抽象层次非常好,广义优化工具。用于排产没有复杂的落地示例
move 真实的规划变量 -> trigger shadowvariable更新 -> StartTimeListener
- https://github.com/apache/incubator-kie-optaplanner/blob/main/optaplanner-examples/src/main/java/org/optaplanner/examples/projectjobscheduling/app/ProjectJobSchedulingApp.java
- https://github.com/eugenp/tutorials/tree/master/timefold-solver
- https://github.com/kisszhu/aps
安装
- java
- maven
配置
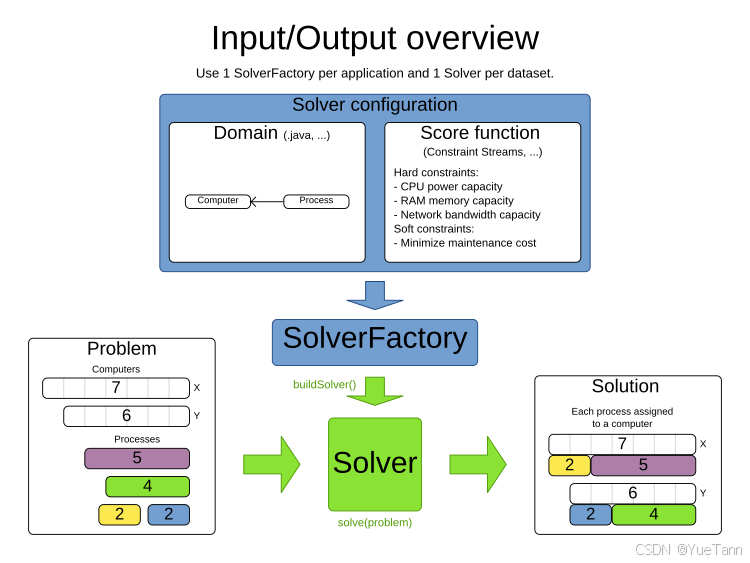
- xml配置
- solutionClass
- entityClass
- constraintProviderClass
- termination: 5min
- constructionHeuristic: FIRST_FIT
- localSearch:
也即是说,先定义对象“entityClass”, 转化为约束“constraintProviderClass”,然后运用 constructionHeuristic + localSearch的方式进行求解
其中,一个整体的任务叫做project, 资源有可再生,非可再生。
工序叫做Job,job跟着若干project。每个工序有自己的资源,ResourceRequirement. 执行模式Execution Mode. 分配allocation.
- resourceRequirement和allocation都要设置execution mode
- 每个工序JOb, 有自己的resourceRequirement, executation mode, allocation
最好先跑一个实例中的quick-start: https://docs.timefold.ai/timefold-solver/latest/quickstart/hello-world/hello-world-quickstart
基本概念
- 最简单的宏观视角来说,构建一个solver = solverFactory.buildSolver(),构建一个问题建模solution=new PlanningSolution(machines, tasks),solver.solve(solution)即可.
- 其中PlanningEntity, 约束位于solution之中; Planning Variable (可设置变化范围)位于PlanningEntity中,由于一些联动的关系,可以设置影子变量ShadowVariable,一个entity的变量改变了,其影子变量也跟着改变,例如下一道工序的开始时间;如果是双向的,及两个变量任意个发生变化,另一个都跟着变化,则设置为InverseRelationShadowVariable
计划相关:https://docs.timefold.ai/timefold-solver/latest/responding-to-change/responding-to-change#continuousPlanning
- PlanningSolution
- 定义Problem,以及解
- planning entity
- Allocation
- planing variable
- executionMode
- delay
- shadow variable
- predecessorsDoneDate
- https://www.optaplanner.org/docs/optaplanner/latest/shadow-variable/shadow-variable.html
- ShadowVariable和VariableListener之间的关系紧密相关
- planning score
- 核心的优化算法
其他任务的domain 模型对如何建模比较重要

Java基本概念
- 反射就是Java可以给我们在运行时获取类的信息,例如在类上加上@Component注解,Spring就帮你创建对象
建模
建模非常关键,也就是想清楚一个计划或分配问题,真正分配的是什么,或者计划过程中,真正变化的什么。很多只是变化引起的
优化过程中,交换的是什么?
课程表
安排课程,也就是将时间和教室分配给课程
拿quick-start中的课程表为例,分配的资源是教室和时间,其中的约束为
- A room can have at most one lesson at the same time.
- A teacher can teach at most one lesson at the same time.
- A student can attend at most one lesson at the same time.
- A teacher prefers to teach all lessons in the same room.
- A teacher prefers to teach sequential lessons and dislikes gaps between lessons.
- A student dislikes sequential lessons on the same subject.

- 其中的planningvariable应该是多对一的,多个planning variable对应到一个其他entity,而不是一个planning variable对应到多个entity。使用到该planning variable的其他entity,是1,可以直接对应到多个planning entity中的planning variable。
车辆规划
每一辆车分给一个任务队列,依次去这些地方
排产-Project Job Scheduling
排产也就是把任务分配给资源和时间.
