注: 以下改进皆为在传统 A* 算法基础下的改进,请先了解传统 A* 算法后再对本文进行了解。
1 邻域改进
当终点相对于当前点在不同象限时,采取不同的搜索邻域能够减小检验节点数量。
首先要确定终点相对于当前节点象限,我们定义向量:
V = [ g o a l . x − c u r . x 2 , g o a l . y − c u r . y 2 ] V=[\frac{goal.x-cur.x}{2},\frac{goal.y-cur.y}{2}] V=[2goal.x−cur.x,2goal.y−cur.y]
其中 g o a l goal goal为目标结点, c u r cur cur为当前节点,则:
{ V ( 1 ) ≥ 0 , V ( 2 ) ≥ 0 第 一 象 限 V ( 1 ) ≤ 0 , V ( 2 ) ≥ 0 第 二 象 限 V ( 1 ) ≤ 0 , V ( 2 ) ≤ 0 第 三 象 限 V ( 1 ) ≥ 0 , V ( 2 ) ≤ 0 第 四 象 限 \begin{cases} V(1)\geq0,V(2)\geq0 & 第一象限 \\ V(1)\leq0,V(2)\geq0 & 第二象限 \\ V(1)\leq0,V(2)\leq0 & 第三象限 \\ V(1)\geq0,V(2)\leq0 & 第四象限 \\ \end{cases} ⎩⎪⎪⎪⎨⎪⎪⎪⎧V(1)≥0,V(2)≥0V(1)≤0,V(2)≥0V(1)≤0,V(2)≤0V(1)≥0,V(2)≤0第一象限第二象限第三象限第四象限
依据象限不同我们对搜索邻域做如下改进
1.1 [8]邻域改进
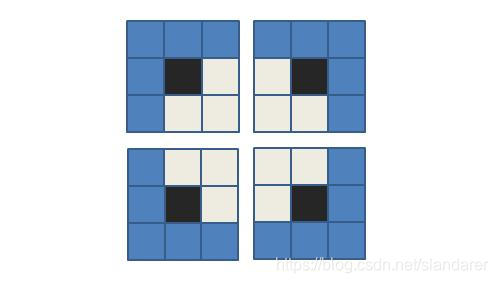
对于不同象限,将传统的8邻域改为5邻域:
如图所示黑色方块代表当前点,蓝色方块表示依据象限搜索的邻域:
1.2 [24]邻域改进
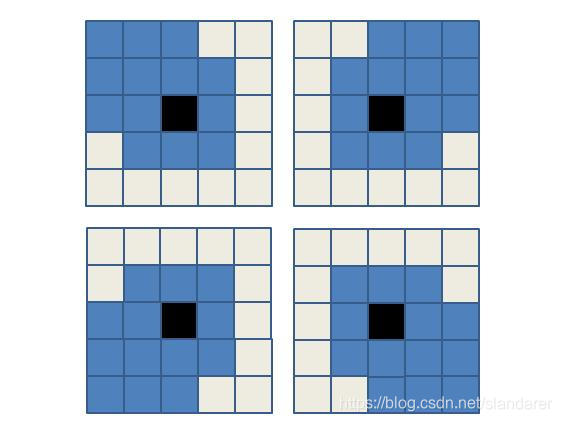
对于不同象限,将24邻域改为13邻域:
如图所示黑色方块代表当前点,蓝色方块表示依据象限搜索的邻域:
2 混合预计耗费估计
2.1 欧几里德距离
当前节点与目标点间无障碍时
采取欧几里德距离x10作为预计耗费 :
H = 10 ∗ ( g x − c x ) 2 + ( g y − c y ) 2 H=10*\sqrt{(g_x-c_x)^2+(g_y-c_y)^2} H=10∗(gx−cx)2+(gy−cy)2
2.2 半圆周距离
如图所示,当起点终点连线穿过障碍物,但至少有一个以当前点和终点的中点为圆心的半圆弧能够无障碍的连接当前点和终点,则采用圆弧长度x10作为预计耗费:
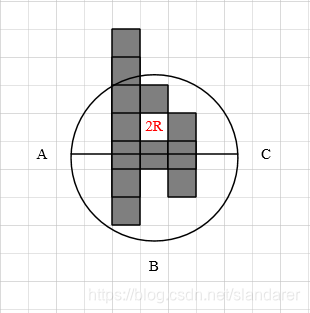
若 A C ‾ = 2 R \overline{AC}=2R AC=2R,则 H = 10 π R H=10\pi R H=10πR
2.3 弧+半径距离
若起点终点间有障碍,且过以中心点为圆心得圆弧两侧都有障碍,则考虑以终点为圆心,当前点及终点距离为半径做圆,若存在圆弧可连接当前点及终点,则考虑(圆弧+半径距离)x10为预计耗费:
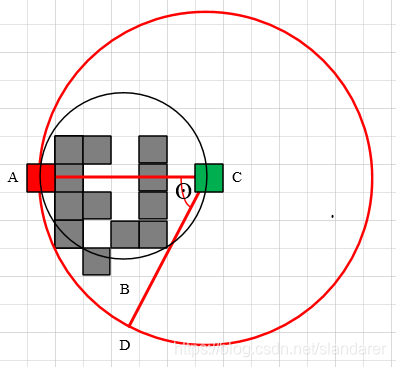
若 A C ‾ = 2 R \overline{AC}=2R AC=2R,则 H = 10 ( 2 θ R + 2 R ) H=10(2\theta R+2R) H=10(2θR+2R)
2.4 曼哈顿距离
在以上任意一种类型路径上均存在障碍物,则采用曼哈顿距离:
H = 10 ∗ ( ∣ g x − c x ∣ + ∣ g y − c y ∣ ) H=10*(|g_x-c_x|+|g_y-c_y|) H=10∗(∣gx−cx∣+∣gy−cy∣)


3 结果展示
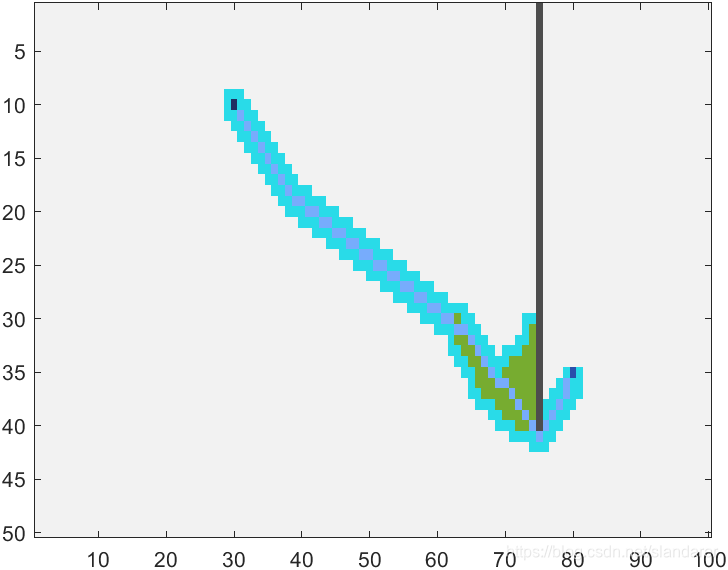
3.1 [5]邻域及[13]邻域效果
5邻域:
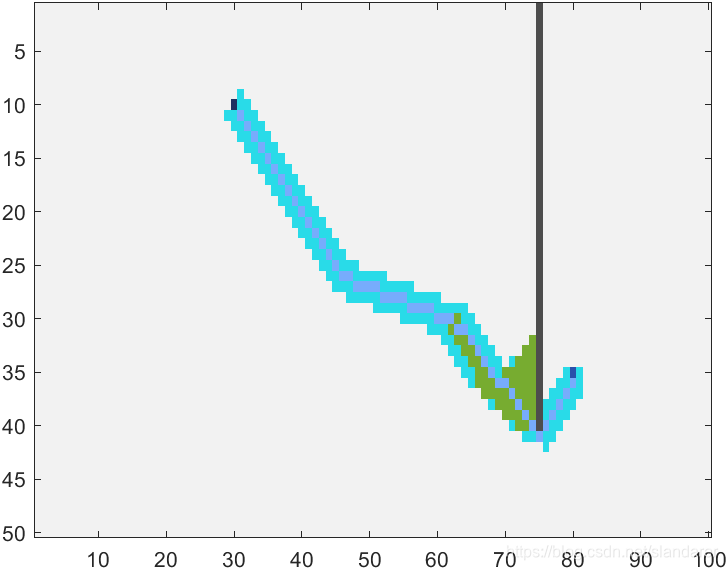
13邻域:
3.2 [13]邻域与传统A*对比一
可以看出改进后的算法搜索范围对比传统方法小了很多
13邻域(左),传统8邻域(右)

3.2 [13]邻域与传统A*对比二
13邻域(左),传统8邻域(右)

4 主要部分代码
4.1 预计耗费部分代码
function H=getH(pnt1,pnt2,obstacle)
%pnt1,pnt2,obstacle
