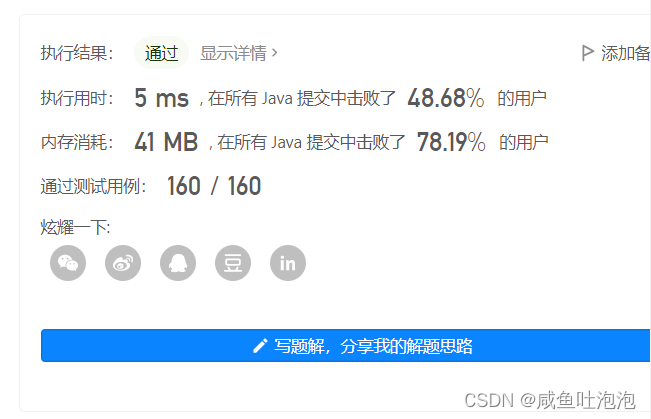
树的概念:树是一种非线性的数据结构,它有n个有限节点组成一个具有层次关系的集合。
树的相关概念:
节点的度:一个节点含有子树的个数称为该节点的度;如上图:A的度为6.
树的度:一棵树中,所有节点的度最大值称为树的度;如上图:树的度为6.
叶子结点或终端节点:度为0的节点称为叶子结点;如上图:B、C、H、I、P...
如果一个节点有子节点,则这个节点称为这个子节点的父节点或双亲节点
孩子节点或子节点:一个节点含有的子树的根节点称为该节点的子节点;如上图:B是A的孩子节点
根节点:一棵树中,没有双清节点的节点;如上图:A
节点的层次:从根节点定义起,根为第一层,根的子节点为第二层,以此类推
树的高度:树的高度是整棵树最大的深度

二叉树
一个根节点上面只有两棵树(左子树、右子树),二叉树可以没有左子树或者没有右子树或者左右子树都没有。
两种特殊的二叉树
1.满二叉树:一颗二叉树,每层的节点数都达到最大值,这样的二叉树称为满二叉树。即一颗二叉树的层数为K,节点总数是(2^k)-1,这棵树就是满二叉树。
如下图
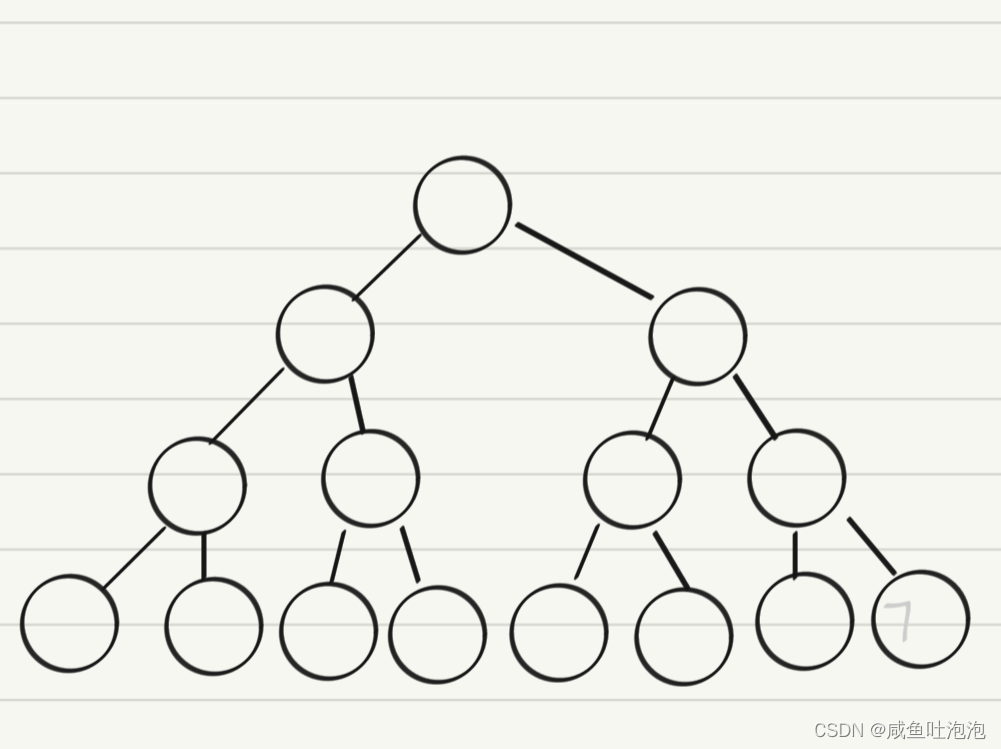
2. 完全二叉树:有n个节点的满二叉树中编号从0至n-1的节点一一对应时称为完全二叉树。完全二叉树是一种特殊的二叉树
二叉树的性质
1.若根节点的层数为1,则一颗非空二叉树的第i层上最多有2^i-1个节点
2.若规定根节点的二叉树的深度为1,则深度为k的二叉树的最大节点数是(2^k)-1
3.对于任何一颗二叉树,如果其叶子结点个数为n0,度为2的非叶子节点个数为n2,则有n0 = n2+1
4.具有n个节点的完全二叉树的深度k为log2(n+1)向上取整
5.对于具有n个节点的完全二叉树,如果按照从上至下从左至右的顺序对所有节点从0开始编号,则对于序号为i的节点有:
若i>0,双亲序号:(i-1)/2;
若2i+1<n,左孩子序号:2i+1;
若2i+1<n,右孩子序号:2i+2;
二叉树的创建和遍历
这里用孩子表示法来创建二叉树
public class BrnaryTree {
public class Tree{//创建树节点
public char val;
public Tree left;
public Tree right;
public Tree(char val) {
this.val = val;
}
}
}我们为了便于理解先用穷举法创建二叉树
public class BrnaryTree {
public class Tree{
public char val;
public Tree left;
public Tree right;
public Tree(char val) {
this.val = val;
}
}
//下面利用穷举法创建二叉树
public Tree createtree(){
Tree A = new Tree('A');
Tree B = new Tree('B');
Tree C = new Tree('C');
Tree D = new Tree('D');
Tree E = new Tree('E');
Tree F = new Tree('F');
Tree G = new Tree('G');
Tree H = new Tree('H');
A.left = B;
A.right = C;
B.left = D;
B.right = E;
C.left = F;
C.right = G;
E.right = H;
return A;
}
}二叉树示意图如下

在主函数里面实现一下
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BrnaryTree tree = new BrnaryTree();
BrnaryTree.Tree subtree = tree.createtree();
}
}下面写遍历方法,这里的遍历方法有三种:前序遍历、中序遍历、后序遍历
1.前序遍历:先输出父节点,在递归遍历左子树和右子树
思路一使用递归:
(1)先输出当前节点
(2)如果左子节点不为空,则递归继续前序遍历
(3)如果右子节点不为空,则递归继续前序遍历
public class BrnaryTree {
public class Tree{
public char val;
public Tree left;
public Tree right;
public Tree(char val) {
this.val = val;
}
}
//下面利用穷举法创建二叉树
public Tree createtree(){
Tree A = new Tree('A');
Tree B = new Tree('B');
Tree C = new Tree('C');
Tree D = new Tree('D');
Tree E = new Tree('E');
Tree F = new Tree('F');
Tree G = new Tree('G');
Tree H = new Tree('H');
A.left = B;
A.right = C;
B.left = D;
B.right = E;
C.left = F;
C.right = G;
E.right = H;
return A;
}
//前序遍历二叉树
public void preorder(Tree subtree){
if(subtree==null)return;
System.out.print(subtree.val+" ");
preorder(subtree.left);
preorder(subtree.right);
}
}
主函数里面实现一下
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BrnaryTree tree = new BrnaryTree();
BrnaryTree.Tree subtree = tree.createtree();
tree.preorder(subtree);
}
}结果
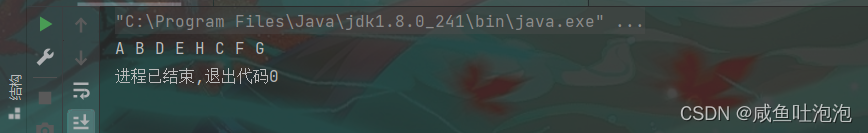
思路二使用迭代器:
1.创建一个集合res和栈stack,判断当前树是否为空树,是就返回res
2.判断当前节点和栈是否为空,是则返回res
3.若当前节点不为空,则将该节点的值加入集合,同时将节点压入栈中。再判断当前节点的左子节点是否为空,不为空继续执行这一步
