题目描述
给定一个单链表,其中的元素按升序排序,将其转换为高度平衡的二叉搜索树。
本题中,一个高度平衡二叉树是指一个二叉树每个节点 的左右两个子树的高度差的绝对值不超过 1。
示例:
给定的有序链表: [-10, -3, 0, 5, 9],
一个可能的答案是:[0, -3, 9, -10, null, 5], 它可以表示下面这个高度平衡二叉搜索树:
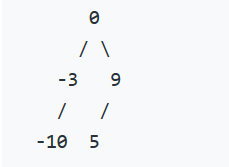
方法思路
Approach 1: Recursion
class Solution {
//Runtime: 1 ms, faster than 99.17%
//Memory Usage: 39 MB, less than 96.90%
private ListNode findMiddleElement(ListNode head) {
// The pointer used to disconnect the left half from the mid node.
ListNode prevPtr = null;
ListNode slowPtr = head;
ListNode fastPtr = head;
// Iterate until fastPr doesn't reach the end of the linked list.
while (fastPtr != null && fastPtr.next != null) {
prevPtr = slowPtr;
slowPtr = slowPtr.next;
fastPtr = fastPtr.next.next;
}
// Handling the case when slowPtr was equal to head.
if (prevPtr != null) {
prevPtr.next = null;
}
return slowPtr;
}
public TreeNode sortedListToBST(ListNode head) {
// If the head doesn't exist, then the linked list is empty
if (head == null) {
return null;
}
// Find the middle element for the list.
ListNode mid = this.findMiddleElement(head);
// The mid becomes the root of the BST.
TreeNode node = new TreeNode(mid.val);
// Base case when there is just one element in the linked list
if (head == mid) {
return node;
}
// Recursively form balanced BSTs using the left and right halves of the original list.
node.left = this.sortedListToBST(head);
node.right = this.sortedListToBST(mid.next);
return node;
}
}
Time Complexity: O(NlogN)
Space Complexity: O(logN)
Approach 2: Recursion + Conversion to Array
This approach is a classic example of the time-space tradeoff.
Find the middle element as (left + right) / 2. Let’s call this element as mid. This is a O(1) time operation and is the only major improvement over the previous algorithm.
class Solution {
//Runtime: 1 ms, faster than 99.17%
private List<Integer> values;
public Solution() {
this.values = new ArrayList<Integer>();
}
private void mapListToValues(ListNode head) {
while (head != null) {
this.values.add(head.val);
head = head.next;
}
}
private TreeNode convertListToBST(int left, int right) {
// Invalid case
if (left > right) {
return null;
}
// Middle element forms the root.
int mid = (left + right) / 2;
TreeNode node = new TreeNode(this.values.get(mid));
// Base case for when there is only one element left in the array
if (left == right) {
return node;
}
// Recursively form BST on the two halves
node.left = convertListToBST(left, mid - 1);
node.right = convertListToBST(mid + 1, right);
return node;
}
public TreeNode sortedListToBST(ListNode head) {
// Form an array out of the given linked list and then
// use the array to form the BST.
this.mapListToValues(head);
// Convert the array to
return convertListToBST(0, this.values.size() - 1);
}
}
Approach 3: Inorder Simulation
class Solution {
//Runtime: 0 ms, faster than 100.00%
private ListNode head;
private int findSize(ListNode head) {
ListNode ptr = head;
int c = 0;
while (ptr != null) {
ptr = ptr.next;
c += 1;
}
return c;
}
private TreeNode convertListToBST(int l, int r) {
// Invalid case
if (l > r) {
return null;
}
int mid = (l + r) / 2;
// First step of simulated inorder traversal. Recursively form
// the left half
TreeNode left = this.convertListToBST(l, mid - 1);
// Once left half is traversed, process the current node
TreeNode node = new TreeNode(this.head.val);
node.left = left;
// Maintain the invariance mentioned in the algorithm
this.head = this.head.next;
// Recurse on the right hand side and form BST out of them
node.right = this.convertListToBST(mid + 1, r);
return node;
}
public TreeNode sortedListToBST(ListNode head) {
// Get the size of the linked list first
int size = this.findSize(head);
this.head = head;
// Form the BST now that we know the size
return convertListToBST(0, size - 1);
}
}