) 5.0 5.000000
Vitamin B1 (mg) 1.8 4.120439
Vitamin B2 (mg) 2.7 2.700000
Niacin (mg) 18.0 27.315981
Vitamin C (mg) 75.0 75.000000
耗时:43 ms,迭代次数14
完整代码:
from ortools.linear_solver import pywraplp
import pandas as pd
# 最低营养素需求
nutrients = [
['Calories (kcal)', 3],
['Protein (g)', 70],
['Calcium (g)', 0.8],
['Iron (mg)', 12],
['Vitamin A (KIU)', 5],
['Vitamin B1 (mg)', 1.8],
['Vitamin B2 (mg)', 2.7],
['Niacin (mg)', 18],
['Vitamin C (mg)', 75],
]
# 每种食品的价格、重量、价格和所包含的营养素
data = [
['Wheat Flour (Enriched)', '10 lb.', 36, 44.7,
1411, 2, 365, 0, 55.4, 33.3, 441, 0],
['Macaroni', '1 lb.', 14.1, 11.6, 418, 0.7, 54, 0, 3.2, 1.9, 68, 0],
['Wheat Cereal (Enriched)', '28 oz.', 24.2, 11.8,
377, 14.4, 175, 0, 14.4, 8.8, 114, 0],
['Corn Flakes', '8 oz.', 7.1, 11.4, 252, 0.1, 56, 0, 13.5, 2.3, 68, 0],
[
'Corn Meal', '1 lb.', 4.6, 36.0, 897, 1.7, 99, 30.9, 17.4, 7.9, 106,
0
],
[
'Hominy Grits', '24 oz.', 8.5, 28.6, 680, 0.8, 80, 0, 10.6, 1.6,
110, 0
],
['Rice', '1 lb.', 7.5, 21.2, 460, 0.6, 41, 0, 2, 4.8, 60, 0],
['Rolled Oats', '1 lb.', 7.1, 25.3, 907, 5.1, 341, 0, 37.1, 8.9, 64, 0],
[
'White Bread (Enriched)', '1 lb.', 7.9, 15.0, 488, 2.5, 115, 0,
13.8, 8.5, 126, 0
],
[
'Whole Wheat Bread', '1 lb.', 9.1, 12.2, 484, 2.7, 125, 0, 13.9,
6.4, 160, 0
],
['Rye Bread', '1 lb.', 9.1, 12.4, 439, 1.1, 82, 0, 9.9, 3, 66, 0],
['Pound Cake', '1 lb.', 24.8, 8.0, 130, 0.4, 31, 18.9, 2.8, 3, 17, 0],
['Soda Crackers', '1 lb.', 15.1, 12.5, 288, 0.5, 50, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
['Milk', '1 qt.', 11, 6.1, 310, 10.5, 18, 16.8, 4, 16, 7, 177],
[
'Evaporated Milk (can)', '14.5 oz.', 6.7, 8.4, 422, 15.1, 9, 26, 3,
23.5, 11, 60
],
['Butter', '1 lb.', 30.8, 10.8, 9, 0.2, 3, 44.2, 0, 0.2, 2, 0],
['Oleomargarine', '1 lb.', 16.1, 20.6, 17, 0.6, 6, 55.8, 0.2, 0, 0, 0],
['Eggs', '1 doz.', 32.6, 2.9, 238, 1.0, 52, 18.6, 2.8, 6.5, 1, 0],
[
'Cheese (Cheddar)', '1 lb.', 24.2, 7.4, 448, 16.4, 19, 28.1, 0.8,
10.3, 4, 0
],
['Cream', '1/2 pt.', 14.1, 3.5, 49, 1.7, 3, 16.9, 0.6, 2.5, 0, 17],
[
'Peanut Butter', '1 lb.', 17.9, 15.7, 661, 1.0, 48, 0, 9.6, 8.1,
471, 0
],
['Mayonnaise', '1/2 pt.', 16.7, 8.6, 18, 0.2, 8, 2.7, 0.4, 0.5, 0, 0],
['Crisco', '1 lb.', 20.3, 20.1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
['Lard', '1 lb.', 9.8, 41.7, 0, 0, 0, 0.2, 0, 0.5, 5, 0],
[
'Sirloin Steak', '1 lb.', 39.6, 2.9, 166, 0.1, 34, 0.2, 2.1, 2.9,
69, 0
],
['Round Steak', '1 lb.', 36.4, 2.2, 214, 0.1, 32, 0.4, 2.5, 2.4, 87, 0],
['Rib Roast', '1 lb.', 29.2, 3.4, 213, 0.1, 33, 0, 0, 2, 0, 0],
['Chuck Roast', '1 lb.', 22.6, 3.6, 309, 0.2, 46, 0.4, 1, 4, 120, 0],
['Plate', '1 lb.', 14.6, 8.5, 404, 0.2, 62, 0, 0.9, 0, 0, 0],
[
'Liver (Beef)', '1 lb.', 26.8, 2.2, 333, 0.2, 139, 169.2, 6.4, 50.8,
316, 525
],
['Leg of Lamb', '1 lb.', 27.6, 3.1, 245, 0.1, 20, 0, 2.8, 3.9, 86, 0],
[
'Lamb Chops (Rib)', '1 lb.', 36.6, 3.3, 140, 0.1, 15, 0, 1.7, 2.7,
54, 0
],
['Pork Chops', '1 lb.', 30.7, 3.5, 196, 0.2, 30, 0, 17.4, 2.7, 60, 0],
[
'Pork Loin Roast', '1 lb.', 24.2, 4.4, 249, 0.3, 37, 0, 18.2, 3.6,
79, 0
],
['Bacon', '1 lb.', 25.6, 10.4, 152, 0.2, 23, 0, 1.8, 1.8, 71, 0],
['Ham, smoked', '1 lb.', 27.4, 6.7, 212, 0.2, 31, 0, 9.9, 3.3, 50, 0],
['Salt Pork', '1 lb.', 16, 18.8, 164, 0.1, 26, 0, 1.4, 1.8, 0, 0],
[
'Roasting Chicken', '1 lb.', 30.3, 1.8, 184, 0.1, 30, 0.1, 0.9, 1.8,
68, 46
],
['Veal Cutlets', '1 lb.', 42.3, 1.7, 156, 0.1, 24, 0, 1.4, 2.4, 57, 0],
[
'Salmon, Pink (can)', '16 oz.', 13, 5.8, 705, 6.8, 45, 3.5, 1, 4.9,
209, 0
],
['Apples', '1 lb.', 4.4, 5.8, 27, 0.5, 36, 7.3, 3.6, 2.7, 5, 544],
['Bananas', '1 lb.', 6.1, 4.9, 60, 0.4, 30, 17.4, 2.5, 3.5, 28, 498],
['Lemons', '1 doz.', 26, 1.0, 21, 0.5, 14, 0, 0.5, 0, 4, 952],
['Oranges', '1 doz.', 30.9, 2.2, 40, 1.1, 18, 11.1, 3.6, 1.3, 10, 1998],
['Green Beans', '1 lb.', 7.1, 2.4, 138, 3.7, 80, 69, 4.3, 5.8, 37, 862],
['Cabbage', '1 lb.', 3.7, 2.6, 125, 4.0, 36, 7.2, 9, 4.5, 26, 5369],
['Carrots', '1 bunch', 4.7, 2.7, 73, 2.8, 43, 188.5, 6.1, 4.3, 89, 608],
['Celery', '1 stalk', 7.3, 0.9, 51, 3.0, 23, 0.9, 1.4, 1.4, 9, 313],
['Lettuce', '1 head', 8.2, 0.4, 27, 1.1, 22, 112.4, 1.8, 3.4, 11, 449],
['Onions', '1 lb.', 3.6, 5.8, 166, 3.8, 59, 16.6, 4.7, 5.9, 21, 1184],
[
'Potatoes', '15 lb.', 34, 14.3, 336, 1.8, 118, 6.7, 29.4, 7.1, 198,
2522
],
['Spinach', '1 lb.', 8.1, 1.1, 106, 0, 138, 918.4, 5.7, 13.8, 33, 2755],
[
'Sweet Potatoes', '1 lb.', 5.1, 9.6, 138, 2.7, 54, 290.7, 8.4, 5.4,
83, 1912
],
[
'Peaches (can)', 'No. 2 1/2', 16.8, 3.7, 20, 0.4, 10, 21.5, 0.5, 1,
31, 196
],
[
'Pears (can)', 'No. 2 1/2', 20.4, 3.0, 8, 0.3, 8, 0.8, 0.8, 0.8, 5,
81
],
[
'Pineapple (can)', 'No. 2 1/2', 21.3, 2.4, 16, 0.4, 8, 2, 2.8, 0.8,
7, 399
],
[
'Asparagus (can)', 'No. 2', 27.7, 0.4, 33, 0.3, 12, 16.3, 1.4, 2.1,
17, 272
],
[
'Green Beans (can)', 'No. 2', 10, 1.0, 54, 2, 65, 53.9, 1.6, 4.3,
32, 431
],
[
'Pork and Beans (can)', '16 oz.', 7.1, 7.5, 364, 4, 134, 3.5, 8.3,
7.7, 56, 0
],
['Corn (can)', 'No. 2', 10.4, 5.2, 136, 0.2, 16, 12, 1.6, 2.7, 42, 218],
[
'Peas (can)', 'No. 2', 13.8, 2.3, 136, 0.6, 45, 34.9, 4.9, 2.5, 37,
370
],
[
'Tomatoes (can)', 'No. 2', 8.6, 1.3, 63, 0.7, 38, 53.2, 3.4, 2.5,
36, 1253
],
[
'Tomato Soup (can)', '10 1/2 oz.', 7.6, 1.6, 71, 0.6, 43, 57.9, 3.5,
2.4, 67, 862
],
[
'Peaches, Dried', '1 lb.', 15.7, 8.5, 87, 1.7, 173, 86.8, 1.2, 4.3,
55, 57
],
[
'Prunes, Dried', '1 lb.', 9, 12.8, 99, 2.5, 154, 85.7, 3.9, 4.3, 65,
257
],
[
'Raisins, Dried', '15 oz.', 9.4, 13.5, 104, 2.5, 136, 4.5, 6.3, 1.4,
24, 136
],
[
'Peas, Dried', '1 lb.', 7.9, 20.0, 1367, 4.2, 345, 2.9, 28.7, 18.4,
162, 0
],
[
'Lima Beans, Dried', '1 lb.', 8.9, 17.4, 1055, 3.7, 459, 5.1, 26.9,
38.2, 93, 0
],
[
'Navy Beans, Dried', '1 lb.', 5.9, 26.9, 1691, 11.4, 792, 0, 38.4,
24.6, 217, 0
],
['Coffee', '1 lb.', 22.4, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 4, 5.1, 50, 0],
['Tea', '1/4 lb.', 17.4, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 2.3, 42, 0],
['Cocoa', '8 oz.', 8.6, 8.7, 237, 3, 72, 0, 2, 11.9, 40, 0],
['Chocolate', '8 oz.', 16.2, 8.0, 77, 1.3, 39, 0, 0.9, 3.4, 14, 0],
['Sugar', '10 lb.', 51.7, 34.9, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
['Corn Syrup', '24 oz.', 13.7, 14.7, 0, 0.5, 74, 0, 0, 0, 5, 0],
['Molasses', '18 oz.', 13.6, 9.0, 0, 10.3, 244, 0, 1.9, 7.5, 146, 0],
[
'Strawberry Preserves', '1 lb.', 20.5, 6.4, 11, 0.4, 7, 0.2, 0.2,
0.4, 3, 0
],
]
nutrients = pd.DataFrame(nutrients, columns=["name", "min_need"]).set_index("name")
# display(nutrients)
columns = ["Commodity", "Unit",
"1939 price (cents)", "Calories (kcal)", "Protein (g)", "Calcium (g)",
"Iron (mg)", "Vitamin A (KIU)", "Vitamin B1 (mg)", "Vitamin B2 (mg)",
"Niacin (mg)", "Vitamin C (mg)"]
data = pd.DataFrame(data, columns=columns)
# 创建默认的GLOP求解器
solver = pywraplp.Solver.CreateSolver('GLOP')
# 每种食物的消费(美元)
foods = [solver.NumVar(0.0, solver.infinity(), item)
for item in data.Commodity.values]
# 添加约束
constraints = data.iloc[:, 3:].multiply(foods, axis="index").sum()
for constraint, min_nutrients in zip(constraints.values, nutrients.min_need.values):
solver.Add(constraint >= min_nutrients)
print('变量数量:', solver.NumVariables())
print('约束数量:', solver.NumConstraints())
# 定义目标函数
solver.Minimize(solver.Sum(foods))
# 调用求解器
status = solver.Solve()
status={
solver.OPTIMAL:"最优解",solver.FEASIBLE:"可行解"}.get(status)
if status is not None:
print(status)
else:
print("无解")
result = [(food.name(), food.solution_value()*365)
for food in foods if food.solution_value() != 0]
result = pd.DataFrame(result, columns=["Commodity", "price_per_year"])
print(result)
print("一年的最少消费(美元):", result.price_per_year.sum(),
solver.Objective().Value()*365)
curr_nutrient = data.loc[data.Commodity.isin(result.Commodity)].iloc[:, 3:].multiply(
result.price_per_year.values, axis="index").sum()/365
nutrients["curr_nutrient"] = curr_nutrient
print(nutrients)
print(f'耗时:{
solver.wall_time()} ms,迭代次数{
solver.iterations()}')
变量数量: 77
约束数量: 9
最优解
Commodity price_per_year
0 Wheat Flour (Enriched) 10.774458
1 Liver (Beef) 0.690783
2 Cabbage 4.093269
3 Spinach 1.827796
4 Navy Beans, Dried 22.275426
一年的最少消费(美元): 39.66173154546625 39.66173154546625
min_need curr_nutrient
name
Calories (kcal) 3.0 3.000000
Protein (g) 70.0 147.413535
Calcium (g) 0.8 0.800000
Iron (mg) 12.0 60.466922
Vitamin A (KIU) 5.0 5.000000
Vitamin B1 (mg) 1.8 4.120439
Vitamin B2 (mg) 2.7 2.700000
Niacin (mg) 18.0 27.315981
Vitamin C (mg) 75.0 75.000000
耗时:16 ms,迭代次数14
医院每天护士人数分配
某县新建一家医院,根据各个科室要求需要配备护士,周一到周日分别最小需要34、25、36、30、28、31、32人,按照规定,一个护士一周要连续上班5天。这家医院至少需要多少个护士?