4.若第三步中当前左子节点为空,就将栈顶元素赋给node 并弹出,再判断当前节点的右子节点(重复2~4)

public List<Character> circlepreOrder(Tree subtree){
List<Character> res = new ArrayList<>();
Stack<Tree> stack = new Stack<>();
Tree node = subtree;
if(node==null){return res;}
while(!stack.empty()||node!=null){
while(node!=null){
res.add(node.val);
stack.push(node);
node = node.left;
}
node = stack.pop();
node = node.right;
}
return res;
}主函数里面实现一下
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BrnaryTree tree = new BrnaryTree();
BrnaryTree.Tree subtree = tree.createtree();
//迭代实现前序遍历
System.out.println(tree.circlepreOrder(subtree));
}
}结果
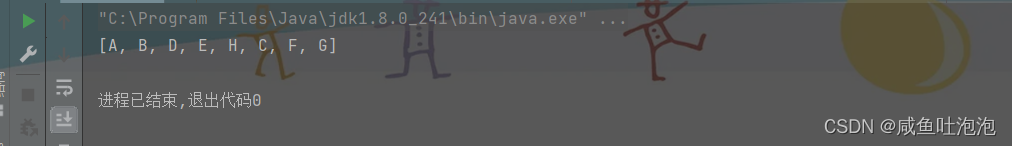
2.中序遍历:先遍历左子树,再输出父节点,再遍历右子树
思路一递归:
(1)如果当前节点的左子节点不为空,则递归中序遍历
(2)输出当前节点
(3)如果当前节点的右子节点不为空,则递归中序遍历
//中序遍历
public void midorder(Tree subtree){
if(subtree==null)return;
midorder(subtree.left);
System.out.print(subtree.val+" ");
midorder(subtree.right);
}
主函数里面实现一下
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BrnaryTree tree = new BrnaryTree();
BrnaryTree.Tree subtree = tree.createtree();
tree.preorder(subtree);
System.out.println();
tree.midorder(subtree);
}
}结果
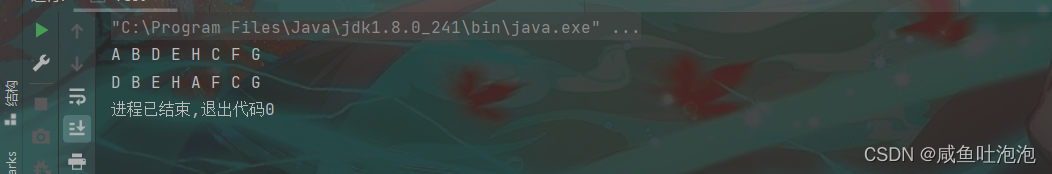
思路二使用迭代器:
1.创建一个集合res和栈stack,判断当前树是否为空树,是就返回res
2.判断当前节点和栈是否为空,是则返回res
3.若当前节点不为空,将节点压入栈中。再判断当前节点的左子节点是否为空,不为空继续执行这一步
4.若第三步为空,就将栈顶元素加入集合,同时赋给node并弹出,再判断右子节点(重复2~4)
public List<Character> circlemidOrder(Tree subtree){
List<Character> res = new ArrayList<>();
Stack<Tree> stack = new Stack<>();
Tree node = subtree;
if(node==null){return res;}
while(!stack.empty()||node!=null){
while(node!=null){
stack.push(node);
node = node.left;
}
res.add(stack.peek().val);
node = stack.pop();
node = node.right;
}
return res;
}主函数里面实现一下
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BrnaryTree tree = new BrnaryTree();
BrnaryTree.Tree subtree = tree.createtree();
//迭代实现中序遍历
System.out.println(tree.circlemidOrder(subtree));
}
}结果
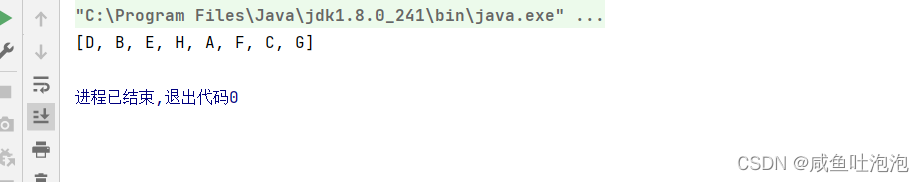
(3)后序遍历:先遍历左子树,再遍历右子树,最后输出父节点
思路一递归:
(1)如果当前节点的左子节点不为空,则递归后序遍历
(2)如果当前节点的右子节点不为空,则递归后序遍历
(3)输出当前节点
//后序遍历
public void lastorder(Tree subtree){
if(subtree==null)return;
lastorder(subtree.left);
lastorder(subtree.right);
System.out.print(subtree.val+" ");
}
主函数里面实现
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BrnaryTree tree = new BrnaryTree();
BrnaryTree.Tree subtree = tree.createtree();
tree.preorder(subtree);
System.out.println();
tree.midorder(subtree);
System.out.println();
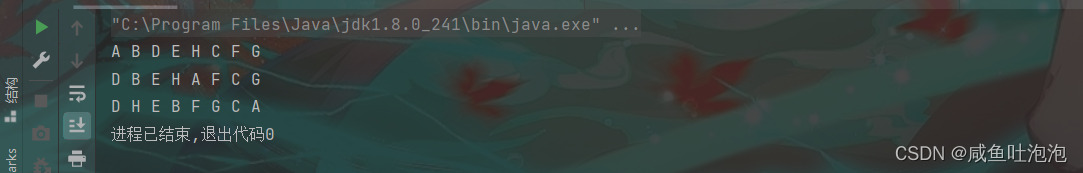
tree.lastorder(subtree);
}
} 
思路二使用迭代器:
1.创建一个集合res和栈stack和一个临时节点prev,判断当前树是否为空树,是就返回res
2.判断当前节点和栈是否为空,是则返回res
3.若当前节点不为空,将节点压入栈中。再判断当前节点的左子节点是否为空,不为空继续执行这一步
4.当第三步为空时,将栈顶元素赋给node并弹出。若node的右子节点为空或者右子节点为prev时,将该节点加入res,prev = root,root = null
5.若第四步右子节点不为空且右子节点不为prev时,将该结点压入栈中,继续判断该结点的右子节点
