2.1 Harris角点检测器
Harris角点检测算法是一个极为简单的角点检测算法。该算法的主要思想是,如果像素周围显示存在多于一个方向的边,我们认为该点为兴趣点,也称为角点。
我们把图像域中点x上的对称半正定矩阵定义为:
其中为包含导数
和
的图像梯度(我们已经在第1章定义了图像的导数和梯度)。由于该定义,
的秩为1,特征值为
和
。选择权重矩阵
,可以得到卷积:
该卷积的目的是得到在周围像素上的局部平均。在不需要实际计算特征值的情况下,为了把重要的情况和其他情况分开,引入了指示函数
为了去除加权常数,通常改为商数作为指示器,即
下面编写Harris角点检测程序
import numpy as np
from scipy.ndimage import gaussian_filter
from PIL import Image
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def compute_harris_response(im, sigma=3):
"""在一幅灰度图像中,对每一个像素计算Harris角点检测器响应函数"""
# 计算导数
imx = np.zeros(im.shape)
gaussian_filter(im, (sigma, sigma), (0, 1), imx)
imy = np.zeros(im.shape)
gaussian_filter(im, (sigma, sigma), (1, 0), imy)
# 计算 Harris 矩阵的分量
Wxx = gaussian_filter(imx * imx, sigma)
Wxy = gaussian_filter(imx * imy, sigma)
Wyy = gaussian_filter(imy * imy, sigma)
# 计算特征值和迹
Wdet = Wxx * Wyy - Wxy * Wxy
Wtr = Wxx + Wyy
return Wdet / Wtr
def get_harris_points(harrisim, min_dist=10, threshold=0.1):
"""从一幅Harris响应图像中返回角点,min_dist为分割角点和图像边界的最少像素数目"""
# 寻找高于阈值的候选角点
corner_threshold = harrisim.max() * threshold
harrisim_t = (harrisim > corner_threshold) * 1
# 得到候选点的坐标
coords = np.array(harrisim_t.nonzero()).T
# 以及它们的 Harris 响应值
candidate_values = [harrisim[c[0], c[1]] for c in coords]
# 对候选点按照 Harris 响应值进行排序
index = np.argsort(candidate_values)
# 将可行点的位置保存到数组中
allowed_locations = np.zeros(harrisim.shape)
allowed_locations[min_dist:-min_dist, min_dist:-min_dist] = 1
# 按照 min_distance 原则,选择最佳 Harris 点
filtered_coords = []
for i in index:
if allowed_locations[coords[i][0], coords[i][1]] == 1:
filtered_coords.append(coords[i])
allowed_locations[coords[i][0] - min_dist:coords[i][0] + min_dist,
coords[i][1] - min_dist:coords[i][1] + min_dist] = 0
return filtered_coords
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 读取图像
im = np.array(Image.open('eg.jpg').convert('L'))
# 计算 Harris 响应
harrisim = compute_harris_response(im)
filtered_coords1 = get_harris_points(harrisim, min_dist=6, threshold=0.1)
filtered_coords2 = get_harris_points(harrisim, min_dist=6, threshold=0.05)
# 显示结果并保存图像
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei']