官方实例中分配资源也就是选择execution mode,目标是减少project delay. 其中真正分配和变化的是execution mode. 也就是选择不同的资源
排产-TaskAssigning
约束
比如排产中的工序依赖关系
import org.timefold.solver.core.api.score.buildin.hardsoft.HardSoftScore;
import org.timefold.solver.core.api.score.stream.ConstraintProvider;
import org.timefold.solver.core.api.score.stream.Constraint;
import org.timefold.solver.core.api.score.stream.ConstraintStream;
import org.timefold.solver.core.api.score.stream.Joiners;
public class JobShopConstraintProvider implements ConstraintProvider {
@Override
public Constraint[] defineConstraints(ConstraintFactory constraintFactory) {
return new Constraint[] {
// Ensure operations follow the sequence within each job
constraintFactory.from(Operation.class)
.join(Operation.class, Joiners.filteringEach(otherOp ->
otherOp.getJob().equals(op.getJob()) &&
otherOp.getSequence() == op.getSequence() + 1
))
.penalize("Operations must follow sequence",
HardSoftScore.ONE_HARD,
(op, otherOp) -> 1),
// Ensure machine constraints are respected
constraintFactory.from(Operation.class)
.join(Operation.class, Joiners.filteringEach((op1, op2) ->
op1.getMachine().equals(op2.getMachine()) &&
op1.getEndTime() > op2.getStartTime() &&
op1.getStartTime() < op2.getEndTime() &&
!op1.equals(op2))
)
.penalize("Machine cannot process two operations at once",
HardSoftScore.ONE_HARD,
(op1, op2) -> 1)
};
}
}
官方示例
入口在APP的main
public static void main(String[] args) {
prepareSwingEnvironment();
new ProjectJobSchedulingApp().init();
}
init
public void init() {
init(null, true);
}
public void init(Component centerForComponent, boolean exitOnClose) {
solutionBusiness = createSolutionBusiness();
solverAndPersistenceFrame = new SolverAndPersistenceFrame<>(solutionBusiness, createSolutionPanel(),
createExtraActions());
solverAndPersistenceFrame
.setDefaultCloseOperation(exitOnClose ? WindowConstants.EXIT_ON_CLOSE : WindowConstants.DISPOSE_ON_CLOSE);
solverAndPersistenceFrame.init(centerForComponent);
solverAndPersistenceFrame.setVisible(true);
}
其中,solution business
- SolverFactory.createFromXmlResource建立了solver
public SolutionBusiness<Solution_, ?> createSolutionBusiness() {
SolutionBusiness<Solution_, ?> solutionBusiness = new SolutionBusiness<>(this,
SolverFactory.createFromXmlResource(solverConfigResource));
solutionBusiness.setDataDir(determineDataDir(dataDirName));
solutionBusiness.setSolutionFileIO(createSolutionFileIO());
solutionBusiness.setImporters(createSolutionImporters());
solutionBusiness.setExporters(createSolutionExporters());
solutionBusiness.updateDataDirs();
return solutionBusiness;
}
在APP类继承的solution中,示例采用的是schedule,也就是planningsolution,作为问题和排产结果
package org.optaplanner.examples.projectjobscheduling.domain;
import java.util.List;
import org.optaplanner.core.api.domain.solution.PlanningEntityCollectionProperty;
import org.optaplanner.core.api.domain.solution.PlanningScore;
import org.optaplanner.core.api.domain.solution.PlanningSolution;
import org.optaplanner.core.api.domain.solution.ProblemFactCollectionProperty;
import org.optaplanner.core.api.score.buildin.hardmediumsoft.HardMediumSoftScore;
import org.optaplanner.examples.common.domain.AbstractPersistable;
import org.optaplanner.examples.projectjobscheduling.domain.resource.Resource;
@PlanningSolution
public class Schedule extends AbstractPersistable {
private List<Project> projectList;
private List<Job> jobList;
private List<ExecutionMode> executionModeList;
private List<Resource> resourceList;
private List<ResourceRequirement> resourceRequirementList;
private List<Allocation> allocationList;
private HardMediumSoftScore score;
public Schedule() {
}
public Schedule(long id) {
super(id);
}
@ProblemFactCollectionProperty
public List<Project> getProjectList() {
return projectList;
}
public void setProjectList(List<Project> projectList) {
this.projectList = projectList;
}
@ProblemFactCollectionProperty
public List<Job> getJobList() {
return jobList;
}
public void setJobList(List<Job> jobList) {
this.jobList = jobList;
}
@ProblemFactCollectionProperty
public List<ExecutionMode> getExecutionModeList() {
return executionModeList;
}
public void setExecutionModeList(List<ExecutionMode> executionModeList) {
this.executionModeList = executionModeList;
}
@ProblemFactCollectionProperty
public List<Resource> getResourceList() {
return resourceList;
}
public void setResourceList(List<Resource> resourceList) {
this.resourceList = resourceList;
}
@ProblemFactCollectionProperty
public List<ResourceRequirement> getResourceRequirementList() {
return resourceRequirementList;
}
public void setResourceRequirementList(List<ResourceRequirement> resourceRequirementList) {
this.resourceRequirementList = resourceRequirementList;
}
@PlanningEntityCollectionProperty
public List<Allocation> getAllocationList() {
return allocationList;
}
public void setAllocationList(List<Allocation> allocationList) {
this.allocationList = allocationList;
}
@PlanningScore
public HardMediumSoftScore getScore() {
return score;
}
public void setScore(HardMediumSoftScore score) {
this.score = score;
}
// ************************************************************************
// Complex methods
// ************************************************************************
}
Timefold 示例
Solver job接受到problem,开始run
@Deprecated(forRemoval = true, since = "1.6.0")
default SolverJob<Solution_, ProblemId_> solve(ProblemId_ problemId,
Solution_ problem, Consumer<? super Solution_> finalBestSolutionConsumer,
BiConsumer<? super ProblemId_, ? super Throwable> exceptionHandler) {
SolverJobBuilder<Solution_, ProblemId_> builder = solveBuilder()
.withProblemId(problemId)
.withProblem(problem);
if (finalBestSolutionConsumer != null) {
builder.withFinalBestSolutionConsumer(finalBestSolutionConsumer);
}
if (exceptionHandler != null) {
builder.withExceptionHandler(exceptionHandler);
}
return builder.run();
}
solverStatus = SolverStatus.SOLVING_ACTIVE;
// Create the consumer thread pool only when this solver job is active.