public List<Character> circlelastOrder(Tree subtree){
List<Character> res = new ArrayList<>();
Stack<Tree> stack = new Stack<>();
if(subtree==null)return res;
Tree prev = null;
Tree node = subtree;
while(node!=null|| !stack.empty()){
while(node!=null){
stack.push(node);
node = node.left;
}
node = stack.pop();
if(node.right==null||node.right==prev){
res.add(node.val);
prev = node;
node = null;
}else{
stack.push(node);
node = node.right;
}
}
return res;
}主函数里面实现一下
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BrnaryTree tree = new BrnaryTree();
BrnaryTree.Tree subtree = tree.createtree();
//迭代实现后序遍历
System.out.println(tree.circlelastOrder(subtree));
}
}结果
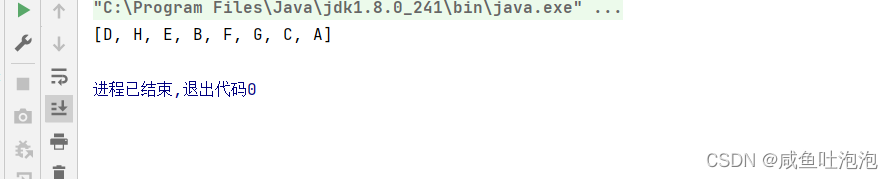
上面的遍历方法都是在遍历的时候输出,也就是不带返回值的。有时我们会遇到要求我们返回遍历的结果,比如力扣
这里我们有两种思路:遍历思路、子问题思路
(1)遍历思路
创建一个LinkedList的链表,利用它里面的方法实现对二叉树的遍历
public static class Solution {
//1.遍历思路
List<Character> ans;
public List<Character> preorderTraversal(Tree subtree) {
ans = new LinkedList<>();
preorder(subtree);
return ans;
}
public void preorder(Tree subtree){
if(subtree==null)return;
ans.add(subtree.val);
preorder(subtree.left);
preorder(subtree.right);
}
}
主函数里面实现一下
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BrnaryTree tree = new BrnaryTree();
BrnaryTree.Tree subtree = tree.createtree();
BrnaryTree.Solution solution = new BrnaryTree.Solution();
List<Character> list = solution.preorderTraversal(subtree);
System.out.println(list);
}
}结果
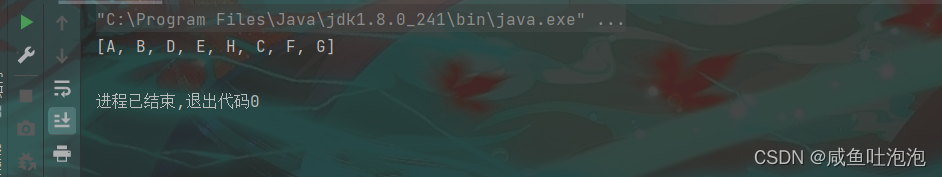
(2)子问题思路
创建LinkedList链表,利用链表中的方法。要遍历一颗二叉树,可以将二叉树分为左子树和右子树分别遍历, 分别将左子树链表遍历的结果和右子树链表遍历的结果加起来,最终返回链表即可
public static class Solution {
//子问题思路
public List<Character> preorderTraversal(Tree subtree){
List<Character> ans = new LinkedList<>();
if(subtree==null)return ans;
ans.add(subtree.val);
List<Character> leftret = preorderTraversal(subtree.left);
ans.addAll(leftret);
List<Character> rightret = preorderTraversal(subtree.right);
ans.addAll(rightret);
return ans;
}
}结果
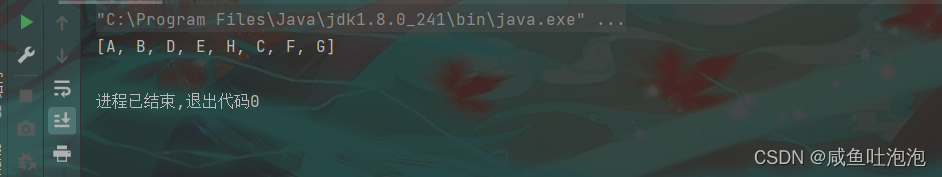
搞完遍历以后,我们继续看二叉树的其他基本操作
1.获取树中节点的个数
方法一:遍历思路
思路:我们在遍历的时候,创建一个用于计数的计数器count,每遇到一个节点 count就加一
//利用前序遍历获取树中节点的个数
public static int count;
//遍历思路
public void size(Tree subtree) {
if(subtree==null)return;
count++;
size(subtree.left);
size(subtree.right);
}主函数里面实现一下
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BrnaryTree tree = new BrnaryTree();
BrnaryTree.Tree subtree = tree.createtree();
tree.size(subtree);
System.out.println("节点个数为"+BrnaryTree.count);
}
}
结果
方法二:子问题思路
思路:树的节点为左子树的节点加上右子树的节点再加上根节点
//子问题思路
public int size2(Tree subtree){
if(subtree==null)return 0;
return 1+size2(subtree.left)+size2(subtree.right);
}主函数里面实现一下
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BrnaryTree tree = new BrnaryTree();
BrnaryTree.Tree subtree = tree.createtree();
System.out.println("节点个数为"+tree.size2(subtree));
}
}结果
