目录
应用场景
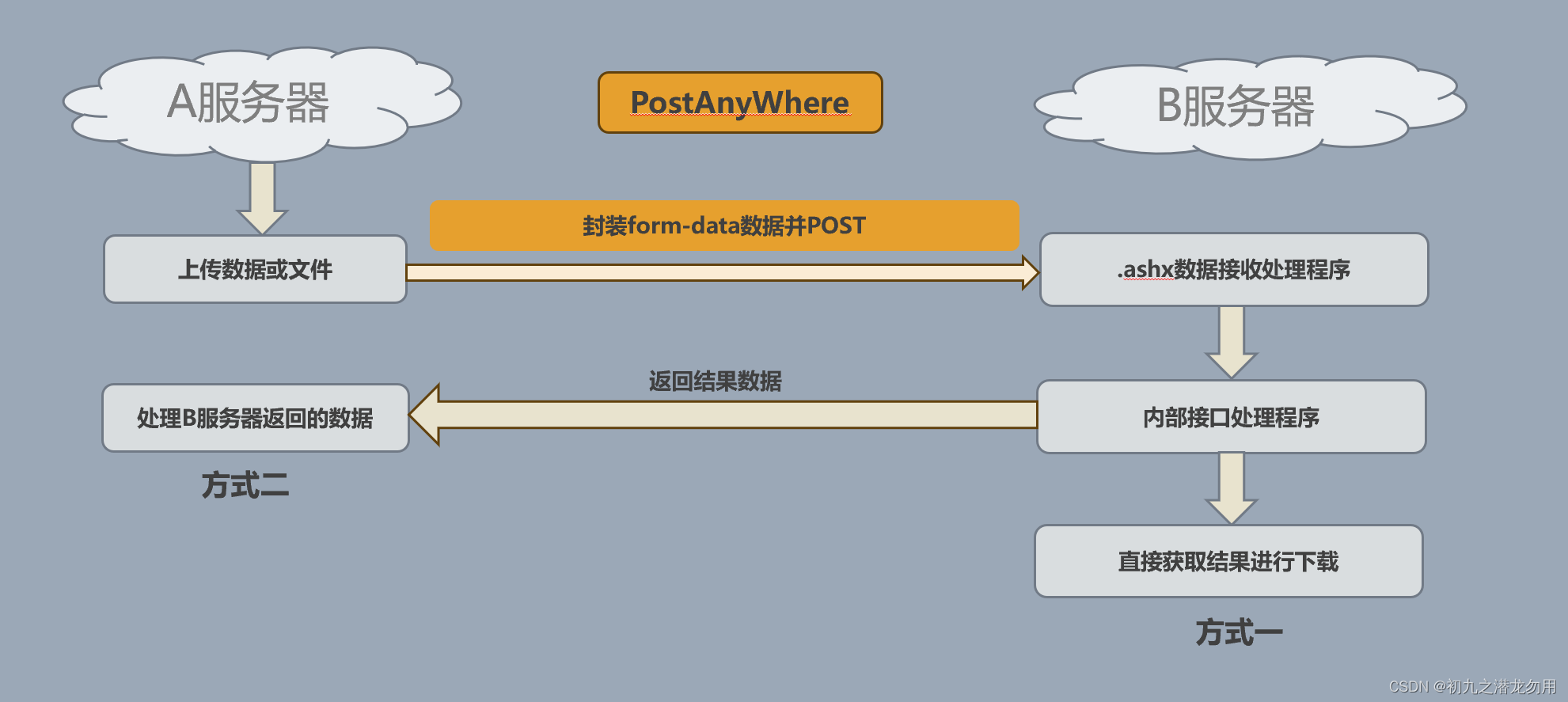
不同的接口服务器处理不同的应用,我们会在实际应用中将A服务器的数据提交给B服务器进行数据接收并处理业务。
比如我们想要处理一个OFFICE文件,由用户上传到A服务器,上传成功后,由B服务器负责进行数据处理和下载工作,这时我们就需要 POST A服务器的文件数据到B服务器进行处理。
实现原理
将用户上传的数据或A服务器已存在的数据,通过form-data的形式POST到B服务器,B服务由指定ashx文件进行数据接收,并转由指定的业务逻辑程序进行处理。如下图:
实现代码
PostAnyWhere类
创建一个 PostAnyWhere 类,
该类具有如下属性:
(1)public string PostUrl 要提交的服务器URL
(2)public List<PostFileItem> PostData 要准备的数据(PostFileItem类可包括数据和文件类型)
该类包含的关键方法如下:
(1)public void AddText(string key, string value)
该方法将指定的字典数据加入到PostData中
(2)public void AddFile(string name, string srcFileName, string desName, string contentType = "text/plain")
该方法将指定的文件添加到PostData中,其中 srcFileName 表示要添加的文件名,desName表示接收数据生成的文件名
(3)public string Send()
该方法将开始POST传送数据
代码如下:
public class PostAnyWhere
{
public string PostUrl { get; set; }
public List<PostFileItem> PostData { get; set; }
public PostAnyWhere()
{
this.PostData = new List<PostFileItem>();
}
public void AddText(string key, string value)
{
this.PostData.Add(new PostFileItem { Name = key, Value = value });
}
public void AddFile(string name, string srcFileName, string desName,string at, string contentType = "text/plain")
{
string[] srcName = Path.GetFileName(srcFileName).Split('.');
string exName = "";
if (srcName.Length > 1)
{
exName = "."+srcName[srcName.Length-1];
}
this.PostUrl = "https://www.xxx.com/test.ashx?guid=" + desName;
ReadyFile(name, GetBinaryData(srcFileName), exName,contentType);
}
void ReadyFile(string name, byte[] fileBytes, string fileExName = "", string contentType = "text/plain")
{
this.PostData.Add(new PostFileItem
{
Type = PostFileItemType.File,
Name = name,
FileBytes = fileBytes,
FileName = fileExName,
ContentType = contentType
});
}
public string Send()
{
var boundary = "----------------------------" + DateTime.Now.Ticks.ToString("x");
var request = (HttpWebRequest)WebRequest.Create(this.PostUrl);
request.ContentType = "multipart/form-data; boundary=" + boundary;
request.Method = "POST";
request.KeepAlive = true;
Stream memStream = new System.IO.MemoryStream();
var boundarybytes = System.Text.Encoding.ASCII.GetBytes("\r\n--" + boundary + "\r\n");
var endBoundaryBytes = System.Text.Encoding.ASCII.GetBytes("\r\n--" + boundary + "--");
var formdataTemplate = "\r\n--" + boundary + "\r\nContent-Disposition: form-data; name=\"{0}\";\r\n\r\n{1}";
var formFields = this.PostData.Where(m => m.Type == PostFileItemType.Text).ToList();
foreach (var d in formFields)
{
var textBytes = System.Text.Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(string.Format(formdataTemplate, d.Name, d.Value));
memStream.Write(textBytes, 0, textBytes.Length);
}
const string headerTemplate = "Content-Disposition: form-data; name=\"{0}\"; filename=\"{1}\"\r\nContent-Type: {2}\r\n\r\n";
var files = this.PostData.Where(m => m.Type == PostFileItemType.File).ToList();
foreach (var fe in files)
{
memStream.Write(boundarybytes, 0, boundarybytes.Length);