% =========================================================================
% 情况一,起始点和终点之间无障碍物
flag1=false;
% 先删除明显离直线过远或者垂直点不在起点终点之间的点
tempSet=obstacle;
tempSet(tempSet(:,1)<min(pnt1(1),pnt2(1)),:)=[];
tempSet(tempSet(:,1)>max(pnt1(1),pnt2(1)),:)=[];
tempSet(tempSet(:,2)<min(pnt1(2),pnt2(2)),:)=[];
tempSet(tempSet(:,2)>max(pnt1(2),pnt2(2)),:)=[];
% 找到垂直于起始终止点之间单位向量
tempV=pnt2-pnt1;
tempV=[tempV(2),-tempV(1)]./norm(tempV);
% 障碍点到直线距离
dis_L=(tempSet-pnt1)*tempV';
tempSet(abs(dis_L)>sqrt(2)/2,:)=[];
dis_L(abs(dis_L)>sqrt(2)/2)=[];
if any(abs(dis_L)<0.5) % 如果有距离小于0.5的点,则一定挡住路径
flag1=true;
else % 如果没有距离小于0.5则检测是否过经过角点
extend1=(tempSet+[.5,.5]-pnt1)*tempV';
extend2=(tempSet+[-.5,.5]-pnt1)*tempV';
extend3=(tempSet+[.5,-.5]-pnt1)*tempV';
extend4=(tempSet+[-.5,-.5]-pnt1)*tempV';
extend=[extend1,extend2,extend3,extend4];
extend=abs(extend)<=1e-10;
if any(sum(extend,2)<1)
flag1=true;
end
end
if ~flag1
H=sqrt((pnt1-pnt2)*(pnt1-pnt2)')*10;
return
end
% =========================================================================
% 情况二,起始点和终点之间有障碍物,弧ABC无阻挡
flag2=false;
R1=sqrt((pnt1-pnt2)*(pnt1-pnt2)')/2; % 圆半径
O1=(pnt1+pnt2)./2; % 圆中心
% 找到在圆周上的障碍物
dis_O1=sqrt(sum((obstacle-O1).^2,2));
bool_O1=(dis_O1<(R1+1/2))&(dis_O1>(R1-1/2));
tempSet=obstacle(bool_O1,:);
% dis_L1为点到起点终点连线距离
% dis_L1有正有负才说明两个圆弧都被堵
dis_L1=(tempSet-pnt1)*tempV';
if any(dis_L1>0)&&any(dis_L1<0)
flag2=true;
end
if ~flag2
H=pi*R1*10;
return
end
% =========================================================================
% 情况三,起始点和终点之间有障碍物,弧ABC有遮挡,弧AD无遮挡
flag3=false;
R2=sqrt((pnt1-pnt2)*(pnt1-pnt2)'); % 圆半径
% 找到在圆周上的障碍物
dis_O2=sqrt(sum((obstacle-pnt2).^2,2));
bool_O2=(dis_O2<(R2+1/2))&(dis_O2>(R2-1/2));
tempSet=obstacle(bool_O2,:);
dis_L2=(tempSet-pnt2)*tempV';% 点到起点终点连线距离
if any(dis_L2>0)&&any(dis_L2<0)
flag3=true;
end
if ~flag3
% 找到在圆内的点
bool_inC=(dis_O2<(R2-1/2));
tempSet=obstacle(bool_inC,:);
tempSet=[tempSet+[.5,.5];
tempSet+[-.5,.5];