consumerSupport = new ConsumerSupport<>(getProblemId(), bestSolutionConsumer, finalBestSolutionConsumer,
firstInitializedSolutionConsumer, exceptionHandler, bestSolutionHolder);
Solution_ problem = problemFinder.apply(problemId);
// add a phase lifecycle listener that unlock the solver status lock when solving started
solver.addPhaseLifecycleListener(new UnlockLockPhaseLifecycleListener());
// add a phase lifecycle listener that consumes the first initialized solution
solver.addPhaseLifecycleListener(new FirstInitializedSolutionPhaseLifecycleListener(consumerSupport));
solver.addEventListener(this::onBestSolutionChangedEvent);
final Solution_ finalBestSolution = solver.solve(problem);
consumerSupport.consumeFinalBestSolution(finalBestSolution);
return finalBestSolution;
理解
-
https://www.optaplanner.org/docs/optaplanner/latest/shadow-variable/shadow-variable.html
-
build_solver/ default_solver_factory
public Solver<Solution_> buildSolver(SolverConfigOverride<Solution_> configOverride) {
Objects.requireNonNull(configOverride, "Invalid configOverride (null) given to SolverFactory.");
var isDaemon = Objects.requireNonNullElse(solverConfig.getDaemon(), false);
var solverScope = new SolverScope<Solution_>();
var monitoringConfig = solverConfig.determineMetricConfig();
solverScope.setMonitoringTags(Tags.empty());
var metricsRequiringConstraintMatchSet = Collections.<SolverMetric> emptyList();
if (!monitoringConfig.getSolverMetricList().isEmpty()) {
solverScope.setSolverMetricSet(EnumSet.copyOf(monitoringConfig.getSolverMetricList()));
metricsRequiringConstraintMatchSet = solverScope.getSolverMetricSet().stream()
.filter(SolverMetric::isMetricConstraintMatchBased)
.filter(solverScope::isMetricEnabled)
.toList();
} else {
solverScope.setSolverMetricSet(EnumSet.noneOf(SolverMetric.class));
}
var environmentMode = solverConfig.determineEnvironmentMode();
var constraintMatchEnabled = !metricsRequiringConstraintMatchSet.isEmpty() || environmentMode.isAsserted();
if (constraintMatchEnabled && !environmentMode.isAsserted()) {
LOGGER.info(
"Enabling constraint matching as required by the enabled metrics ({}). This will impact solver performance.",
metricsRequiringConstraintMatchSet);
}
var innerScoreDirector = scoreDirectorFactory.buildScoreDirector(true, constraintMatchEnabled);
solverScope.setScoreDirector(innerScoreDirector);
solverScope.setProblemChangeDirector(new DefaultProblemChangeDirector<>(innerScoreDirector));
var moveThreadCount = resolveMoveThreadCount(true);
var bestSolutionRecaller = BestSolutionRecallerFactory.create().<Solution_> buildBestSolutionRecaller(environmentMode);
var randomFactory = buildRandomFactory(environmentMode);
var configPolicy = new HeuristicConfigPolicy.Builder<>(
environmentMode,
moveThreadCount,
solverConfig.getMoveThreadBufferSize(),
solverConfig.getThreadFactoryClass(),
solverConfig.getNearbyDistanceMeterClass(),
randomFactory.createRandom(),
scoreDirectorFactory.getInitializingScoreTrend(),
solutionDescriptor,
ClassInstanceCache.create()).build();
var basicPlumbingTermination = new BasicPlumbingTermination<Solution_>(isDaemon);
var termination = buildTerminationConfig(basicPlumbingTermination, configPolicy, configOverride);
