链表是基于顺序表之后的一种更加高效的数据结构,他能够有效的增删改查,比顺序表的效率提高了很多。下面我们来实现这一数据结构。
不光是实现,我们还需要通过几个功能来加深大家对链表的理解,这列功能包括链表中的节点我们都设置在一个Linkedlist类里面
public class Linkedlist {
}然后让主类来实现它Linkedlist类里面的方法
public class MyLinkedlist {
public static void main(String[] args) {
}
}首先单链表是有一个一个的节点连接起来的一串数据,单链表就好比我们现实生活中的火车,上一节车厢是紧挨着下一节车厢的,车厢与车厢之间用铁钩连接起来。那我们怎样将这一事物抽象化,形成代码呐?这个我们就要用到类和对象的思想,将火车车厢实例化一个一个节点,铁钩实例化一个指针,下面请看代码
//链表类
static class Node{//将火车实例化为Node
public Integer no;//将车厢通过一个整形数字来表示
public Node next;//将铁钩实例化为next指针,因为他负责连接一个个车厢,所以它的类型就是Node
public Node(Integer no) {//这里给一个构造器,因为不知道下一节车厢的铁钩连接到哪个车厢,所以不用考虑next
this.no = no;
}
}这里我们还需要定义一个headNode来表示单链表的头引用
public class Linkedlist {
//链表类
static class Node{
public Integer no;
public Node next;
public Node(Integer no) {
this.no = no;
}
}
public Node headNode;//表示单链表的头节点引用
}在完成最基本的元素添加以后,我们就可以创建节点了。通过节点的一个next属性将下一个节点连接起来,在完成链表的创建以后(这里为了好理解,我们采用穷举的方式来实现),我们需要打印出来看一下(这里需要讲解一下,因为每一个节点,我们在定义节点的时候只传了一个整形数字,也就是说节点的另一个属性next是为null的。我们在打印的时候如果遇到node.next==null时,就代表这个节点是最后一个节点。与此同时,我们需要定义一个临时节点去代替headNode节点遍历单链表,因为我们后面还需要用到这个headNode)
public class Linkedlist {
//链表类
static class Node{
public Integer no;
public Node next;
public Node(Integer no) {
this.no = no;
}
}
public Node headNode;//表示单链表的头节点引用
//创建一个链表
public void creatlist(){//创建一个链表
Node node1 = new Node(11);
Node node2 = new Node(22);
Node node3 = new Node(21);
Node node4 = new Node(21);
Node node5 = new Node(34);
Node node6 = new Node(13);
node1.next = node2;
node2.next = node3;
node3.next = node4;
node4.next = node5;
node5.next = node6;
headNode = node1;
}
//遍历链表
public void printList(){
Node temp = headNode;
while(temp!=null){
System.out.print(temp.no+" ");
temp = temp.next;
}
}
}主函数里面实现一下
public static void main1(String[] args) {
Linkedlist linkedlist = new Linkedlist();
linkedlist.creatlist();//穷举创建单链表
linkedlist.printList();//打印链表
}结果

好了,到这里我们已经实现了无头节点单链表的实现,光实现还不够,我们还需要实现一些增删改查功能
1.增加节点:
我们这里增加节点有三种方式分别是:尾插法、头插法、在任意位置插入
(1)尾插法
在头结点的后面依次增加节点;这里我们需要注意两点,第一头结点可能为空,也就是一个节点都没有,这种情况只需要将新节点的地址给headNode即可。第二头结点不为空,单链表中有元素,这时我们就需要找到最后一个节点,然后将新的节点加载他后面即可
public class Linkedlist {
/**
*尾插法:遍历找到最后的节点,将新的节点插在最后节点后面
*/
public void finallAdd(int data){
Node node = new Node(data);
if(headNode==null){
headNode = node;
}else{
Node temp = headNode;
while(true){
if(temp.next==null){//当temp.next==null时候,说明已经找到最后一个节点了
temp.next = node;
break;
}
temp = temp.next;//遍历链表
}
}
}
}
在主函数里面实现一下
public static void main(String[] args) {
Linkedlist linkedlist = new Linkedlist();
linkedlist.creatlist();//穷举创建单链表
linkedlist.printList();//打印链表
System.out.println();
linkedlist.finallAdd(520);
linkedlist.printList();
}结果
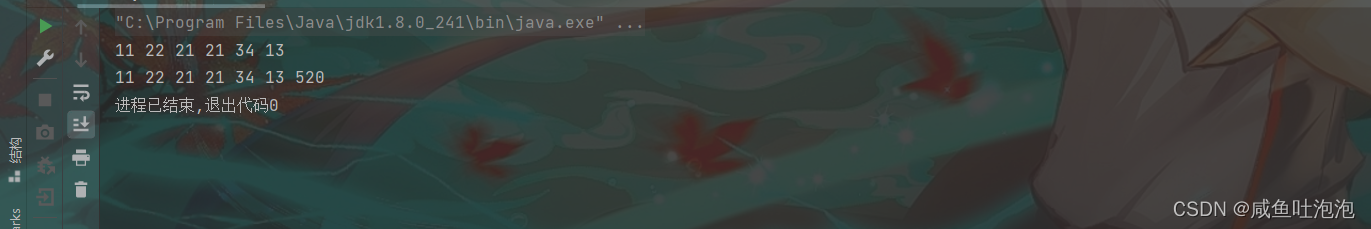
现在我们也可以不用穷举的方式来创建链表 ,而是单个单个的创建(用到的就是尾插法)
public static void main2(String[] args) {//验证尾插法
Linkedlist linkedlist = new Linkedlist();