2.获取叶子节点的个数
/** * 获取叶子节点的个数 * 思路:当节点的左子节点和右子节点都为空时,该节点就是叶子节点,每遇到一个这样的节点count就 *加一 * 方法:遍历思路、子问题思路 */
//遍历思路
public void getLeafNodeCount(Tree subtree){
if(subtree==null)return;
if(subtree.left==null&&subtree.right==null){count++;}
getLeafNodeCount(subtree.left);
getLeafNodeCount(subtree.right);
}主函数里面实现一下
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BrnaryTree tree = new BrnaryTree();
BrnaryTree.Tree subtree = tree.createtree();
tree.getLeafNodeCount(subtree);
System.out.println("叶子结点个数为:"+BrnaryTree.count);
}
}
结果
//子问题思路
public int getLeafNodeCount2(Tree subtree){
if(subtree==null)return 0;
if(subtree.left==null&&subtree.right==null){return 1;}
count = getLeafNodeCount2(subtree.left)+getLeafNodeCount2(subtree.right);
return count;
}主函数里面实现
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BrnaryTree tree = new BrnaryTree();
BrnaryTree.Tree subtree = tree.createtree();
System.out.println("叶子结点个数为:"+tree.getLeafNodeCount2(subtree));
}
}结果
3.获取第K层节点的个数
//获取第k层节点的个数
public int getKLevelNodeCount(Tree subtree,int k){
if(subtree==null)return 0;
if(k==1)return 1;
return getKLevelNodeCount(subtree.left,k-1)+getKLevelNodeCount(subtree.right,k-1);
}主函数里面实现一下
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BrnaryTree tree = new BrnaryTree();
BrnaryTree.Tree subtree = tree.createtree();
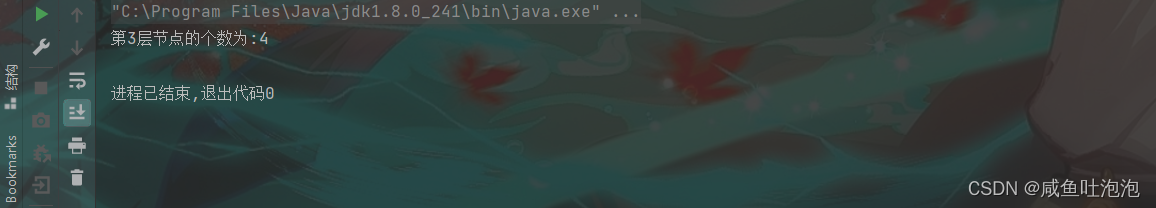
System.out.println("第3层节点的个数为:"+tree.getKLevelNodeCount(subtree,3));
}
}结果
4.获取二叉树的高度
/** * 获取二叉树的高度:树的高度为左树高度与右树高度中的较大值加上根节点所在一层的高度 */
int getHeight(Tree subtree){
if(subtree==null)return 0;
int leftDepth = getHeight(subtree.left);
int rightDepth = getHeight(subtree.right);
return Math.max(leftDepth,rightDepth)+1;
}主函数里面实现一下
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BrnaryTree tree = new BrnaryTree();
BrnaryTree.Tree subtree = tree.createtree();
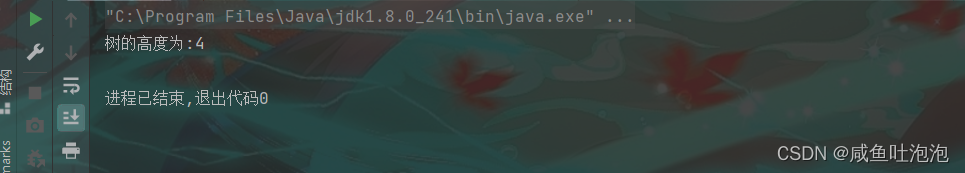
System.out.println("树的高度为:"+tree.getHeight(subtree));
}
}结果
5.检测值为value的元素是否存在
//在二叉树中查找某个值
public Tree findtreenode(Tree tree,char val){
if(tree==null)return null;
if(tree.val == val)return tree;
Tree node1 = findtreenode(tree.left,val);
if(node1!=null)return node1;
else {
Tree node2 = findtreenode(tree.right,val);
return node2;
}
}主函数里面实现一下
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BrnaryTree tree = new BrnaryTree();
BrnaryTree.Tree subtree = tree.createtree();
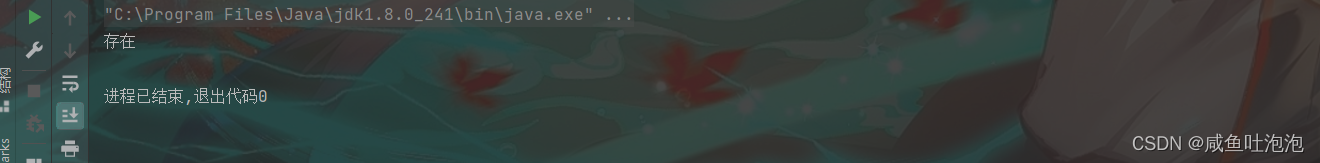
BrnaryTree.Tree node = tree.findtreenode(subtree, 'E');
if(node==null)System.out.println("不存在");
else System.out.println("存在");
}
}
结果
6.层序遍历
思路:
1.判断当前树是否为空,是就返回,不是就创建一个队列。将该节点压入队列中。
2.以队列是否为空为判断条件。不为空,就创建一个指针node,该指针指向队列中的首元素。
将队列中的元素弹出并打印,如果node的左子节点不为空,就将该左子节点压入队列中。如果node的右子节点不为空,就将该右子节点压入队列中。
3.当队列为空的时候,说明已经遍历完了,退出循环。
//层序遍历
public void leveorder(Tree subtree){
if(subtree==null)return;