解答:
一个护士一周要连续上班5天,我们假设有从周一开始连续上班的护士人数为x1,周二x2,…,以此类推。对于周一这天,除了从周二和周三开始上班的护士外,其他护士都会在这天上班,其他日期也同理。
同时可以预估每天所需的护士数最大为36/2=18,那么我们就可以用线性规划解决很简单的这个问题:
from ortools.linear_solver import pywraplp
# 创建默认的GLOP求解器
solver = pywraplp.Solver.CreateSolver('SCIP')
infinity = solver.infinity()
x = [solver.IntVar(0, 18, f'x{
i}') for i in range(1, 8)]
min_nums = [34, 25, 36, 30, 28, 31, 32]
solver.Minimize(sum(x))
for i, num in enumerate(x):
solver.Add(sum(x)-x[(i+1) % 7]-x[(i+2) % 7] >= min_nums[i])
# 调用求解器
status = solver.Solve()
if status == solver.OPTIMAL:
print("有最优解")
elif status == solver.FEASIBLE:
print("有可行解")
else:
print('无最优解')
print(f"最少护士人数 z={
solver.Objective().Value():.0f}", )
print("周1到周日开始上班的护士人数分别为:", [x[i].solution_value() for i in range(7)])
print("周一到周日上班人数分别为:", [(sum(x)-x[(i+1) % 7]-x[(i+2) % 7]).solution_value()
for i in range(7)])
有最优解
最少护士人数 z=44
周1到周日开始上班的护士人数分别为: [11.0, 1.0, 8.0, 8.0, 0.0, 14.0, 2.0]
周一到周日上班人数分别为: [35.0, 28.0, 36.0, 30.0, 28.0, 31.0, 32.0]
数据包络分析(DEA)
数据包络分析方法(Data Envelopment Analysis,DEA)是运筹学、管理科学与数理经济学交叉研究的一个新领域。它是根据多项投入指标和多项产出指标,利用线性规划的方法,对具有可比性的同类型单位进行相对有效性评价的一种数量分析方法。
例如,某银行的某区域有六个分理处,它们的投入产出情况如下:
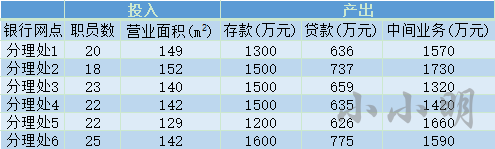
现在需要分析分理处1是否可以通过其他分理处的组合达到投入更少产出更多的效果。
from ortools.linear_solver import pywraplp
import numpy as np
# 创建GLOP求解器
solver = pywraplp.Solver.CreateSolver('GLOP')
# 搜索时间限制为15秒
solver.set_time_limit(15)
data = [[20, 149, 1300, 636, 1570],
[18, 152, 1500, 737, 1730],
[23, 140, 1500, 659, 1320],
[22, 142, 1500, 635, 1420],
[22, 129, 1200, 626, 1660],
[25, 142, 1600, 775, 1590]]
# 定义6个变量
x = [solver.NumVar(0, 1, f'x{
i}') for i in range(1, 7)]
# 定义期望E
e = solver.NumVar(0, 1, "e")
solver.Minimize(e)
# 办事处1的数据
office1 = data[0]
# 各办事处的加权平均值
office_wavg = np.sum(data*np.array(x)[:, None], axis=0)
# 权重之和为1
solver.Add(sum(x) == 1)
# 投入更少
for i in range(2):
solver.Add(office_wavg[i] <= office1[i]*e)
# 产出更多
for i in range(2, len(data[0])):
solver.Add(office_wavg[i] >= office1[i])
# 调用求解器
status = solver.Solve()
if status == solver.OPTIMAL:
print("有最优解")
elif status == solver.FEASIBLE:
print("有可行解")
else:
print('无最优解')
print(f"目标函数的最小值z={
solver.Objective().Value()},此时目标函数的决策变量为:",
{
v.name(): v.solution_value() for v in solver.variables()})
print("组合后的投入和产出:", [
f"{
office_wavg[i].solution_value():.2f}" for i in range(len(data[0]))])
背包与装箱问题
背包问题
例如:对于一组不同重量、不可分割的物品,选择一些装入背包,在满足背包最大重量限制的前提下,背包中物品总重量的最大值是多少呢?
升级版则会引入价值这一个变量:对于一组不同重量、不同价值、不可分割的物品,选择将某些物品装入背包,在满足背包最大重量限制的前提下,背包中可装入物品的总价值最大是多少呢?
对于这类问题传统的编程采用了回溯或动态规划的算法,但是假如直接使用现成的or-tools包则会非常简单。
**示例:**假设要将50个球装进一个容量为850的箱子里,每个球有对应的重量和价值,目标是找到一组可以在不超过容量的情况下总价值最大化的物品:
from ortools.algorithms import pywrapknapsack_solver
# 每个球的价值
values = [
360, 83, 59, 130, 431, 67, 230, 52, 93, 125, 670, 892, 600, 38, 48, 147,
78, 256, 63, 17, 120, 164, 432, 35, 92, 110, 22, 42, 50, 323, 514, 28,
87, 73, 78, 15, 26, 78, 210, 36, 85, 189, 274, 43, 33, 10, 19, 389, 276,
312
]
# 每个球的重量
weights = [[
7, 0, 30, 22, 80, 94, 11, 81, 70, 64, 59, 18, 0, 36, 3, 8, 15, 42, 9, 0,
42, 47, 52, 32, 26, 48, 55, 6, 29, 84, 2, 4, 18, 56, 7, 29, 93, 44, 71,
3, 86, 66, 31, 65, 0, 79, 20, 65, 52, 13
]]
# 总容量
capacities = [850]
# 申明求解器,使用分支定界算法(仅支持整数)
solver = pywrapknapsack_solver.KnapsackSolver(
pywrapknapsack_solver.KnapsackSolver.
KNAPSACK_MULTIDIMENSION_BRANCH_AND_BOUND_SOLVER, 'KnapsackExample')
solver.Init(values, weights, capacities)
computed_value = solver.Solve()
print('总价值 =', computed_value)
packed_items, packed_values, packed_weights = [], [], []
for i in range(len(values)):
if solver.BestSolutionContains(i):
packed_items.append(i)
packed_values.append(values[i])
packed_weights.append(weights[0][i])
print("总重量:", sum(packed_weights))
print("选中的球的索引:", packed_items)
print("选中的球的价值:", packed_values)
print("选中的球的重量:", packed_weights)
结果:
总价值 = 7534
总重量: 850
选中的球的索引: [0, 1, 3, 4, 6, 10, 11, 12, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 21, 22, 24, 27, 28, 29, 30, 31, 32, 34, 38, 39, 41, 42, 44, 47, 48, 49]
选中的球的价值: [360, 83, 130, 431, 230, 670, 892, 600, 48, 147, 78, 256, 63, 17, 164, 432, 92, 42, 50, 323, 514, 28, 87, 78, 210, 36, 189, 274, 33, 389, 276, 312]
选中的球的重量: [7, 0, 22, 80, 11, 59, 18, 0, 3, 8, 15, 42, 9, 0, 47, 52, 26, 6, 29, 84, 2, 4, 18, 7, 71, 3, 66, 31, 0, 65, 52, 13]
对于简化版的问题,我们只需要将重量设置为价值即可。
多背包问题
将一批物品打包到5个箱子中,每个箱子的最大容量为100,求总打包的最大值。
完整代码示例:
from ortools.linear_solver import pywraplp
import numpy as np
weights = np.array([48, 30, 42, 36, 36, 48, 42,
42, 36, 24, 30, 30, 42, 36, 36])
values = np.array([10, 30, 25, 50, 35, 30, 15, 40, 30, 35, 45, 10, 20, 30, 25])
bin_capacities = [100, 100, 100, 100, 100]
solver = pywraplp.Solver.CreateSolver('SCIP')
x = np.array([[solver.BoolVar(f'x_{
b}_{
i}') for i in range(len(values))]
for b in range(len(bin_capacities))])
# 每个物品最多只能放在一个箱子里
for item in x.sum(axis=0):
solver.Add(item <= 1)
# 每个箱子包装的总重量不超过它的容量
for pack, bin_capacitie in zip((x*weights).sum(axis=1), bin_capacities):
solver.Add(pack <= bin_capacitie)
# 打包项的总价值
solver.Maximize((x*values).sum())
status = solver.Solve()
result = np.frompyfunc(lambda x: x.solution_value(), 1, 1)(x).astype(bool)
print("总价值:", solver.Objective().Value())
print("总总量:", (x*weights).sum().solution_value())
index = np.arange(values.shape[0])
for i, row in enumerate(result):
print(f"\n第{
i}个箱子")
print("选中的球:", index[row])
print("选中的球的重量:", weights[row], ",总重量:", weights[row].sum())
print("选中的球的价值:", values[row], ",总价值:", values[row].sum())
结果:
总价值: 395.0
总总量: 438.0
第0个箱子
选中的球: [2 7]
选中的球的重量: [42 42] ,总重量: 84
选中的球的价值: [25 40] ,总价值: 65
第1个箱子
选中的球: [ 1 8 10]
选中的球的重量: [30 36 30] ,总重量: 96
选中的球的价值: [30 30 45] ,总价值: 105
第2个箱子
选中的球: [12 13]
选中的球的重量: [42 36] ,总重量: 78
选中的球的价值: [20 30] ,总价值: 50
第3个箱子
选中的球: [ 4 9 14]
选中的球的重量: [36 24 36] ,总重量: 96
选中的球的价值: [35 35 25] ,总价值: 95
第4个箱子
选中的球: [3 5]
选中的球的重量: [36 48] ,总重量: 84
选中的球的价值: [50 30] ,总价值: 80
装箱问题
有很多容量相同的箱子,使用最少数量的箱子来容纳所有的物品。
例如物品的重量和箱子的容量如下:
weights = [48, 30, 19, 36, 36, 27, 42, 42, 36, 24, 30]
bin_capacity = 100
完整代码:
from ortools.linear_solver import pywraplp
import numpy as np
weights = np.array([48, 30, 19, 36, 36, 27, 42, 42, 36, 24, 30])
items = np.arange(weights.shape[0])
bin_capacity = 100
solver = pywraplp.Solver.CreateSolver('SCIP')
# 最大是每个物品装一个箱子
x = np.array([[solver.BoolVar(f'x_{
b}_{
i}') for i in items]
for b in items])
# 标记箱子是否被使用
y = [solver.BoolVar(f'y_{
i}') for i in items]
# 每个物品必须正好放在一个箱子里
for item in x.sum(axis=0):
solver.Add(item == 1)
# 每个箱子包装的总重量不超过它的容量
for j, pack in enumerate((x*weights).sum(axis=1)):
solver.Add(pack <= y[j] * bin_capacity)
solver.Minimize(solver.Sum(y))
status = solver.Solve()
print("使用箱子个数:", solver.Objective().Value())
result = np.frompyfunc(lambda x: x.solution_value(), 1, 1)(x).astype(bool)
for i, row in enumerate(result):
if y[i].solution_value() != 1:
continue
print(f"\n第{
i}个箱子")
print("选中的球:", items[row], "重量:", weights[row],
",总重量:", weights[row].sum())
结果:
使用箱子个数: 4.0
第0个箱子
选中的球: [0 1 2] 重量: [48 30 19] ,总重量: 97
第1个箱子
选中的球: [3 4 5] 重量: [36 36 27] ,总重量: 99
第2个箱子
选中的球: [6 7] 重量: [42 42] ,总重量: 84
第3个箱子
选中的球: [ 8 9 10] 重量: [36 24 30] ,总重量: 90
双11购物的凑单问题
淘宝的“双十一”购物节有各种促销活动,比如“满 200 元减 50 元”。假设你的购物车中有 n 个(n>100)想买的商品,希望从里面选几个,在凑够满减条件的前提下,让选出来的商品价格总和最大程度地接近满减条件(200 元):
from ortools.linear_solver import pywraplp
items_info = np.array([48, 30, 19, 36, 36, 27, 42, 42, 36, 24, 40, 70, 32])
items = np.arange(items_info.shape[0])
solver = pywraplp.Solver.CreateSolver('SCIP')
x = [solver.BoolVar(f'x_{
i}') for i in range(len(items_info))]
obj = (x*items_info).sum()
solver.Add(obj >= 200)
solver.Minimize(obj)
status = solver.Solve()
print("总重量:", solver.Objective().Value())
result = np.frompyfunc(lambda x: x.solution_value(), 1, 1)(x).astype(bool)
print("选中商品的索引:", items[result])
print("选中商品的重量:", items_info[result])
分配问题
假设一组工作者需要执行一组任务,对于每个工作者和任务,都有一个将工作者分配到任务的成本,最多只给每个工人分配一个任务,没有两个工人同时执行相同的任务,如何使总成本最小化。
基础示例
有5个工人(编号0-4)和4个任务(编号0-3):
| Worker | Task 0 | Task 1 | Task 2 | Task 3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 90 | 80 | 75 | 70 |
| 1 | 35 | 85 | 55 | 65 |
| 2 | 125 | 95 | 90 | 95 |
| 3 | 45 | 110 | 95 | 115 |
| 4 | 50 | 100 | 90 | 100 |
由于工作者多于任务,一个工作者不会被分配任务。如何给工人分配任务能够使成本最低呢?