tempSet+[.5,-.5];
tempSet+[-.5,-.5]];
% 计算角度
dis_L_inC=(tempSet-pnt2)*tempV';
dis_inC=sqrt(sum((tempSet-pnt2).^2,2));
asin_inC=asin(dis_L_inC./dis_inC);
if all(dis_L2>0)
tempTheta=asin_inC(asin_inC<0);
else
tempTheta=asin_inC(asin_inC>0);
end
maxTheta=max(abs(tempTheta));
H=(R2*maxTheta+R2)*10;
return
end
% =========================================================================
% 情况四,起始点和终点之间有障碍物,弧ABC有遮挡,弧AD有遮挡
H=sum(abs(pnt1-pnt2))*10;
end
4.2 象限改进[5]邻域AStar代码
function [path,close,open]=AStar_quadrant_5(obstacle,map)
% obstacle :障碍物坐标,mx2大小数组
% map :包含以下元素的结构体
% map.start [x1,y1] 起点
% map.goal [x2,y2] 终点
% 用于存储路径
path=[];
close=[];
% open集合初始化
% [节点X坐标 ,节点Y坐标 ,代价值F=G+H ,代价值G,父节点X ,父节点Y ]
open=[map.start(1),map.start(2),0+getH(map.start,map.goal,obstacle),0 ,map.start(1), map.start(2)];
while true
% 若open集合被取完,则无路径
if isempty(open(:,1))
disp('No path to goal!!');
return;
end
% 判断目标点是否出现在open列表中
[~,~,IndexGoal]=intersect(map.goal,open(:,1:2),'rows');
if ~isempty(IndexGoal)
disp('Find Goal!!');
close=[open(IndexGoal,:);close];
break;
end
[~,IndexSort] = sort(open(:,3)); % 获取OpenList中第三列大小顺序
open=open(IndexSort,:); % 将open集合按照Index排序
% 将最小open移至close集合并作为当前点
close=[open(1,:);close];
current=open(1,:);
open(1,:)=[];
% 获取当前位置与目标点的坐标,判断要搜索的象限。
% 目标点map.goal,当前点close(1,1:2)
% 并依据规则获取当前点的子节点
next=getNext_5(current(1:2),map.goal);
for i=1:size(next,1)
newNode=[current(1)+next(i,1),current(2)+next(i,2),0,0,0,0];
newNode(4)=current(4)+next(i,3); % 相邻节点G值
newNode(3)=getH(newNode(1:2),map.goal,obstacle)+newNode(4);% 相邻节点F值
% 如果它不可达,忽略它
if ~isempty(intersect(newNode(1:2),obstacle,'rows'))
continue;
end
% 如果它与父节点之间有障碍物,忽略它
if ~isempty(intersect((round(newNode(1:2)+current(1:2))./2),obstacle,'rows'))
continue;
end
% 如果它在close集合中,忽略它
if ~isempty(intersect(newNode(1:2),close(:,1:2),'rows'))
continue;
end
% 如果它不在open集合中
if isempty(intersect(newNode(1:2),open(:,1:2),'rows'))
newNode(5:6)=current(1:2); % 将当前节点作为其父节点