plt.subplot(151), plt.imshow(im, cmap='gray'), plt.title('原图'), plt.axis('off')
plt.subplot(152), plt.imshow(harrisim, cmap='gray'), plt.title('角点响应图'), plt.axis('off')
plt.subplot(153), plt.imshow(im, cmap='gray'), plt.plot([p[1] for p in filtered_coords1],
[p[0] for p in filtered_coords1], 'r.'),
plt.title('阈值为0.1'), plt.axis('off')
plt.subplot(154), plt.imshow(im, cmap='gray'), plt.plot([p[1] for p in filtered_coords2],
[p[0] for p in filtered_coords2], 'r.'),
plt.title('阈值为0.05'), plt.axis('off')
# 保存图像为文件
plt.savefig('harris.jpg', dpi=300, bbox_inches='tight')
# 显示图像
plt.show()其运行结果如下图所示:

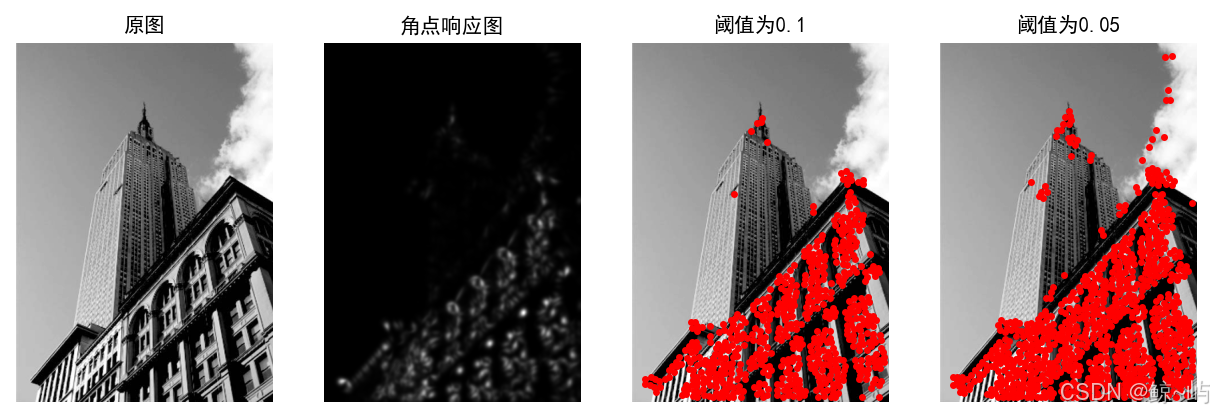
2.2 SIFT(尺度不变特征变换)
SIFT(尺度不变特征变换,Scale-Invariant Feature Transform)是一种用于图像特征提取和描述的计算机视觉算法。它可以有效地检测和描述图像中的局部特征,具有对图像缩放、旋转和光照变化的较强不变性。
2.2.1 兴趣点
SIFT 特征使用高斯差分函数来定位兴趣点:
其中,是二维高斯核,
是使用
模糊的灰度图像,
是决定相差尺度的常数。兴趣点是在图像位置和尺度变化下
的最大值和最小值点。
2.2.2 描述子
SIFT描述子在每个像素点附近选取子区域网格,在每个子区域内计算图像梯度方向直方图,每个子区域的直方图拼接起来组成描述子向量。
2.2.3 检测兴趣点
我们使用书上的示例代码运行不出来,故使用opencv库来检测兴趣点,运行代码如下所示:
import cv2
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def detect_and_plot_features(image_path):
# 读取图像并转换为灰度
image = cv2.imread(image_path)
gray_image = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
# 创建 SIFT 检测器
sift = cv2.SIFT_create()
# 检测 SIFT 特征点
keypoints, descriptors = sift.detectAndCompute(gray_image, None)
# 绘制特征点
image_with_keypoints = cv2.drawKeypoints(image, keypoints, None)
# 显示图像
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 10))
plt.imshow(cv2.cvtColor(image_with_keypoints, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB))
plt.axis('off')
plt.title('SIFT KeyPoints')
plt.show()
# 调用函数
detect_and_plot_features('touxiang.jpg') # 替换为您自己的图像路径绘制出的SIFT特征位置图像如下所示:

2.2.4 匹配描述子
在计算机视觉中,描述子匹配是特征匹样本分析中的一个重要步骤,特别是在图像匹配和物体识别任务中。描述子匹配的核心思想是找到两个图像之间相似的特征点,并用相应的描述子进行匹配。以下是使用 OpenCV 进行描述子匹配的示例代码,采用 SIFT 特征。
import cv2
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def match_descriptors(image1_path, image2_path):
# 读取图像并转换为灰度
img1 = cv2.imread(image1_path)
img2 = cv2.imread(image2_path)
gray1 = cv2.cvtColor(img1, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