from ortools.linear_solver import pywraplp
import numpy as np
costs = [
[90, 80, 75, 70],
[35, 85, 55, 65],
[125, 95, 90, 95],
[45, 110, 95, 115],
[50, 100, 90, 100],
]
num_workers = len(costs)
num_tasks = len(costs[0])
solver = pywraplp.Solver.CreateSolver('SCIP')
# 申明是否分配的变量
mask = np.array([[solver.BoolVar(f'x_{
i}_{
j}') for j in range(num_tasks)]
for i in range(num_workers)])
# 每个工人最多分配一个任务
for num in mask.sum(axis=1):
solver.Add(num <= 1)
# 每个任务必须分配给一个工人
for num in mask.sum(axis=0):
solver.Add(num == 1)
# 目标函数:总成本最小
costs_mask = costs*mask
solver.Minimize(costs_mask.sum())
# 求解结果
status = solver.Solve()
status = {
solver.OPTIMAL: "最优解", solver.FEASIBLE: "可行解"}.get(status)
print(status)
print('最低总成本:', solver.Objective().Value())
result = np.frompyfunc(lambda x: int(x.solution_value()), 1, 1)(costs_mask)
print("分配方案:\n", result)
最优解
最低总成本: 265.0
分配方案:
[[0 0 0 70]
[0 0 55 0]
[0 95 0 0]
[45 0 0 0]
[0 0 0 0]]
小组任务分配
有6个工人(编号0-4)和4个任务(编号0-3):
| Worker | Task 0 | Task 1 | Task 2 | Task 3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 90 | 76 | 75 | 70 |
| 1 | 35 | 85 | 55 | 65 |
| 2 | 125 | 95 | 90 | 105 |
| 3 | 45 | 110 | 95 | 115 |
| 4 | 60 | 105 | 80 | 75 |
| 5 | 45 | 65 | 110 | 95 |
与上一个问题类似,区别在于这6个工人已经被分在了2个小组内,每个小组最大只能执行两个任务。
其中工人0/2/4被分配到一个小组,工人1/3/5被分配到一组。
from ortools.linear_solver import pywraplp
import numpy as np
costs = np.array([
[90, 76, 75, 70],
[35, 85, 55, 65],
[125, 95, 90, 105],
[45, 110, 95, 115],
[60, 105, 80, 75],
[45, 65, 110, 95],
])
num_workers = len(costs)
num_tasks = len(costs[0])
team1 = [0, 2, 4]
team2 = [1, 3, 5]
# 创建一个mip求解器
solver = pywraplp.Solver.CreateSolver('SCIP')
mask = np.array([[solver.BoolVar(f'x_{
i}_{
j}') for j in range(num_tasks)]
for i in range(num_workers)])
# 每个工人最多分配一个任务
for num in mask.sum(axis=1):
solver.Add(num <= 1)
# 每个任务必须分配给一个工人
for num in mask.sum(axis=0):
solver.Add(num == 1)
# 每组最大只能执行两个任务
solver.Add(mask[team1].sum() <= 2)
solver.Add(mask[team2].sum() <= 2)
# 目标函数:总成本最小
costs_mask = costs*mask
solver.Minimize(costs_mask.sum())
# 求解结果
status = solver.Solve()
status = {
solver.OPTIMAL: "最优解", solver.FEASIBLE: "可行解"}.get(status)
print(status)
print('最低总成本:', solver.Objective().Value())
result = np.frompyfunc(lambda x: int(x.solution_value()), 1, 1)(costs_mask)
print("分配方案:\n", result)
最优解
最低总成本: 249.99999999999997
分配方案:
[[0 0 75 0]
[35 0 0 0]
[0 0 0 0]
[0 0 0 0]
[0 0 0 75]
[0 65 0 0]]
小组任务分配2
有12个工人(编号0-11)和6个任务(编号0-5):
| Worker | Task 0 | Task 1 | Task 2 | Task 3 | Task 4 | Task 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 90 | 76 | 75 | 70 | 50 | 74 |
| 1 | 35 | 85 | 55 | 65 | 48 | 101 |
| 2 | 125 | 95 | 90 | 105 | 59 | 120 |
| 3 | 45 | 110 | 95 | 115 | 104 | 83 |
| 4 | 60 | 105 | 80 | 75 | 59 | 62 |
| 5 | 45 | 65 | 110 | 95 | 47 | 31 |
| 6 | 38 | 51 | 107 | 41 | 69 | 99 |
| 7 | 47 | 85 | 57 | 71 | 92 | 77 |
| 8 | 39 | 63 | 97 | 49 | 118 | 56 |
| 9 | 47 | 101 | 71 | 60 | 88 | 109 |
| 10 | 17 | 39 | 103 | 64 | 61 | 92 |
| 11 | 101 | 45 | 83 | 59 | 92 | 27 |
这12个工人分别属于3个工作组,每个工作组可能的组合如下:
group1 = [[2, 3], [1, 3], [1, 2], [0, 1], [0, 2]]
group2 = [[6, 7], [5, 7], [5, 6], [4, 5], [4, 7]]
group3 = [[10, 11], [9, 11], [9, 10], [8, 10], [8, 11]]
每个组取其中一个可能的组合,所以所有运行的组的可能数为5 * 5 * 5 = 125。
可以发现,本质上每组相当于从4个工人任意取2个工人,但是不能同时是第一个和最后一个。
最终编码:
import pandas as pd
from ortools.linear_solver import pywraplp
import numpy as np
costs = np.array([
[90, 76, 75, 70, 50, 74],
[35, 85, 55, 65, 48, 101],
[125, 95, 90, 105, 59, 120],
[45, 110, 95, 115, 104, 83],
[60, 105, 80, 75, 59, 62],
[45, 65, 110, 95, 47, 31],
[38, 51, 107, 41, 69, 99],
[47, 85, 57, 71, 92, 77],
[39, 63, 97, 49, 118, 56],
[47, 101, 71, 60, 88, 109],
[17, 39, 103, 64, 61, 92],
[101, 45, 83, 59, 92, 27],
])
num_workers = len(costs)
num_tasks = len(costs[0])
# 创建一个mip求解器
solver = pywraplp.Solver.CreateSolver('SCIP')
mask = np.array([[solver.BoolVar(f'x_{
i}_{
j}') for j in range(num_tasks)]
for i in range(num_workers)])
# 每个工人最多分配一个任务
for num in mask.sum(axis=1):
solver.Add(num <= 1)
# 每个任务必须分配给一个工人
for num in mask.sum(axis=0):
solver.Add(num == 1)
# 从每组的4个工人任意取2个工人,但是不能同时是第一个和最后一个。
solver.Add(mask[:4].sum() == 2)
solver.Add(mask[0].sum()+mask[3].sum() <= 1)
solver.Add(mask[4:8].sum() == 2)
solver.Add(mask[4].sum()+mask[7].sum() <= 1)
solver.Add(mask[8:12].sum() == 2)
solver.Add(mask[8].sum()+mask[11].sum() <= 1)
# 目标函数:总成本最小
costs_mask = costs*mask
solver.Minimize(costs_mask.sum())
# 求解结果
status = solver.Solve()
status = {
solver.OPTIMAL: "最优解", solver.FEASIBLE: "可行解"}.get(status)
if status is not None:
print(status)
print('最低总成本:', solver.Objective().Value())
print("分配方案:")
result = pd.DataFrame(costs_mask,
index=[f"Worker {
i}" for i in range(12)],
columns=[f"Task {
i}" for i in range(6)])
result = result.applymap(lambda x: x.solution_value()).astype("int16")
result = result[(result != 0).any(axis=1)]
print(result)
else:
print("无解")
工作量约束的任务分配
每个工人并不是固定的只能做一个任务,现在每个任务具备不同的工作量大小,每个工人能够工作的工作量有限。
每个工人处理的成本表如下:
| Worker | Task 0 | Task 1 | Task 2 | Task 3 | Task 4 | Task 5 | Task 6 | Task 7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 90 | 76 | 75 | 70 | 50 | 74 | 12 | 68 |
| 1 | 35 | 85 | 55 | 65 | 48 | 101 | 70 | 83 |
| 2 | 125 | 95 | 90 | 105 | 59 | 120 | 36 | 73 |
| 3 | 45 | 110 | 95 | 115 | 104 | 83 | 37 | 71 |
| 4 | 60 | 105 | 80 | 75 | 59 | 62 | 93 | 88 |
| 5 | 45 | 65 | 110 | 95 | 47 | 31 | 81 | 34 |
| 6 | 38 | 51 | 107 | 41 | 69 | 99 | 115 | 48 |
| 7 | 47 | 85 | 57 | 71 | 92 | 77 | 109 | 36 |
| 8 | 39 | 63 | 97 | 49 | 118 | 56 | 92 | 61 |
| 9 | 47 | 101 | 71 | 60 | 88 | 109 | 52 | 90 |
每个任务的工作量大小如下:
| Task 0 | Task 1 | Task 2 | Task 3 | Task 4 | Task 5 | Task 6 | Task 7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 7 | 3 | 12 | 15 | 4 | 11 | 5 |
每个工人能够工作的最大工作量为15。
import pandas as pd
from ortools.linear_solver import pywraplp
import numpy as np
costs = np.array([
[90, 76, 75, 70, 50, 74, 12, 68],
[35, 85, 55, 65, 48, 101, 70, 83],
[125, 95, 90, 105, 59, 120, 36, 73],
[45, 110, 95, 115, 104, 83, 37, 71],
[60, 105, 80, 75, 59, 62, 93, 88],
[45, 65, 110, 95, 47, 31, 81, 34],
[38, 51, 107, 41, 69, 99, 115, 48],
[47, 85, 57, 71, 92, 77, 109, 36],
[39, 63, 97, 49, 118, 56, 92, 61],
[47, 101, 71, 60, 88, 109, 52, 90],
])
num_workers = len(costs)
num_tasks = len(costs[0])
task_sizes = [10, 7, 3, 12, 15, 4, 11, 5]
total_size_max = 15
# 创建一个mip求解器
solver = pywraplp.Solver.CreateSolver('SCIP')
mask = np.array([[solver.BoolVar(f'x_{
i}_{
j}') for j in range(num_tasks)]
for i in range(num_workers)])
# 每个工人的工作量不得超过限制
task_sizes_mask = task_sizes*mask
for num in task_sizes_mask.sum(axis=1):
solver.Add(num <= total_size_max)
# 每个任务必须分配给一个工人
for num in mask.sum(axis=0):
solver.Add(num == 1)
# 目标函数:总成本最小
costs_mask = costs*mask
solver.Minimize(costs_mask.sum())
# 求解结果
status = solver.Solve()
status = {
solver.OPTIMAL: "最优解", solver.FEASIBLE: "可行解"}.get(status)
if status is not None:
print(status)
print('最低总成本:', solver.Objective().Value())
print("分配方案:")
result = pd.DataFrame(costs_mask,
index=[f"Worker {
i}" for i in range(10)],
columns=[f"Task {
i}" for i in range(8)])
result = result.applymap(lambda x: x.solution_value()).astype("int16")
print(result)
else:
print("无解")
最优解
最低总成本: 326.0
分配方案:
Task 0 Task 1 Task 2 Task 3 Task 4 Task 5 Task 6 Task 7
Worker 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 12 0
Worker 1 35 0 55 0 0 0 0 0
Worker 2 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Worker 3 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Worker 4 0 0 0 0 59 0 0 0
Worker 5 0 0 0 0 0 31 0 34
Worker 6 0 51 0 0 0 0 0 0
Worker 7 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Worker 8 0 0 0 49 0 0 0 0
Worker 9 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
车辆路线图(VRPs)
车辆路线图**(Vehicle Routing)**的目标是在一组路径中找到总距离或总成本最少的最佳路线。
例如旅行销售人员问题(TSP) : 到达所有拜访地点并返回起点,寻找最短路径。例如下图有abcd四个节点,从a出发返回a。例如:
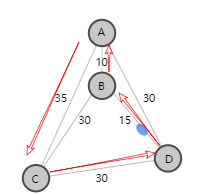
通过观察可以看到最短路径是 ACDBA,其总距离为35 + 30 + 15 + 10 = 90。当地点数达到10个时,路线的数量是362880条。在20个地点,这个数字跃升至2432902008176640000。对所有可能的路线进行详尽的搜索可以保证找到最短的路线,对于较大的问题,需要使用最优化技术智能地搜索解空间并找到最优(或接近最优)解。
而车辆路径问题中有多个车辆,车辆可能存在最大重量或最大体积的限制,要求在指定时间内到达指定地点。我们先看只有一辆车的路径问题:
旅行推销员问题
共13个点,距离矩阵如下:
distance_matrix = [
[0, 2451, 713, 1018, 1631, 1374, 2408, 213, 2571, 875, 1420, 2145, 1972],
[2451, 0, 1745, 1524, 831, 1240, 959, 2596, 403, 1589, 1374, 357, 579],
[713, 1745, 0, 355, 920, 803, 1737, 851, 1858, 262, 940, 1453, 1260],
[1018, 1524, 355, 0, 700, 862, 1395, 1123, 1584, 466, 1056, 1280, 987],
[1631, 831, 920, 700, 0, 663, 1021, 1769, 949, 796, 879, 586, 371],
[1374, 1240, 803, 862, 663, 0, 1681, 1551, 1765, 547, 225, 887, 999],
[2408, 959, 1737, 1395, 1021, 1681, 0, 2493, 678, 1724, 1891, 1114, 701],
[213, 2596, 851, 1123, 1769, 1551, 2493, 0, 2699, 1038, 1605, 2300, 2099],
[2571, 403, 1858, 1584, 949, 1765, 678, 2699, 0, 1744, 1645, 653, 600],
[875, 1589, 262, 466, 796, 547, 1724, 1038, 1744, 0, 679, 1272, 1162],
[1420, 1374, 940, 1056, 879, 225, 1891, 1605, 1645, 679, 0, 1017, 1200],
[2145, 357, 1453, 1280, 586, 887, 1114, 2300, 653, 1272, 1017, 0, 504],
[1972, 579, 1260, 987, 371, 999, 701, 2099, 600, 1162, 1200, 504, 0],
]
起始点是0号,需要经过所有其他点之后,最终会返回0号点。
from ortools.constraint_solver import routing_enums_pb2
from ortools.constraint_solver import pywrapcp
distance_matrix = [
[0, 2451, 713, 1018, 1631, 1374, 2408, 213, 2571, 875, 1420, 2145, 1972],
[2451, 0, 1745, 1524, 831, 1240, 959, 2596, 403, 1589, 1374, 357, 579],
[713, 1745, 0, 355, 920, 803, 1737, 851, 1858, 262, 940, 1453, 1260],
[1018, 1524, 355, 0, 700, 862, 1395, 1123, 1584, 466, 1056, 1280, 987],
[1631, 831, 920, 700, 0, 663, 1021, 1769, 949, 796, 879, 586, 371],
[1374, 1240, 803, 862, 663, 0, 1681, 1551, 1765, 547, 225, 887, 999],
[2408, 959, 1737, 1395, 1021, 1681, 0, 2493, 678, 1724, 1891, 1114, 701],
[213, 2596, 851, 1123, 1769, 1551, 2493, 0, 2699, 1038, 1605, 2300, 2099],
[2571, 403, 1858, 1584, 949, 1765, 678, 2699, 0, 1744, 1645, 653, 600],
