目录
扫描二维码关注公众号,回复:
17562772 查看本文章


5.非递归快速排序(Non-Recursive Quick Sort)
10.非递归归并排序(Non-Recursive Merge Sort)
引言
排序算法是计算机科学的基石之一。本文将系统讲解7种经典排序算法,通过:
✅ 分步图解算法流程
✅ 语言代码实现
✅ 实测性能对比
帮助你彻底掌握排序算法的核心原理与应用场景。
1. 希尔排序(Shell Sort)
原理:
插入排序的改进版,通过将数组按增量序列分组(如间隔 gap = length/2),对每组进行插入排序,逐步缩小增量直至为1,最终进行一次全数组插入排序。
关键点:
-
增量序列的选择影响效率(常用
gap = gap/3 + 1)。 -
时间复杂度:平均O(n log n) ~ O(n²)。
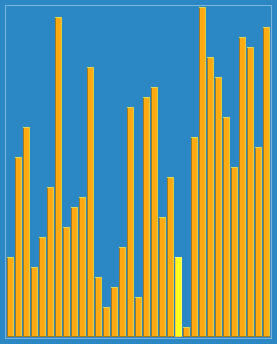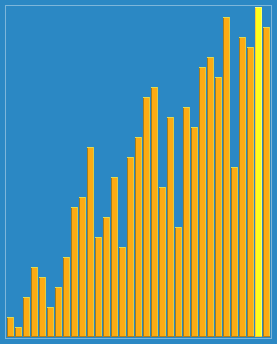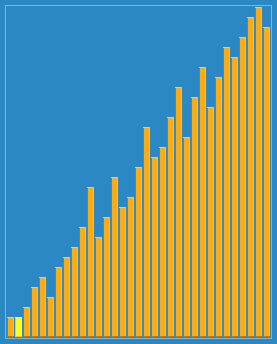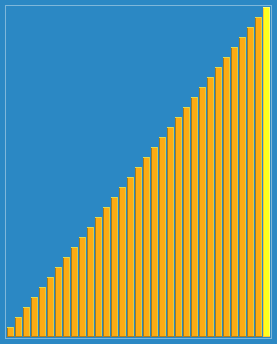
代码:
void ShellSort(int* a, int n)//希尔排序
{
int gap = 10;
while (gap > 1)
{
gap /= 2;
for (int j = 0;j < gap;j++)
{
for (int i = j;i < n - gap;i = i + gap)
{
int end = i;
int tmp = a[end + gap];
while (end >= 0)
{
if (tmp <a[end])
{
a[end + gap] = a[end];
end -= gap;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
a[end + gap] = tmp;
}
}
}
}2. 堆排序(Heap Sort)
原理:
-
建堆:将数组视为完全二叉树,调整成最大堆(父节点值 ≥ 子节点)。
-
排序:交换堆顶元素(最大值)与末尾元素,缩小堆范围并重新调整堆,重复直至有序。
关键点: -
时间复杂度:O(n log n),且是原地排序。
-
不稳定排序。
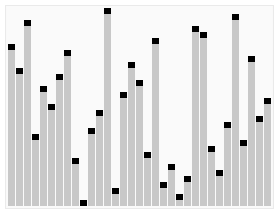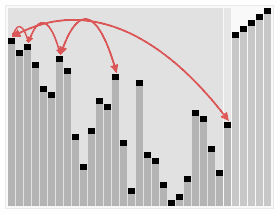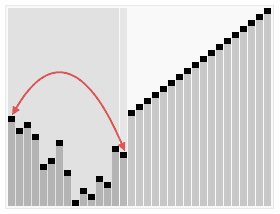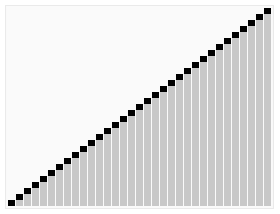
实现该代码需要我们把堆建立起来
堆代码:
//这是stack.h的代码
#pragma once
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<stdbool.h>
#include<assert.h>
typedef int STDataType;
typedef struct Stack
{
STDataType * a;
int capacity;
int top;
}ST;
void STInit(ST*ps);
void STPush(ST* ps,STDataType x);
void STPop(ST* ps);
int STSize(ST* ps);
bool STEmpty(ST* ps);
void STDestroy(ST* ps);
STDataType STTop(ST* ps);
//这是stack.c的代码
#include"stack.h"
void STInit(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
ps->a = malloc(sizeof(STDataType) * 4);
if (ps->a == NULL)
{
perror("malloc fail");
return;
}
ps-> capacity = 4;
ps->top = 0;
}
void STPush(ST* ps, STDataType x)
{
assert(ps);
if (ps->top == ps->capacity)
{
STDataType* tmp = (STDataType*)realloc(ps->a, sizeof(STDataType) * ps->capacity * 2);//新建一个变量加进去,需要我进行空间创建,然后扩容
if (tmp == NULL)
{
perror("realloc fail");
return;
}
ps->a = tmp;
ps->capacity *= 2;
}
ps->a[ps->top] = x;
ps->top++;
}
void STDestroy(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
free(ps->a);
ps->a = NULL;
ps->top = 0;
ps->capacity = 0;
}
void STPop(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(!STEmpty(ps));//等于空就报错
ps->top--;
}
int STSize(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->top;
}
bool STEmpty(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->top == 0;
}
STDataType STTop(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(!STEmpty(ps));//空的话咱们就不能取值了
return ps->a[ps->top - 1];//是空的话就越界了,哥们
}//访问栈顶元素堆排序代码:
void HeapSort(int* a, int n)//栈排序
{
for (int i = (n - 1 - 1) / 2;i >= 0;--i)
{
AdjustDown(a, n, i);
}
int end = n - 1;
while (end > 0)
{
Swap(&a[end], &a[0]);
AdjustDown(a, end, 0);
--end;
}
}3. 快速排序(Quick Sort)
原理:
-
分治策略:选基准值(pivot),将数组分为“小于pivot”和“大于pivot”两部分。
-
递归排序:对左右子数组递归执行快排。
关键点: -
时间复杂度:平均O(n log n),最坏O(n²)(可通过随机选pivot优化)。
-
不稳定排序。
代码:
(1)PartSort1(快排原型)
int PartSort1