1、继承
#include "iostream"
#include "string"
using namespace std;
class Person//基类,也称为父类
{
public:
string name;
string sex;
int age;
};
//继承语法:子类 : 继承方式 父类
class Rich : public Person//子类,也称为派生类
{
public:
string car;
};
class Beggar : public Person
{
public:
string bike;
};
void test1()
{
Rich p1;
Beggar p2;
p1.age = 20;
p1.car = "宝马";
p1.name = "小明";
p1.sex = "他的";
p2.age = 40;
p2.name = "小红";
p2.sex = "她的";
p2.bike = "八大杆";
cout << p1.name << "骑着" << p1.sex << p1.car << "去吃饭" << endl;
cout << p2.name << "骑着" << p2.sex << p2.bike << "去吃饭" << endl;
}
int main()
{
test1();
system("pause");
return 0;
}


#include "iostream"
#include "string"
using namespace std;
class Person
{
public:
int a;
private:
int b;
};
class Rich : public Person
{
public:
int c;
};
void test1()
{
Rich p;
cout << "Rich类的大小=" << sizeof(p) << "byte" << endl;
}
int main()
{
test1();
system("pause");
return 0;
}

利用Vs2017的命令提示符工具可以显示类的内存具体情况。

//将路径cd到.cpp目录下,输入下面的命令,我的文件名是C++_leaning.cpp
cl /d1 reportSingleClassLayoutRich "C++_leaning.cpp"

#include "iostream"
#include "string"
using namespace std;
class Person
{
public:
Person()
{
cout << "父类构造函数调用" << endl;
}
~Person()
{
cout << "父类析构函数调用" << endl;
}
int a;
private:
int b;
};
class Rich : public Person
{
public:
Rich()
{
cout << "子类构造函数调用" << endl;
}
~Rich()
{
cout << "子类析构函数调用" << endl;
}
int c;
};
void test1()
{
Rich p;
//先构造父类,再构造子类;析构与之相反
}
int main()
{
test1();
system("pause");
return 0;
}

#include "iostream"
#include "string"
using namespace std;
class Person
{
public:
int a;
void func()
{
cout << "父类函数调用" << endl;
}
};
class Rich : public Person
{
public:
int c;
void func()
{
cout << "子类函数调用" << endl;
}
};
void test1()
{
Rich p;
//默认调用子类的同名函数
p.func();
//加作用域可以调用父类的同名函数
p.Person::func();
}
int main()
{
test1();
system("pause");
return 0;
}

#include "iostream"
#include "string"
using namespace std;
class Person
{
public:
static int a;
static void func()
{
cout << "父类静态函数调用" << endl;
}
};
class Rich : public Person
{
public:
static int a;
static void func()
{
cout << "子类静态函数调用" << endl;
}
};
int Rich::a = 10;
int Person::a = 100;
void test1()
{
Rich p;
//默认访问子类的静态成员变量和函数
cout << "p.a=" << p.a << endl;
p.func();
//通过作用域访问父类变量和函数
cout << "p.Person::a=" << p.Person::a << endl;
p.Person::func();
//通过类名访问父类变量和函数
cout << "Rich::Person::a=" << Rich::Person::a << endl;
Rich::Person::func();
}
int main()
{
test1();
system("pause");
return 0;
}

#include "iostream"
#include "string"
using namespace std;
class Person1
{
public:
int a=10;
};
class Person2
{
public:
int a=100;
};
//多类继承语法:子类 :继承方式 父类,继承方式 父类......
class Rich : public Person1,public Person2
{
public:
int c;
};
void test1()
{
//在C++实际开发中不建议用多继承
Rich p;
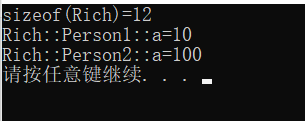
cout << "sizeof(Rich)=" << sizeof(Rich) << endl;
//当不同父类中出现同名变量,加作用域
cout << "Rich::Person1::a=" << p.Person1::a << endl;
cout << "Rich::Person2::a=" << p.Person2::a << endl;
}
int main()
{
test1();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
2、多态

#include "iostream"
#include "string"
using namespace std;
//动态多态
//条件:1、有继承 2、父类的虚函数与子类对应的函数返回类型,函数名,形参完全相同
class Animal
{
public:
virtual void speak()//虚函数
{
cout << "Animal is speaking" << endl;
}
};
class cat : public Animal
{
public:
void speak()
{
cout << "cat is speaking" << endl;
}
};
class dog : public Animal
{
public:
void speak()
{
cout << "dog is speaking" << endl;
}
};
void do_speak(Animal &a)//这个函数并没有固定地址,由传入的参数决定,因此称为多态
{
a.speak();
}
void test1()
{
cat my_cat;
dog my_dog;
do_speak(my_cat);
do_speak(my_dog);
}
int main()
{
test1();
system("pause");
return 0;
}


#include <stdio.h>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class person
{
public:
//纯虚函数,有一个纯虚函数的类叫做抽象类
//抽象类的子类必须重写父类的纯虚函数
virtual void speak()=0;
};
class laoxi:public person
{
public:
void speak()
{
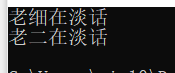
cout<<"老细在淡话"<<endl;
}
};
class laoer:public person
{
public:
void speak()
{
cout<<"老二在淡话"<<endl;
}
};
int main()
{
laoxi lx;
laoer le;
lx.speak();
le.speak();
return 0;
}
3、文本操作



扫描二维码关注公众号,回复:
14487971 查看本文章


#include <stdio.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
//1、包含头文件
//2、创建类
ofstream ofs;//也可以用fstream类
//3、打开文件
ofs.open("test.txt", ios::out);//生成的文件放在项目路径
//4、文件操作
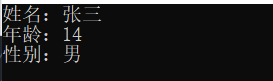
ofs << "姓名:张三" << endl;
ofs << "年龄:14" << endl;
ofs << "性别:男" << endl;
//5、关闭文件
ofs.close();
return 0;
}


#include <stdio.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
//1、包含头文件
//2、创建对象
ifstream ifs;//也可以用fstream类
//3、打开文件并判断是否有打开
ifs.open("test.txt", ios::in);//访问的文件放在项目路径
if (!ifs.is_open())
{
cout << "文件打开失败!" << endl;
return 0;
}
//4、读文件操作的四种操作
①
//char buf[1024] = { 0 };
//while (ifs >> buf)
//{
// cout << buf << endl;
//}
②
//char buf[1024] = { 0 };
//while (ifs.getline(buf,sizeof(buf)))
//{
// cout << buf << endl;
//}
//③
string buf;
while (getline(ifs, buf))
{
cout << buf << endl;
}
④
//char c;
//while ( (c = ifs.get()) != EOF ) // EOF end of file
//{
// cout << c;
//}
//5、关闭文件
ifs.close();
return 0;
}