【二叉树进阶题目1】(算法题详细简介)
前言
下面是本文讲解的题目链接,大家可以先自己尝试一下,再看下文题解~
1. 用非递归的方法实现中序遍历(力扣94)
1.1 题目链接
相信大家已经掌握了用递归方法实现中序遍历,那么如何使用非递归的方法实现呢?
下面是题目链接,大家一起动手尝试一下吧!
用非递归的方法实现中序遍历
1.2 示例分析

现在先梳理一下中序遍历的实现思路
- 当root!=null时,root=root.left 直至找到左子树为空

while(root!=null){
root=root.left;
}
- 此时root==null, 找到 root 的根节点
- 利用栈存储遍历的根节点,如果root 不为空,stack.add
- 如果root 为空,stack.pop 找到最后储存的根节点
Stack<TreeNode> stack=new Stack<>();
while(root!=null){
stack.add(root);
root=root.left;
}
root=stack.pop();
- 由于该题目返回值为List 类型,所以创建一个List 存储中序遍历的树的值
- 当root 遍历到左子树为空时,List.add(root.val)
- 然后返回根节点,存储根节点的值
- 最后接着遍历右子树
while(root!=null){
stack.add(root);
root=root.left;
}
root=stack.pop();
list.add(root.val);
root=root.right;
- 当栈不为空时循环遍历结束
大家可以画一个栈尝试一下循环结束的条件,得出结论是当栈不为空时循环遍历结束。
但是,在刚开始创建完栈时,遍历还没开始,此时应该如何进入遍历循环呢?
只需要将循环条件改为 root不为空 或者 栈不为空 就可以了。
1.3 代码实现
下面是该题的完整代码实现
class Solution {
public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> list=new ArrayList<>();
Stack<TreeNode> stack=new Stack<>();
while(root!=null||!stack.isEmpty()){
while(root!=null){
stack.add(root);
root=root.left;
}
root=stack.pop();
list.add(root.val);
root=root.right;
}
return list;
}
}
2. 用非递归的方法实现先序遍历(力扣144)
2.1 题目链接
下面是题目链接,大家一起动手尝试一下吧!
非递归的方法实现先序遍历
2.2 示例分析
先序遍历的实现方法与中序遍历相似,如果已经掌握上述中序遍历,先序肯定也就不在话下了,
所以本题就不在赘述了,直接是代码实现。
2.3 代码实现
class Solution {
public List<Integer> preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> list=new ArrayList<>();
Stack<TreeNode> stack=new Stack<>();
while(root!=null||!stack.isEmpty()){
while(root!=null){
stack.add(root);
list.add(root.val);
root=root.left;
}
root=stack.pop();
root=root.right;
}
return list;
}
}
3. 从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树(力扣106)
3.1 题目链接
3.2 示例分析
3.2.1 图示讲解
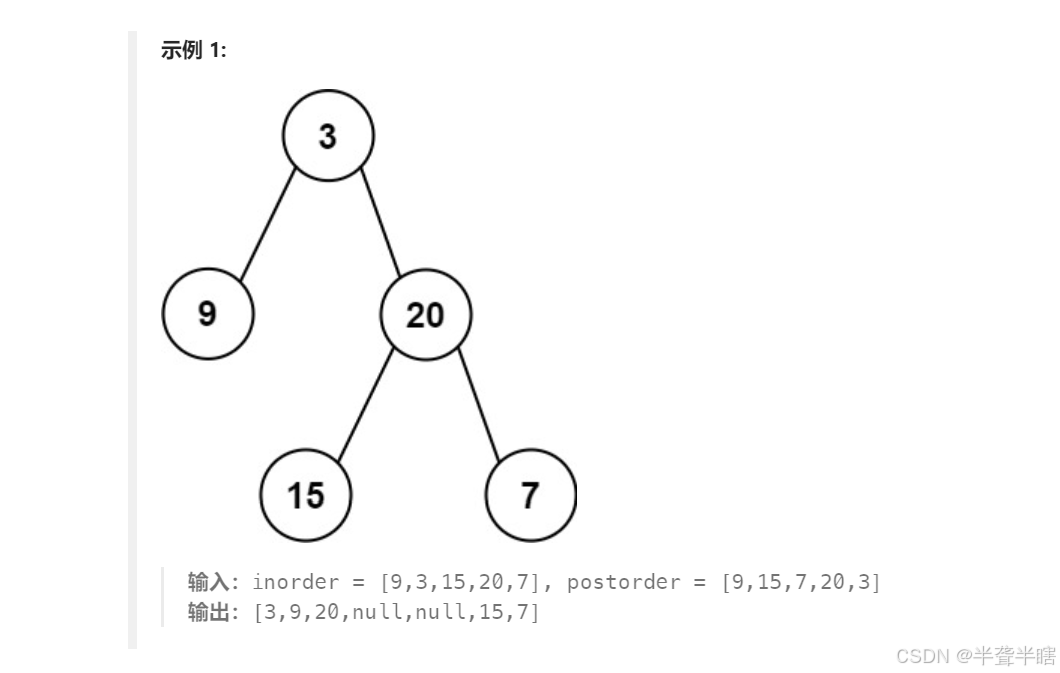
已知中序遍历的顺序为 左-根-右,后序遍历 的遍历顺序为 左-右-根 ,首先我们先模拟一下二叉树的构造
- 第一次分树
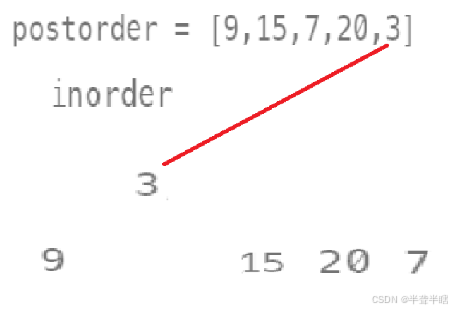
- 第二次分树