gray2 = cv2.cvtColor(img2, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
# 创建 SIFT 检测器
sift = cv2.SIFT_create()
# 检测特征点及计算描述子
keypoints1, descriptors1 = sift.detectAndCompute(gray1, None)
keypoints2, descriptors2 = sift.detectAndCompute(gray2, None)
# 使用 BFMatcher 进行匹配
bf = cv2.BFMatcher(cv2.NORM_L2) # 使用 L2 距离
matches = bf.knnMatch(descriptors1, descriptors2, k=2) # 找到每个描述子的 2 个最佳匹配
# 筛选出良好的匹配(比率测试)
good_matches = []
for m, n in matches:
if m.distance < 0.75 * n.distance: # Lowe's ratio test
good_matches.append(m)
# 绘制匹配结果
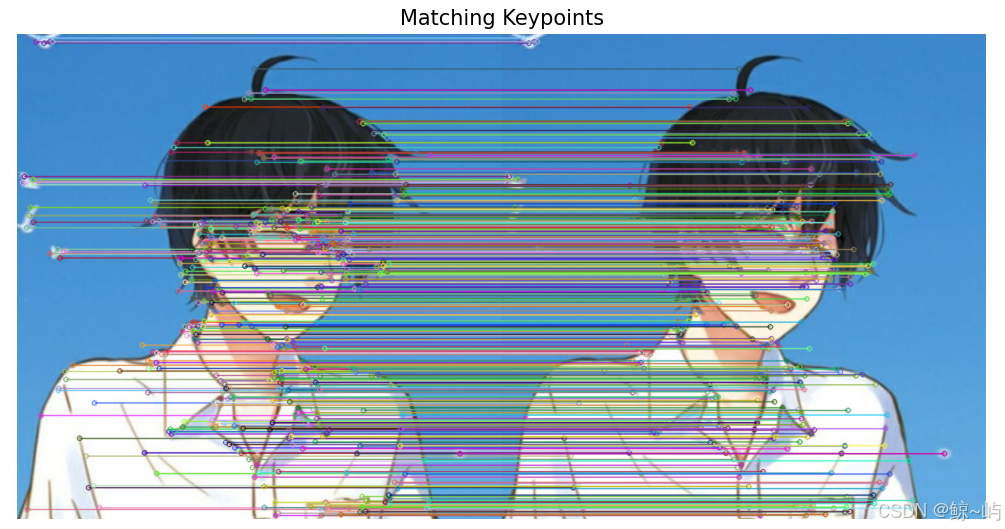
match_image = cv2.drawMatches(img1, keypoints1, img2, keypoints2, good_matches, None,
flags=cv2.DrawMatchesFlags_NOT_DRAW_SINGLE_POINTS)
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 10))
plt.imshow(cv2.cvtColor(match_image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB))
plt.axis('off')
plt.title('Matching Keypoints')
plt.show()
# 调用函数,替换图像路径
match_descriptors('touxiang.jpg', 'touxiang.jpg') # 替换为您自己的图像路径匹配结果如下图

2.3 匹配地理标记图像
我们使用局部描述子来匹 配带有地理标记的图像。
2.3.1 从百度地图下载地理标记图像
从百度地图下载地理标记图像的过程涉及 API 的使用,但百度地图的 API 并不直接支持下载图像。通常情况下,我们可以从地图 API 获取地理标记、位置信息及其相关图像的链接,然后手动下载或使用 Python 下载图像。
1.获取百度地图 API 密钥
在使用百度地图 API 之前,您需要先注册一个百度开发者账户并申请一个 API 密钥。可以访问https://lbsyun.baidu.com来申请。
2.使用 Python 获取相关数据
以下是一个基本的示例,展示如何使用 Python 和百度地图 API 查找某个地点的位置信息,并下载该地点的静态地图图像。
import requests
import os
# 百度地图 API 配置
AK = 'YOUR_BAIDU_MAP_API_KEY' # 替换为您的 API 密钥
location = '39.915,116.404' # 替换为目标地理位置的经纬度,例如北京的经纬度
# 构建百度地图静态地图 API 请求 URL
map_url = f'http://api.map.baidu.com/staticimage/v2?ak={AK}¢er={location}&width=600&height=400&markers={location}&markerStyles=l,red&zoom=12'
# 发起请求并下载图像
response = requests.get(map_url)
# 创建用于保存图像的目录
os.makedirs('baidu_maps', exist_ok=True)
# 指定保存的文件名
image_path = os.path.join('baidu_maps', 'map_image.jpg')
# 保存图像
with open(image_path, 'wb') as file:
file.write(response.content)
print(f"地图图像已下载到: {image_path}") 2.3.2 使用局部描述子匹配
我们刚才已经下载了这些图像,下面需要对这些图像提取局部描述子。在这种情 况下,我们将使用前面部分讲述的SIFT特征描述子。
import sift
nbr_images = len(imlist)
matchscores = zeros((nbr_images,nbr_images))