var header = string.Format(headerTemplate, fe.Name, fe.FileName ?? "System.Byte[]", fe.ContentType ?? "text/plain");
var headerbytes = System.Text.Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(header);
memStream.Write(headerbytes, 0, headerbytes.Length);
memStream.Write(fe.FileBytes, 0, fe.FileBytes.Length);
}
memStream.Write(endBoundaryBytes, 0, endBoundaryBytes.Length);
request.ContentLength = memStream.Length;
HttpWebResponse response;
try
{
using (var requestStream = request.GetRequestStream())
{
memStream.Position = 0;
var tempBuffer = new byte[memStream.Length];
memStream.Read(tempBuffer, 0, tempBuffer.Length);
memStream.Close();
requestStream.Write(tempBuffer, 0, tempBuffer.Length);
}
response = (HttpWebResponse)request.GetResponse();
}
catch (WebException webException)
{
response = (HttpWebResponse)webException.Response;
}
if (response == null)
{
throw new Exception("HttpWebResponse is null");
}
var responseStream = response.GetResponseStream();
if (responseStream == null)
{
throw new Exception("ResponseStream is null");
}
using (var streamReader = new StreamReader(responseStream))
{
return streamReader.ReadToEnd();
}
}
}
public class PostFileItem
{
public PostFileItem()
{
this.Type = PostFileItemType.Text;
}
public PostFileItemType Type { get; set; }
public string Value { get; set; }
public byte[] FileBytes { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public string FileName { get; set; }
public string ContentType { get; set; }
}
public enum PostFileItemType
{
Text = 0,
File = 1
}
public byte[] GetBinaryData(string filename)
{
if(!File.Exists(filename))
{
return null;
}
try
{
FileStream fs = new FileStream(filename, FileMode.Open, FileAccess.Read);
byte[] imageData = new Byte[fs.Length];
fs.Read( imageData, 0,Convert.ToInt32(fs.Length));
fs.Close();
return imageData;
}
catch(Exception)
{
return null;
}
finally
{
}
}
ashx文件部署
在B服务器上部署ashx文件接收数据,ashx程序即,一般处理程序(HttpHandler),一个httpHandler接受并处理一个http请求,需要实现IHttpHandler接口,这个接口有一个IsReusable成员,一个待实现的方法ProcessRequest(HttpContextctx) 。.ashx程序适合产生供浏览器处理的、不需要回发处理的数据格式。
示例代码如下:
<%@ WebHandler Language="C#" Class="Handler" %>
using System;
using System.Web;
using System.IO;
public class Handler : IHttpHandler {
public void ProcessRequest (HttpContext context) {
if (context.Request.Files.Count > 0)
{
string strPath = System.Web.HttpContext.Current.Server.MapPath("~/app_data/test/");
string strName = context.Request.Files[0].FileName;
string ext=Path.GetExtension(strName);
string filename =HttpContext.Current.Request.QueryString["guid"].ToString()+Path.GetFileNameWithoutExtension(strName);
if(ext!=""){
filename = filename + ext;
}
context.Request.Files[0].SaveAs(System.IO.Path.Combine(strPath, filename));
}
}
public bool IsReusable {
get {
return false;
}
}
}小结
ashx处理接收的数据后,后续还需要配合实际的接口功能继续处理应用。另外,对于ashx页面,实际的应用则需要使用安全访问控制,只有正常登录或提供合法访问令牌的用户才可以进行访问。
以上代码仅供参考,欢迎大家指正,再次感谢您的阅读!