Queue<Tree> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(subtree);
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
Tree node = queue.poll();
if(node.left!=null){
queue.offer(node.left);
}
if(node.right!=null){
queue.offer(node.right);
}
System.out.print(node.val+" ");
}
}主函数里面实现一下
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BrnaryTree tree = new BrnaryTree();
BrnaryTree.Tree subtree = tree.createtree();
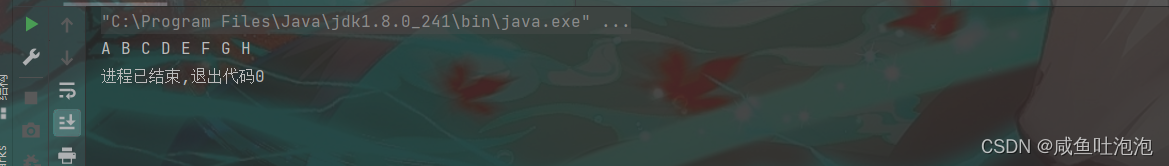
tree.leveorder(subtree);
}
}结果
6.带返回值的层序遍历
//带返回值的层次遍历
public List<List<Character>> levelOrder(Tree root) {
List<List<Character>> ret = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null) return ret;
Queue<Tree> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
List<Character> list = new ArrayList<>();
int len = queue.size();
while(len-->0){
Tree cur = queue.poll();
list.add(cur.val);
if(cur.left!=null){
queue.offer(cur.left);
}
if(cur.right!=null){
queue.offer(cur.right);
}
}
ret.add(list);
}
return ret;
}主函数里面实现一下
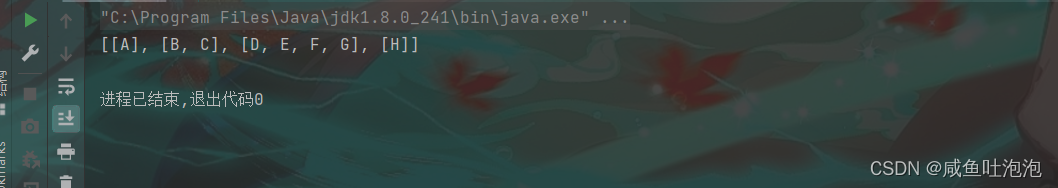
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BrnaryTree tree = new BrnaryTree();
BrnaryTree.Tree subtree = tree.createtree();
List<List<Character>> lists = tree.levelOrder(subtree);
System.out.println(lists);
}
}
结果
7.判断一棵树是不是完全二叉树
思路:
1.创建一个队列,如果不是空树,就将根节点放入队列中
2.只要队列不为空,则创建一个临时指针cur。将队列顶的数据弹出并用cur接收。只要cur!=null,就将cur.left、cur.right放入队列中,若cur==null,则退出循环
3.第二步执行完毕以后,队列里面有两种情况:(1)队列不为空,且全部都是null;(2)队列不为空,且里面即含有有效节点,又含有null。如果是第一种情况,则为完全二叉树,返回true,若为第二种情况,则不是完全二叉树,返回false
//判断一棵树是否是完全二叉树
boolean isCompleteTree(Tree subtree){
if(subtree==null)return false;
Queue<Tree> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(subtree);
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
Tree cur = queue.poll();
if(cur!=null){
queue.offer(cur.left);
queue.offer(cur.right);
}else{
break;
}
}
//判断队列里面的情况
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
if(queue.peek()==null){
queue.poll();
}else{
return false;
}
}
return true;
}主函数里面实现一下
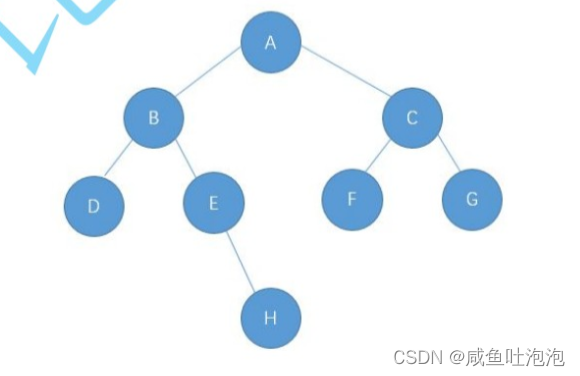
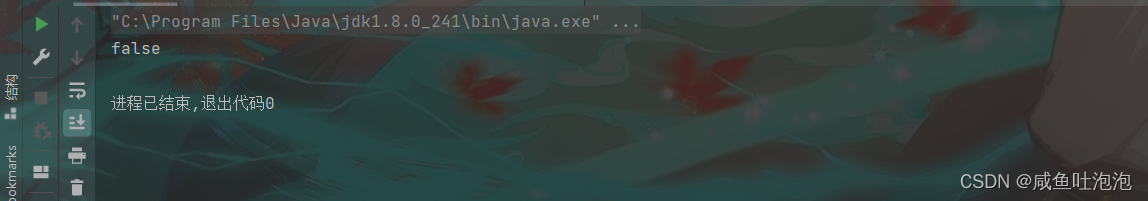
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BrnaryTree tree = new BrnaryTree();
BrnaryTree.Tree subtree = tree.createtree();
//判断一棵树是否是完全二叉树
System.out.println(tree.isCompleteTree(subtree));
}
}二叉树示意图
结果
面试题
1.检查两棵树是否相同力扣
思路:
1.先判断树p、树q是否为空,如果其中两个为空,则返回true
2.若p、q其中一个为空或者p.val!=q,val,则返回false。若不满住上面,则创建布尔类型的变量p1,让p1接收p和q的左子树比较的结果。同时创建q1接收p和q的右子树比较的结果
3.若p1、q1中有一个为false,就返回false,否者返回true
class Solution {
public boolean isSameTree(TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if(p==null&&q==null)return true;
if(p==null||q==null||p.val!=q.val)return false;
boolean p1 = isSameTree(p.left,q.left);
boolean q1 = isSameTree(p.right,q.right);
if(p1==false||q1==false)return false;
return true;
}
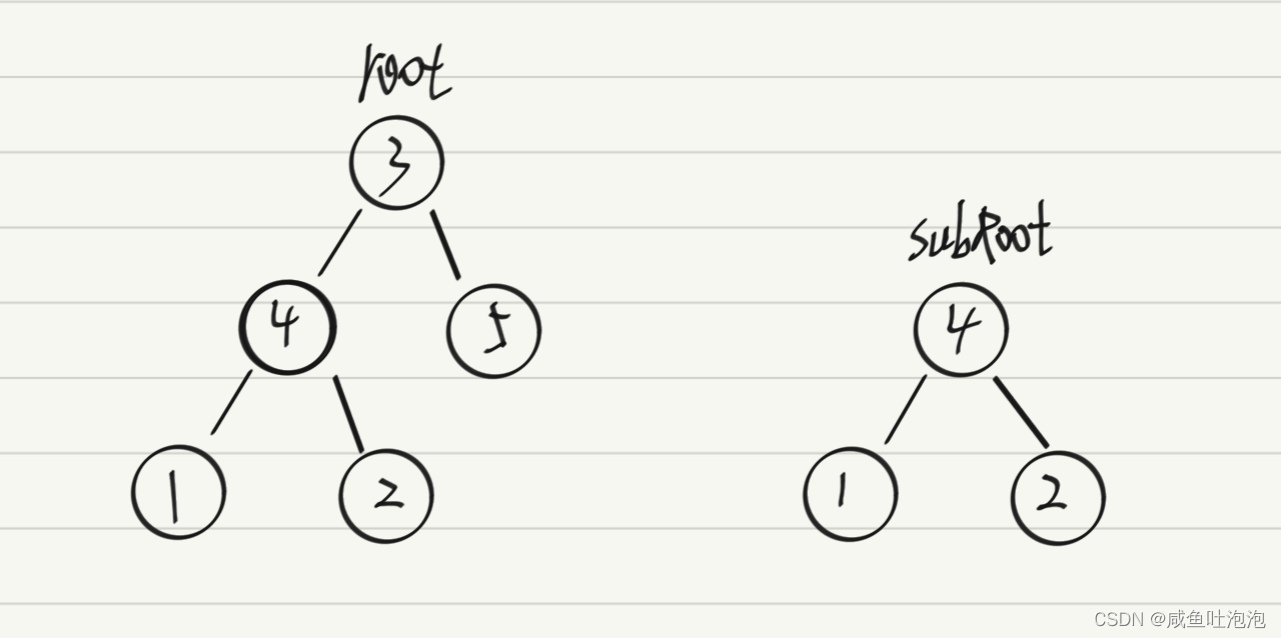