for i in range(nbr_images):
for j in range(i,nbr_images): # 仅仅计算上三角
print('comparing', imlist[i], imlist[j])
l1, d1 = sift.read_features_from_file(featlist[i])
l2, d2 = sift.read_features_from_file(featlist[j])
matches = sift.match_twosided(d1, d2)
nbr_matches = sum(matches > 0)
print('number of matches = ', nbr_matches)
matchscores[i, j] = nbr_matches
# 复制值
for i in range(nbr_images):
for j in range(i + 1, nbr_images): # 不需要复制对角线
matchscores[j, i] = matchscores[i, j]2.3.3 可视化连接图像
为了可视化连接通过局部特征匹配找到的图像,您可以使用 OpenCV 将匹配的特征绘制在一起。下述步骤将展示如何使用 Python 和 OpenCV 可视化连接匹配的图像。
import cv2
import numpy as np
# 加载图像
img1 = cv2.imread('baidu_maps/map_image.jpg') # 百度地图图像
img2 = cv2.imread('your_other_image.jpg') # 要匹配的另一张图像
# 转换为灰度图
gray1 = cv2.cvtColor(img1, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
gray2 = cv2.cvtColor(img2, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
# 创建 ORB 检测器
orb = cv2.ORB_create()
# 找到关键点和描述子
keypoints1, descriptors1 = orb.detectAndCompute(gray1, None)
keypoints2, descriptors2 = orb.detectAndCompute(gray2, None)
# 创建 BFMatcher 对象
bf = cv2.BFMatcher(cv2.NORM_HAMMING, crossCheck=True)
# 匹配描述子
matches = bf.match(descriptors1, descriptors2)
# 排序匹配结果
matches = sorted(matches, key=lambda x: x.distance)
# 获取关键点的位置
points1 = np.zeros((len(matches), 2), dtype=np.float32)
points2 = np.zeros((len(matches), 2), dtype=np.float32)
for i, match in enumerate(matches):
points1[i, :] = keypoints1[match.queryIdx].pt # 图像1的关键点
points2[i, :] = keypoints2[match.trainIdx].pt # 图像2的关键点
# 连接图像
# 创建一个新图像,宽度为两幅图像的宽度之和
height = max(img1.shape[0], img2.shape[0])
new_width = img1.shape[1] + img2.shape[1]
result = np.zeros((height, new_width, 3), dtype=np.uint8)
result[:img1.shape[0], :img1.shape[1]] = img1
result[:img2.shape[0], img1.shape[1]:] = img2
# 绘制匹配结果
for i in range(len(matches)):
pt1 = (int(points1[i, 0]), int(points1[i, 1]))
pt2 = (int(points2[i, 0]) + img1.shape[1], int(points2[i, 1]))
cv2.line(result, pt1, pt2, (0, 255, 0), 1) # 绘制线条,颜色为绿色
# 显示结果
cv2.imshow("Matched Image", result)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()