完整的二叉树为

了解了大概二叉树的构建过程,下面是代码部分的构建二叉树
根据上述图示可知 ,在构建二叉树的过程中
- 首先根据后序遍历找到根节点
- 然后在中序遍历中找到根节点
- 根节点左侧为左子树,右侧为右子树
3.2.2 代码讲解
现在就利用代码一步步实现上述思路
- 首先根据后序遍历找到根节点
public int i=1;
public TreeNode buildChlid(int left,int right,int[] inorder, int[] postorder) {
TreeNode root=new TreeNode(postorder[postorder.length-i]);
//确保每次递归得到的根节点不同
}
- 然后在中序遍历中找到根节点
public int i=1;
public int findroot(int[] inorder,int key){
for (int j = 0; j < inorder.length; j++) {
if(inorder[j]==key) return j;
}
return -1;
}
public TreeNode buildChlid(int left,int right,int[] inorder, int[] postorder) {
TreeNode root=new TreeNode(postorder[postorder.length-i]);
int center=findroot(inorder,root.val);
}
- 根节点左侧为左子树,右侧为右子树
public TreeNode buildChlid(int left,int right,int[] inorder, int[] postorder) {
if(left>right) return null;
if(i>inorder.length) return null;
TreeNode root=new TreeNode(postorder[postorder.length-i]);
i++;
int center=findroot(inorder,root.val);
root.right=buildChlid(center+1,right,inorder,postorder);
root.left=buildChlid(left,center-1,inorder,postorder);
//这里的left=0, right=inorder.length-1
return root;
}
3.2 代码实现
完整的代码如下
class Solution {
public int i=1;
public int findroot(int[] inorder,int key){
for (int j = 0; j < inorder.length; j++) {
if(inorder[j]==key) return j;
}
return -1;
}
public TreeNode buildChlid(int left,int right,int[] inorder, int[] postorder) {
if(left>right) return null;
if(i>inorder.length) return null;
TreeNode root=new TreeNode(postorder[postorder.length-i]);
i++;
int center=findroot(inorder,root.val);
root.right=buildChlid(center+1,right,inorder,postorder);
root.left=buildChlid(left,center-1,inorder,postorder);
return root;
}
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] inorder, int[] postorder) {
int left=0;
int right=inorder.length-1;
TreeNode root=buildChlid(left,right,inorder,postorder);
return root;
}
}
4. 从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树(力扣105)
4.1 题目链接
下面是题目链接,大家一起动手尝试一下吧!
从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树
4.2 示例分析
由于该题与 从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树(力扣106) 方法相似
所以本题就不在赘述了,直接是代码实现。
4.3 代码实现
class Solution {
public int i=0;
public int findroot(int[] inorder,int key){
for (int j = 0; j < inorder.length; j++) {
if(inorder[j]==key) return j;
}
return -1;
}
public TreeNode buildChlid(int left,int right,int[] preorder, int[] inorder) {
if(left>right) return null;
if(i>inorder.length) return null;
TreeNode root=new TreeNode(preorder[i]);
i++;
int center=findroot(inorder,root.val);
root.left=buildChlid(left,center-1,preorder,inorder);
root.right=buildChlid(center+1,right,preorder,inorder);
return root;
}
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] preorder, int[] inorder) {
int left=0;
int right=inorder.length-1;
TreeNode root=buildChlid(left,right,preorder,inorder);
return root;
}
}
该文章到此结束,希望对你有所帮助~