linkedlist.finallAdd(11);
linkedlist.finallAdd(22);
linkedlist.finallAdd(33);
linkedlist.finallAdd(44);
linkedlist.printList();
}结果
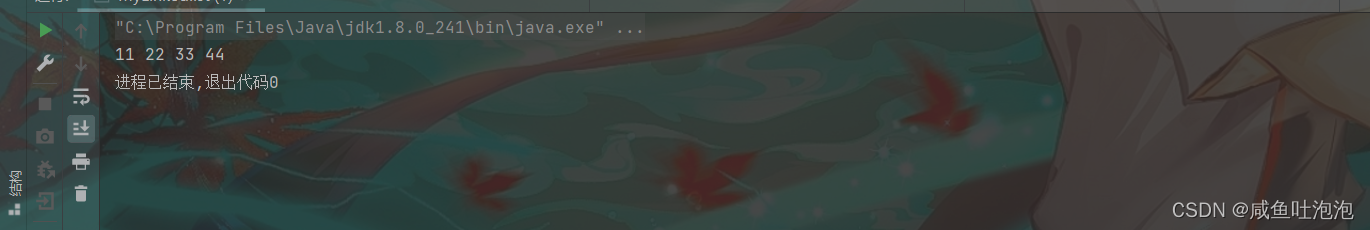
(2)头插法:
在头结点的前面一个一个节点的插入
我们在使用头插法的时候理一下思路:有两个节点,一个是头结点,是否为空不影响我们的使用。另一个是待插入的节点node, 可以知道的是node.next==null。既然要插入到头结点的前面,那么只需要让node.next==headNode即可。但是为了后面的节点能够插入,我们还需要令headNode==node;看图

public class Linkedlist {
/**
*头插法:在头结点的前面插入新的节点,然后另新的头结点==新的节点
*/
public void fristAdd(int data){
Node node = new Node(data);
node.next = headNode;
headNode = node;
}
}
在主函数里面实现一下
public static void main(String[] args) {
Linkedlist linkedlist = new Linkedlist();
linkedlist.creatlist();//穷举创建单链表
linkedlist.printList();//打印链表
System.out.println();
linkedlist.fristAdd(5);
linkedlist.printList();
}结果
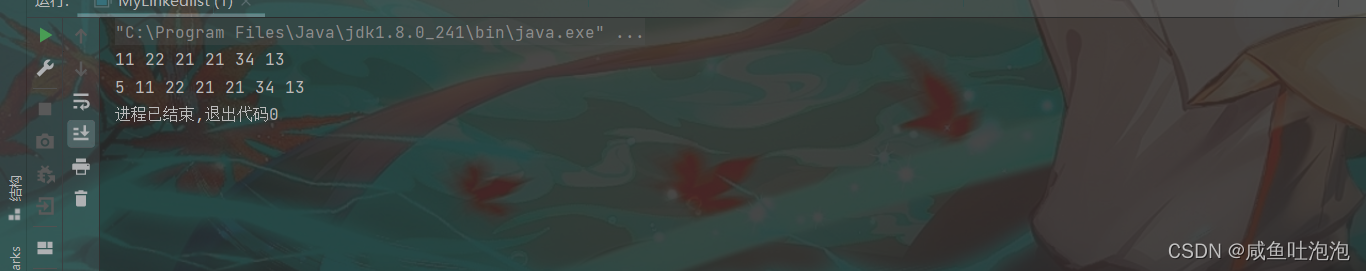
同样可以直接用头插法创建链表
public static void main(String[] args) {//验证头插法
Linkedlist linkedlist = new Linkedlist();
linkedlist.fristAdd(1);
linkedlist.fristAdd(2);
linkedlist.fristAdd(3);
linkedlist.fristAdd(4);
linkedlist.fristAdd(5);
linkedlist.printList();
}结果
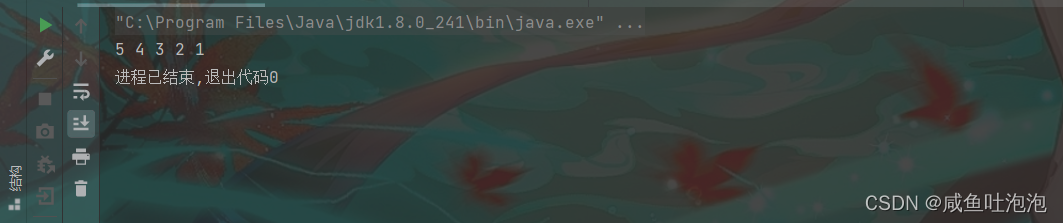
(3)在任意位置插入节点:
根据下标指示链表插入
不过在任意位置插入节点需要注意以下事项:
1.判断插入位置的合法性:插入的区间[0,lenth()],这里的lenth()是链表的长度
2.如果下标index==0,那就直接调用头插法,index==lenth()就直接调用尾插法
3.当插在链表的中间某个位置时,就需要找到插入位置的前一个节点,比如要在链表中下标为1的位置插入一个新节点node,就需要找到这个位置的前一个节点temp,让node.next = temp.next;同时让temp.next = node;
也就是说我们只需要找到index-1哪个位置的节点,然后执行插入操作
public class Linkedlist {
/**
*在任意位置插入节点
* 1.首先要判断插入位置的合法性,index的合法区间是[0,lenthlist()]
* 2.遍历要插入位置的前一个节点temp = temp.next;
* 3.找到要插入位置前一个节点temp,然后node.next = temp.next;temp.next = node;
*/
public void indexAdd(int index,int data){
if(index<0||index>lenthlist()){
throw new RuntimeException("插入位置不合法");
}
if(index==0){
fristAdd(data);
return;
}
if(index==lenthlist()){
finallAdd(data);
return;
}
Node node = new Node(data);
Node temp = FindIndexSubOne(index);
node.next = temp.next;
temp.next = node;
}
//计算链表长度
public int lenthlist(){
Node temp = this.headNode;
int lenth = 0;
while(temp!=null){
lenth++;
temp = temp.next;
}
return lenth;
}
//找到index-1位置的节点
public Node FindIndexSubOne(int index){
Node temp = headNode;
while(index-1!=0){
temp = temp.next;
index--;
}
return temp;
}
}在主函数里面实现一下
public static void main(String[] args) {
Linkedlist linkedlist = new Linkedlist();
linkedlist.creatlist();//穷举创建单链表
linkedlist.printList();//打印链表
System.out.println();
linkedlist.indexAdd(5,2020);
linkedlist.printList();
}结果

上面实现的是单链表的增加操作,下面实现单链表中查找某个节点的操作
查找节点的时候可能会遇到链表为空的情况,也有可能链表中没有要查找的数据,这两种情况我们只需要返回false即可
public class Linkedlist {
//在链表中判断是否包含关键字Key
public boolean justKey(int key){
Node temp = headNode;
while(temp!=null){
if(key== temp.no){
return true;
}
temp = temp.next;
}
return false;
}
}在主函数里面实现一下
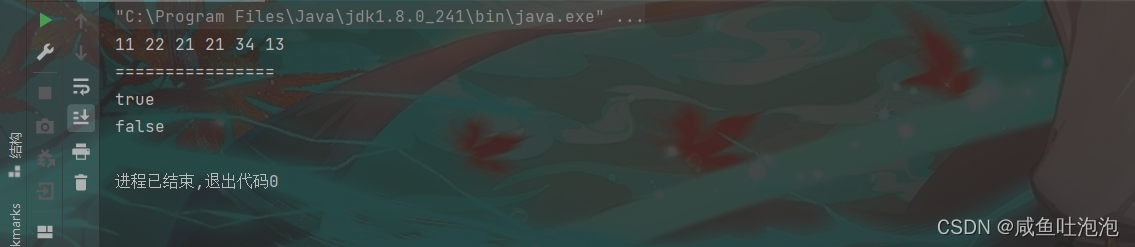
public static void main(String[] args) {