open=[open;newNode]; % 将此相邻节点加放OpenList中
else % 若在
[~,~,IndexInOpen]=intersect(newNode(1:2),open(:,1:2),'rows');
if newNode(3)<open(IndexInOpen,3)
% 若F更小,则将此相邻节点的父节点设置为当前节点,否则不作处理
newNode(5:6)=current(1:2); % 将当前节点作为其父节点
open(IndexInOpen,:)=newNode; % 将此相邻节点在OpenList中的数据更新
end
end
end
end
%追溯路径
Index=1;
while 1
path=[path;close(Index,1:2)];
if isequal(close(Index,1:2),map.start)
break;
end
[~,IndexInClose,~]=intersect(close(:,1:2),close(Index,5:6),'rows');
Index=IndexInClose;
end
end
4.3 象限改进[13]邻域AStar代码
与5邻域代码类似,但是需要检测邻域和父节点之间是否有障碍,防止穿墙情况发生,同时路径还原要将不相连路径找到过渡点将其连接起来:
function [path,close,open]=AStar_quadrant_13(obstacle,map)
% obstacle :障碍物坐标,mx2大小数组
% map :包含以下元素的结构体
% map.start [x1,y1] 起点
% map.goal [x2,y2] 终点
% 用于存储路径
path=[];
close=[];
% open集合初始化
% [节点X坐标 ,节点Y坐标 ,代价值F=G+H ,代价值G,父节点X ,父节点Y ]
open=[map.start(1),map.start(2),0+getH(map.start,map.goal,obstacle),0 ,map.start(1), map.start(2)];
while true
% 若open集合被取完,则无路径
if isempty(open(:,1))
disp('No path to goal!!');
return;
end
% 判断目标点是否出现在open列表中
[~,~,IndexGoal]=intersect(map.goal,open(:,1:2),'rows');
if ~isempty(IndexGoal)
disp('Find Goal!!');
close=[open(IndexGoal,:);close];
break;
end
[~,IndexSort] = sort(open(:,3)); % 获取OpenList中第三列大小顺序
open=open(IndexSort,:); % 将open集合按照Index排序
current=open(1,:);
close=[open(1,:);close];
open(1,:)=[];
% 获取当前位置与目标点的坐标,判断要搜索的象限。
% 目标点map.goal,当前点close(1,1:2)
% 并依据规则获取当前点的子节点
next=getNext13(current(1:2),map.goal);
for i=1:size(next,1)
newNode=[current(1)+next(i,1),current(2)+next(i,2),0,0,0,0];
newNode(4)=current(4)+next(i,3); % 相邻节点G值
newNode(3)=getH(newNode(1:2),map.goal,obstacle)+newNode(4);% 相邻节点F值
% 如果它不可达,忽略它
if ~isempty(intersect(newNode(1:2),obstacle,'rows'))
continue;
end
% 如果它与父节点之间有障碍物,忽略它
midPnt=(newNode(1:2)+current(1:2))./2;
if any(midPnt-round(midPnt)==0)&&any(midPnt-round(midPnt)~=0)
tempPnt1=ceil(midPnt);
tempPnt2=floor(midPnt);