var phaseList = buildPhaseList(configPolicy, bestSolutionRecaller, termination);
return new DefaultSolver<>(environmentMode, randomFactory, bestSolutionRecaller, basicPlumbingTermination,
termination, phaseList, solverScope,
moveThreadCount == null ? SolverConfig.MOVE_THREAD_COUNT_NONE : Integer.toString(moveThreadCount));
}
solver的主流程
@Override
public final Solution_ solve(Solution_ problem) {
if (problem == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("The problem (" + problem + ") must not be null.");
}
// No tags for these metrics; they are global
LongTaskTimer solveLengthTimer = Metrics.more().longTaskTimer(SolverMetric.SOLVE_DURATION.getMeterId());
Counter errorCounter = Metrics.counter(SolverMetric.ERROR_COUNT.getMeterId());
solverScope.setBestSolution(problem);
solverScope.setSolver(this);
outerSolvingStarted(solverScope);
boolean restartSolver = true;
while (restartSolver) {
LongTaskTimer.Sample sample = solveLengthTimer.start();
try {
// solvingStarted will call registerSolverSpecificMetrics(), since
// the solverScope need to be fully initialized to calculate the
// problem's scale metrics
solvingStarted(solverScope);
runPhases(solverScope);
solvingEnded(solverScope);
} catch (Exception e) {
errorCounter.increment();
solvingError(solverScope, e);
throw e;
} finally {
sample.stop();
unregisterSolverSpecificMetrics();
}
restartSolver = checkProblemFactChanges();
}
outerSolvingEnded(solverScope);
return solverScope.getBestSolution();
}
- run_phase /abstract_solver
protected void runPhases(SolverScope<Solution_> solverScope) {
if (!solverScope.getSolutionDescriptor().hasMovableEntities(solverScope.getScoreDirector())) {
logger.info("Skipped all phases ({}): out of {} planning entities, none are movable (non-pinned).",
phaseList.size(), solverScope.getWorkingEntityCount());
return;
}
Iterator<Phase<Solution_>> it = phaseList.iterator();
while (!solverTermination.isSolverTerminated(solverScope) && it.hasNext()) {
Phase<Solution_> phase = it.next();
phase.solve(solverScope);
// If there is a next phase, it starts from the best solution, which might differ from the working solution.
// If there isn't, no need to planning clone the best solution to the working solution.
if (it.hasNext()) {
solverScope.setWorkingSolutionFromBestSolution();
}
}
}
-
solver外面的phase, PhaseFactory
-
dostep
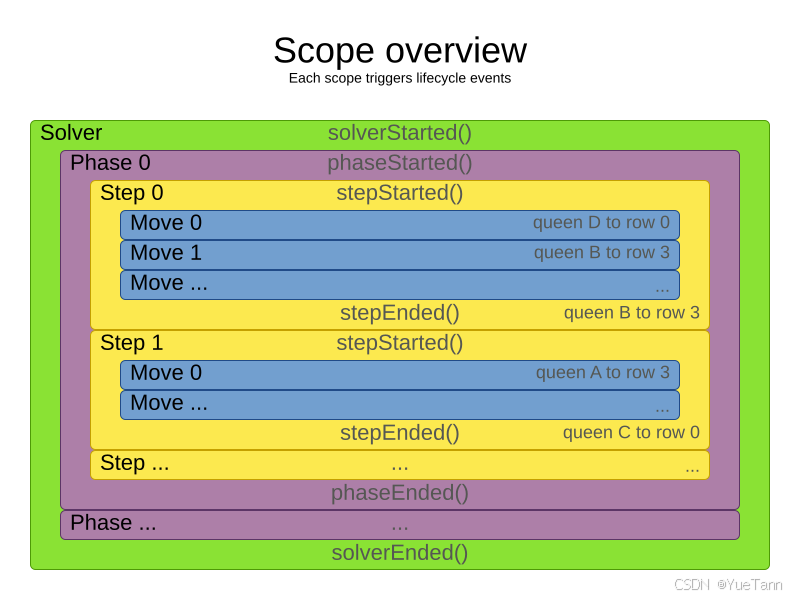
局部搜索在当前解上尝试多个移动,并选择最佳的被接受的移动作为这一步。A step is the winning Move。在每一步,它尝试所有选定的移动,除非是选定的step,否则它不会进一步研究那个解。这就是局部搜索具有很高可扩展性的原因之一。
private void doStep(CustomStepScope<Solution_> stepScope, CustomPhaseCommand<Solution_> customPhaseCommand) {
InnerScoreDirector<Solution_, ?> scoreDirector = stepScope.getScoreDirector();
customPhaseCommand.changeWorkingSolution(scoreDirector);
calculateWorkingStepScore(stepScope, customPhaseCommand);
solver.getBestSolutionRecaller().processWorkingSolutionDuringStep(stepScope);
}
- 决定下一步
- A MoveSelector which selects the possible moves of the current solution. See the chapter move and neighborhood selection.
- An Acceptor which filters out unacceptable moves.
- A Forager which gathers accepted moves and picks the next step from them.
<localSearch>
<unionMoveSelector>
...
</unionMoveSelector>
<acceptor>
...
</acceptor>
<forager>
...
