目录
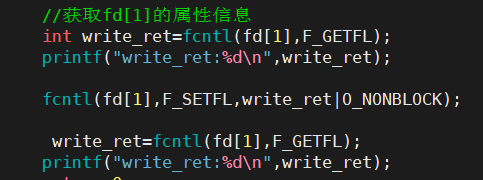
1系统接口当中,文件打开方式的宏,在内核当中的使用方式为位图
1系统接口当中,文件打开方式的宏,在内核当中的使用方式为位图
- 例如: O_ RDONLY, O_ CREAT, O_ NONBLOCK
- 验证:
-
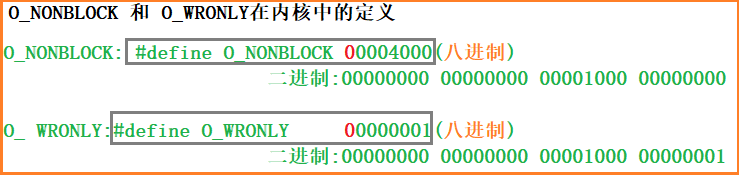
- O_RDONLY ,O_WRONLY , O_RDWR,O_CREAT,O_TRUNC,O_APPAND,O_NONBLOCK,本质上操作系统内核都是采用位图的方式进行使用
-

2命名管道
2.1 mkfifo命令
- fifo是first input first output的缩写
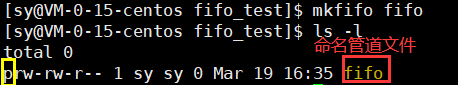
- 命名管道文件,相当于内核缓冲区的标识符。不同的进程通过这个文件,都可以找 到内核的缓冲区;
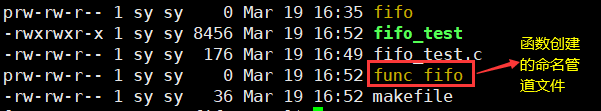
2.2mdfifo函数
- int mkfifo (const char *pathname,mode_t mode);
- 参数:
- pathname:要创建的命名管道文件的路径以及文件名
- mode_t:命名管道文件的权限,八进制数组(0664)
- 返回值:
- 成功: 0
- 失败: -1
-
#include <stdio.h> #include <sys/stat.h> int main(){ int ret=mkfifo("./func_fifo",0664); if(ret<0){ perror("mkfifo:"); return 0; } return 0; } -
-
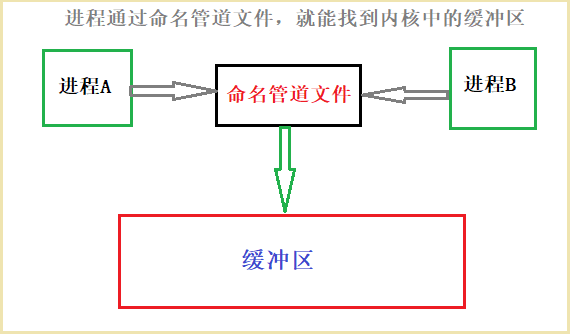
2.3特性
- 支持不同进程进行进程间通信,不依赖亲缘性。
2.4代码验证
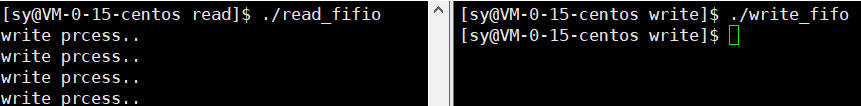
- 负责写的进程
-
#include <stdio.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <fcntl.h> #include <string.h> int main(){ //1.打开命名管道文件 int fd=open("../fifo",O_WRONLY); if(fd<0){ perror("open:"); } //调用write往管道里写 while(1){ const char* content="write prcess.."; write(fd,content,strlen(content)); sleep(1); } close(fd); return 0; } - 负责读的进程
-
#include <stdio.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <fcntl.h> int main(){ int fd=open("../fifo",O_RDONLY); if(fd<0){ perror("open:"); return 0; } while(1){ char buf[1024]={0}; read(fd,buf,sizeof(buf)-1); printf("%s\n",buf); } close(fd); return 0; } -
-