Linkedlist linkedlist = new Linkedlist();
linkedlist.creatlist();//穷举创建单链表
linkedlist.printList();//打印链表
System.out.println();
System.out.println("================");
System.out.println(linkedlist.justKey(11));//判断链表中是否包含某关键字
System.out.println(linkedlist.justKey(100));
}结果
下面实现单链表中某个数据的删除操作
删除操作:(1)删除链表中某个元素;(2)删除链表中的所有Key节点;(3)清空单链表
(1)删除链表中某个元素
删除链表中数据的时候,可能会遇到链表为空的情况,也有可能会遇到链表中找不到指定数据删除的情况,这时也只需要返回false即可。当删除的数据是头结点或者删除链表当中的某个节点以后,返回true。然后在主函数里面实现一下即可。(这里需要注意,如果删除的是头结点,只需要让头节点移动到下一个节点即可,因为要遍历链表,所以就必须要有一个头结点)
public class Linkedlist {
/**
*删除链表中的某个元素
* 1.判断链表是否为空,为空就不能删除
* 2.判断是否删除的是第一个节点,是则让headNode = headNode.next;
* 3.不满足上面两种清空,则可进行遍历删除(其中包含了链表中不存在要删除的数据)
*/
public boolean deleteNode(int data){
if(headNode==null){
System.out.println("链表为空,不能删除");
return false;
}
if(headNode.no==data){//删除头结点
headNode = headNode.next;
return true;
}
Node temp = headNode;
while(temp.next!=null){
if(data==temp.next.no){//找到要删除节点的前一个位置,然后进行删除
temp.next = temp.next.next;
return true;
}
temp = temp.next;
}
return false;
}
}主函数里面实现一下
public static void main(String[] args) {
Linkedlist linkedlist = new Linkedlist();
linkedlist.finallAdd(11);
linkedlist.finallAdd(22);
linkedlist.finallAdd(33);
linkedlist.finallAdd(44);
linkedlist.printList();
System.out.println();
System.out.println("===================");
boolean flag = linkedlist.deleteNode(11);
if(flag){
linkedlist.printList();
}else{
System.out.println("链表为空,或者链表中没有要删除的数据");
}
}结果

(2)删除链表中的所有Key节点
比如一个链表中,节点为[1,3,5,1,4,1],删除该链表中的所有为1的节点,则删除以后链表中的节点为[3,5,4]。
思路:
1.首先先判断链表是否为空,如果为空,则返回null
2.从头结点的下一个节点开始遍历,即cur = temp.next
便利条件为cur!=null,如果找到的是要删除的节点,则cur = cur.next;temp.next = cur;
如果找到的不是要删除的节点,则temp = cur;cur = cur.next;
3.如果头结点是要删除的节点,则另headNode = headNode.next;
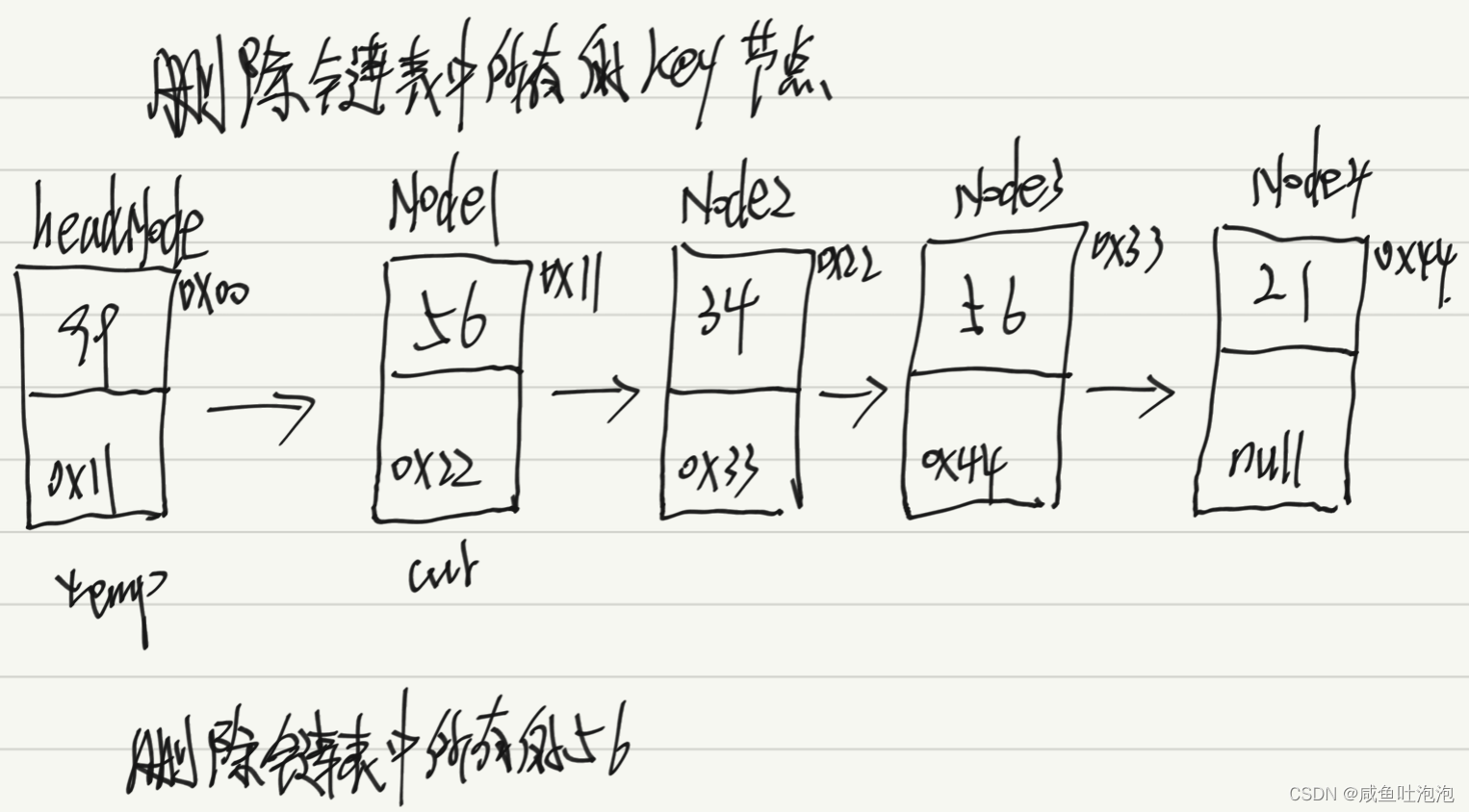
public class Linkedlist {
/**
*删除链表中的所有key节点
* 1.首先先判断单链表是否为空,如果为空,则返回null
* 2.从头结点的下一个节点遍历要删除的节点cur = temp.next;
* 便利条件cur!=null,如果找到的是要删除的节点,则cur = cur.next;temp.next = cur;
* 如果找到的不是要删除的节点,则temp = cur;cur = cur.next;
* 3.如果头结点是要删除的节点,则headNode = headNode.next;
*/
public void deleteAllKey(int key){
if(headNode==null){
return;
}
Node temp = headNode;
Node cur = temp.next;
while(cur!=null){
if(key== cur.no){
cur = cur.next;
temp.next = cur;
}else{
temp = cur;
cur = cur.next;
}
}
if(headNode.no==key){
headNode = headNode.next;
}
}
}在主函数里面实现一下
public static void main(String[] args) {//验证删除链表中所有的Key节点
Linkedlist linkedlist = new Linkedlist();
linkedlist.finallAdd(11);
linkedlist.finallAdd(21);
linkedlist.finallAdd(33);
linkedlist.finallAdd(11);
linkedlist.printList();
System.out.println();
System.out.println("===================");
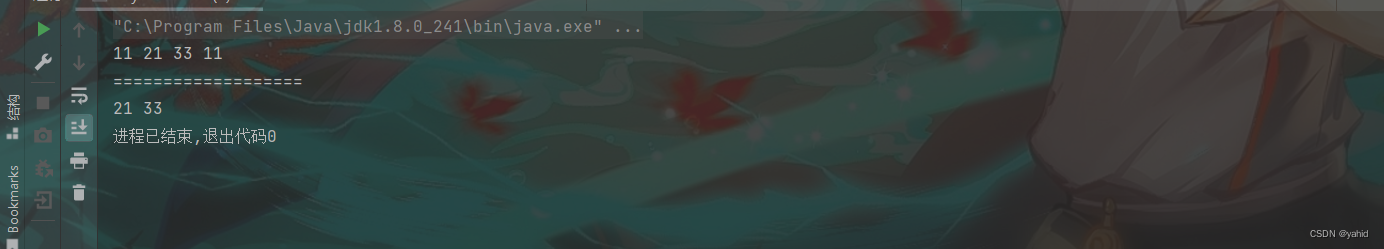
linkedlist.deleteAllKey(11);
linkedlist.printList();
}结果
(3)清空单链表
清空链表有两种方式,第一种直接暴力清空,将头结点置为空,因为遍历不到,则清空了;第二种就是将每一个节点都置为空,这样就形成了孤零零的节点,这些节点因为没有被引用,所以就会被java回收机制给回收