}2.判断一棵树是否是另一颗树的子树力扣
思路:
1.判断root是否是null,是则返回false
2.判断subRoot是不是和root是相同的两棵树
3.判断subRoot是不是root的左树的子树
4.判断subRoot是不是root的右树的子树
class Solution {
public boolean isSameTree(TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if(p==null&&q==null)return true;
if(p==null||q==null||p.val!=q.val)return false;
boolean p1 = isSameTree(p.left,q.left);
boolean q1 = isSameTree(p.right,q.right);
if(p1==false||q1==false)return false;
return true;
}
public boolean isSubtree(TreeNode root, TreeNode subRoot) {
if(root==null)return false;
if(isSameTree(root,subRoot))return true;
if(isSubtree(root.left,subRoot))return true;//如果subroot和root的左子树相同,返回true
if(isSubtree(root.right,subRoot))return true;//如果subroot和root的右子树相同,返回true
return false;
}
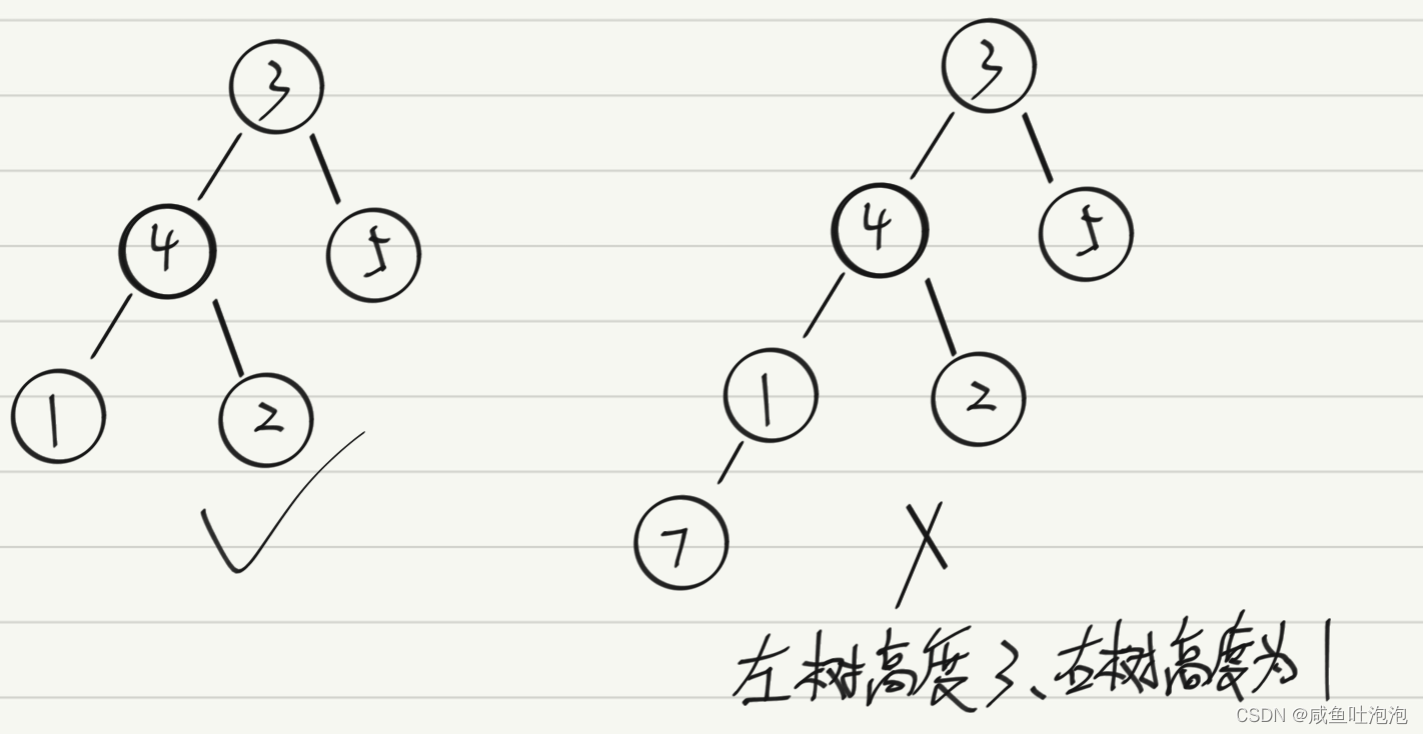
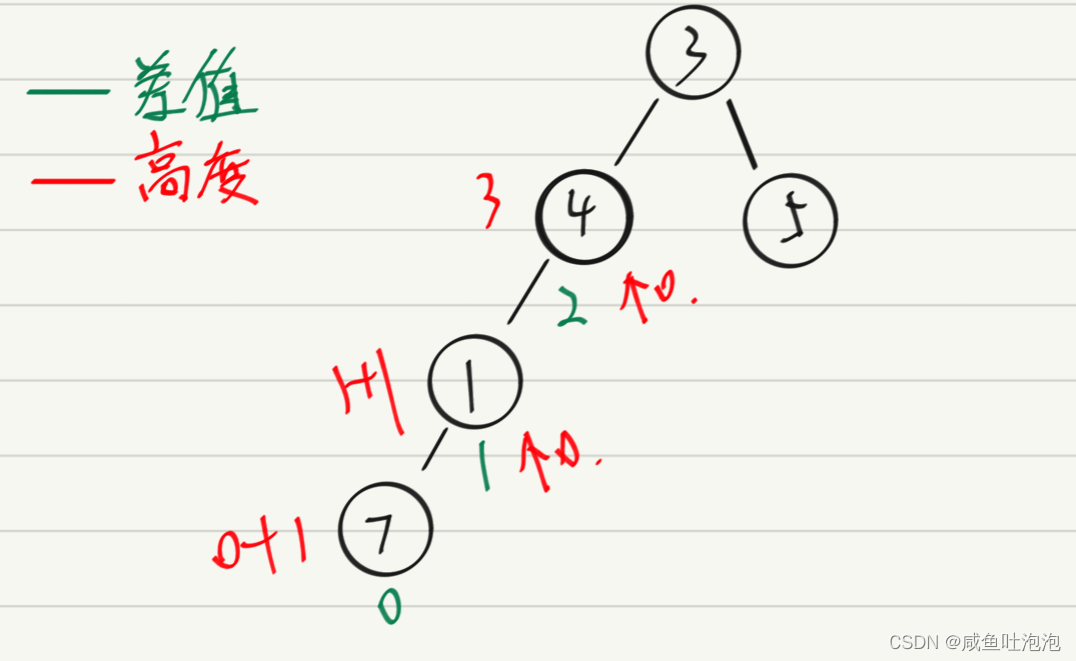
}3.判断一棵树是否是平衡二叉树力扣
高度平衡二叉树:左、右树高度差<=1
思路:整棵树高度平衡、左右树高度也要平衡
方法一:每个节点都去求一下左右高度差是不是<=1(时间复杂度O(n2))
class Solution {
//求整棵树的高度
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
if(root==null)return 0;
if(root.left==null&&root.right==null)return 1;
int leftDepth = maxDepth(root.left);
int rightDepth = maxDepth(root.right);
return Math.max(leftDepth,rightDepth)+1;
}
public boolean isBalanced(TreeNode root) {
if(root==null)return true;//如果是空树,也是一颗平衡二叉树
//求左树和右树的高度,差值如果大于1就返回false
return Math.abs(maxDepth(root.left)-maxDepth(root.right))<=1 && isBalanced(root.left) && isBalanced(root.right);
}
}方法二:求高度的过程中,就检查高度是否<=1(时间复杂度O(n))
class Solution {
//求整棵树的高度
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
if(root==null)return 0;
if(root.left==null&&root.right==null)return 1;
int leftDepth = maxDepth(root.left);
int rightDepth = maxDepth(root.right);
if(leftDepth>=0 && rightDepth>=0 && Math.abs(leftDepth-rightDepth)<=1){
return Math.max(leftDepth,rightDepth)+1;
}else{
return -1;
}
}
public boolean isBalanced(TreeNode root) {
if(root==null)return true;//如果是空树,也是一颗平衡二叉树
return maxDepth(root)>=0?true:false;
}
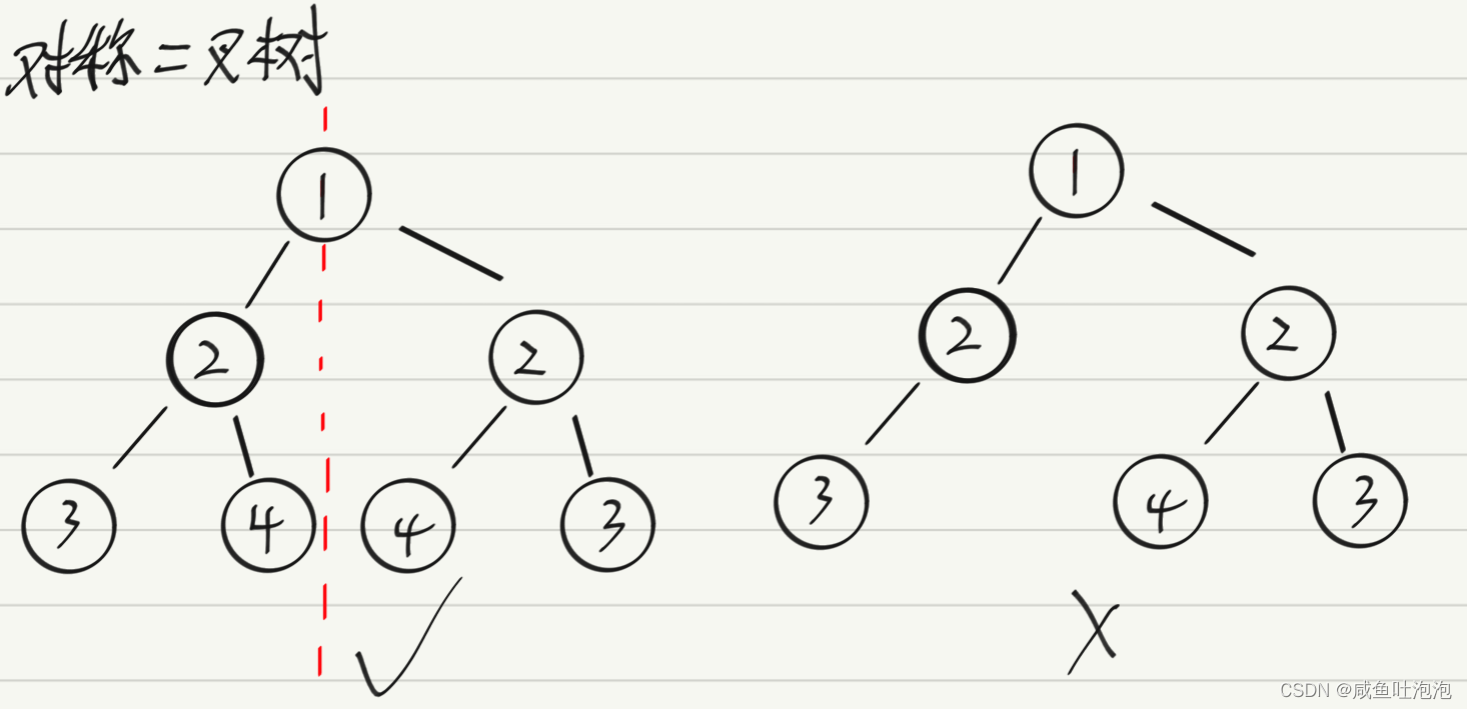
}4.对称二叉树力扣
思路:
1.判断左、右子树是否对称
2.若左、右子树都为空,即空树那也是对称的返回true。若左、右子树有一个为空或左、右子树的值不相等,不对成返回false
3.深度遍历,返回最终比较得结果
class Solution {
public boolean isSymmetricchild(TreeNode leftroot,TreeNode rightroot) {//判断左树和右树对不对称
if(leftroot==null&&rightroot==null)return true;//左右树都为空也是对称的
if(leftroot==null||rightroot==null||leftroot.val!=rightroot.val)return false;
return isSymmetricchild(leftroot.left,rightroot.right) && isSymmetricchild(leftroot.right,rightroot.left);
}
public boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode root) {
if(root==null)return true;
return isSymmetricchild(root.left,root.right);
}
}5.二叉树的构建和遍历 二叉树遍历_牛客题霸_牛客网


import java.util.*;
class Tree{//构建树节点
public char val;
public Tree left;
public Tree right;
public Tree(char val){
this.val = val;
}
}
public class Main{
public static int i;
