注:机翻,未校。
OSPF Header Format and Packets Types [Explained with Wireshark Captures]
Bilel
February 7, 2023
![OSPF Header Format and Packets Types [Explained with Wireshark Captures]](https://i-blog.csdnimg.cn/blog_migrate/96d20ca90da7efd33a7a526783c86687.png)
OSPF runs over Internet Protocol (IP) either IPv4 or IPv6, but does not leverage a transport protocol like UDP or TCP. It encapsulates its data directly in IP packets with protocol number 89. This is in contrast to other routing protocols, as an example Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) uses TCP port 179. OSPF implements its own transport error detection and correction functions.
OSPF 通过 IPv4 或 IPv6 的 Internet 协议 (IP) 运行,但不利用 UDP 或 TCP 等传输协议。它直接将其数据封装在协议编号为 89 的 IP 数据包中。这与其他路由协议形成鲜明对比,例如,边界网关协议 (BGP) 使用 TCP 端口 179。OSPF实现了自己的传输错误检测和纠正功能。
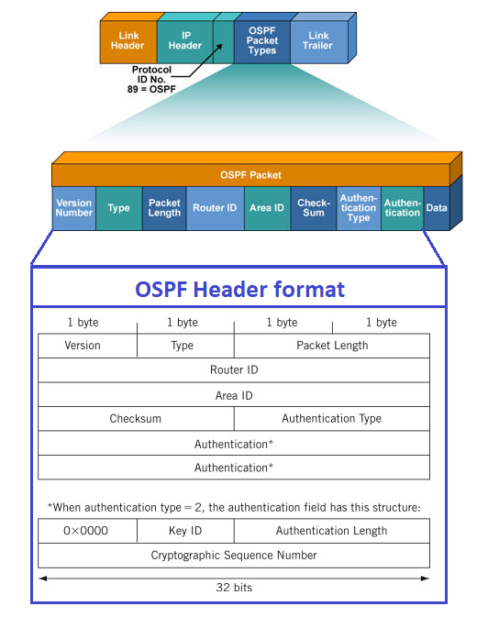
an OSPF routers uses 5 types of packets to communicate with its neighbors:
OSPF 路由器使用 5 种类型的数据包与其邻居进行通信:
- Type 1: Hello 类型1:Hello
- Type 2: Database description (DBD)
类型 2:数据库描述 (DBD) - Type 3: Link State Request (LSR)
类型 3:链路状态请求 (LSR) - Type 4: Link State Update (LSU)
类型 4:链路状态更新 (LSU) - Type 5: Link State Acknowledgement (LSAck)
类型 5:链路状态确认 (LSAck)
Type 1: Hello 类型1:Hello
The Hello packet are sent to Multicast address (224.0.0.5 or 224.0.0.6 to the DR), it’s the key message in order establish relationships between adjacencies devices. It define the key parameters on how an OSPF neighbor represent itself in the Area. The information provided like Area, timers and Authentication will indicate if the adjacency will form or not:
Hello 数据包被发送到组播地址(224.0.0.5 或 224.0.0.6 到 DR),它是在邻接设备之间建立关系的关键消息。它定义了 OSPF 邻居如何在区域中表示自身的关键参数。提供的信息(如区域、计时器和身份验证)将指示是否形成邻接关系:

Let’s take and Example of an OSPF Hello Packet from a Wireshark capture:
让我们以 Wireshark 捕获的 OSPF Hello 数据包为例:

Type 2: Database description (DBD) 类型 2:数据库描述 (DBD)
Database description messages contain descriptions of the topology of the autonomous system or area. They convey the contents of the link-state database (LSDB) for the area from one router to another.
数据库描述消息包含自治系统或区域的拓扑描述。它们将该区域的链路状态数据库 (LSDB) 的内容从一个路由器传送到另一个路由器。
During the OSPF exchange state, A master and slave election will take place, the master will start the Exchange of the DBD and he is responsible for incrementing the sequence number.
在 OSPF 交换状态期间,将进行主从选举,主服务器将开始 DBD 的交换,他负责递增序列号。
At first both assure master role and start with a sequence number, but, after the slave will use the sequence of the master to send its DBD and only the master is responsible to increment it.
起初,两者都确保主服务器角色并从序列号开始,但是,在从服务器将使用主机的序列发送其DBD,并且只有主机负责增加它。
- Please note that this election isn’t related to DR and BDR election.
请注意,此次选举与 DR 和 BDR 选举无关。

The main fields/flags of the DBD are:
DBD 的主要字段/标志是:
- Interface MTU: Specifies the largest IP datagram in bytes that the interface can send without fragmentation (can cause the adjacency to be stuck in the Exchange state, if mismatch)
接口 MTU:指定接口可以在不分段的情况下发送的最大 IP 数据报(以字节为单位)(如果不匹配,可能导致邻接关系停滞在 Exchange 状态) - I (Initial):
– set to 1 if the packet is the first DD packet.
– It is set to 0 if not.
I(初始): – 如果数据包是第一个 DD 数据包,则设置为 1。 – 如果不是,则设置为 0。 - M (More):
– set to 0 if the packet is the last DD packet.
– It is set to 1 if more DD packets are to follow.
M (更多): – 如果数据包是最后一个 DD 数据包,则设置为 0。 – 如果要跟踪更多 DD 数据包,则将其设置为 1。 - MS (Master/Slave): The Master/Slave bit.
– When set to 1, it indicates that the router is the master during the database exchange process.
– When set to 0, the router is the slave router.
MS(Master/Slave):主/从位。 – 设置为 1 时,表示路由器是数据库交换过程中的主路由器。 – 当设置为 0 时,路由器为从路由器。 - DD sequence number: Used to sequence the collection of DD packets.
The initial value is set by the master. The DD sequence number then increments until the complete database description has been sent.
DD 序列号:用于对 DD 数据包的收集进行排序。 初始值由主机设置。然后,DD 序列号会递增,直到发送完完整的数据库描述。
Let’s take and Example of an OSPF BDB Packet from a Wireshark capture:
让我们以 Wireshark 捕获的 OSPF BDB 数据包为例:
In this case, the router 192.168.1.1 is elected as master for the DBD exchange and he is incrementing the DBD Sequence:
在本例中,路由器 192.168.1.1 被选为 DBD 交换的主服务器,并且他正在递增 DBD 序列:
- DBD message From Slave (sequence 9015):
来自从站的 DBD 消息(序列 9015):