第二种清空思路:
创建两个辅助变量temp、cur来执行清空操作。cur用来记录当前的节点,temp用来记录当前节点的下一个节点,清空条件cur.next!=null
清空操作:cur==null;cur = temp;temp = temp.next;
public void clearList(){
if(headNode==null){
return;
}
Node temp = headNode.next;//记录当前节点的下一个节点
Node cur = headNode;//记录当前节点
while(temp!=null){
cur.next=null;
cur = temp;
temp = temp.next;
}
headNode = null;
}在主函数里面实现一下
public static void main(String[] args) {//验证清空链表
Linkedlist linkedlist = new Linkedlist();
linkedlist.finallAdd(11);
linkedlist.finallAdd(21);
linkedlist.finallAdd(33);
linkedlist.finallAdd(11);
linkedlist.printList();
System.out.println();
System.out.println("===================");
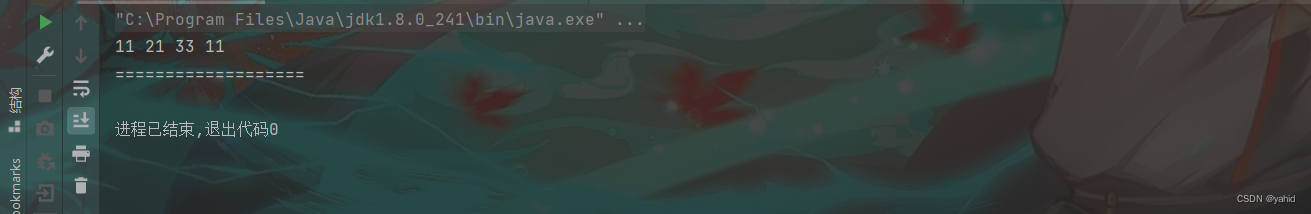
linkedlist.clearList();
linkedlist.printList();
}结果
修改链表中的数据:
思路
1.首先先判断链表是否为空,如果为空直接返回;
2.当链表不为空时,找到要修改数据的哪个节点temp,然后另temp.no = curdata;break;
如果遍历完链表以后没有找到要修改的数据,则打印一句“没有找到要修改的数据”然后返回
public void modifyNode(int predata,int curdata){
if(headNode==null){
return;
}
Node temp = headNode;
while(temp!=null){
if(temp.no==predata){
temp.no = curdata;
break;
}
temp = temp.next;
}
if(temp==null){
System.out.println("链表中没有找到要修改的数据");
}
}在主函数里面实现一下
public static void main(String[] args) {//验证修改链表中的某个数据
Linkedlist linkedlist = new Linkedlist();
linkedlist.finallAdd(11);
linkedlist.finallAdd(21);
linkedlist.finallAdd(33);
linkedlist.finallAdd(0);
linkedlist.printList();
System.out.println();
System.out.println("===================");
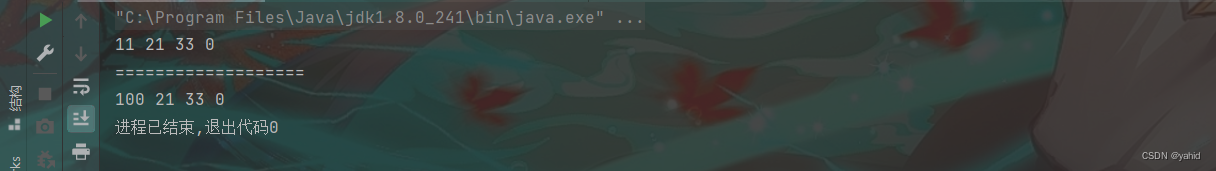
linkedlist.modifyNode(11,100);
linkedlist.printList();
}结果
下面通过几个OJ题,加深对链表的掌握
1.单链表的反转力扣
思路:
1.链表为空和链表的长度等于1直接返回
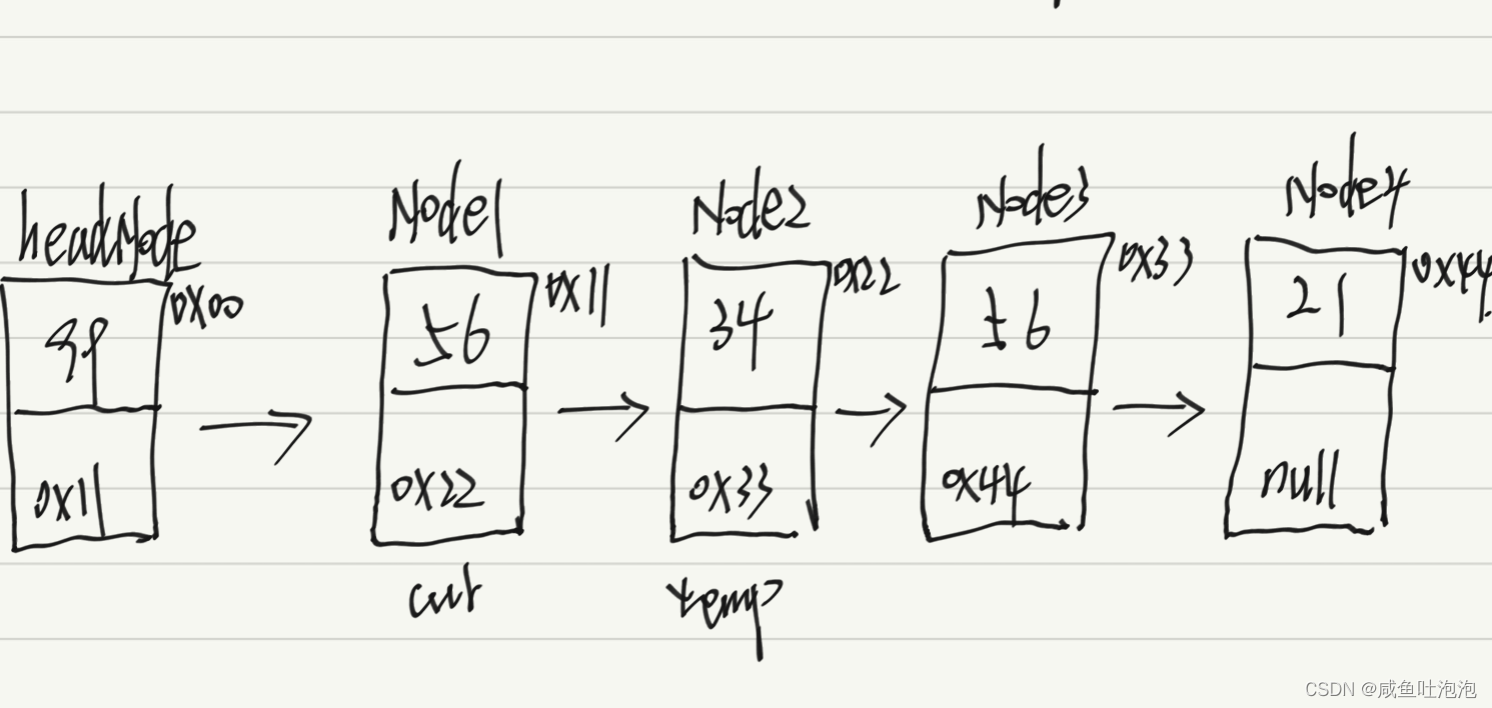
2.不满住条件1的话,创建两个辅助变量帮助链表反转。第一个变量cur = headNode.next;用于记录头结点的下一个位置。第二个变量temp = cur.next;用于记录头结点下一个位置的下一个位置。
首先先让headNode.next = null;
然后遍历链表实现反转,便利条件cur!=null,执行遍历反转操作
temp = cur.next;cur.next = headNode;headNode = cur;cur = temp;
public void turnList(){
if(headNode==null||lenthlist()==1){
return;
}
Node cur = headNode.next;
headNode.next = null;
Node temp = null;
while(cur!=null){
temp = cur.next;
cur.next = headNode;
headNode = cur;
cur = temp;
}
}
public int lenthlist(){
Node temp = this.headNode;
int lenth = 0;
while(temp!=null){
lenth++;
temp = temp.next;
}
return lenth;
}在主函数里面实现一下
public static void main(String[] args) {//验证链表反转
Linkedlist linkedlist = new Linkedlist();
linkedlist.finallAdd(11);
linkedlist.finallAdd(21);
linkedlist.finallAdd(33);
linkedlist.finallAdd(1);
linkedlist.printList();
System.out.println();
System.out.println("===================");
linkedlist.turnList();
linkedlist.printList();
}结果
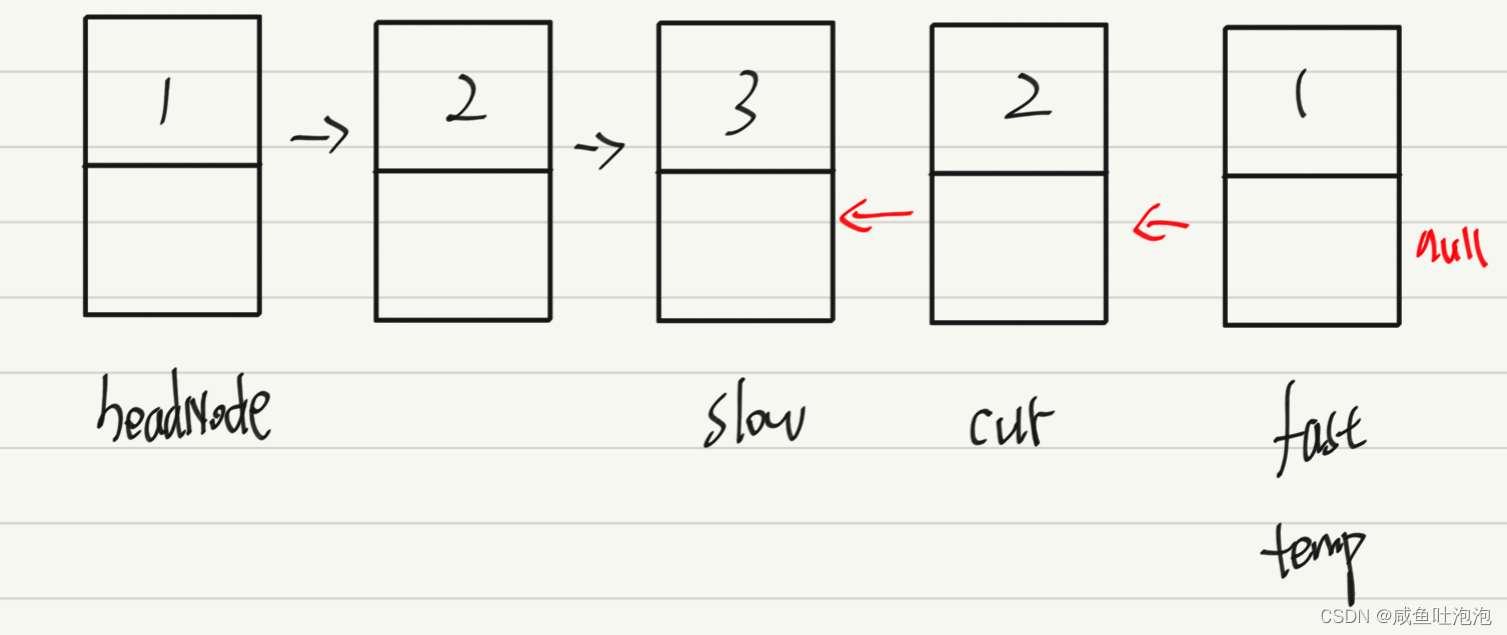
2.给定一个带有头结点head的非空单链表,返回链表的中间节点,如果有两个中间节点,则返回第二个中间节点力扣
思路:
快慢指针(当路程一定时,如果速度是两倍,则一个到达终点时,另一个一定是在中点位置)
创建两个引用fast、slow。fast代表速度为2倍的节点,slow代表速度为1倍的节点
Node fast = headNode; Node slow = headNode;