</forager>
</localSearch>
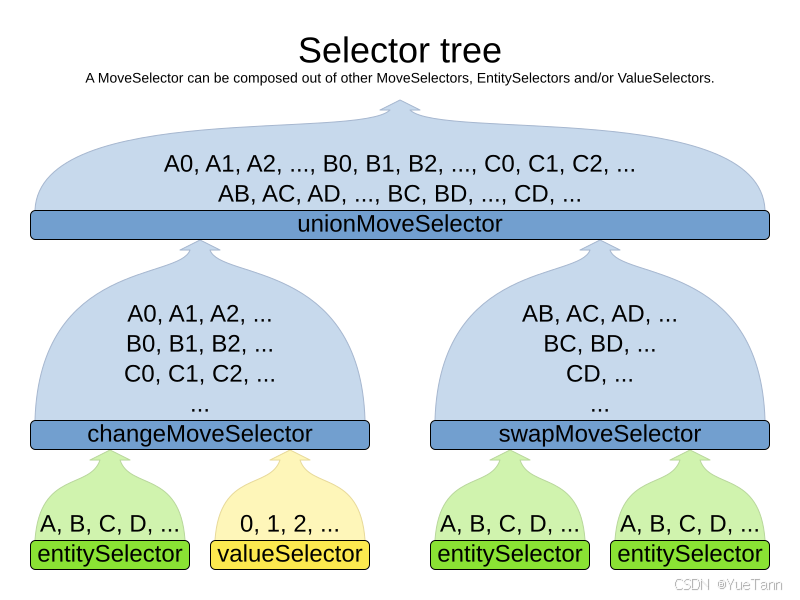
从底向上看,理解可能的move。如果是entity+value组合,或者是entity和entity进行新的组合。也许这就是叫做组合优化的原因?
chatgpt产生的一些简单代码
// File: pom.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>org.example</groupId>
<artifactId>jobshop-scheduler</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<properties>
<maven.compiler.source>17</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>17</maven.compiler.target>
<timefold.version>1.6.0</timefold.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>ai.timefold.solver</groupId>
<artifactId>timefold-solver-core</artifactId>
<version>${
timefold.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<version>1.18.30</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>ch.qos.logback</groupId>
<artifactId>logback-classic</artifactId>
<version>1.4.11</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>
// File: src/main/resources/logback.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<configuration>
<appender name="STDOUT" class="ch.qos.logback.core.ConsoleAppender">
<encoder>
<pattern>%d{
HH:mm:ss.SSS} [%thread] %-5level %logger{
36} - %msg%n</pattern>
</encoder>
</appender>
<logger name="ai.timefold.solver" level="info"/>
<root level="warn">
<appender-ref ref="STDOUT"/>
</root>
</configuration>
// File: src/main/resources/solver-config.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<solver xmlns="https://timefold.ai/xsd/solver" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="https://timefold.ai/xsd/solver https://timefold.ai/xsd/solver/solver.xsd">
<solutionClass>org.example.jobshop.domain.JobShopSchedule</solutionClass>
<entityClass>org.example.jobshop.domain.JobAllocation</entityClass>
<scoreDirectorFactory>
<constraintProviderClass>org.example.jobshop.solver.JobShopConstraintProvider</constraintProviderClass>
</scoreDirectorFactory>
<termination>
<minutesSpentLimit>5</minutesSpentLimit>
</termination>
<constructionHeuristic>
<constructionHeuristicType>FIRST_FIT_DECREASING</constructionHeuristicType>
</constructionHeuristic>
<localSearch>
<unionMoveSelector>
<changeMoveSelector/>
<swapMoveSelector/>
<moveListFactory>
<moveListFactoryClass>org.example.jobshop.solver.JobAllocationMoveFactory</moveListFactoryClass>
</moveListFactory>
</unionMoveSelector>
<acceptor>
<lateAcceptanceSize>400</lateAcceptanceSize>
</acceptor>
<forager>
<acceptedCountLimit>4</acceptedCountLimit>
</forager>
</localSearch>
</solver>
// File: src/main/java/org/example/jobshop/domain/Project.java
package org.example.jobshop.domain;
@lombok.Data
@lombok.NoArgsConstructor
@lombok.AllArgsConstructor
public class Project {
private String id;
private String name;
private LocalDateTime releaseDate;
private LocalDateTime dueDate;
private List<Job> jobs;
}
// File: src/main/java/org/example/jobshop/domain/Job.java
package org.example.jobshop.domain;
@lombok.Data
@lombok.NoArgsConstructor
@lombok.AllArgsConstructor
public class Job {
private String id;
private String name;
private Project project;
private Duration processingTime;
private List<Resource> compatibleResources;
private Job previousJob;
private Job nextJob;
}
// File: src/main/java/org/example/jobshop/domain/Resource.java
package org.example.jobshop.domain;
@lombok.Data
@lombok.NoArgsConstructor
@lombok.AllArgsConstructor
public class Resource {
private String id;
private String name;
private ResourceType type;
private LocalDateTime availableFrom;
private double costPerHour;
}
// File: src/main/java/org/example/jobshop/domain/JobAllocation.java
package org.example.jobshop.domain;
@PlanningEntity
@lombok.Data
@lombok.NoArgsConstructor
@lombok.AllArgsConstructor
public class JobAllocation {
private String id;
private Job job;
@PlanningVariable(valueRangeProvider = "resourceRange")
private Resource resource;
@PlanningVariable(valueRangeProvider = "allocationRange")
private JobAllocation previousAllocation;
@CustomShadowVariable(
variableListenerClass = StartTimeUpdatingVariableListener.class,
sources = {
@PlanningVariableReference(variableName = "previousAllocation"),
@PlanningVariableReference(variableName = "resource")})
private LocalDateTime startTime;
private LocalDateTime endTime;
// ... other methods from previous versions
}
// File: src/main/java/org/example/jobshop/solver/JobShopSolver.java
package org.example.jobshop.solver;
import ai.timefold.solver.core.api.solver.SolverFactory;
import ai.timefold.solver.core.config.solver.SolverConfig;
public class JobShopSolver {
private final SolverFactory<JobShopSchedule> solverFactory;
public JobShopSolver() {