[875, 1589, 262, 466, 796, 547, 1724, 1038, 1744, 0, 679, 1272, 1162],
[1420, 1374, 940, 1056, 879, 225, 1891, 1605, 1645, 679, 0, 1017, 1200],
[2145, 357, 1453, 1280, 586, 887, 1114, 2300, 653, 1272, 1017, 0, 504],
[1972, 579, 1260, 987, 371, 999, 701, 2099, 600, 1162, 1200, 504, 0],
]
n = len(distance_matrix)
# RoutingIndexManager 的参数为 位置的数目,车辆数量,起始位置
manager = pywrapcp.RoutingIndexManager(n, 1, 0)
# 创建路由模型
routing = pywrapcp.RoutingModel(manager)
# 创建距离回调函数
transit_callback_index = routing.RegisterTransitCallback(
lambda i, j: distance_matrix[i % n][j % n])
# 设置两点之间的运输成本计算方法
routing.SetArcCostEvaluatorOfAllVehicles(transit_callback_index)
# 设置默认的搜索参数和用于寻找第一个解决方案的启发式方法:
search_parameters = pywrapcp.DefaultRoutingSearchParameters()
search_parameters.first_solution_strategy = (
routing_enums_pb2.FirstSolutionStrategy.PATH_CHEAPEST_ARC)
# 计算并获取最短距离
solution = routing.SolveWithParameters(search_parameters)
print("最短距离:", solution.ObjectiveValue())
# 保存最短路径
index = routing.Start(0)
route = [manager.IndexToNode(index)]
while not routing.IsEnd(index):
index = solution.Value(routing.NextVar(index))
route.append(index % n)
print(" -> ".join(map(str, route)))
最短距离: 7293
0 -> 7 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 12 -> 6 -> 8 -> 1 -> 11 -> 10 -> 5 -> 9 -> 0
在官方的代码中index % n使用如下代码替代:
manager.IndexToNode(index)
当存在多辆车时可以使用如下方法获取距离(vehicle表示车辆编号):
routing.GetArcCostForVehicle(from_index, to_index, vehicle)
注意:距离矩阵必须由整数构成,如果存在小数时,可以考虑先统一乘以100倍之后再转换为整数。
示例: 钻一块电路板
用自动钻孔机在电路板上钻孔,需要找到最短的路径钻取所有的孔:
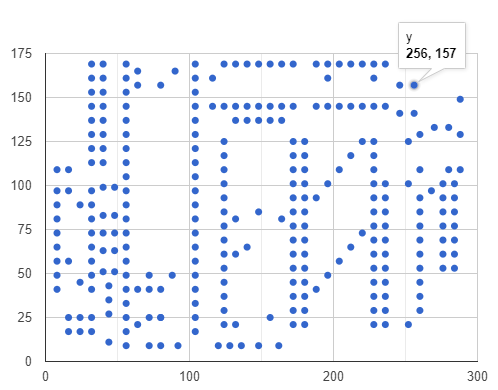
该问题的数据由平面上的280个点组成,前10个点的坐标示例如下:
(288, 149), (288, 129), (270, 133), (256, 141), (256, 157), (246, 157),
(236, 169), (228, 169), (228, 161), (220, 169), (212, 169), (204, 169),
最终完整实现代码:
import math
from ortools.constraint_solver import routing_enums_pb2
from ortools.constraint_solver import pywrapcp
from functools import lru_cache
locations = [
(288, 149), (288, 129), (270, 133), (256, 141), (256, 157), (246, 157),
(236, 169), (228, 169), (228, 161), (220, 169), (212, 169), (204, 169),
(196, 169), (188, 169), (196, 161), (188, 145), (172, 145), (164, 145),
(156, 145), (148, 145), (140, 145), (148, 169), (164, 169), (172, 169),
(156, 169), (140, 169), (132, 169), (124, 169), (116, 161), (104, 153),
(104, 161), (104, 169), (90, 165), (80, 157), (64, 157), (64, 165),
(56, 169), (56, 161), (56, 153), (56, 145), (56, 137), (56, 129),
(56, 121), (40, 121), (40, 129), (40, 137), (40, 145), (40, 153),
(40, 161), (40, 169), (32, 169), (32, 161), (32, 153), (32, 145),
(32, 137), (32, 129), (32, 121), (32, 113), (40, 113), (56, 113),
(56, 105), (48, 99), (40, 99), (32, 97), (32, 89), (24, 89),
(16, 97), (16, 109), (8, 109), (8, 97), (8, 89), (8, 81),
(8, 73), (8, 65), (8, 57), (16, 57), (8, 49), (8, 41),
(24, 45), (32, 41), (32, 49), (32, 57), (32, 65), (32, 73),
(32, 81), (40, 83), (40, 73), (40, 63), (40, 51), (44, 43),
(44, 35), (44, 27), (32, 25), (24, 25), (16, 25), (16, 17),
(24, 17), (32, 17), (44, 11), (56, 9), (56, 17), (56, 25),
(56, 33), (56, 41), (64, 41), (72, 41), (72, 49), (56, 49),
(48, 51), (56, 57), (56, 65), (48, 63), (48, 73), (56, 73),
(56, 81), (48, 83), (56, 89), (56, 97), (104, 97), (104, 105),
(104, 113), (104, 121), (104, 129), (104, 137), (104, 145), (116, 145),
(124, 145), (132, 145), (132, 137), (140, 137), (148, 137), (156, 137),
(164, 137), (172, 125), (172, 117), (172, 109), (172, 101), (172, 93),
(172, 85), (180, 85), (180, 77), (180, 69), (180, 61), (180, 53),
(172, 53), (172, 61), (172, 69), (172, 77), (164, 81), (148, 85),
(124, 85), (124, 93), (124, 109), (124, 125), (124, 117), (124, 101),
(104, 89), (104, 81), (104, 73), (104, 65), (104, 49), (104, 41),
(104, 33), (104, 25), (104, 17), (92, 9), (80, 9), (72, 9),
(64, 21), (72, 25), (80, 25), (80, 25), (80, 41), (88, 49),
(104, 57), (124, 69), (124, 77), (132, 81), (140, 65), (132, 61),
(124, 61), (124, 53), (124, 45), (124, 37), (124, 29), (132, 21),
(124, 21), (120, 9), (128, 9), (136, 9), (148, 9), (162, 9),
(156, 25), (172, 21), (180, 21), (180, 29), (172, 29), (172, 37),
(172, 45), (180, 45), (180, 37), (188, 41), (196, 49), (204, 57),
(212, 65), (220, 73), (228, 69), (228, 77), (236, 77), (236, 69),
(236, 61), (228, 61), (228, 53), (236, 53), (236, 45), (228, 45),
(228, 37), (236, 37), (236, 29), (228, 29), (228, 21), (236, 21),
(252, 21), (260, 29), (260, 37), (260, 45), (260, 53), (260, 61),
(260, 69), (260, 77), (276, 77), (276, 69), (276, 61), (276, 53),
(284, 53), (284, 61), (284, 69), (284, 77), (284, 85), (284, 93),
(284, 101), (288, 109), (280, 109), (276, 101), (276, 93), (276, 85),
(268, 97), (260, 109), (252, 101), (260, 93), (260, 85), (236, 85),
(228, 85), (228, 93), (236, 93), (236, 101), (228, 101), (228, 109),
(228, 117), (228, 125), (220, 125), (212, 117), (204, 109), (196, 101),
(188, 93), (180, 93), (180, 101), (180, 109), (180, 117), (180, 125),
(196, 145), (204, 145), (212, 145), (220, 145), (228, 145), (236, 145),
(246, 141), (252, 125), (260, 129), (280, 133)
]
n = len(locations)
# RoutingIndexManager 的参数为 位置的数目,车辆数量,起始位置
manager = pywrapcp.RoutingIndexManager(n, 1, 0)
# 创建路由模型
routing = pywrapcp.RoutingModel(manager)
def distance_callback(from_index, to_index):
"""距离计算公式"""
from_index %= n
to_index %= n
if from_index == to_index:
return 0
x1, y1 = locations[from_index]
x2, y2 = locations[to_index]
return int(math.hypot(x1-x2, y1-y2))
# 创建距离回调函数
transit_callback_index = routing.RegisterTransitCallback(distance_callback)
# 设置两点之间的运输成本计算方法
routing.SetArcCostEvaluatorOfAllVehicles(transit_callback_index)
# 设置默认的搜索参数和用于寻找第一个解决方案的启发式方法:
search_parameters = pywrapcp.DefaultRoutingSearchParameters()
search_parameters.first_solution_strategy = (
routing_enums_pb2.FirstSolutionStrategy.PATH_CHEAPEST_ARC)
# 计算并获取最短距离
solution = routing.SolveWithParameters(search_parameters)
# 打印结果
print("最短距离:", solution.ObjectiveValue())
# 保存最短路径
index = routing.Start(0)
route = [manager.IndexToNode(index)]
while not routing.IsEnd(index):
index = solution.Value(routing.NextVar(index))
route.append(index % n)
print(" -> ".join(map(str, route)))
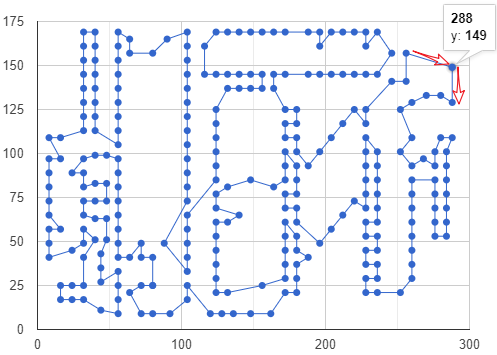
最短距离: 2790
0 -> 1 -> 279 -> 2 -> 278 -> 277 -> 248 -> 247 -> 243 -> 242 -> 241 -> 240 -> 239 -> 238 -> 245 -> 244 -> 246 -> 249 -> 250 -> 229 -> 228 -> 231 -> 230 -> 237 -> 236 -> 235 -> 234 -> 233 -> 232 -> 227 -> 226 -> 225 -> 224 -> 223 -> 222 -> 218 -> 221 -> 220 -> 219 -> 202 -> 203 -> 204 -> 205 -> 207 -> 206 -> 211 -> 212 -> 215 -> 216 -> 217 -> 214 -> 213 -> 210 -> 209 -> 208 -> 251 -> 254 -> 255 -> 257 -> 256 -> 253 -> 252 -> 139 -> 140 -> 141 -> 142 -> 143 -> 199 -> 201 -> 200 -> 195 -> 194 -> 193 -> 191 -> 190 -> 189 -> 188 -> 187 -> 163 -> 164 -> 165 -> 166 -> 167 -> 168 -> 169 -> 171 -> 170 -> 172 -> 105 -> 106 -> 104 -> 103 -> 107 -> 109 -> 110 -> 113 -> 114 -> 116 -> 117 -> 61 -> 62 -> 63 -> 65 -> 64 -> 84 -> 85 -> 115 -> 112 -> 86 -> 83 -> 82 -> 87 -> 111 -> 108 -> 89 -> 90 -> 91 -> 102 -> 101 -> 100 -> 99 -> 98 -> 97 -> 96 -> 95 -> 94 -> 93 -> 92 -> 79 -> 88 -> 81 -> 80 -> 78 -> 77 -> 76 -> 74 -> 75 -> 73 -> 72 -> 71 -> 70 -> 69 -> 66 -> 68 -> 67 -> 57 -> 56 -> 55 -> 54 -> 53 -> 52 -> 51 -> 50 -> 49 -> 48 -> 47 -> 46 -> 45 -> 44 -> 43 -> 58 -> 60 -> 59 -> 42 -> 41 -> 40 -> 39 -> 38 -> 37 -> 36 -> 35 -> 34 -> 33 -> 32 -> 31 -> 30 -> 29 -> 124 -> 123 -> 122 -> 121 -> 120 -> 119 -> 118 -> 156 -> 157 -> 158 -> 173 -> 162 -> 161 -> 160 -> 174 -> 159 -> 150 -> 151 -> 155 -> 152 -> 154 -> 153 -> 128 -> 129 -> 130 -> 131 -> 18 -> 19 -> 20 -> 127 -> 126 -> 125 -> 28 -> 27 -> 26 -> 25 -> 21 -> 24 -> 22 -> 23 -> 13 -> 12 -> 14 -> 11 -> 10 -> 9 -> 7 -> 8 -> 6 -> 5 -> 275 -> 274 -> 273 -> 272 -> 271 -> 270 -> 15 -> 16 -> 17 -> 132 -> 149 -> 177 -> 176 -> 175 -> 178 -> 179 -> 180 -> 181 -> 182 -> 183 -> 184 -> 186 -> 185 -> 192 -> 196 -> 197 -> 198 -> 144 -> 145 -> 146 -> 147 -> 148 -> 138 -> 137 -> 136 -> 135 -> 134 -> 133 -> 269 -> 268 -> 267 -> 266 -> 265 -> 264 -> 263 -> 262 -> 261 -> 260 -> 258 -> 259 -> 276 -> 3 -> 4 -> 0
上面默认的搜索器总是会受到局部极小值的影响,我们可以更换为引导局部搜索器降低影响,从而获取整体更优解。可由原本的 routing_enums_pb2.FirstSolutionStrategy.PATH_CHEAPEST_ARC 更换为routing_enums_pb2.LocalSearchMetaheuristic.GUIDED_LOCAL_SEARCH
注意: 使用 GUIDED_LOCAL_SEARCH 等启发式算法时,需要为求解器设置时间限制,否则求解器不会终止。
search_parameters.time_limit.seconds = 30可将时间限制设置为30秒。
运行一下(前面的代码与上述一致):
# 创建距离回调函数
transit_callback_index = routing.RegisterTransitCallback(distance_callback)
# 设置两点之间的运输成本计算方法
routing.SetArcCostEvaluatorOfAllVehicles(transit_callback_index)
# 设置默认的搜索参数和 引导局部搜索器:
search_parameters = pywrapcp.DefaultRoutingSearchParameters()
search_parameters.local_search_metaheuristic = (
routing_enums_pb2.LocalSearchMetaheuristic.GUIDED_LOCAL_SEARCH)
search_parameters.time_limit.seconds = 30
search_parameters.log_search = True
# 计算并获取最短距离
solution = routing.SolveWithParameters(search_parameters)
# 打印结果
print("最短距离:", solution.ObjectiveValue())
# 保存最短路径
index = routing.Start(0)
route = [manager.IndexToNode(index)]
while not routing.IsEnd(index):
index = solution.Value(routing.NextVar(index))
route.append(index % n)
print(" -> ".join(map(str, route)))
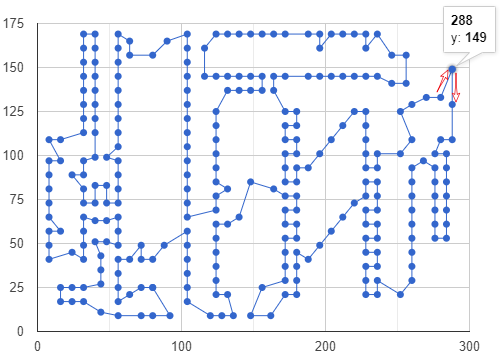
最短距离: 2671