public Node returnMidNode(){
Node fast = headNode;
Node slow = headNode;
while(fast!=null&&fast.next!=null){//如果这里用||当fast==null时
//fast.next就会发生空指针异常
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
return slow;
}在主函数里面实现一下
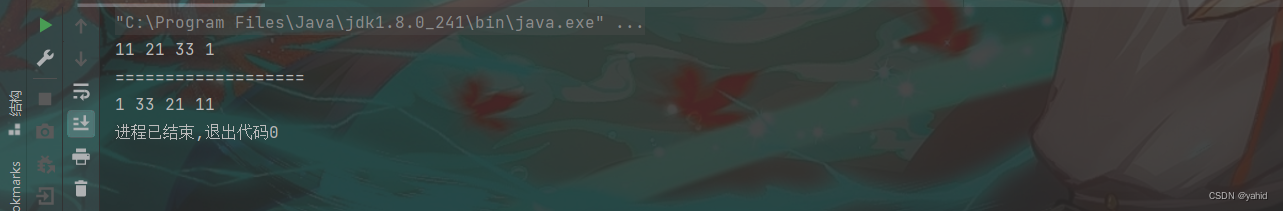
public static void main11(String[] args) {//验证链表中的中间节点
Linkedlist linkedlist = new Linkedlist();
linkedlist.finallAdd(11);
linkedlist.finallAdd(21);
linkedlist.finallAdd(33);
linkedlist.finallAdd(1);
linkedlist.finallAdd(100);
linkedlist.finallAdd(0);
linkedlist.printList();
System.out.println();
System.out.println("===================");
Linkedlist.Node res = linkedlist.returnMidNode();
System.out.println(res.no);
}结果
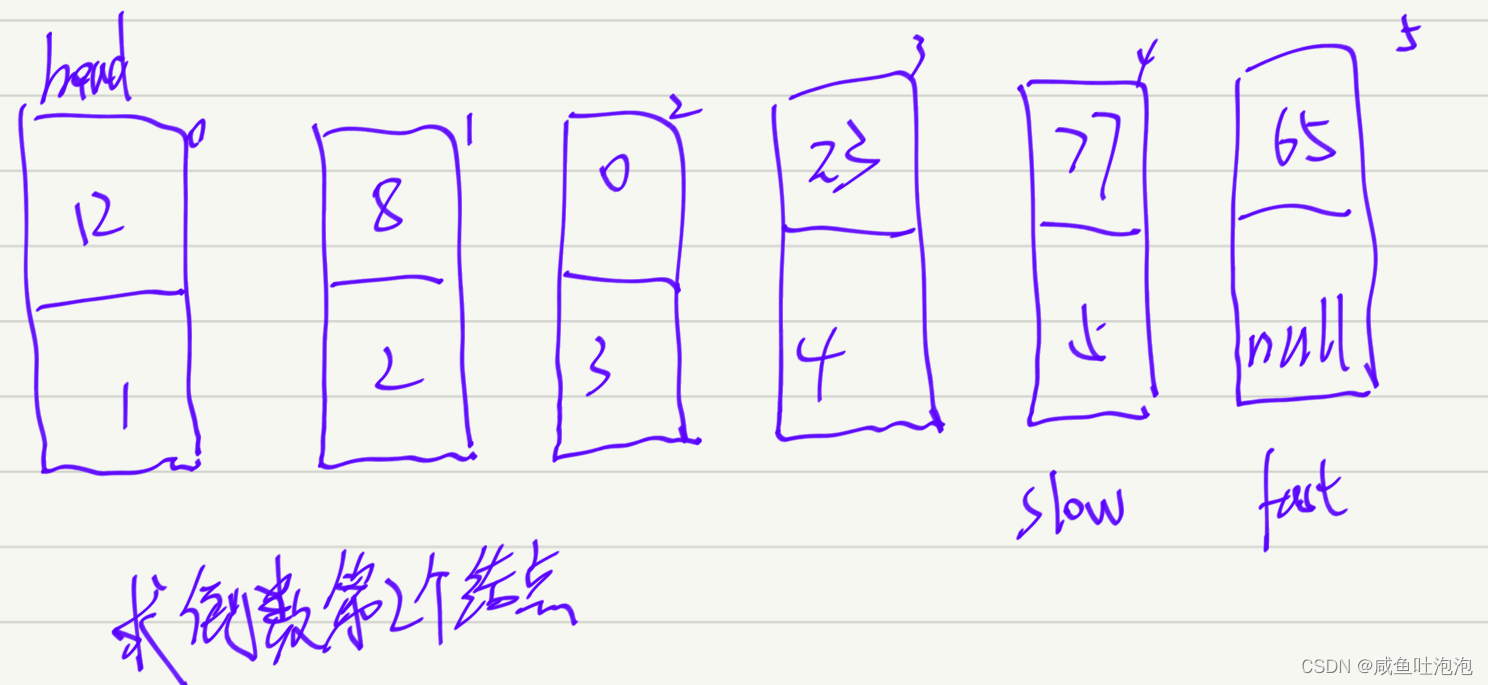
3.输出一个链表,输出该链表中倒数第K个节点链表中倒数第k个结点_牛客题霸_牛客网
思路:快慢指针
求倒数第K个节点,则先让fast走K-1步(这里也可以走K步,但是判断条件要变成fast!=null),然后fast、slow一起向前走,当fast.next ==null时,slow所在的节点就是倒数第K个节点
public Node printseveralNode(int k){
if(headNode==null||k<=0){
return null;
}
Node fast = headNode;
Node slow = headNode;
while(k-1>0){
fast = fast.next;
if(fast==null){//这里是防止K大于链表的长度这种情况引起的异常
return null;
}
k--;
}
while(fast.next!=null){
fast = fast.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
return slow;
}主函数里面实现一下
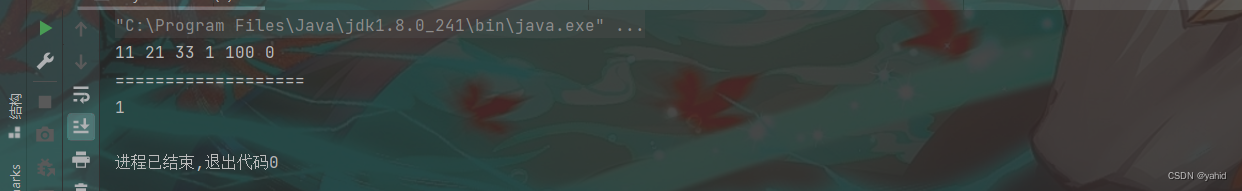
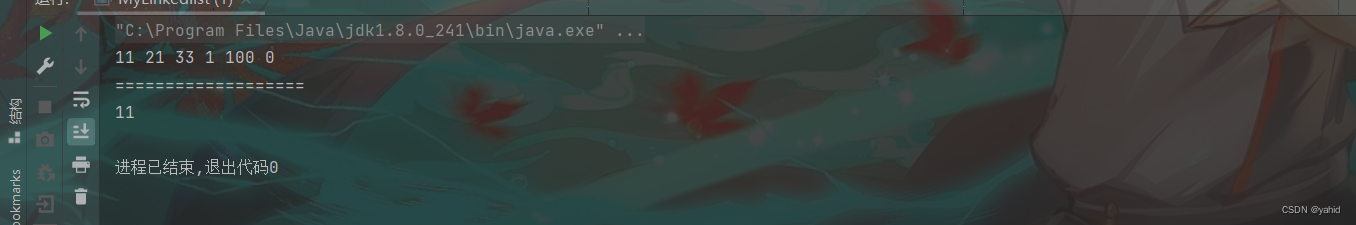
public static void main(String[] args) {//验证链表当中倒数第K个节点
Linkedlist linkedlist = new Linkedlist();
linkedlist.finallAdd(11);
linkedlist.finallAdd(21);
linkedlist.finallAdd(33);
linkedlist.finallAdd(1);
linkedlist.finallAdd(100);
linkedlist.finallAdd(0);
linkedlist.printList();
System.out.println();
System.out.println("===================");
try {
Linkedlist.Node res = linkedlist.printseveralNode(6);
System.out.println(res.no);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}结果
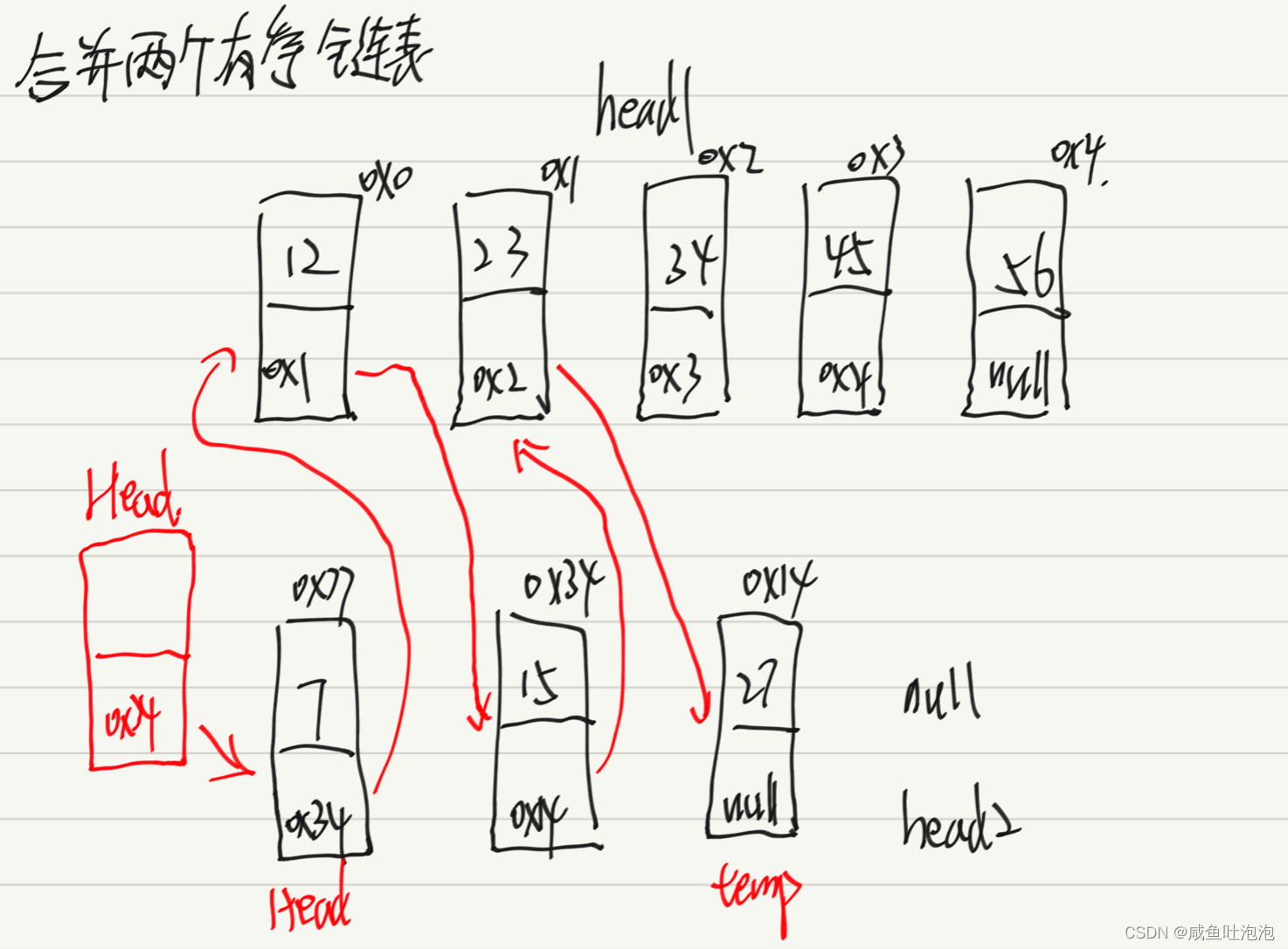
4.将两个有序链表合并成一个有序链表并返回。新链表是通过给定的两个链表的所有节点组成的
思路:
* 1.判断两个链表是否为空,如果其中一个为空,返回另一个链表,两个都为空返回null * 2.如果两个链表都有数据,则 * (1)head1与head2比较,谁小就让Head.next指向谁; * (2)哪个小,哪个就往后走(head1 = head1.next;head2 = head2.next;) temp = temp.next; * (3)当不满足head1==null&&head2==null时,执行temp.next==剩下链表的第一个节点的地址 * (4)返回Head.next;
public static Linkedlist.Node mergeTwoLists(Linkedlist.Node head1,
Linkedlist.Node head2) {
if(head1==null&&head2==null){//两个链表都为空,则返回null
return null;
}
if(head1==null||head2==null){//一个链表为空,就返回另一个链表
return head1==null?head2:head1;
}
Linkedlist.Node Head = null;
if(head1.no<=head2.no){//谁小谁就做头结点
Head = head1;
head1 = head1.next;
}else{
Head = head2;
head2 = head2.next;
}
Linkedlist.Node temp = Head;//创建一个辅助变量来遍历链表
while(head1!=null&&head2!=null){
temp.next = head1.no<=head2.no?head1:head2;
if(head1.no<=head2.no){
head1 = head1.next;
}else{
head2 = head2.next;
}
temp = temp.next;
}
temp.next = (head1==null?head2:head1);
return Head;