tempBool1=~isempty(intersect(tempPnt1,obstacle,'rows'));
tempBool2=~isempty(intersect(tempPnt2,obstacle,'rows'));
if tempBool1&&tempBool2
continue;
end
end
if ~isempty(intersect(midPnt,obstacle,'rows'))
continue;
end
% 如果它在close集合中,忽略它
if ~isempty(intersect(newNode(1:2),close(:,1:2),'rows'))
continue;
end
% 如果它不在open集合中
if isempty(intersect(newNode(1:2),open(:,1:2),'rows'))
newNode(5:6)=current(1:2); % 将当前节点作为其父节点
open=[open;newNode]; % 将此相邻节点加放OpenList中
else % 若在
[~,~,IndexInOpen]=intersect(newNode(1:2),open(:,1:2),'rows');
if newNode(3)<open(IndexInOpen,3)
% 若F更小,则将此相邻节点的父节点设置为当前节点,否则不作处理
newNode(5:6)=current(1:2); % 将当前节点作为其父节点
open(IndexInOpen,:)=newNode; % 将此相邻节点在OpenList中的数据更新
end
end
end
end
%追溯路径
Index=1;
while 1
path=[path;close(Index,1:2)];
if isequal(close(Index,1:2),map.start)
break;
end
[~,IndexInClose,~]=intersect(close(:,1:2),close(Index,5:6),'rows');
% 以下为找到中间点的过程
midPnt=(close(Index,1:2)+close(Index,5:6))./2;
if ~all(midPnt~=round(midPnt))% 若中点两个数值均不是整数,则说明两节点间中间点
% 若有一个数字不是整数,或两个数字均为整数
% 下向上向下取整
tempPnt1=floor(midPnt);
tempPnt2=ceil(midPnt);
tempPntSet=[tempPnt1;tempPnt2];
% 判断取整后节点是否和原节点重合
[~,tempIndex1,~]=intersect(tempPntSet,close(Index,1:2),'rows');
tempPntSet(tempIndex1,:)=[];
[~,tempIndex2,~]=intersect(tempPntSet,close(Index,5:6),'rows');
tempPntSet(tempIndex2,:)=[];
% 判断中间点是否为障碍物,并选择F值最小的中间点
openAndCloseSet=[open;close];
[~,~,tempIndex]=intersect(tempPntSet,openAndCloseSet(:,1:2),'rows');
tempF=openAndCloseSet(tempIndex,3);
if ~isempty(tempF)
tempIndex3=find(tempF==min(tempF));
tempIndex3=tempIndex3(1);
midPnt=openAndCloseSet(tempIndex(tempIndex3),:);
path=[path;midPnt(1:2)];
end
end
Index=IndexInClose;
end
end
5 文件下载
MATLAB 基础好的同学应该已经可以依据完整代码还原整个流程了,事实上本博文省缺的只有简单的根据象限改变搜索范围以及绘图函数,完整的 象限改进5邻域代码, 象限改进13邻域代码,以及通过交并运算更改的更加简洁的 传统A*算法 程序包下载连接如下:
参考文献:
[1] 程传奇,郝向阳,李建胜,张振杰,孙国鹏.融合改进A*算法和动态窗口法的全局动态路径规划[J].西安交通大学学报,2017,51(11):137-143.
[2] 赵卫东,蒋超.两阶段搜索的A*全局路径规划算法[J].计算机应用与软件,2020,37(12):249-253.