0 -> 4 -> 3 -> 276 -> 259 -> 258 -> 260 -> 261 -> 262 -> 263 -> 264 -> 265 -> 139 -> 140 -> 147 -> 146 -> 141 -> 142 -> 145 -> 144 -> 198 -> 197 -> 196 -> 192 -> 185 -> 186 -> 184 -> 183 -> 182 -> 181 -> 179 -> 178 -> 149 -> 148 -> 138 -> 137 -> 136 -> 266 -> 267 -> 135 -> 134 -> 268 -> 269 -> 133 -> 132 -> 131 -> 18 -> 17 -> 16 -> 15 -> 270 -> 271 -> 272 -> 273 -> 274 -> 275 -> 5 -> 6 -> 8 -> 7 -> 9 -> 10 -> 11 -> 14 -> 12 -> 13 -> 23 -> 22 -> 24 -> 21 -> 25 -> 26 -> 27 -> 28 -> 125 -> 126 -> 127 -> 20 -> 19 -> 130 -> 129 -> 128 -> 153 -> 154 -> 152 -> 155 -> 151 -> 150 -> 177 -> 176 -> 175 -> 180 -> 161 -> 160 -> 174 -> 159 -> 158 -> 157 -> 156 -> 118 -> 119 -> 120 -> 121 -> 122 -> 123 -> 124 -> 29 -> 30 -> 31 -> 32 -> 33 -> 34 -> 35 -> 36 -> 37 -> 38 -> 39 -> 40 -> 41 -> 42 -> 59 -> 60 -> 58 -> 43 -> 44 -> 45 -> 46 -> 47 -> 48 -> 49 -> 50 -> 51 -> 52 -> 53 -> 54 -> 55 -> 56 -> 57 -> 67 -> 68 -> 66 -> 69 -> 70 -> 71 -> 72 -> 73 -> 75 -> 74 -> 76 -> 77 -> 78 -> 80 -> 81 -> 88 -> 79 -> 92 -> 93 -> 94 -> 95 -> 96 -> 97 -> 98 -> 99 -> 100 -> 101 -> 102 -> 91 -> 90 -> 89 -> 108 -> 111 -> 87 -> 82 -> 83 -> 86 -> 112 -> 115 -> 85 -> 84 -> 64 -> 65 -> 63 -> 62 -> 61 -> 117 -> 116 -> 114 -> 113 -> 110 -> 109 -> 107 -> 103 -> 104 -> 105 -> 106 -> 173 -> 172 -> 170 -> 171 -> 169 -> 168 -> 167 -> 166 -> 165 -> 164 -> 163 -> 162 -> 187 -> 188 -> 189 -> 190 -> 191 -> 193 -> 194 -> 195 -> 200 -> 201 -> 199 -> 143 -> 202 -> 203 -> 204 -> 205 -> 206 -> 207 -> 252 -> 253 -> 256 -> 257 -> 255 -> 254 -> 251 -> 208 -> 209 -> 210 -> 211 -> 212 -> 213 -> 214 -> 215 -> 216 -> 217 -> 218 -> 219 -> 220 -> 221 -> 222 -> 223 -> 224 -> 225 -> 226 -> 227 -> 232 -> 233 -> 234 -> 235 -> 236 -> 237 -> 230 -> 231 -> 228 -> 229 -> 250 -> 245 -> 238 -> 239 -> 240 -> 241 -> 242 -> 243 -> 244 -> 246 -> 249 -> 248 -> 247 -> 277 -> 278 -> 2 -> 279 -> 1 -> 0
程序在运行30秒后停止搜索得到如上结果。
Dimensions维度
后面涉及多辆车的问题都需要使用维度对象,路线结算器使用维度对象跟踪车辆路线上的累计值,例如行驶时间,总重量,累积运行距离等。约束和目标函数都需要定义一个维度来指定它们。
一般使用AddDimension方法定义一个维度:
routing.AddDimension(
callback_index,
slack_max,
capacity,
fix_start_cumul_to_zero,
dimension_name)
- callback_index: 由 RegisterTransitCallback 或 RegisterUnitaryTransitCallback 等方法创建计算两个点之间成本的函数。
- slack_max: 松弛变量的最大值,一般用于表示位置的等待时间,如果这个维度不涉及等待时间,通常可以将其最大值设置为0。
- capacity:每条路线累积值的最大值。
- fix_start_cumul_to_zero:一般情况下,应该设置为True表示每辆车起始累积值从0开始;但一些车辆可能由于时间窗口限制不得不在0时间之后启动,就需要将其设置为False。
- dimension_name:维度名称,后续可以通过它访问该维度的其他变量。
AddDimension采用单个容量值,假定了所有车辆具有相同的容量;AddDimensionWithVehicleCapacity 方法则可以给每辆车设置不同的容量。
Slack variables松弛变量示例:
假设一辆车在某个路线从位置 i 到位置 j,车辆的累计行驶时间在i是100分钟,在j处是200分钟,从i到j的行驶时间是75分钟。
此时车辆到底位置i后必须等待25分钟才能继续向j行驶,否则在位置j的累积时间就是175。此时位置i的松弛度为25。
对于这样的问题,设置最大松弛时间限制了车辆在一个地点等待的最大时间,然后前往下一个地点。如果等待多久并不重要,可以把最大值设置为一个非常大的数字。
假设车辆从位置 i 到位置 j,松弛变量与以下值有关:
slack(i) = cumul(j) - cumul(i) - transit(i, j)
每个地点的累积总量通过dimension_name.CumulVar(i)获取。
车辆路径问题
目标是为访问一组地点的多辆车寻找最佳路线。当只有一辆车的时候,这个问题可以简化为旅行销售人员问题。一般VRP 问题的“最佳路线”指总距离最小的路线。
对于VRP问题还可能包含如下约束:
- 容量限制: 车辆需要在每个地点提取物品,而且有最大的承重限制。
- 时间窗口: 必须在特定的时间窗口内访问每个位置。
如果目标是尽快完成所有交付,确定最优路线的一个更好的方法是最小化所有车辆中最长的单一路线的长度。
**VRP示例:**有四辆车从黑色点出发,要到达所有蓝色点并返回起点,求最短的方案。

相对于前面的问题除了车辆数增加外主要是需要额外添加距离维度的约束:
# 添加距离约束
dimension_name = 'Distance'
# 创建一个距离维度用于计算每辆车沿其路线行驶的累计距离
routing.AddDimension(
transit_callback_index,
0, # 无松弛度
3000, # 每辆车的最大行驶距离
True, # 起步累积值为0
dimension_name)
distance_dimension = routing.GetDimensionOrDie(dimension_name)
# 设置全局跨度
distance_dimension.SetGlobalSpanCostCoefficient(100)
完整代码:
from ortools.constraint_solver import routing_enums_pb2
from ortools.constraint_solver import pywrapcp
distance_matrix = [
[0, 548, 776, 696, 582, 274, 502, 194, 308,
194, 536, 502, 388, 354, 468, 776, 662],
[548, 0, 684, 308, 194, 502, 730, 354, 696,
742, 1084, 594, 480, 674, 1016, 868, 1210],
[776, 684, 0, 992, 878, 502, 274, 810, 468,
742, 400, 1278, 1164, 1130, 788, 1552, 754],
[696, 308, 992, 0, 114, 650, 878, 502, 844,
890, 1232, 514, 628, 822, 1164, 560, 1358],
[582, 194, 878, 114, 0, 536, 764, 388, 730,
776, 1118, 400, 514, 708, 1050, 674, 1244],
[274, 502, 502, 650, 536, 0, 228, 308, 194,
240, 582, 776, 662, 628, 514, 1050, 708],
[502, 730, 274, 878, 764, 228, 0, 536, 194,
468, 354, 1004, 890, 856, 514, 1278, 480],
[194, 354, 810, 502, 388, 308, 536, 0, 342,
388, 730, 468, 354, 320, 662, 742, 856],
[308, 696, 468, 844, 730, 194, 194, 342, 0,
274, 388, 810, 696, 662, 320, 1084, 514],
[194, 742, 742, 890, 776, 240, 468, 388, 274,
0, 342, 536, 422, 388, 274, 810, 468],
[536, 1084, 400, 1232, 1118, 582, 354, 730,
388, 342, 0, 878, 764, 730, 388, 1152, 354],
[502, 594, 1278, 514, 400, 776, 1004, 468,
810, 536, 878, 0, 114, 308, 650, 274, 844],
[388, 480, 1164, 628, 514, 662, 890, 354, 696,
422, 764, 114, 0, 194, 536, 388, 730],
[354, 674, 1130, 822, 708, 628, 856, 320, 662,
388, 730, 308, 194, 0, 342, 422, 536],
[468, 1016, 788, 1164, 1050, 514, 514, 662,
320, 274, 388, 650, 536, 342, 0, 764, 194],
[776, 868, 1552, 560, 674, 1050, 1278, 742,
1084, 810, 1152, 274, 388, 422, 764, 0, 798],
[662, 1210, 754, 1358, 1244, 708, 480, 856,
514, 468, 354, 844, 730, 536, 194, 798, 0]
]
num_vehicles, depot = 4, 0
# RoutingIndexManager 的参数为 位置的数目,车辆数量,起始位置
manager = pywrapcp.RoutingIndexManager(
len(distance_matrix), num_vehicles, depot)
# 创建路由模型
routing = pywrapcp.RoutingModel(manager)
# 创建距离回调函数
transit_callback_index = routing.RegisterTransitCallback(
lambda i, j: distance_matrix[manager.IndexToNode(i)][manager.IndexToNode(j)])
# 对所有车辆设置两点之间的运输成本计算函数
routing.SetArcCostEvaluatorOfAllVehicles(transit_callback_index)
# 添加距离约束
dimension_name = 'Distance'
# 创建一个距离维度用于计算每辆车沿其路线行驶的累计距离
routing.AddDimension(transit_callback_index, 0, 3000, True, dimension_name)
distance_dimension = routing.GetDimensionOrDie(dimension_name)
# 设置全局跨度
distance_dimension.SetGlobalSpanCostCoefficient(100)
# 设置默认的搜索参数和用于寻找第一个解决方案的启发式方法:
search_parameters = pywrapcp.DefaultRoutingSearchParameters()
search_parameters.first_solution_strategy = (
routing_enums_pb2.FirstSolutionStrategy.PATH_CHEAPEST_ARC)
# 开始计算
solution = routing.SolveWithParameters(search_parameters)
# 获取目标值
print("目标值:", solution.ObjectiveValue())
max_route_distance = 0
route_distances = []
for vehicle_id in range(num_vehicles):
index = routing.Start(vehicle_id)
print(f"第{
vehicle_id}号车")
route = [manager.IndexToNode(index)]
route_distance = 0
while not routing.IsEnd(index):
previous_index = index
index = solution.Value(routing.NextVar(index))
route.append(manager.IndexToNode(index))
route_distance += routing.GetArcCostForVehicle(
previous_index, index, vehicle_id)
route_distances.append(route_distance)
max_route_distance = max(route_distance, max_route_distance)
print(" -> ".join(map(str, route)))
print("运行距离:", route_distance)
print(f"最长路线的距离:{
max_route_distance} m,总距离:{
sum(route_distances)} m")
目标值: 161408
第0号车
0 -> 8 -> 6 -> 2 -> 5 -> 0
运行距离: 1552
第1号车
0 -> 7 -> 1 -> 4 -> 3 -> 0
运行距离: 1552
第2号车
0 -> 9 -> 10 -> 16 -> 14 -> 0
运行距离: 1552
第3号车
0 -> 12 -> 11 -> 15 -> 13 -> 0
运行距离: 1552
最长路线的距离:1552 m,总距离:6208 m
可视化如下:
常见设置
基本搜索限制
设置搜索的时间限制为30秒:
search_parameters = pywrapcp.DefaultRoutingSearchParameters()
search_parameters.time_limit.seconds = 30
设置搜索的解决方案个数限制:
search_parameters = pywrapcp.DefaultRoutingSearchParameters()
search_parameters.solution_limit = 100
| 名称 | 类型 | 默认值 | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
solution_limit |
int64 | kint64max | 限制在搜索过程中产生的解决方案的数量 |
time_limit.seconds |
int64 | kint64max | 限制搜索时间(单位:秒) |
lns_time_limit.seconds |
int64 | 100 | 限制本地搜索邻居的时间(单位:秒) |
first_solution_strategy设置
前面我们PATH_CHEAPEST_ARC策略表示从起点开始不断迭代链接到最近的节点直到最后一个节点来扩展路由。
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
AUTOMATIC |
让求解器根据要求解的模型自动检测要使用的策略。 |
PATH_CHEAPEST_ARC |
从起点开始不断迭代链接到最近的节点直到最后一个节点来扩展路由. |
PATH_MOST_CONSTRAINED_ARC |
类似于 PATH_CHEAPEST_ARC, 但使用了基于比较的选择器。使用了ArcIsMoreConstrainedThanArc()方法分配arcs选择器到路由模型中。 |
EVALUATOR_STRATEGY |
类似于 PATH_CHEAPEST_ARC,除了成本计算外,还使用SetFirstSolutionEvaluator()函数传递数据。 |
SAVINGS |
Savings算法(作者:Clarke & Wright). 参考: Clarke, G. & Wright, J.W.: “Scheduling of Vehicles from a Central Depot to a Number of Delivery Points”, 运筹学,1964年第12卷,第568-581页。 |
SWEEP |
Sweep 算法(作者:Wren & Holliday). 参考文献: Anthony Wren & Alan Holliday: Computer Scheduling of Vehicles from One or More Depots to a Number of Delivery Points Operational Research Quarterly (1970-1977),第23卷,第3期(1972年9月) ,333-344页 |
CHRISTOFIDES |
Christofides 算法的变体,是旅行商问题在度量空间(即距离对称且满足三角不等式)上的一个近似算法。该算法可以保证相对最优哈密尔顿回路长度有3/2的近似比。 |
ALL_UNPERFORMED |
使所有节点处于非活动状态。只有当节点是可选的(存在有限惩罚成本)时才能找到解。 |
BEST_INSERTION |
迭代的构建解决方案,将成本最低的节点插入到最理想的位置。插入代价是基于路由模型的全局代价函数。 |
PARALLEL_CHEAPEST_INSERTION |
迭代的构建解决方案,将成本最低的节点插入到最理想的位置。基于arc成本函数计算成本,相对 BEST_INSERTION速度更快。 |
LOCAL_CHEAPEST_INSERTION |
相对PARALLEL_CHEAPEST_INSERTION考虑了节点的创建顺序,速度快于PARALLEL_CHEAPEST_INSERTION。 |
GLOBAL_CHEAPEST_ARC |
迭代连接生成最便宜路由段的两个节点。 |
LOCAL_CHEAPEST_ARC |
选择具有未绑定后续节点的第一个节点,并将其连接到生成最便宜路由段的节点。 |
FIRST_UNBOUND_MIN_VALUE |
选择具有未绑定后续节点的第一个节点,并将其连接到第一个可用节点。 |
本地搜索选项
| 选项 | 描述 |
|---|---|
AUTOMATIC |
自动选择元启发式(meta-heuristic)随机搜索算法。 |
GREEDY_DESCENT |
梯度下降法 |
GUIDED_LOCAL_SEARCH |
使用引导局部搜索来避免局部极小值。 |
SIMULATED_ANNEALING |
使用模拟退火来避免局部极小值。参考 :http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/simulated_annealing |
TABU_SEARCH |
使用禁忌搜索来避免局部极小值。参考 :http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/tabu_search |
OBJECTIVE_TABU_SEARCH |
利用禁忌搜索对解的目标值避免局部极小值 |
定义初始路径
有时我们希望能够基于一组初始路径寻找解决方案,可以使用 ReadAssignmentFromRoutes 方法创建初始解决方案:
initial_routes = [
[8, 16, 14, 13, 12, 11],
[3, 4, 9, 10],
[15, 1],
[7, 5, 2, 6],
]
initial_solution = routing.ReadAssignmentFromRoutes(initial_routes, True)
同时计算时也需要也需要将其传入routing:
solution = routing.SolveFromAssignmentWithParameters(
initial_solution, search_parameters)
最终基于初始路径的计算结果如下:
目标值: 161408
第0号车
0 -> 9 -> 10 -> 16 -> 14 -> 0
运行距离: 1552
第1号车
0 -> 12 -> 11 -> 15 -> 13 -> 0
运行距离: 1552
第2号车
0 -> 3 -> 4 -> 1 -> 7 -> 0
运行距离: 1552
第3号车
0 -> 5 -> 2 -> 6 -> 8 -> 0
运行距离: 1552
最长路线的距离:1552 m,总距离:6208 m
自定义每辆车的起始和结束位置
目前所有的示例都假设所有的车辆开始和结束在一个单一的位置0:
manager = pywrapcp.RoutingIndexManager(
len(distance_matrix), num_vehicles, 0)
还可以给每车辆设置不同的开始和结束位置:
starts = [1, 2, 15, 16]
ends = [0, 0, 0, 0]
manager = pywrapcp.RoutingIndexManager(
len(distance_matrix), num_vehicles, starts, ends)
允许任意的开始和结束位置
只需修改距离矩阵,使得从仓库到任何其他位置的距离为0,这就把仓库变成了一个虚拟的地点。例如:
distance_matrix = [[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]
[0, 0, 684, 308, 194, 502, 730, 354, 696, 742,
1084, 594, 480, 674, 1016, 868, 1210],
[0, 684, 0, 992, 878, 502, 274, 810, 468, 742,
400, 1278, 1164, 1130, 788, 1552, 754],
