[JavaScript 刷题] 树 - 二叉搜索树迭代器, leetcode 173
github repo 地址: https://github.com/GoldenaArcher/js_leetcode,Github 的目录 大概 会更新的更勤快一些。
题目地址:173. Binary Search Tree Iterator
题目
如下:
Implement the
BSTIteratorclass that represents an iterator over the in-order traversal of a binary search tree (BST):
BSTIterator(TreeNode root)Initializes an object of the BSTIterator class. The root of the BST is given as part of the constructor. The pointer should be initialized to a non-existent number smaller than any element in the BST.
boolean hasNext()Returnstrueif there exists a number in the traversal to the right of the pointer, otherwise returnsfalse.
int next()Moves the pointer to the right, then returns the number at the pointer.Notice that by initializing the pointer to a non-existent smallest number, the first call to
next()will return the smallest element in the BST.You may assume that
next()calls will always be valid. That is, there will be at least a next number in the in-order traversal whennext()is called.
解题思路
这是让写一个迭代器,用于获取容器下一个值的方法。本题中的迭代器也是如此,并且,本题中要求迭代顺序为中序遍历。
更多二叉树的遍历相关内容参考:[JavaScript 刷题] 二叉树先序、中序、后序及层次四种遍历,这里不多赘述。
总体来说,这题可以接受的解法有两种:
-
直接将整个二叉搜索树放到数组中去,然后通过一个变量去控制当前数组遍历的位置
这样的做法,时间复杂度为 O ( n ) O(n) O(n),空间复杂度也为 O ( n ) O(n) O(n),在调用
next和hasNext时的时空复杂度均为 O ( 1 ) O(1) O(1) -
一边遍历二叉树一边将值输出
这个解法是 follow up 的解法:
Could you implement
next()andhasNext()to run in averageO(1)time and useO(h)memory, where h is the height of the tree?这个 follow up 的提示挺明显的,说是 average
O(1)time and useO(h)memory,这个就是提示不在 constructor 内将二叉树转化为数组进行遍历。也就是用迭代遍历的方法去实现,参考一下 inorder traversal 的实现:
var inorderTraversal = function (root) { const stack = [], res = []; let curr = root, counter = 0; while (curr || stack.length) { if (curr) stack.push(curr); while (curr?.left) { stack.push(curr.left); curr = curr.left; } curr = stack.pop(); res.push(curr.val); curr = curr.right; } return res; };以题目中的
[7, 3, 15, null, null, 9, 20]为例: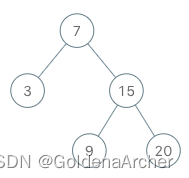
-
将 7 压入栈中,并且将 7 的左子树压入 stack 中
此时栈中的结果为
[7, 3]此时调用
next()会将栈中最后一个值退出,调用hasNext()会检查栈的最后一个值是否为空。3 没有子结点,因此不需要检查左右子树。
再次调用
next()会将 7 弹出,这时候进行下一步操作 -
将指针指向 7 的右子树 15,并且继续迭代将 15 的左子树全都压入 stack 中
此时栈中的结果为
[15, 7]重复这样该操作就能完成 iterator 的实现。
整个操作的时间复杂度(amortized time complexity, AKA expected Time Complexity,预计时间复杂度) 为 O ( 1 ) O(1) O(1),空间复杂度为 O ( h ) O(h) O(h),因为只需要数据结构区保存树的深度即可(主要的空间用在保存左子树上)。
-
使用 JavaScript 解题
解法 1
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
*/
var BSTIterator = function (root) {
const inorder = (root) => {
if (!root) return [];
return [...inorder(root.left), root.val, ...inorder(root.right)];
};
this.arr = inorder(root);
this.idx = -1;
};
/**
* @return {number}
*/
BSTIterator.prototype.next = function () {
return this.arr[++this.idx];
};
/**
* @return {boolean}
*/
BSTIterator.prototype.hasNext = function () {
return this.arr[this.idx + 1] !== undefined;
};
/**
* Your BSTIterator object will be instantiated and called as such:
* var obj = new BSTIterator(root)
* var param_1 = obj.next()
* var param_2 = obj.hasNext()
*/
follow up
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
*/
var BSTIterator = function (root) {
this.curr = root;
this.stack = [];
this.iterateTree();
};
BSTIterator.prototype.iterateTree = function () {
if (this.curr) this.stack.push(this.curr);
while (this.curr?.left) {
this.stack.push(this.curr.left);
this.curr = this.curr.left;
}
};
/**
* @return {number}
*/
BSTIterator.prototype.next = function () {
if (!this.curr && !this.stack.length) return null;
let returnedVal = this.stack.pop();
this.curr = returnedVal.right;
this.iterateTree();
return returnedVal.val;
};
/**
* @return {boolean}
*/
BSTIterator.prototype.hasNext = function () {
return this.stack.length > 0 || this.curr !== null;
};