SolverConfig solverConfig = SolverConfig.createFromXmlResource(
"solver-config.xml");
this.solverFactory = SolverFactory.create(solverConfig);
}
public JobShopSchedule solve(JobShopSchedule problem) {
return solverFactory.buildSolver().solve(problem);
}
}
// File: src/main/java/org/example/jobshop/Main.java
package org.example.jobshop;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create sample problem
JobShopSchedule problem = createSampleProblem();
// Create and run solver
JobShopSolver solver = new JobShopSolver();
JobShopSchedule solution = solver.solve(problem);
// Print solution
printSolution(solution);
}
private static JobShopSchedule createSampleProblem() {
// Create resources
List<Resource> resources = new ArrayList<>();
resources.add(new Resource("R1", "Machine 1", ResourceType.MACHINE,
LocalDateTime.now(), 100.0));
resources.add(new Resource("R2", "Machine 2", ResourceType.MACHINE,
LocalDateTime.now(), 150.0));
// Create projects and jobs
List<Project> projects = new ArrayList<>();
List<JobAllocation> allocations = new ArrayList<>();
Project project1 = new Project("P1", "Project 1",
LocalDateTime.now(), LocalDateTime.now().plusDays(5), new ArrayList<>());
// Create jobs for project 1
Job job1 = new Job("J1", "Job 1", project1, Duration.ofHours(4),
resources, null, null);
Job job2 = new Job("J2", "Job 2", project1, Duration.ofHours(3),
resources, job1, null);
job1.setNextJob(job2);
project1.setJobs(Arrays.asList(job1, job2));
projects.add(project1);
// Create allocations
allocations.add(new JobAllocation("A1", job1, null, null, null, null));
allocations.add(new JobAllocation("A2", job2, null, null, null, null));
return new JobShopSchedule(projects, allocations, resources);
}
private static void printSolution(JobShopSchedule solution) {
System.out.println("\nSolution found:");
// Print by resource
for (Resource resource : solution.getResources()) {
System.out.println("\nResource: " + resource.getName());
// Find all allocations for this resource and sort by start time
List<JobAllocation> resourceAllocations = solution.getAllocations().stream()
.filter(a -> a.getResource() == resource)
.sorted(Comparator.comparing(JobAllocation::getStartTime))
.collect(Collectors.toList());
for (JobAllocation allocation : resourceAllocations) {
System.out.printf(" %s: %s -> %s (%s)\n",
allocation.getJob().getName(),
allocation.getStartTime().format(DateTimeFormatter.ISO_LOCAL_TIME),
allocation.getEndTime().format(DateTimeFormatter.ISO_LOCAL_TIME),
allocation.getJob().getProject().getName());
}
}
// Print by project
for (Project project : solution.getProjects()) {
System.out.println("\nProject: " + project.getName());
List<JobAllocation> projectAllocations = solution.getAllocations().stream()
.filter(a -> a.getJob().getProject() == project)
.sorted(Comparator.comparing(JobAllocation::getStartTime))
.collect(Collectors.toList());
for (JobAllocation allocation : projectAllocations) {
System.out.printf(" %s: %s on %s\n",
allocation.getJob().getName(),
allocation.getStartTime().format(DateTimeFormatter.ISO_LOCAL_TIME),
allocation.getResource().getName());
}
}
}
}
// Domain classes
@PlanningEntity
public class Allocation {
private Job job;
@PlanningVariable(valueRangeProviderRefs = "resourceRange")
private Resource resource;
// This is the anchor planning variable
@PlanningVariable(valueRangeProviderRefs = "allocationRange")
private Allocation previousAllocation;
// Shadow variables that get updated automatically
@CustomShadowVariable(
variableListenerClass = StartTimeUpdatingVariableListener.class,
sources = {
@PlanningVariableReference(variableName = "previousAllocation"),
@PlanningVariableReference(variableName = "resource")})
private Integer startTime;
@CustomShadowVariable(
variableListenerClass = EndTimeUpdatingVariableListener.class,
sources = {
@PlanningVariableReference(variableName = "startTime")})
private Integer endTime;
}
// Move implementation for changing resources
public class ResourceChangeMove extends AbstractMove<JobShopSchedule> {
private final Allocation allocation;
private final Resource toResource;
@Override
protected void doMoveOnGenuineVariables(ScoreDirector<JobShopSchedule> scoreDirector) {
// Step 1: Change the resource
scoreDirector.beforeVariableChanged(allocation, "resource");
allocation.setResource(toResource);
scoreDirector.afterVariableChanged(allocation, "resource");
// Step 2: Update the chain
// The allocation becomes the last in the new resource's chain
Allocation lastInResource = findLastAllocationInResource(toResource);
scoreDirector.beforeVariableChanged(allocation, "previousAllocation");