[0, 308, 992, 0, 114, 650, 878, 502, 844, 890,
1232, 514, 628, 822, 1164, 560, 1358],
[0, 194, 878, 114, 0, 536, 764, 388, 730, 776,
1118, 400, 514, 708, 1050, 674, 1244],
[0, 502, 502, 650, 536, 0, 228, 308, 194, 240, 582, 776, 662, 628, 514, 1050, 708],
[0, 730, 274, 878, 764, 228, 0, 536, 194,
468, 354, 1004, 890, 856, 514, 1278, 480],
[0, 354, 810, 502, 388, 308, 536, 0, 342, 388, 730, 468, 354, 320, 662, 742, 856],
[0, 696, 468, 844, 730, 194, 194, 342, 0, 274, 388, 810, 696, 662, 320, 1084, 514],
[0, 742, 742, 890, 776, 240, 468, 388, 274, 0, 342, 536, 422, 388, 274, 810, 468],
[0, 1084, 400, 1232, 1118, 582, 354, 730, 388,
342, 0, 878, 764, 730, 388, 1152, 354],
[0, 594, 1278, 514, 400, 776, 1004, 468, 810,
536, 878, 0, 114, 308, 650, 274, 844],
[0, 480, 1164, 628, 514, 662, 890, 354, 696,
422, 764, 114, 0, 194, 536, 388, 730],
[0, 674, 1130, 822, 708, 628, 856, 320, 662,
388, 730, 308, 194, 0, 342, 422, 536],
[0, 1016, 788, 1164, 1050, 514, 514, 662, 320,
274, 388, 650, 536, 342, 0, 764, 194],
[0, 868, 1552, 560, 674, 1050, 1278, 742, 1084,
810, 1152, 274, 388, 422, 764, 0, 798],
[0, 1210, 754, 1358, 1244, 708, 480, 856, 514, 468, 354, 844, 730, 536, 194, 798, 0]]
带承重限制的VRP问题
假如每个地点都需要装载一定重量的货物,每辆车的最大承重为15。其他条件与上一个问题一样,每的地点的货物重量在右下角显示:
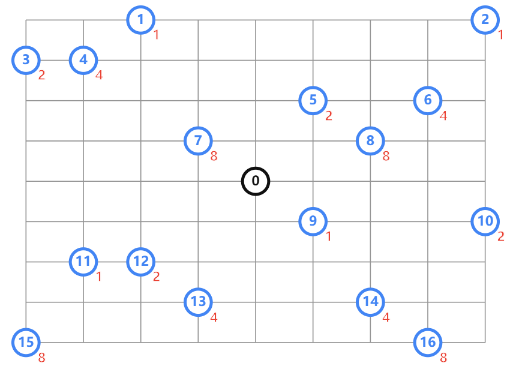
这类问题需要在之前的基础上增加容量维度的约束:
demands = [0, 1, 1, 2, 4, 2, 4, 8, 8, 1, 2, 1, 2, 4, 4, 8, 8]
demand_callback_index = routing.RegisterUnaryTransitCallback(
lambda i: demands[manager.IndexToNode(i)])
routing.AddDimensionWithVehicleCapacity(
demand_callback_index,
0, # 无容量松弛度
[15]*4, # 每辆车的最大容量
True,
'Capacity')
再添加容量维度的约束后不再需要添加距离维度的约束。完整代码:
from ortools.constraint_solver import routing_enums_pb2
from ortools.constraint_solver import pywrapcp
distance_matrix = [
[0, 548, 776, 696, 582, 274, 502, 194, 308,
194, 536, 502, 388, 354, 468, 776, 662],
[548, 0, 684, 308, 194, 502, 730, 354, 696,
742, 1084, 594, 480, 674, 1016, 868, 1210],
[776, 684, 0, 992, 878, 502, 274, 810, 468,
742, 400, 1278, 1164, 1130, 788, 1552, 754],
[696, 308, 992, 0, 114, 650, 878, 502, 844,
890, 1232, 514, 628, 822, 1164, 560, 1358],
[582, 194, 878, 114, 0, 536, 764, 388, 730,
776, 1118, 400, 514, 708, 1050, 674, 1244],
[274, 502, 502, 650, 536, 0, 228, 308, 194,
240, 582, 776, 662, 628, 514, 1050, 708],
[502, 730, 274, 878, 764, 228, 0, 536, 194,
468, 354, 1004, 890, 856, 514, 1278, 480],
[194, 354, 810, 502, 388, 308, 536, 0, 342,
388, 730, 468, 354, 320, 662, 742, 856],
[308, 696, 468, 844, 730, 194, 194, 342, 0,
274, 388, 810, 696, 662, 320, 1084, 514],
[194, 742, 742, 890, 776, 240, 468, 388, 274,
0, 342, 536, 422, 388, 274, 810, 468],
[536, 1084, 400, 1232, 1118, 582, 354, 730,
388, 342, 0, 878, 764, 730, 388, 1152, 354],
[502, 594, 1278, 514, 400, 776, 1004, 468,
810, 536, 878, 0, 114, 308, 650, 274, 844],
[388, 480, 1164, 628, 514, 662, 890, 354, 696,
422, 764, 114, 0, 194, 536, 388, 730],
[354, 674, 1130, 822, 708, 628, 856, 320, 662,
388, 730, 308, 194, 0, 342, 422, 536],
[468, 1016, 788, 1164, 1050, 514, 514, 662,
320, 274, 388, 650, 536, 342, 0, 764, 194],
[776, 868, 1552, 560, 674, 1050, 1278, 742,
1084, 810, 1152, 274, 388, 422, 764, 0, 798],
[662, 1210, 754, 1358, 1244, 708, 480, 856,
514, 468, 354, 844, 730, 536, 194, 798, 0]
]
demands = [0, 1, 1, 2, 4, 2, 4, 8, 8, 1, 2, 1, 2, 4, 4, 8, 8]
num_vehicles, depot = 4, 0
# RoutingIndexManager 的参数为 位置的数目,车辆数量,起始位置
manager = pywrapcp.RoutingIndexManager(
len(distance_matrix), num_vehicles, depot)
# 创建路由模型
routing = pywrapcp.RoutingModel(manager)
# 创建距离回调函数
transit_callback_index = routing.RegisterTransitCallback(
lambda i, j: distance_matrix[manager.IndexToNode(i)][manager.IndexToNode(j)])
# 对所有车辆设置两点之间的运输成本计算函数
routing.SetArcCostEvaluatorOfAllVehicles(transit_callback_index)
# 添加容量维度的约束
demand_callback_index = routing.RegisterUnaryTransitCallback(
lambda i: demands[manager.IndexToNode(i)])
routing.AddDimensionWithVehicleCapacity(
demand_callback_index, 0, [15]*4, True, 'Capacity')
# 设置默认的搜索参数和用于寻找第一个解决方案的启发式方法
search_parameters = pywrapcp.DefaultRoutingSearchParameters()
search_parameters.first_solution_strategy = (
routing_enums_pb2.FirstSolutionStrategy.PATH_CHEAPEST_ARC)
# 设置本地化的启发式搜索方法
search_parameters.local_search_metaheuristic = (
routing_enums_pb2.LocalSearchMetaheuristic.GUIDED_LOCAL_SEARCH)
# 设置最大计算时长
search_parameters.time_limit.FromSeconds(1)
# 开始计算
solution = routing.SolveWithParameters(search_parameters)
# 获取目标值
print("目标值:", solution.ObjectiveValue())
max_route_distance = 0
route_distances = []
total_load = 0
for vehicle_id in range(num_vehicles):
index = routing.Start(vehicle_id)
print(f"第{
vehicle_id}号车")
route_distance, route_load = 0, 0
route_loads = [(manager.IndexToNode(index), 0)]
while not routing.IsEnd(index):
route_load += demands[manager.IndexToNode(index)]
previous_index = index
index = solution.Value(routing.NextVar(index))
route_loads.append((manager.IndexToNode(index), route_load))
route_distance += routing.GetArcCostForVehicle(
previous_index, index, vehicle_id)
route_distances.append(route_distance)
max_route_distance = max(route_distance, max_route_distance)
total_load += route_load
print(" -> ".join(map(str, route_loads)))
print("运行距离:", route_distance)
print()
print(
f"最长路线的距离:{
max_route_distance} m,总距离:{
sum(route_distances)} m,总承重:{
total_load}")
目标值: 6208
第0号车
(0, 0) -> (4, 0) -> (3, 4) -> (1, 6) -> (7, 7) -> (0, 15)
运行距离: 1552
第1号车
(0, 0) -> (14, 0) -> (16, 4) -> (10, 12) -> (9, 14) -> (0, 15)
运行距离: 1552
第2号车
(0, 0) -> (12, 0) -> (11, 2) -> (15, 3) -> (13, 11) -> (0, 15)
运行距离: 1552
第3号车
(0, 0) -> (8, 0) -> (2, 8) -> (6, 9) -> (5, 13) -> (0, 15)
运行距离: 1552
最长路线的距离:1552 m,总距离:6208 m,总承重:60
惩罚并放弃访问点
还是上一节的问题,假设每个地点的货物重量修改为如下情形:
各地点的货物重量定义:
demands = [0, 1, 1, 3, 6, 3, 6, 8, 8, 1, 2, 1, 2, 6, 6, 8, 8]
在所有地点的总需求超过车辆的总容量时,会出现没有可行解的情况。例如上图中所有地点的总货物重量为70,而4辆车的总承重进60。
此时车辆必须放弃访问一些地点才可以得到可行解。此时我们可以通过增加总行驶距离设置成本惩罚,每当一个地点的访问被放弃时则增加相应的惩罚值,然后求解器找到一条最小化总行驶距离和惩罚总和的路线。
**惩罚大小的设置:**一般情况下我们可以设置惩罚大于所以位置之间的距离之和,这样在丢弃一个位置使问题可行之后,求解器不会丢弃任何额外的位置。分配较小的惩罚则可能导致求解器会删除使问题可行所需的更多位置。
假设设置惩罚为1000:
# 允许取消访问地点并设置惩罚
penalty = 1000
for node in range(1, len(distance_matrix)):
routing.AddDisjunction([manager.NodeToIndex(node)], penalty)
完整代码:
from ortools.constraint_solver import routing_enums_pb2
from ortools.constraint_solver import pywrapcp
distance_matrix = [
[0, 548, 776, 696, 582, 274, 502, 194, 308,
194, 536, 502, 388, 354, 468, 776, 662],
[548, 0, 684, 308, 194, 502, 730, 354, 696,
742, 1084, 594, 480, 674, 1016, 868, 1210],
[776, 684, 0, 992, 878, 502, 274, 810, 468,
742, 400, 1278, 1164, 1130, 788, 1552, 754],
[696, 308, 992, 0, 114, 650, 878, 502, 844,
890, 1232, 514, 628, 822, 1164, 560, 1358],
[582, 194, 878, 114, 0, 536, 764, 388, 730,
776, 1118, 400, 514, 708, 1050, 674, 1244],
[274, 502, 502, 650, 536, 0, 228, 308, 194,
240, 582, 776, 662, 628, 514, 1050, 708],
[502, 730, 274, 878, 764, 228, 0, 536, 194,
468, 354, 1004, 890, 856, 514, 1278, 480],
[194, 354, 810, 502, 388, 308, 536, 0, 342,
388, 730, 468, 354, 320, 662, 742, 856],
[308, 696, 468, 844, 730, 194, 194, 342, 0,
274, 388, 810, 696, 662, 320, 1084, 514],
[194, 742, 742, 890, 776, 240, 468, 388, 274,
0, 342, 536, 422, 388, 274, 810, 468],
[536, 1084, 400, 1232, 1118, 582, 354, 730,
388, 342, 0, 878, 764, 730, 388, 1152, 354],
[502, 594, 1278, 514, 400, 776, 1004, 468,
810, 536, 878, 0, 114, 308, 650, 274, 844],
[388, 480, 1164, 628, 514, 662, 890, 354, 696,
422, 764, 114, 0, 194, 536, 388, 730],
[354, 674, 1130, 822, 708, 628, 856, 320, 662,
388, 730, 308, 194, 0, 342, 422, 536],
[468, 1016, 788, 1164, 1050, 514, 514, 662,
320, 274, 388, 650, 536, 342, 0, 764, 194],
[776, 868, 1552, 560, 674, 1050, 1278, 742,
1084, 810, 1152, 274, 388, 422, 764, 0, 798],
[662, 1210, 754, 1358, 1244, 708, 480, 856,
514, 468, 354, 844, 730, 536, 194, 798, 0]
]
demands = [0, 1, 1, 3, 6, 3, 6, 8, 8, 1, 2, 1, 2, 6, 6, 8, 8]
num_vehicles, depot = 4, 0
# RoutingIndexManager 的参数为 位置的数目,车辆数量,起始位置
manager = pywrapcp.RoutingIndexManager(
len(distance_matrix), num_vehicles, depot)
# 创建路由模型
routing = pywrapcp.RoutingModel(manager)
# 创建距离回调函数
transit_callback_index = routing.RegisterTransitCallback(
lambda i, j: distance_matrix[manager.IndexToNode(i)][manager.IndexToNode(j)])
# 对所有车辆设置两点之间的运输成本计算函数
routing.SetArcCostEvaluatorOfAllVehicles(transit_callback_index)
# 添加容量维度的约束
demand_callback_index = routing.RegisterUnaryTransitCallback(
lambda i: demands[manager.IndexToNode(i)])
routing.AddDimensionWithVehicleCapacity(
demand_callback_index, 0, [15]*4, True, 'Capacity')
# 允许取消访问地点并设置惩罚
penalty = 1000
for node in range(1, len(distance_matrix)):
routing.AddDisjunction([manager.NodeToIndex(node)], penalty)
# 设置默认的搜索参数和用于寻找第一个解决方案的启发式方法
search_parameters = pywrapcp.DefaultRoutingSearchParameters()
search_parameters.first_solution_strategy = (
routing_enums_pb2.FirstSolutionStrategy.PATH_CHEAPEST_ARC)
# 设置本地化的启发式搜索方法
search_parameters.local_search_metaheuristic = (
routing_enums_pb2.LocalSearchMetaheuristic.GUIDED_LOCAL_SEARCH)
# 设置最大计算时长
search_parameters.time_limit.FromSeconds(1)
# 开始计算
solution = routing.SolveWithParameters(search_parameters)
# 获取目标值
print("目标值:", solution.ObjectiveValue())
max_route_distance = 0
route_distances = []
total_load = 0
for vehicle_id in range(num_vehicles):
index = routing.Start(vehicle_id)
print(f"第{
vehicle_id}号车")
route_distance, route_load = 0, 0
route_loads = [(manager.IndexToNode(index), 0)]
while not routing.IsEnd(index):
route_load += demands[manager.IndexToNode(index)]
previous_index = index
index = solution.Value(routing.NextVar(index))
route_loads.append((manager.IndexToNode(index), route_load))
route_distance += routing.GetArcCostForVehicle(
previous_index, index, vehicle_id)
route_distances.append(route_distance)
max_route_distance = max(route_distance, max_route_distance)
total_load += route_load
print(" -> ".join(map(str, route_loads)))