} //指定节点遍历
public void printList(Node node){
Node temp = node;
while(temp!=null){
System.out.print(temp.no+" ");
temp = temp.next;
}
}主函数里面实现一下
public static void main13(String[] args) {//验证将两个有序链表合并成一个有序链表
Linkedlist linkedlist1 = new Linkedlist();
linkedlist1.finallAdd(11);
linkedlist1.finallAdd(21);
linkedlist1.finallAdd(33);
linkedlist1.finallAdd(44);
linkedlist1.printList();
System.out.println();
System.out.println("===================");
Linkedlist linkedlist2 = new Linkedlist();
linkedlist2.finallAdd(13);
linkedlist2.finallAdd(22);
linkedlist2.finallAdd(34);
linkedlist2.finallAdd(200);
linkedlist2.printList();
System.out.println();
System.out.println("===================");
System.out.println("合并链表");
Linkedlist.Node ret = mergeTwoLists(linkedlist1.headNode,linkedlist2.headNode);
linkedlist1.printList(ret);
}结果

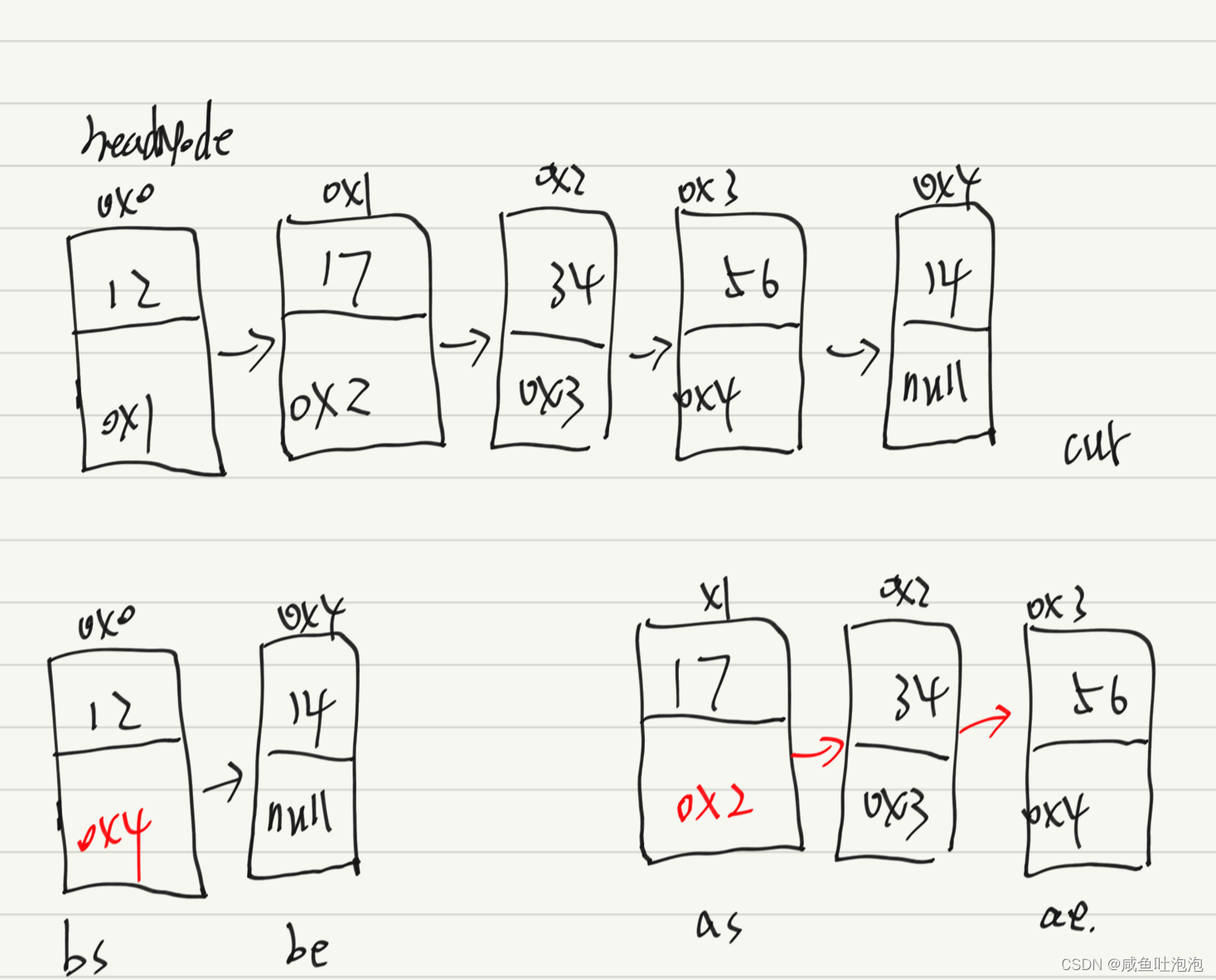
5.分割链表编写代码,以给定值x为基准将链表分割成两部分,所有小于x的结点排在大于或等于x的结点之前 链表分割_牛客题霸_牛客网
思路:
1.首先先判断链表是否为空,是则返回null
2.创建一个辅助变量cur来帮助遍历链表
3.创建动态变化的两个区间,第一个区间为[bs,be] ,第二个区间为[as,ae],这里的bs、be、as、ae的类型是节点
4.执行分区操作
5.注意事项
public Node partition(int x) {
if(headNode==null){
return null;
}
Node bs = null;
Node be = null;
Node as = null;
Node ae = null;
Node cur = headNode;
while(cur!=null){
//分区操作
if(cur.no<x){
if(bs==null){
bs = cur;
be = cur;
}else{
be.next = cur;
be = be.next;
}
}else{
if(as==null){
as = cur;
ae = cur;
}else{
ae.next = cur;
ae = ae.next;
}
}
cur = cur.next;
}
if(bs==null){
return as;
}
be.next = as;
if(as!=null){
ae.next = null;
}
return bs;
}
//指定节点遍历
public void printList(Node node){
Node temp = node;
while(temp!=null){
System.out.print(temp.no+" ");
temp = temp.next;
}
}主函数里面实现一下
public static void main(String[] args) {
//验证分割链表
Linkedlist linkedlist1 = new Linkedlist();
linkedlist1.finallAdd(12);
linkedlist1.finallAdd(17);
linkedlist1.finallAdd(34);
linkedlist1.finallAdd(56);
linkedlist1.finallAdd(14);
Linkedlist.Node node = linkedlist1.partition(15);
linkedlist1.printList(node);
}结果
6.链表的回文结构:链表的回文结构_牛客题霸_牛客网
思路: 1.首先先判断链表是否为空,如果为空返回false、判断链表是否只有一个节点,是则返回true 2.创建两个辅助变量fast、slow。找到中间节点(快慢指针)slow 3.创建cur = slow.next;temp;使链表后半截反转,反转条件cur!=null 执行反转:temp = cur.next;cur.next = slow;slow = cur;cur = temp; 4.判断headNode.no与slow.no是否相等,不相等则返回false,相等则headNode=headNode.next; slow = slow.next继续比较 当headNode==slow时,返回true
public boolean palindromeList(){
if(headNode==null){
return false;
}
if(headNode.next==null){
//链表中只有一个节点,该链表就是回文链表
return true;
}
Node fast = headNode;
Node slow = headNode;
//找中间节点slow
while(fast!=null&&fast.next!=null){
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
Node cur = slow.next;
Node temp = null;
//反转链表后半截
while(cur!=null){
temp = cur.next;
cur.next = slow;
slow = cur;
cur = temp;
}
//判断是否为回文
while(headNode!=slow){
if(headNode.no!=slow.no){
return false;
}