allocation.setPreviousAllocation(lastInResource);
scoreDirector.afterVariableChanged(allocation, "previousAllocation");
}
}
// Move implementation for sequence changes
public class SequenceChangeMove extends AbstractMove<JobShopSchedule> {
private final Allocation allocation;
private final Allocation beforeAllocation;
@Override
protected void doMoveOnGenuineVariables(ScoreDirector<JobShopSchedule> scoreDirector) {
// Step 1: Update the chain links
Allocation oldNextAllocation = allocation.getNextAllocation();
Allocation oldPreviousAllocation = allocation.getPreviousAllocation();
// Connect old previous and next allocations
if (oldNextAllocation != null) {
scoreDirector.beforeVariableChanged(oldNextAllocation, "previousAllocation");
oldNextAllocation.setPreviousAllocation(oldPreviousAllocation);
scoreDirector.afterVariableChanged(oldNextAllocation, "previousAllocation");
}
// Step 2: Insert allocation in new position
Allocation newNextAllocation = beforeAllocation.getNextAllocation();
scoreDirector.beforeVariableChanged(allocation, "previousAllocation");
allocation.setPreviousAllocation(beforeAllocation);
scoreDirector.afterVariableChanged(allocation, "previousAllocation");
if (newNextAllocation != null) {
scoreDirector.beforeVariableChanged(newNextAllocation, "previousAllocation");
newNextAllocation.setPreviousAllocation(allocation);
scoreDirector.afterVariableChanged(newNextAllocation, "previousAllocation");
}
}
}
// Variable Listener for updating start times
public class StartTimeUpdatingVariableListener
implements VariableListener<JobShopSchedule, Allocation> {
@Override
public void afterEntityAdded(ScoreDirector<JobShopSchedule> scoreDirector,
Allocation allocation) {
updateStartTime(scoreDirector, allocation);
}
@Override
public void afterVariableChanged(ScoreDirector<JobShopSchedule> scoreDirector,
Allocation allocation) {
updateStartTime(scoreDirector, allocation);
}
private void updateStartTime(ScoreDirector<JobShopSchedule> scoreDirector,
Allocation allocation) {
Allocation previousAllocation = allocation.getPreviousAllocation();
Integer newStartTime;
if (previousAllocation == null) {
// First in resource - can start at 0
newStartTime = 0;
} else {
// Must wait for previous allocation to finish
newStartTime = previousAllocation.getEndTime();
}
// Consider job dependencies (if this job must wait for other jobs)
for (Job prerequisite : allocation.getJob().getPrerequisites()) {
Allocation prerequisiteAllocation = findAllocationForJob(prerequisite);
if (prerequisiteAllocation != null) {
newStartTime = Math.max(newStartTime,
prerequisiteAllocation.getEndTime());
}
}
scoreDirector.beforeVariableChanged(allocation, "startTime");
allocation.setStartTime(newStartTime);
scoreDirector.afterVariableChanged(allocation, "startTime");
}
}
package org.example.jobshop.solver;
import ai.timefold.solver.core.api.score.director.ScoreDirector;
import ai.timefold.solver.core.impl.phase.custom.CustomPhaseCommand;
import java.util.*;
public class JobShopInitializer implements CustomPhaseCommand<JobShopSchedule> {
@Override
public void changeWorkingSolution(ScoreDirector<JobShopSchedule> scoreDirector) {
JobShopSchedule schedule = scoreDirector.getWorkingSolution();
// Step 1: Sort jobs by priority and dependencies
List<JobAllocation> sortedAllocations = prioritizeAllocations(schedule);
// Step 2: Initialize all allocations to unassigned
for (JobAllocation allocation : schedule.getAllocations()) {
scoreDirector.beforeVariableChanged(allocation, "resource");
allocation.setResource(null);
scoreDirector.afterVariableChanged(allocation, "resource");
scoreDirector.beforeVariableChanged(allocation, "previousAllocation");
allocation.setPreviousAllocation(null);
scoreDirector.afterVariableChanged(allocation, "previousAllocation");
}
// Step 3: Assign jobs considering both resource and sequence constraints
Map<Resource, JobAllocation> lastAllocationByResource = new HashMap<>();
Map<Job, LocalDateTime> jobEndTimes = new HashMap<>();
for (JobAllocation allocation : sortedAllocations) {
// Find best resource and position
ResourceAssignment bestAssignment = findBestAssignment(
allocation,
schedule.getResources(),
lastAllocationByResource,
jobEndTimes,
schedule);
// Apply the assignment
if (bestAssignment != null) {
// Assign resource
scoreDirector.beforeVariableChanged(allocation, "resource");
allocation.setResource(bestAssignment.resource);
scoreDirector.afterVariableChanged(allocation, "resource");
// Assign previous allocation
scoreDirector.beforeVariableChanged(allocation, "previousAllocation");