print("运行距离:", route_distance)
print()
print(
f"最长路线的距离:{
max_route_distance} m,总距离:{
sum(route_distances)} m,总承重:{
total_load}")
目标值: 7548
第0号车
(0, 0) -> (8, 0) -> (14, 8) -> (9, 14) -> (0, 15)
运行距离: 1096
第1号车
(0, 0) -> (1, 0) -> (3, 1) -> (4, 4) -> (11, 10) -> (12, 11) -> (0, 13)
运行距离: 1872
第2号车
(0, 0) -> (7, 0) -> (13, 8) -> (0, 14)
运行距离: 868
第3号车
(0, 0) -> (5, 0) -> (6, 3) -> (2, 9) -> (10, 10) -> (0, 12)
运行距离: 1712
最长路线的距离:1872 m,总距离:5548 m,总承重:54
物流配送相关的VRP问题
在前面的问题基础上,对于每个项目都有一个提货地址和送货地址:
对于这类问题,我们需要为每一个项目创建一个取货和送货请求,添加每个项目必须由同一辆车辆取货和送货的约束,添加每个项目在送货前必须先取货。
routing.AddPickupAndDelivery(pickup_index, delivery_index)
routing.solver().Add(
routing.VehicleVar(pickup_index) ==
routing.VehicleVar(delivery_index))
routing.solver().Add(
distance_dimension.CumulVar(pickup_index) <=
distance_dimension.CumulVar(delivery_index))
完整代码:
from ortools.constraint_solver import routing_enums_pb2
from ortools.constraint_solver import pywrapcp
distance_matrix = [
[0, 548, 776, 696, 582, 274, 502, 194, 308,
194, 536, 502, 388, 354, 468, 776, 662],
[548, 0, 684, 308, 194, 502, 730, 354, 696,
742, 1084, 594, 480, 674, 1016, 868, 1210],
[776, 684, 0, 992, 878, 502, 274, 810, 468,
742, 400, 1278, 1164, 1130, 788, 1552, 754],
[696, 308, 992, 0, 114, 650, 878, 502, 844,
890, 1232, 514, 628, 822, 1164, 560, 1358],
[582, 194, 878, 114, 0, 536, 764, 388, 730,
776, 1118, 400, 514, 708, 1050, 674, 1244],
[274, 502, 502, 650, 536, 0, 228, 308, 194,
240, 582, 776, 662, 628, 514, 1050, 708],
[502, 730, 274, 878, 764, 228, 0, 536, 194,
468, 354, 1004, 890, 856, 514, 1278, 480],
[194, 354, 810, 502, 388, 308, 536, 0, 342,
388, 730, 468, 354, 320, 662, 742, 856],
[308, 696, 468, 844, 730, 194, 194, 342, 0,
274, 388, 810, 696, 662, 320, 1084, 514],
[194, 742, 742, 890, 776, 240, 468, 388, 274,
0, 342, 536, 422, 388, 274, 810, 468],
[536, 1084, 400, 1232, 1118, 582, 354, 730,
388, 342, 0, 878, 764, 730, 388, 1152, 354],
[502, 594, 1278, 514, 400, 776, 1004, 468,
810, 536, 878, 0, 114, 308, 650, 274, 844],
[388, 480, 1164, 628, 514, 662, 890, 354, 696,
422, 764, 114, 0, 194, 536, 388, 730],
[354, 674, 1130, 822, 708, 628, 856, 320, 662,
388, 730, 308, 194, 0, 342, 422, 536],
[468, 1016, 788, 1164, 1050, 514, 514, 662,
320, 274, 388, 650, 536, 342, 0, 764, 194],
[776, 868, 1552, 560, 674, 1050, 1278, 742,
1084, 810, 1152, 274, 388, 422, 764, 0, 798],
[662, 1210, 754, 1358, 1244, 708, 480, 856,
514, 468, 354, 844, 730, 536, 194, 798, 0]
]
num_vehicles, depot = 4, 0
pickups_deliveries = [
[1, 6], [2, 10], [4, 3], [5, 9],
[7, 8], [15, 11], [13, 12], [16, 14],
]
# RoutingIndexManager 的参数为 位置的数目,车辆数量,起始位置
manager = pywrapcp.RoutingIndexManager(
len(distance_matrix), num_vehicles, depot)
# 创建路由模型
routing = pywrapcp.RoutingModel(manager)
# 创建距离回调函数
transit_callback_index = routing.RegisterTransitCallback(
lambda i, j: distance_matrix[manager.IndexToNode(i)][manager.IndexToNode(j)])
# 对所有车辆设置两点之间的运输成本计算函数
routing.SetArcCostEvaluatorOfAllVehicles(transit_callback_index)
# 添加距离约束
dimension_name = 'Distance'
# 创建一个距离维度用于计算每辆车沿其路线行驶的累计距离,3000位每辆车的最大行驶距离
routing.AddDimension(transit_callback_index, 0, 3000, True, dimension_name)
distance_dimension = routing.GetDimensionOrDie(dimension_name)
# 设置全局跨度
distance_dimension.SetGlobalSpanCostCoefficient(100)
solver = routing.solver()
for pickup_index, delivery_index in pickups_deliveries:
# 创建对应的取货和送货请求
routing.AddPickupAndDelivery(pickup_index, delivery_index)
# 每个项目必须由同一辆车辆取货和送货
solver.Add(routing.VehicleVar(pickup_index) == routing.VehicleVar(
delivery_index))
# 取货后才能送货
solver.Add(distance_dimension.CumulVar(pickup_index) <=
distance_dimension.CumulVar(delivery_index))
# 设置默认的搜索参数和用于寻找第一个解决方案的启发式方法
search_parameters = pywrapcp.DefaultRoutingSearchParameters()
search_parameters.first_solution_strategy = (
routing_enums_pb2.FirstSolutionStrategy.PARALLEL_CHEAPEST_INSERTION)
# 开始计算
solution = routing.SolveWithParameters(search_parameters)
# 获取目标值
print("目标值:", solution.ObjectiveValue())
max_route_distance = 0
route_distances = []
for vehicle_id in range(num_vehicles):
index = routing.Start(vehicle_id)
print(f"------ 第{
vehicle_id}号车 ------")
route = [manager.IndexToNode(index)]
route_distance = 0
while not routing.IsEnd(index):
previous_index = index
index = solution.Value(routing.NextVar(index))
route.append(manager.IndexToNode(index))
route_distance += routing.GetArcCostForVehicle(
previous_index, index, vehicle_id)
route_distances.append(route_distance)
max_route_distance = max(route_distance, max_route_distance)
print(" -> ".join(map(str, route)))
print("运行距离:", route_distance)
print(f"最长路线的距离:{
max_route_distance} m,总距离:{
sum(route_distances)} m")
目标值: 226116
------ 第0号车 ------
0 -> 13 -> 15 -> 11 -> 12 -> 0
运行距离: 1552
------ 第1号车 ------
0 -> 5 -> 2 -> 10 -> 16 -> 14 -> 9 -> 0
运行距离: 2192
------ 第2号车 ------
0 -> 4 -> 3 -> 0
运行距离: 1392
------ 第3号车 ------
0 -> 7 -> 1 -> 6 -> 8 -> 0
运行距离: 1780
最长路线的距离:2192 m,总距离:6916 m
带有时间窗口的VRP问题
这类问题要求每个位置只能在特定的时间范围内访问,下图中时间窗口显示在每个位置的上方:
目标是最小化车辆的总行驶时间。
首先,我们准备所需的数据:
def create_data_model():
data = {
}
data['time_matrix'] = [
[0, 6, 9, 8, 7, 3, 6, 2, 3, 2, 6, 6, 4, 4, 5, 9, 7],
[6, 0, 8, 3, 2, 6, 8, 4, 8, 8, 13, 7, 5, 8, 12, 10, 14],
[9, 8, 0, 11, 10, 6, 3, 9, 5, 8, 4, 15, 14, 13, 9, 18, 9],
[8, 3, 11, 0, 1, 7, 10, 6, 10, 10, 14, 6, 7, 9, 14, 6, 16],
[7, 2, 10, 1, 0, 6, 9, 4, 8, 9, 13, 4, 6, 8, 12, 8, 14],
[3, 6, 6, 7, 6, 0, 2, 3, 2, 2, 7, 9, 7, 7, 6, 12, 8],
[6, 8, 3, 10, 9, 2, 0, 6, 2, 5, 4, 12, 10, 10, 6, 15, 5],
[2, 4, 9, 6, 4, 3, 6, 0, 4, 4, 8, 5, 4, 3, 7, 8, 10],
[3, 8, 5, 10, 8, 2, 2, 4, 0, 3, 4, 9, 8, 7, 3, 13, 6],
[2, 8, 8, 10, 9, 2, 5, 4, 3, 0, 4, 6, 5, 4, 3, 9, 5],
[6, 13, 4, 14, 13, 7, 4, 8, 4, 4, 0, 10, 9, 8, 4, 13, 4],
[6, 7, 15, 6, 4, 9, 12, 5, 9, 6, 10, 0, 1, 3, 7, 3, 10],
[4, 5, 14, 7, 6, 7, 10, 4, 8, 5, 9, 1, 0, 2, 6, 4, 8],
[4, 8, 13, 9, 8, 7, 10, 3, 7, 4, 8, 3, 2, 0, 4, 5, 6],
[5, 12, 9, 14, 12, 6, 6, 7, 3, 3, 4, 7, 6, 4, 0, 9, 2],
[9, 10, 18, 6, 8, 12, 15, 8, 13, 9, 13, 3, 4, 5, 9, 0, 9],
[7, 14, 9, 16, 14, 8, 5, 10, 6, 5, 4, 10, 8, 6, 2, 9, 0],
]
data['time_windows'] = [
(0, 5), # 起始点depot
(7, 12), (10, 15), (16, 18), (10, 13), (0, 5), # 1-5
(5, 10), (0, 4), (5, 10), (0, 3), (10, 16), # 6-10
(10, 15), (0, 5), (5, 10), (7, 8), (10, 15), (11, 15), # 11-16
]
data['num_vehicles'] = 4
data['depot'] = 0
return data
数据说明:
time_matrix: 由于所有的车辆都以相同的速度行驶,行驶距离是行驶时间的常数倍,所有数据已简化为到底目的地的行驶时间。time_windows: 一组时间窗口,车辆必须在其时间窗口内访问一个地点。num_vehicles: 车队中车辆的数量。depot: 起始点的索引。
最终完整代码:
from ortools.constraint_solver import routing_enums_pb2
from ortools.constraint_solver import pywrapcp
def create_data_model():
"""所需数据"""
data = {
}
data['time_matrix'] = [
[0, 6, 9, 8, 7, 3, 6, 2, 3, 2, 6, 6, 4, 4, 5, 9, 7],
[6, 0, 8, 3, 2, 6, 8, 4, 8, 8, 13, 7, 5, 8, 12, 10, 14],
[9, 8, 0, 11, 10, 6, 3, 9, 5, 8, 4, 15, 14, 13, 9, 18, 9],
[8, 3, 11, 0, 1, 7, 10, 6, 10, 10, 14, 6, 7, 9, 14, 6, 16],
[7, 2, 10, 1, 0, 6, 9, 4, 8, 9, 13, 4, 6, 8, 12, 8, 14],
[3, 6, 6, 7, 6, 0, 2, 3, 2, 2, 7, 9, 7, 7, 6, 12, 8],
[6, 8, 3, 10, 9, 2, 0, 6, 2, 5, 4, 12, 10, 10, 6, 15, 5],
[2, 4, 9, 6, 4, 3, 6, 0, 4, 4, 8, 5, 4, 3, 7, 8, 10],
[3, 8, 5, 10, 8, 2, 2, 4, 0, 3, 4, 9, 8, 7, 3, 13, 6],
[2, 8, 8, 10, 9, 2, 5, 4, 3, 0, 4, 6, 5, 4, 3, 9, 5],
[6, 13, 4, 14, 13, 7, 4, 8, 4, 4, 0, 10, 9, 8, 4, 13, 4],
[6, 7, 15, 6, 4, 9, 12, 5, 9, 6, 10, 0, 1, 3, 7, 3, 10],
[4, 5, 14, 7, 6, 7, 10, 4, 8, 5, 9, 1, 0, 2, 6, 4, 8],
[4, 8, 13, 9, 8, 7, 10, 3, 7, 4, 8, 3, 2, 0, 4, 5, 6],
[5, 12, 9, 14, 12, 6, 6, 7, 3, 3, 4, 7, 6, 4, 0, 9, 2],
[9, 10, 18, 6, 8, 12, 15, 8, 13, 9, 13, 3, 4, 5, 9, 0, 9],
[7, 14, 9, 16, 14, 8, 5, 10, 6, 5, 4, 10, 8, 6, 2, 9, 0],
]
data['time_windows'] = [
(7, 12), (10, 15), (16, 18), (10, 13), (0, 5), # 1-5
(5, 10), (0, 4), (5, 10), (0, 3), (10, 16), # 6-10
(10, 15), (0, 5), (5, 10), (7, 8), (10, 15), (11, 15), # 11-16
]
data['num_vehicles'] = 4
data['depot'] = 0
return data
def print_solution(data, manager, routing, solution):
"""打印结果"""
print(f'目标: {
solution.ObjectiveValue()}')
time_dimension = routing.GetDimensionOrDie('Time')
total_time = 0
for vehicle_id in range(data['num_vehicles']):
index = routing.Start(vehicle_id)
print(f"------ 第{
vehicle_id}号车 ------")
while not routing.IsEnd(index):
# 获取当前车辆在该位置的累计行驶时间
time_var = time_dimension.CumulVar(index)
print('{0} [{1},{2}]'.format(
manager.IndexToNode(index), solution.Min(time_var),
solution.Max(time_var)), end=" -> ")
index = solution.Value(routing.NextVar(index))
time_var = time_dimension.CumulVar(index)
print('{0} [{1},{2}]'.format(
manager.IndexToNode(index), solution.Min(time_var),
solution.Max(time_var)))
print(f"运输时间:{
solution.Min(time_var)}min")
total_time += solution.Min(time_var)
print(f'总运输数据: {
total_time}min')
data = create_data_model()
# RoutingIndexManager 的参数为 位置的数目,车辆数量,与仓库对应的节点
manager = pywrapcp.RoutingIndexManager(
len(data['time_matrix']), data['num_vehicles'], data['depot'])
# 创建路由模型
routing = pywrapcp.RoutingModel(manager)
# 创建距离回调函数
transit_callback_index = routing.RegisterTransitCallback(
lambda i, j: data['time_matrix'][manager.IndexToNode(i)][manager.IndexToNode(j)])
# 对所有车辆设置两点之间的运输成本计算函数
routing.SetArcCostEvaluatorOfAllVehicles(transit_callback_index)
# 添加时间窗口约束
time = 'Time'
# 添加时间维度跟踪车辆路线上累积的时间
routing.AddDimension(
transit_callback_index,
30, # 允许的等待时间
30, # 每辆车的最大时间
False, # 每辆车的路线开始时,不将累积变量设置为零
time)
time_dimension = routing.GetDimensionOrDie(time)
# 添加时间窗口约束
for location_idx, (start, end) in enumerate(data['time_windows'], 1):
index = manager.NodeToIndex(location_idx)
time_dimension.CumulVar(index).SetRange(start, end)
# 对每个车辆启动节点添加时间窗口约束。
for vehicle_id in range(data['num_vehicles']):
index = routing.Start(vehicle_id)
time_dimension.CumulVar(index).SetRange(0, 5)
# 对每辆车限制累积时间范围
for i in range(data['num_vehicles']):
routing.AddVariableMinimizedByFinalizer(
time_dimension.CumulVar(routing.Start(i)))
routing.AddVariableMinimizedByFinalizer(