if(headNode.next==slow){
//当链表长度为偶数时
return true;
}
headNode = headNode.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
return true;
}主函数里面实现一下
public static void main(String[] args) {
//验证回文链表
Linkedlist linkedlist1 = new Linkedlist();
linkedlist1.finallAdd(11);
linkedlist1.finallAdd(21);
linkedlist1.finallAdd(11);
linkedlist1.finallAdd(11);
boolean b = linkedlist1.palindromeList();
if(b){
System.out.println("是回文链表");
}else{
System.out.println("不是回文链表");
}
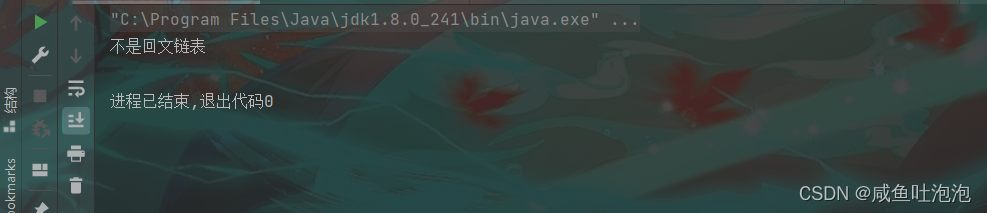
}结果
7.输入两个链表,找出它们的第一个公共节点。力扣
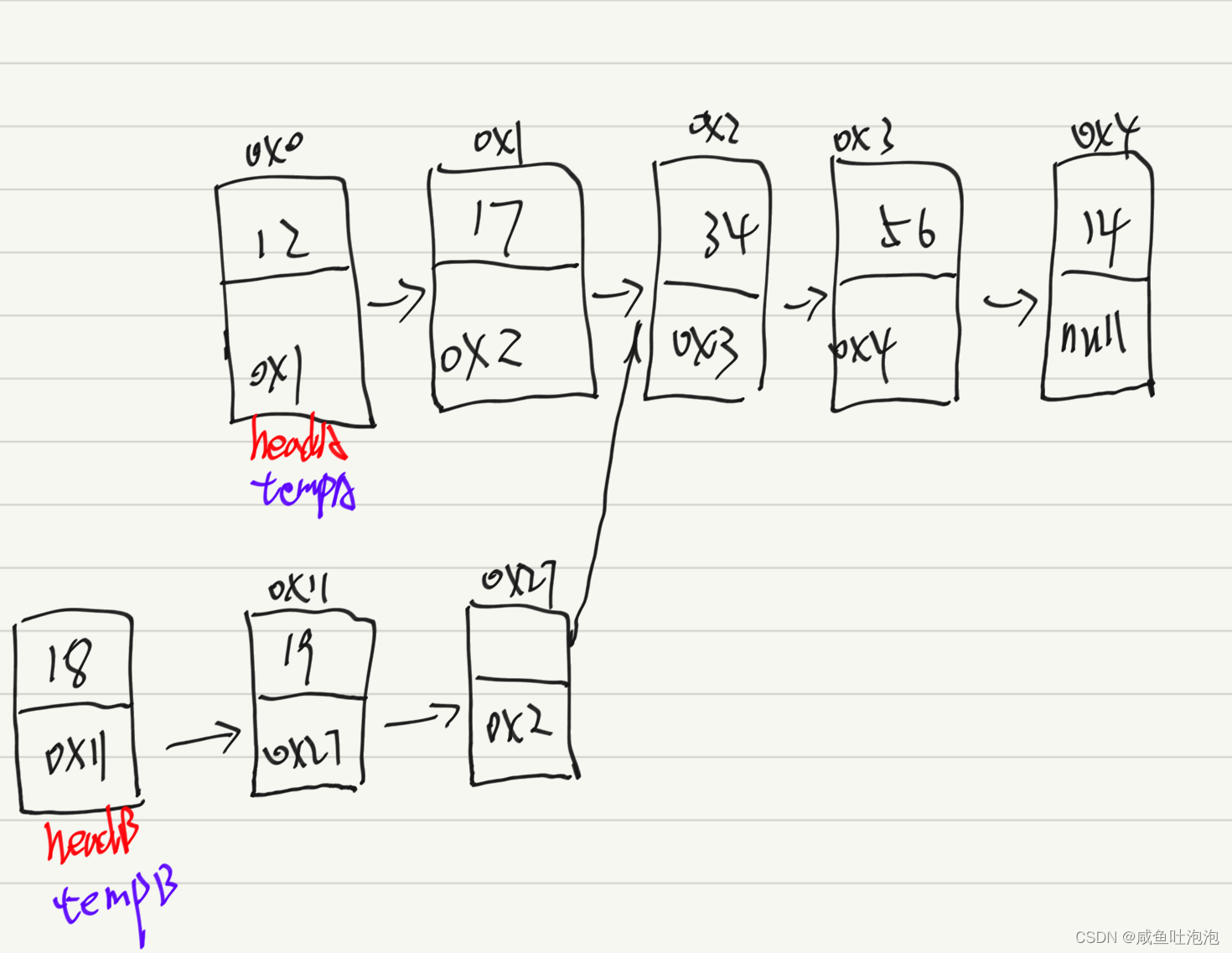
上面链表headA和headB就有公共节点(这里的公共节点是指节点的地址相同,而不是节点的值相同)
思路:快慢指针
1.创建两个辅助变量tempA、tempB,让tempA = headA;tempB = headB;分别计算两个链表的长度
2.让长度长的链表先走两个长度的差值,随后判断tempA是否与tempB相等,不相等则tempA = tempA.next;tempB = tempB.next;
3.最后返回tempA
public static Linkedlist.Node getIntersectionNode(
Linkedlist.Node headA, Linkedlist.Node headB) {
if(headA==null||headB==null){
return null;
}
Linkedlist.Node tempA = headA;//这里先假定链表headA要长一些,让tempA始终指向长的链表
Linkedlist.Node tempB = headB;
int countA = 0;
int countB = 0;
//计算两个链表长度
while(tempA!=null){
countA++;
tempA = tempA.next;
}
while(tempB!=null){
countB++;
tempB = tempB.next;
}
tempA = headA;
tempB = headB;
int len = countA-countB;
while(len>0){
//让长的链表先走长度的差值
tempA = tempA.next;
len--;
}
while(len<0){
//让长的链表先走长度的差值
tempB = tempB.next;
len++;
}
while(tempA!=tempB){
tempA = tempA.next;
tempB = tempB.next;
}
return tempA;
}主函数里面实现一下
public static Linkedlist.Node getIntersectionNode(
Linkedlist.Node headA, Linkedlist.Node headB) {
if(headA==null||headB==null){
return null;
}
Linkedlist.Node tempA = headA;//这里先假定链表headA要长一些,让tempA始终指向长的链表
Linkedlist.Node tempB = headB;
int countA = 0;
int countB = 0;
//计算两个链表长度
while(tempA!=null){
countA++;
tempA = tempA.next;
}
while(tempB!=null){
countB++;
tempB = tempB.next;
}
tempA = headA;
tempB = headB;
int len = countA-countB;
while(len>0){
//让长的链表先走长度的差值
tempA = tempA.next;
len--;
}
while(len<0){
//让长的链表先走长度的差值
tempB = tempB.next;
len++;
}
while(tempA!=tempB){
tempA = tempA.next;
tempB = tempB.next;
}
return tempA;
}
public static void intersection(Linkedlist.Node headA, Linkedlist.Node headB){
//人为制造交点
headA.next.next = headB.next.next;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
//验证两链表的公共节点
Linkedlist linkedlist1 = new Linkedlist();
linkedlist1.finallAdd(12);
linkedlist1.finallAdd(17);
linkedlist1.finallAdd(34);
linkedlist1.finallAdd(56);
linkedlist1.finallAdd(14);
linkedlist1.printList();
System.out.println();
System.out.println("=====================");
Linkedlist linkedlist2 = new Linkedlist();
linkedlist2.finallAdd(12);
linkedlist2.finallAdd(17);
linkedlist2.finallAdd(34);
linkedlist2.finallAdd(56);
linkedlist2.finallAdd(14);
linkedlist2.printList();
System.out.println();