public static Tree creattree(String str){//利用前序遍历创建二叉树
Tree root = null;
if(str.charAt(i)!='#'){
root = new Tree(str.charAt(i));
i++;
root.left = creattree(str);
root.right = creattree(str);
}else{
i++;
}
return root;
}
public static void inorder(Tree tree){//中序遍历二叉树
if(tree==null)return;
inorder(tree.left);
System.out.print(tree.val+" ");
inorder(tree.right);
}
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
while(scan.hasNextLine()){
String str = scan.nextLine();
Tree tree = creattree(str);
inorder(tree);
}
}
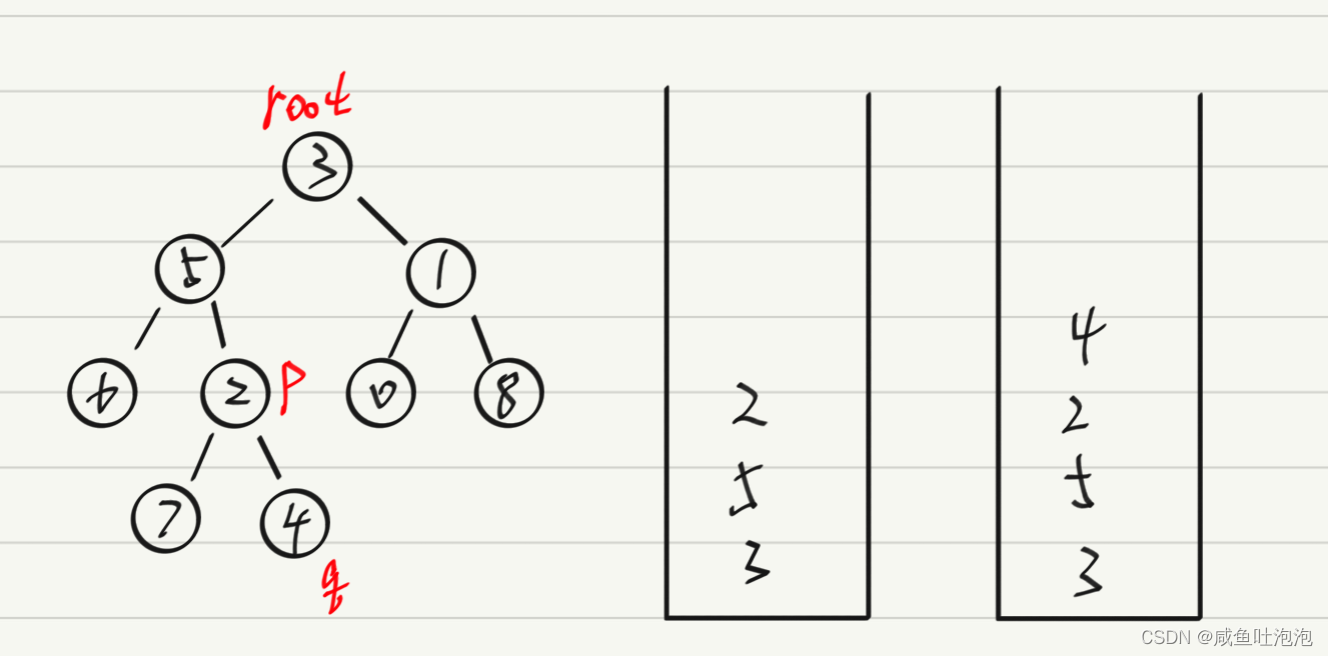
}6.找一个数中结点最近的公共祖先 力扣
思路一:
如果二叉树的表示方式是孩子双亲表示法。那么此时,这个最近公共祖先可以被化为求链表的交点
思路二:
1.使用2个栈,存储从根节点到指定节点路径上所有节点
2.比较两个栈的大小,让栈中多的出差值个数据
3.执行第二步以后,两个栈同时出栈,如果栈顶元素相同,那么此时这个值就是最近的公共祖先
class Solution {
public boolean getPath(TreeNode root, TreeNode s,Stack<TreeNode> stack){//获取从root节点到指定节点的路径
if(root==null||s==null)return false;
stack.push(root);
if(root==s)return true;
boolean leftret = getPath(root.left,s,stack);
if(leftret)return true;
boolean rightret = getPath(root.right,s,stack);
if(rightret)return true;
stack.pop();
return false;
}
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
Stack<TreeNode> stack1 = new Stack<>();
getPath(root,p,stack1);
Stack<TreeNode> stack2 = new Stack<>();
getPath(root,q,stack2);
int size1 = stack1.size();
int size2 = stack2.size();
if(size1>size2){
int len = size1-size2;
while(len-->0){
stack1.pop();
}
}else{
int len = size2-size1;
while(len-->0){
stack2.pop();
}
}
while(!stack1.empty()&&!stack2.empty()){
if(stack1.peek()==stack2.peek()){
return stack2.peek();
}else{
stack1.pop();
stack2.pop();
}
}
return null;
}
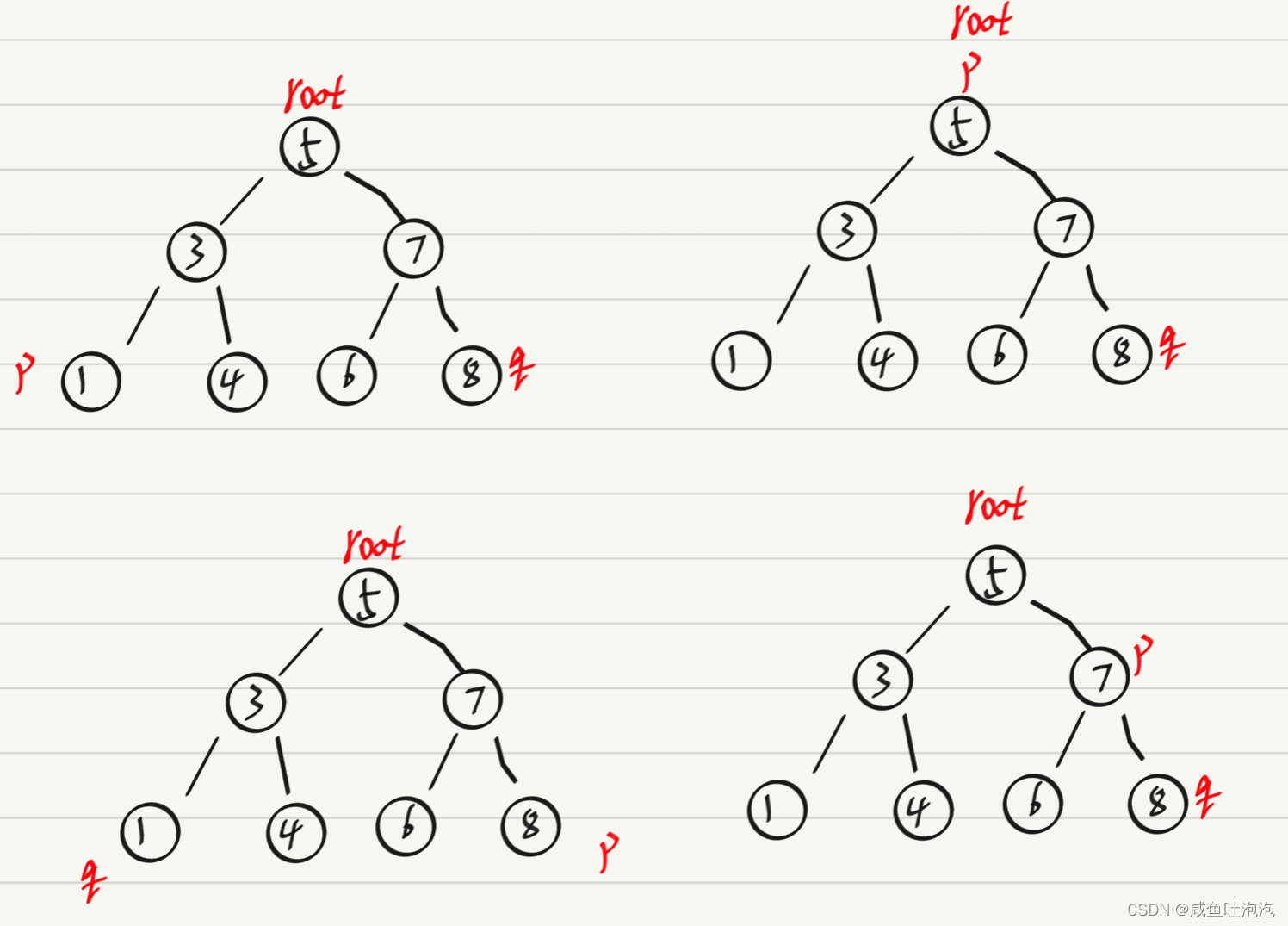
}思路二:
如果这个课树,是一颗二叉搜索树(二叉搜索树:根节点一定比左子节点大,比右子节点小的树)
1.如果p或者q中的一个为root节点,则它们最近的公共祖先是root
2.如果p、q分别在二叉树的左右两边,则它们最近的公共祖先是root
3.如果p、q在二叉树中左子树或右子树,则按照前面的思路递归二叉树
class Solution {
public boolean getPath(TreeNode root, TreeNode s,Stack<TreeNode> stack){
if(root==null)return null;
if(p==root||q==root)return root;//如果p、q中有一个为根节点就返回该节点
TreeNode leftret = lowestCommonAncestor(root.left,p,q);
TreeNode rightret = lowestCommonAncestor(root.right,p,q);
if(leftret!=null&&rightret!=null){//如果左右都不为空,说明p、q分别在二叉树左右两边.此时根节点就是它们最近的公共祖先
return root;
}else if(leftret!=null){//说明p、q都在二叉树的左子树中
return leftret;
}else if(rightret!=null){//说明p、q都在二叉树的右子树中
return rightret;
}
return null;//说明p、q既不在左子树又不在右子树当中
}
} 
7.二叉搜索树转换成双向链表 二叉搜索树与双向链表_牛客题霸_牛客网
思路:
大体思路:让二叉树left作为前驱,right作为后继;中序遍历二叉搜索树
1.中序遍历找到二叉搜索树最左边的节点,用一个临时变量pCur记录当前节点的位置
2.在最开始的时候创建一个辅助变量pRev,用来记录pCur节点左子节点的位置
3.pCur.left = pRev(让当前节点的前驱为当前节点的左子节点),若pCur!=null,则让pRev.right = pCur(让当前节点的左子节点的后继为当前节点)
4.中序遍历执行上面的操作,直到遍历完整颗二叉搜索树
public class Solution {
TreeNode prev = null;
public void Convertchild(TreeNode pCur){//1.将二叉树的left作为前驱,right作为后继;2.中序遍历二叉树实现转换
if(pCur==null)return;
Convertchild(pCur.left);