time_dimension.CumulVar(routing.End(i)))
# 设置默认的启发式求解器
search_parameters = pywrapcp.DefaultRoutingSearchParameters()
search_parameters.first_solution_strategy = (
routing_enums_pb2.FirstSolutionStrategy.PATH_CHEAPEST_ARC)
# 设置搜索参数
solution = routing.SolveWithParameters(search_parameters)
print_solution(data, manager, routing, solution)
目标: 71
------ 第0号车 ------
0 [0,0] -> 9 [2,3] -> 14 [7,8] -> 16 [11,11] -> 0 [18,18]
运输时间:18min
------ 第1号车 ------
0 [0,0] -> 7 [2,4] -> 1 [7,11] -> 4 [10,13] -> 3 [16,16] -> 0 [24,24]
运输时间:24min
------ 第2号车 ------
0 [0,0] -> 12 [4,4] -> 13 [6,6] -> 15 [11,11] -> 11 [14,14] -> 0 [20,20]
运输时间:20min
------ 第3号车 ------
0 [0,0] -> 5 [3,3] -> 8 [5,5] -> 6 [7,7] -> 2 [10,10] -> 10 [14,14] -> 0 [20,20]
运输时间:20min
总运输数据: 82min
考虑在仓库装卸货的耗时
进一步该问题还可以增加装卸货的限制,每辆车需要在出发点仓库装货,然后在回到仓库终点后卸货,仓库可以同时为多辆车装卸货也存在限制。
新问题的时间窗口限制如下:
data['time_windows'] = [
(7, 12), (10, 15), (5, 14), (5, 13), (0, 5), # 1-5
(5, 10), (0, 10), (5, 10), (0, 5), (10, 16), # 6-10
(10, 15), (0, 5), (5, 10), (7, 12), (10, 15), (5, 15), # 11-16
]
该问题增加了下面几个参数:
data['vehicle_load_time'] = 5
data['vehicle_unload_time'] = 5
data['depot_capacity'] = 2
表示装货和卸货的时间都是5秒,仓库同时可装卸的车辆的最大数量为2。
通过以下代码可以增加装货和卸货时间窗口:
# 对仓库增加资源限制
solver = routing.solver()
intervals = []
for i in range(data['num_vehicles']):
# 装货耗时
intervals.append(
solver.FixedDurationIntervalVar(
time_dimension.CumulVar(routing.Start(i)),
data['vehicle_load_time'], 'depot_interval'))
# 卸货耗时
intervals.append(
solver.FixedDurationIntervalVar(
time_dimension.CumulVar(routing.End(i)),
data['vehicle_unload_time'], 'depot_interval'))
depot_usage = [1 for i in range(len(intervals))]
solver.Add(
solver.Cumulative(intervals, depot_usage, data['depot_capacity'], 'depot'))
完整代码为:
from ortools.constraint_solver import routing_enums_pb2
from ortools.constraint_solver import pywrapcp
def create_data_model():
"""所需数据"""
data = {
}
data['time_matrix'] = [
[0, 6, 9, 8, 7, 3, 6, 2, 3, 2, 6, 6, 4, 4, 5, 9, 7],
[6, 0, 8, 3, 2, 6, 8, 4, 8, 8, 13, 7, 5, 8, 12, 10, 14],
[9, 8, 0, 11, 10, 6, 3, 9, 5, 8, 4, 15, 14, 13, 9, 18, 9],
[8, 3, 11, 0, 1, 7, 10, 6, 10, 10, 14, 6, 7, 9, 14, 6, 16],
[7, 2, 10, 1, 0, 6, 9, 4, 8, 9, 13, 4, 6, 8, 12, 8, 14],
[3, 6, 6, 7, 6, 0, 2, 3, 2, 2, 7, 9, 7, 7, 6, 12, 8],
[6, 8, 3, 10, 9, 2, 0, 6, 2, 5, 4, 12, 10, 10, 6, 15, 5],
[2, 4, 9, 6, 4, 3, 6, 0, 4, 4, 8, 5, 4, 3, 7, 8, 10],
[3, 8, 5, 10, 8, 2, 2, 4, 0, 3, 4, 9, 8, 7, 3, 13, 6],
[2, 8, 8, 10, 9, 2, 5, 4, 3, 0, 4, 6, 5, 4, 3, 9, 5],
[6, 13, 4, 14, 13, 7, 4, 8, 4, 4, 0, 10, 9, 8, 4, 13, 4],
[6, 7, 15, 6, 4, 9, 12, 5, 9, 6, 10, 0, 1, 3, 7, 3, 10],
[4, 5, 14, 7, 6, 7, 10, 4, 8, 5, 9, 1, 0, 2, 6, 4, 8],
[4, 8, 13, 9, 8, 7, 10, 3, 7, 4, 8, 3, 2, 0, 4, 5, 6],
[5, 12, 9, 14, 12, 6, 6, 7, 3, 3, 4, 7, 6, 4, 0, 9, 2],
[9, 10, 18, 6, 8, 12, 15, 8, 13, 9, 13, 3, 4, 5, 9, 0, 9],
[7, 14, 9, 16, 14, 8, 5, 10, 6, 5, 4, 10, 8, 6, 2, 9, 0],
]
data['time_windows'] = [
(7, 12), (10, 15), (5, 14), (5, 13), (0, 5), # 1-5
(5, 10), (0, 10), (5, 10), (0, 5), (10, 16), # 6-10
(10, 15), (0, 5), (5, 10), (7, 12), (10, 15), (5, 15), # 11-16
]
data['num_vehicles'] = 4
data['depot'] = 0
data['vehicle_load_time'] = 5
data['vehicle_unload_time'] = 5
data['depot_capacity'] = 2
return data
def print_solution(data, manager, routing, solution):
"""打印结果"""
print(f'目标: {
solution.ObjectiveValue()}')
time_dimension = routing.GetDimensionOrDie('Time')
total_time = 0
for vehicle_id in range(data['num_vehicles']):
index = routing.Start(vehicle_id)
print(f"------ 第{
vehicle_id}号车 ------")
while not routing.IsEnd(index):
# 获取当前车辆在该位置的累计行驶时间
time_var = time_dimension.CumulVar(index)
print('{0} [{1},{2}]'.format(
manager.IndexToNode(index), solution.Min(time_var),
solution.Max(time_var)), end=" -> ")
index = solution.Value(routing.NextVar(index))
time_var = time_dimension.CumulVar(index)
print('{0} [{1},{2}]'.format(
manager.IndexToNode(index), solution.Min(time_var),
solution.Max(time_var)))
print(f"运输时间:{
solution.Min(time_var)}min")
total_time += solution.Min(time_var)
print(f'总运输数据: {
total_time}min')
data = create_data_model()
# RoutingIndexManager 的参数为 位置的数目,车辆数量,与仓库对应的节点
manager = pywrapcp.RoutingIndexManager(
len(data['time_matrix']), data['num_vehicles'], data['depot'])
# 创建路由模型
routing = pywrapcp.RoutingModel(manager)
# 创建距离回调函数
transit_callback_index = routing.RegisterTransitCallback(
lambda i, j: data['time_matrix'][manager.IndexToNode(i)][manager.IndexToNode(j)])
# 对所有车辆设置两点之间的运输成本计算函数
routing.SetArcCostEvaluatorOfAllVehicles(transit_callback_index)
# 添加时间窗口约束
time = 'Time'
# 添加时间维度跟踪车辆路线上累积的时间
routing.AddDimension(
transit_callback_index,
30, # 允许的等待时间
30, # 每辆车的最大时间
False, # 每辆车的路线开始时,不将累积变量设置为零
time)
time_dimension = routing.GetDimensionOrDie(time)
# 添加时间窗口约束
for location_idx, (start, end) in enumerate(data['time_windows'], 1):
index = manager.NodeToIndex(location_idx)
time_dimension.CumulVar(index).SetRange(start, end)
# 对每个车辆启动节点添加时间窗口约束。
for vehicle_id in range(data['num_vehicles']):
index = routing.Start(vehicle_id)
time_dimension.CumulVar(index).SetRange(0, 5)
# 对仓库增加资源限制
solver = routing.solver()
intervals = []
for i in range(data['num_vehicles']):
# 装货耗时
intervals.append(
solver.FixedDurationIntervalVar(
time_dimension.CumulVar(routing.Start(i)),
data['vehicle_load_time'], 'depot_interval'))
# 卸货耗时
intervals.append(
solver.FixedDurationIntervalVar(
time_dimension.CumulVar(routing.End(i)),
data['vehicle_unload_time'], 'depot_interval'))
depot_usage = [1 for i in range(len(intervals))]
solver.Add(
solver.Cumulative(intervals, depot_usage, data['depot_capacity'], 'depot'))
# 对每辆车限制累积时间范围
for i in range(data['num_vehicles']):
routing.AddVariableMinimizedByFinalizer(
time_dimension.CumulVar(routing.Start(i)))
routing.AddVariableMinimizedByFinalizer(
time_dimension.CumulVar(routing.End(i)))
# 设置默认的启发式求解器
search_parameters = pywrapcp.DefaultRoutingSearchParameters()
search_parameters.first_solution_strategy = (
routing_enums_pb2.FirstSolutionStrategy.PATH_CHEAPEST_ARC)
# 设置搜索参数
solution = routing.SolveWithParameters(search_parameters)
print_solution(data, manager, routing, solution)
目标: 71
------ 第0号车 ------
0 [5,5] -> 8 [8,9] -> 14 [11,12] -> 16 [13,15] -> 0 [25,25]
运输时间:25min
------ 第1号车 ------
0 [0,0] -> 12 [4,4] -> 13 [6,6] -> 15 [11,11] -> 11 [14,14] -> 0 [20,20]
运输时间:20min
------ 第2号车 ------
0 [5,5] -> 7 [7,7] -> 1 [11,11] -> 4 [13,13] -> 3 [14,14] -> 0 [24,24]
运输时间:24min
------ 第3号车 ------
0 [0,0] -> 9 [2,3] -> 5 [4,5] -> 6 [6,9] -> 2 [10,12] -> 10 [14,16] -> 0 [29,29]
运输时间:29min
总运输数据: 98min
网络流(Network Flows)
最大流量(Maximum Flows)
最大流量问题:找出从单个源点到单个目标点之间可以通过的最大流量。
示例1:
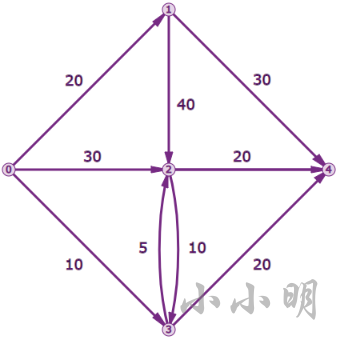
上图中每条边标识了允许的最大流量,现在需要将材料从节点0传输到节点4。现在需要良好规划流向使整体流量最大:
from ortools.graph import pywrapgraph
max_flow = pywrapgraph.SimpleMaxFlow()
start_nodes = [0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 2, 2, 3, 3]
end_nodes = [1, 2, 3, 2, 4, 3, 4, 2, 4]
capacities = [20, 30, 10, 40, 30, 10, 20, 5, 20]
for start_node, end_node, capacitie in zip(start_nodes, end_nodes, capacities):
max_flow.AddArcWithCapacity(start_node, end_node, capacitie)
print("总路线数:", max_flow.NumArcs())
status = max_flow.Solve(0, 4)
print("status is OPTIMAL:", status == max_flow.OPTIMAL)
print('最大流量值:', max_flow.OptimalFlow())
for i in range(max_flow.NumArcs()):
if max_flow.Flow(i) == 0:
continue
print(f"{
max_flow.Tail(i)} -> {
max_flow.Head(i)} ({
max_flow.Flow(i): >2d}/{
max_flow.Capacity(i): >2d})")
总路线数: 9
status is OPTIMAL: True
最大流量值: 60
0 -> 1 (20/20)
0 -> 2 (30/30)
0 -> 3 (10/10)
1 -> 4 (20/30)
2 -> 3 (10/10)
2 -> 4 (20/20)
3 -> 4 (20/20)
可以看到最大流量为60。
**示例2:**路径和最大容量如下所示。
from ortools.graph import pywrapgraph
max_flow = pywrapgraph.SimpleMaxFlow()
edges = [(0, 1), (0, 2), (1, 2), (1, 3), (2, 1),
(2, 4), (3, 2), (3, 5), (4, 3), (4, 5)]
capacities = [16, 13, 10, 12, 4, 14, 9, 20, 7, 4]
for (start_node, end_node), capacitie in zip(edges, capacities):
max_flow.AddArcWithCapacity(start_node, end_node, capacitie)
print("总路线数:", max_flow.NumArcs())
status = max_flow.Solve(0, 5)
print("status is OPTIMAL:", status == max_flow.OPTIMAL)
print('最大流量值:', max_flow.OptimalFlow())
for i in range(max_flow.NumArcs()):
if max_flow.Flow(i) == 0:
continue
print(f"{
max_flow.Tail(i)} -> {
max_flow.Head(i)} ({
max_flow.Flow(i): >2d}/{
max_flow.Capacity(i): >2d})")
结果:
总路线数: 10
status is OPTIMAL: True
最大流量值: 23
0 -> 1 (16/16)
0 -> 2 ( 7/13)
1 -> 2 ( 4/10)
1 -> 3 (12/12)
2 -> 4 (11/14)
3 -> 5 (19/20)
4 -> 3 ( 7/ 7)
4 -> 5 ( 4/ 4)

最小成本流(Minimum Cost Flows)
最小成本流问题:将物料从供应节点传输到需求节点,找出成本最低的传输路线。
节点0为供应节点共20单位的物料需要进行传输,分别传输到节点3和节点4,需求分别为-5和-15。每条边的数字对分别表示容量和传输每1单位物料所消耗的成本。
from ortools.graph import pywrapgraph
min_cost_flow = pywrapgraph.SimpleMinCostFlow()
start_nodes = [0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 3, 4]
end_nodes = [1, 2, 2, 3, 4, 3, 4, 4, 2]
capacities = [15, 8, 20, 4, 10, 15, 4, 20, 5]
unit_costs = [4, 4, 2, 2, 6, 1, 3, 2, 3]
for start_node, end_node, capacitie, unit_cost in zip(start_nodes, end_nodes, capacities, unit_costs):
min_cost_flow.AddArcWithCapacityAndUnitCost(
start_node, end_node, capacitie, unit_cost)
print("总路线数:", max_flow.NumArcs())
# 每个节点对应的供应和需求
supplies = [20, 0, 0, -5, -15]
for i, supply in enumerate(supplies):
min_cost_flow.SetNodeSupply(i, supply)
status = min_cost_flow.Solve()
print("status is OPTIMAL:", status == max_flow.OPTIMAL)
print('最小成本: ', min_cost_flow.OptimalCost())
text = "{} -> {} ({: >2d}/{: >2d}) 成本:{: >2d}"
for i in range(min_cost_flow.NumArcs()):
if min_cost_flow.Flow(i) == 0:
continue
print(text.format(min_cost_flow.Tail(i), min_cost_flow.Head(i),
min_cost_flow.Flow(i), min_cost_flow.Capacity(i),
min_cost_flow.Flow(i) * min_cost_flow.UnitCost(i)))
结果:
总路线数: 10
status is OPTIMAL: False
最小成本: 150
0 -> 1 (12/15) 成本:48
0 -> 2 ( 8/ 8) 成本:32
1 -> 2 ( 8/20) 成本:16
1 -> 3 ( 4/ 4) 成本: 8
2 -> 3 (12/15) 成本:12
2 -> 4 ( 4/ 4) 成本:12
3 -> 4 (11/20) 成本:22