- DBD message From Master (sequence 9015 + 1):
来自主服务器的 DBD 消息(序列 9015 + 1):

Type 3: Link State Request 类型 3:链接状态请求
If a portion of the LSDB is missing, Link state request messages can be by one router to request updated information . The message specifies the link(s) for which the requesting device wants more current information.
如果LSDB的一部分丢失,则链路状态请求消息可以由一个路由器请求更新的信息。该消息指定了请求设备需要更多最新信息的链接。
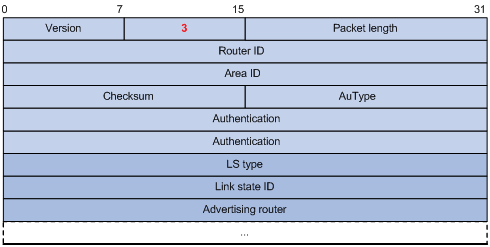
In this Example, the router 192.168.1.2 is requesting the state of the link: 192.168.2.4
在此示例中,路由器 192.168.1.2 正在请求链路的状态:192.168.2.4

Type 4: Link State Update 类型 4:链路状态更新
-
Link-state update messages contain updated information about the state of certain links on the LSDB. They are sent in response to a link state request message, and also broadcast or multicast by routers on a regular basis. Their contents are used to update the information in the LSDBs of routers that receive them.
链路状态更新消息包含有关 LSDB 上某些链路状态的更新信息。它们是为了响应链路状态请求消息而发送的,并且还由路由器定期广播或组播。它们的内容用于更新接收它们的路由器的 LSDB 中的信息。 -
Link State Update (LSU) enable the flooding of LSAs. Each LSA contains routing, metric and topology information to describe a portion of OSPF network. The LSA are advertised within an LSU packet to its neighboring routers.
链路状态更新 (LSU) 启用 LSA 泛洪。每个 LSA 都包含路由、度量和拓扑信息,用于描述 OSPF 网络的一部分。LSA 在 LSU 数据包中通告到其相邻路由器。

Let’s look at the response of the last LSR from the previous example:
让我们看一下上一个示例中最后一个 LSR 的响应:

The capture illustrates the LSU as an answer for LSR about the Link state ID 192.168.2.4
捕获说明了 LSU 作为 LSR 关于链路状态 ID 192.168.2.4 的答案
The Router 192.168.2.4 is the DROther for the network 192.168.2.0/24, as a result, it will send a transit sub-LSA for it indicating the DR IP address and his own IP.
路由器 192.168.2.4 是网络 192.168.2.0/24 的 DROther,因此,它将为其发送一个传输子 LSA,指示 DR IP 地址和他自己的 IP。
To understand the advertised LSA, let’s check the Router LSA sub-types:
要了解播发的 LSA,让我们检查路由器 LSA 子类型:
| OSPF LSA-Type-1 Sub-Types OSPF LSA-Type-1 亚型 | P2P | Transit 通过 | Stub | Virtual Link 虚拟链接 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Link ID 链接 ID | Neighbor’s ID 邻居的 ID | IP Address of the DR DR 的 IP 地址 | IP Network Number IP 网络号码 | Neighbor’s ID 邻居的 ID |
| Link Data 链接数据 | Interface IP Address 接口 IP 地址 | Interface IP 接口 IP | Subnet mask 子网掩码 | Interface IP Address 接口 IP 地址 |
| Network type 网络类型 | Point to point (P2P) 点对点 (P2P) | Broadcast (default) 广播 (默认) | Non-Broadcast Multi-Access (NBMA) 非广播 多路接入 (国家银行业局) | Point to Multipoint 点对多点 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Imported in to OSPF LSDB as: 作为以下方式导入到 OSPF LSDB: | Stub and p2p 存根和 p2p | Transit 通过 | Transit 通过 | Stub and p2p 存根和 p2p |
Note: If the link type Broadcast, but the router didn’t learn any neighbor on that link, it will advertise it as stub sub-LSA-1 (Network IP and mask)
注意:如果链路类型为广播,但路由器未了解该链路上的任何邻居,则会将其通告为末节子LSA-1(网络IP和掩码)
Type 5: Link State Acknowledgement (LSAck) 类型 5:链路状态确认 (LSAck)
Link-state acknowledgment messages is used for acknowledging receipt of a Link State Update message. It ensure the reliability to the link-state exchange process.
链路状态确认消息用于确认收到链路状态更新消息。它确保了链路状态交换过程的可靠性。


via:
-
OSPF Header Format and Packets Types [Explained with Wireshark Captures]