pCur.left = prev;
if(prev!=null){prev.right = pCur;}
prev = pCur;
Convertchild(pCur.right);
}
public TreeNode Convert(TreeNode pRootOfTree) {
if(pRootOfTree==null)return null;
Convertchild(pRootOfTree);
while(pRootOfTree.left!=null){
pRootOfTree = pRootOfTree.left;//找到双向链表的头结点
}
return pRootOfTree;//返回双向链表的头结点
}
}
8.根据一棵树的前序遍历与中序遍历创建一颗二叉树 力扣
思路:
1.定义Index前序遍历这个数组
2.在中序遍历的[befor,last]区间,找到rootIndex的下标位置
3.此时rootIndex左边的就是左树,rootIndex右边的就是右树
4.递归创建左树和递归创建右树
5.当befor>last的时候,说明没有了左树或者右树

注意index是全局变量,它不会随着归而变回原来的值
public class Tree {
public static class TreeNode{
public char val;
public TreeNode left;
public TreeNode right;
public TreeNode(char val) {
this.val = val;
}
}
public static class Solution {
public int index = 0;
public TreeNode buildTreechild(char[] pre, char[] mid, int befor, int last){
if(befor>last)return null;//说明此时,没有左树或者没有右树
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(pre[index]);//以前序遍历的结果创建根节点
//找到根节点在中序遍历当中的位置
int rootIndex = findInRootIndex(mid,befor,last,pre[index]);
index++;
root.left = buildTreechild(pre,mid,befor,rootIndex-1);
root.right = buildTreechild(pre,mid,rootIndex+1,last);
return root;
}
public int findInRootIndex(char[] mid,int befor,int last,int val){//在中序数组区间之间找一个val值,以这个val划分区间
for(int i = befor;i<=last;i++){
if(mid[i]==val){
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
public TreeNode buildTree(char[] preorder, char[] inorder) {
return buildTreechild(preorder,inorder,0,inorder.length-1);
}
}
//后序遍历二叉树
public void lastorder(TreeNode node){
if(node==null)return;
lastorder(node.left);
lastorder(node.right);
System.out.print(node.val+" ");
}
}
主函数里面实现一下
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
char[] preorder = new char[]{'E','F','H','I','G','J','K'};
char[] inorder = new char[]{'H','F','I','E','J','K','G'};
Tree tree = new Tree();
Tree.Solution solution = new Tree.Solution();
Tree.TreeNode node = solution.buildTree(preorder, inorder);//根据前序遍历和中序遍历创建二叉树
System.out.println("后序遍历二叉树结果:");
tree.lastorder(node);//后序遍历二叉树
}
}
结果:
9.二叉树创建字符串力扣
方法一:递归
思路:
-
如果当前节点有两个孩子,那我们在递归时,需要在两个孩子的结果外都加上一层括号;
-
如果当前节点没有孩子,那我们不需要在节点后面加上任何括号;
- 如果当前节点只有左孩子,那我们在递归时,只需要在左孩子的结果外加上一层括号,而不需要给右孩子加上任何括号;
- 如果当前节点只有右孩子,那我们在递归时,需要先加上一层空的括号 \text{`()'}‘()’ 表示左孩子为空,再对右孩子进行递归,并在结果外加上一层括号。
class Solution {
public String tree2str(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return "";
}
if (root.left == null && root.right == null) {
return Integer.toString(root.val);
}
if (root.right == null) {//如果只有左孩子,只需要在做孩子的结果上加上一层括号
return new StringBuffer().append(root.val).append("(").append(tree2str(root.left)).append(")").toString();
}
//如果只有右孩子,需要加上一层空括号,再对右孩子加上一层括号
return new StringBuffer().append(root.val).append("(").append(tree2str(root.left)).append(")(").append(tree2str(root.right)).append(")").toString();
}
}