allocation.setPreviousAllocation(bestAssignment.previousAllocation);
scoreDirector.afterVariableChanged(allocation, "previousAllocation");
// Update tracking maps
lastAllocationByResource.put(bestAssignment.resource, allocation);
jobEndTimes.put(allocation.getJob(), bestAssignment.endTime);
}
}
}
private List<JobAllocation> prioritizeAllocations(JobShopSchedule schedule) {
List<JobAllocation> sortedAllocations = new ArrayList<>(schedule.getAllocations());
// Create job dependency graph
Map<Job, Set<Job>> dependencies = new HashMap<>();
Map<Job, Integer> inDegree = new HashMap<>();
for (Project project : schedule.getProjects()) {
for (Job job : project.getJobs()) {
dependencies.putIfAbsent(job, new HashSet<>());
inDegree.putIfAbsent(job, 0);
if (job.getNextJob() != null) {
dependencies.get(job).add(job.getNextJob());
inDegree.merge(job.getNextJob(), 1, Integer::sum);
}
}
}
// Topological sort with additional priority factors
sortedAllocations.sort((a1, a2) -> {
Job job1 = a1.getJob();
Job job2 = a2.getJob();
// First priority: dependency order
int dep1 = inDegree.getOrDefault(job1, 0);
int dep2 = inDegree.getOrDefault(job2, 0);
if (dep1 != dep2) return dep1 - dep2;
// Second priority: project due date
int dueDate = job1.getProject().getDueDate()
.compareTo(job2.getProject().getDueDate());
if (dueDate != 0) return dueDate;
// Third priority: processing time (longer first)
return job2.getProcessingTime().compareTo(job1.getProcessingTime());
});
return sortedAllocations;
}
@lombok.Data
@lombok.AllArgsConstructor
private static class ResourceAssignment {
private Resource resource;
private JobAllocation previousAllocation;
private LocalDateTime startTime;
private LocalDateTime endTime;
private double score;
}
private ResourceAssignment findBestAssignment(
JobAllocation allocation,
List<Resource> resources,
Map<Resource, JobAllocation> lastAllocationByResource,
Map<Job, LocalDateTime> jobEndTimes,
JobShopSchedule schedule) {
ResourceAssignment bestAssignment = null;
double bestScore = Double.NEGATIVE_INFINITY;
Job job = allocation.getJob();
// Get earliest start time based on job dependencies
LocalDateTime earliestStart = job.getPreviousJob() != null ?
jobEndTimes.getOrDefault(job.getPreviousJob(), LocalDateTime.MIN) :
LocalDateTime.now();
// Try each compatible resource
for (Resource resource : job.getCompatibleResources()) {
JobAllocation lastAllocation = lastAllocationByResource.get(resource);
// Calculate possible start time
LocalDateTime startTime = calculateStartTime(
earliestStart,
lastAllocation,
resource);
LocalDateTime endTime = startTime.plus(job.getProcessingTime());
// Calculate assignment score
double score = calculateAssignmentScore(
resource,
startTime,
endTime,
job,
schedule);
if (score > bestScore) {
bestScore = score;
bestAssignment = new ResourceAssignment(
resource, lastAllocation, startTime, endTime, score);
}
}
return bestAssignment;
}
private LocalDateTime calculateStartTime(
LocalDateTime earliestStart,
JobAllocation lastAllocation,
Resource resource) {
LocalDateTime resourceAvailable = lastAllocation != null ?
lastAllocation.getEndTime() :
resource.getAvailableFrom();
return earliestStart.isAfter(resourceAvailable) ?
earliestStart : resourceAvailable;
}
private double calculateAssignmentScore(
Resource resource,
LocalDateTime startTime,
LocalDateTime endTime,
Job job,
JobShopSchedule schedule) {
double score = 0.0;
// Factor 1: Resource utilization balance
score -= getResourceUtilization(resource, schedule) * 2;
// Factor 2: Start time (earlier is better)
score -= startTime.until(job.getProject().getDueDate(), ChronoUnit.HOURS);
// Factor 3: Resource cost
score -= resource.getCostPerHour() *
job.getProcessingTime().toHours();
// Factor 4: Project critical path consideration
if (isOnCriticalPath(job)) {
score += 1000; // Prioritize critical path jobs
}
return score;
}
private double getResourceUtilization(Resource resource, JobShopSchedule schedule) {
return schedule.getAllocations().stream()
.filter(a -> a.getResource() == resource)
.mapToDouble(a -> a.getJob().getProcessingTime().toHours())
.sum();
}
private boolean isOnCriticalPath(Job job) {
// Simple critical path detection
Job current = job;
while (current.getNextJob() != null) {
current = current.getNextJob();
}
return current.getProject().getDueDate()
.minusHours(calculatePathDuration(job))
.isBefore(LocalDateTime.now());
}
private long calculatePathDuration(Job startJob) {
long duration = 0;
Job current = startJob;
while (current != null) {
duration += current.getProcessingTime().toHours();
current = current.getNextJob();
}
return duration;
}
}

