汉诺塔
汉诺塔(Towers of Hanoi)是法国人M.Claus(Lucas)于1883年从泰国带至法国的,河内为越战时北越的首都,即现在的胡志明市;1883年法国数学家Edouard Lucas曾提及这个故事,据说创世纪时Benares有一座波罗教塔,是由三支钻石棒(Pag)所支撑,开始时神在第一根棒上放置64
个由上至下依由小至大排列的金盘(Disc),并命令僧侣将所有的金盘从第一根石棒移至第三根石棒,且搬运过程中遵守大盘子在小盘子之下的原则,若每日仅搬一个盘子,则当盘子全数搬运完毕之时,此塔将毁损,而也就是世界末日来临之时。
解法
如果柱子标为ABC,要由A搬至C,在只有一个盘子时,就将它直接搬至C,当有两个盘子,就将B当作辅助柱。如果盘数超过2个,将第三个以下的盘子遮起来,就很简单了,每次处理两个盘子,也就是:A->B、A ->C、B->C这三个步骤,而被遮住的部份,其实就是进入程式的递回处理。
事实上,若有n个盘子,则移动完毕所需之次数为2^n - 1,所以当盘数为64时,则所需次数为:
2的64次方- 1 = 18446744073709551615为5.05390248594782e+16年,也就是约5000世纪,如果对这数字没什么概念,就假设每秒钟搬一个盘子好了,也要约5850亿年左右。
#include <stdio.h>
void hanoi(int n, char A, char B, char C) {
if(n == 1) {//当只有一块时,A=>C
printf("Move sheet %d from %c to %c\n", n, A, C);
}
else {
hanoi(n-1, A, C, B);//将n-1块全部从A搬到B。
printf("Move sheet %d from %c to %c\n", n, A, C);//剩下的一块搬到C。
hanoi(n-1, B, A, C);//再将这n-1块从B,搬到C。
}
}
int main() {
int n;
printf("请输入盘数:");
scanf("%d", &n);
hanoi(n, 'A', 'B', 'C');
return 0;
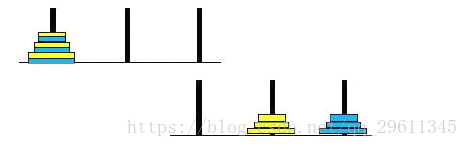
}双色汉诺塔【分离型】
参考自博客
双色河内塔是由之前所介绍过的河内塔规则衍生而来,双色河内塔的目的是将下图左上的圆环位置经移动成为右下的圆环位置:具体见引用博客。清楚了题目后,再开始看代码。
#include <stdio.h>
void hanoi(int disks, char source, char temp, char target) {
if (disks == 1) {//注意,这里是两块不同颜色,相同大小的块,所以需要移动两次,才算一个大小的块
printf("move disk from %c to %c\n", source, target);
printf("move disk from %c to %c\n", source, target);
} else {
hanoi(disks-1, source, target, temp);
hanoi(1, source, temp, target);
hanoi(disks-1, temp, source, target);
}
}
void hanoi2colors(int disks) {
char source = 'A';
char temp = 'B';
char target = 'C';
int i;
for(i = disks / 2; i > 1; i--) {
hanoi(i-1, source, temp, target);//n-1块移到A=》C
printf("move disk from %c to %c\n", source, temp);//A=>B两次
printf("move disk from %c to %c\n", source, temp);
hanoi(i-1, target, temp, source);//n-1块从C移回来,C=》A
printf("move disk from %c to %c\n", temp, target);//最重要的一步来了,所有的步骤都是为了这一步,将最大的两块分离~
}
printf("move disk from %c to %c\n", source, temp);
printf("move disk from %c to %c\n", source, target);
}
int main() {
int n;
printf("请输入盘数:");
scanf("%d", &n);
hanoi2colors(n);
return 0;
}
三色河内塔
#include <stdio.h>
void hanoi(int disks, char source, char temp, char target) {
if (disks == 1) {
printf("move disk from %c to %c\n", source, target);
printf("move disk from %c to %c\n", source, target);
printf("move disk from %c to %c\n", source, target);
} else {
hanoi(disks-1, source, target, temp);
hanoi(1, source, temp, target);
hanoi(disks-1, temp, source, target);
}
}
void hanoi3colors(int disks) {
char source = 'A';
char temp = 'B';
char target = 'C';
int i;
if(disks == 3) {
printf("move disk from %c to %c\n", source, temp);
printf("move disk from %c to %c\n", source, temp);
printf("move disk from %c to %c\n", source, target);
printf("move disk from %c to %c\n", temp, target);
printf("move disk from %c to %c\n", temp, source);
printf("move disk from %c to %c\n", target, temp);;
}
else {
hanoi(disks/3-1, source, temp, target);
printf("move disk from %c to %c\n", source, temp);
printf("move disk from %c to %c\n", source, temp);
printf("move disk from %c to %c\n", source, temp);
hanoi(disks/3-1, target, temp, source);
printf("move disk from %c to %c\n", temp, target);
printf("move disk from %c to %c\n", temp, target);
printf("move disk from %c to %c\n", temp, target);
hanoi(disks/3-1, source, target, temp);
printf("move disk from %c to %c\n", target, source);
printf("move disk from %c to %c\n", target, source);
hanoi(disks/3-1, temp, source, target);
printf("move disk from %c to %c\n", source, temp);
for (i = disks / 3 - 1; i > 0; i--) {
if (i>1) {
hanoi(i-1, target, source, temp);
}
printf("move disk from %c to %c\n",target, source);
printf("move disk from %c to %c\n",target, source);
if (i>1) {
hanoi(i-1, temp, source, target);
}
printf("move disk from %c to %c\n", source, temp);
}
}
}
int main() {
int n;
printf("请输入盘数:");
scanf("%d", &n);
hanoi3colors(n);
return 0;
}