intersection(linkedlist1.headNode,linkedlist2.headNode);
System.out.println("交点是"+getIntersectionNode(linkedlist1.headNode, linkedlist2.headNode).no);
}结果

如果不人为制造交点,两个链表是独立的,肯定是没交点的
8.给定一个链表,判断链表中是否有环力扣
思路:快慢指针
1.首先判断链表是否为空,是则返回false
2.创建两个辅助变量fast、slow来遍历链表,fast每次走两步,slow每次走一步。当fast==slow时返回true跳出循环
3.当循环条件不满足时,则说明链表没环

public boolean hasCycle(Node head) {
if(head==null){
return false;
}
Node fast = head;
Node slow = head;
while(fast!=null&&fast.next!=null){
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
if(fast==slow){
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
//人为制造环
public void creatcycle(){
Node temp = headNode;
while(temp.next!=null){
//遍历原先的链表找到最后一个节点
temp = temp.next;
}
temp.next = headNode.next.next;//让最后一个节点的next链表头的第三个节点
}在主函数里面实现一下
public static void main(String[] args) {
//测试链表是否有环
Linkedlist linkedlist1 = new Linkedlist();
linkedlist1.finallAdd(12);
linkedlist1.finallAdd(13);
linkedlist1.finallAdd(14);
linkedlist1.finallAdd(15);
linkedlist1.creatcycle();
boolean flag = linkedlist1.hasCycle(linkedlist1.headNode);
if(flag){
System.out.println("有环");
}else{
System.out.println("没环");
}
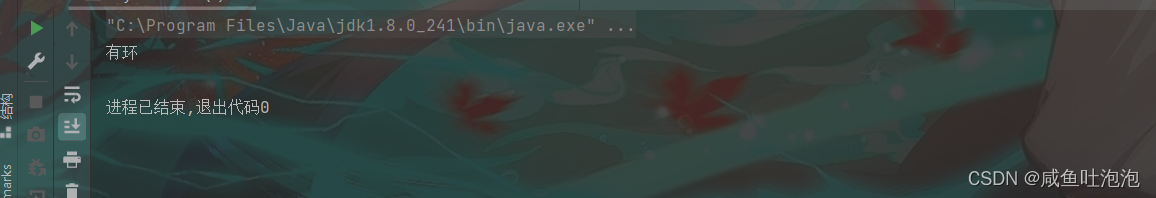
}结果
9.给定一个链表,返回链表开始入环的第一个节点。如果链表无环,则返回null力扣
思路:快慢指针
* 1.首先先判断链表是否为空,是则返回null * 2.创建两个辅助变量fast、slow。fast每次走两步,slow每次走一步,如果有环fast比slow先入环 * (1)设起点到入环点的距离为x * (2)设环的周长为c * (3)设相遇点到环入口点的距离为y * 当两个fast和slow相遇之后,因为fast的速度是slow的2倍,所以此时fast走过的路程是slow的2倍,则有下列函数关系 * fast走的路程:x+c+c-y; * slow走的路程:x+c-y * 则:2*(x+c-y) = x+c+c-y,解的x = y,也即是说此时将solw = headNode,和fast一起走以相同的速度运动,当fast==slow时,该位置的节点就是环的入口点。 * 也有可能环很小,fast在环里面转了很多圈,slow才入圈,然后fast在追击slow。此时的函数关系就是2*(x+c-y) = x+n*c+c-y,解得x = (n-1)*c+y。 * 也就是说此时的x很大,x!=y。但是没关系,我们让slow = headNode走x的距离,此时的slow和fast一定会相遇
public Node detectCycle(Node head) {
if(head==null){
return null;
}
Node fast = head;
Node slow = head;
while(fast!=null&&fast.next!=null){
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
if(fast==slow){
//说明有环
break;
}
}
//判断此时出来的是有环还是没环
if(fast==null||fast.next==null){
//没环
return null;
}
slow = head;
while(slow!=fast){
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next;
}
return slow;
}
//人为制造环
public void creatcycle(){
Node temp = headNode;
while(temp.next!=null){
//遍历原先的链表找到最后一个节点
temp = temp.next;
}
temp.next = headNode.next.next;//让最后一个节点的next链表头的第三个节点
}主函数里面实现一下
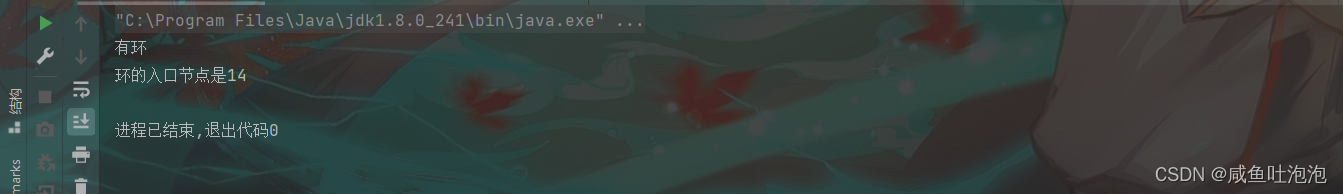
public static void main(String[] args) {
//测试链表是否有环,并测试环的入口节点
Linkedlist linkedlist1 = new Linkedlist();
linkedlist1.finallAdd(12);
linkedlist1.finallAdd(13);
linkedlist1.finallAdd(14);
linkedlist1.finallAdd(15);
linkedlist1.creatcycle();
boolean flag = linkedlist1.hasCycle(linkedlist1.headNode);
if(flag){
System.out.println("有环");
System.out.println("环的入口节点是"+linkedlist1.detectCycle(linkedlist1.headNode).no);
}else{
System.out.println("没环");
}
}结果