NIO基本类
在开始之前,需要先对Java NIO的下面个类有所了解
- Seletor
- SelectableChannel
- SelectionKey
可以看下JAVA NIO的基本类
服务器启动注册流程
接前面的服务器启动注册流程,
public abstract class AbstractChannel extends DefaultAttributeMap implements Channel {
public final void register(EventLoop eventLoop, final ChannelPromise promise) {
..
AbstractChannel.this.eventLoop = eventLoop;
if (eventLoop.inEventLoop()) {
register0(promise);
} else {
try {
//注册的时候会往taskQueue里放入一个注册的线程
eventLoop.execute(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
register0(promise);
}
});
} catch (Throwable t) {
...
}
}
}
private void register0(ChannelPromise promise) {
doRegister();
}
}
注册就是把ServerSocketChannel注册到selector里
//为什么这里是0而是SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT?
//在AbstractNioChannel.doBeginRead里会改,这个bind里再分析
protected void doRegister() throws Exception {
selectionKey = javaChannel().register(eventLoop().selector, 0, this);
}
前面分析过注册其实是加入到NioEventLoop的taskQueue里的。
看NioEventLoop里run()是怎么样执行上面的这个task的注册。
NioEventLoop 的 run 方法,其实执行2个方法
-
processSelectedKeys() 执行I/O 任务,即 selectionKey 中 ready 的事件,如 accept、connect、read、write 等
-
runAllTasks() 执行非 IO 任务,添加到 taskQueue 中的任务,如 register0、bind0 等任务
请看下面的代码里注释说明
protected void run() {
for (;;) {
try {
switch
//计算出每次循环要干什么事
(selectStrategy.calculateStrategy(selectNowSupplier, hasTasks())) {
case SelectStrategy.CONTINUE:
continue;
//处理I/O操作
case SelectStrategy.SELECT:
select(wakenUp.getAndSet(false));
if (wakenUp.get()) {
selector.wakeup();
}
default:
// fallthrough
}
cancelledKeys = 0;
needsToSelectAgain = false;
//一次处理包括了processSelectedKeys()+runAllTasks() ioRatio是指processSelectedKeys()即处理IO事件的占据的比例, 默认是50,
final int ioRatio = this.ioRatio;
//如果是100,那就是处理完所有的I/O 再处理完所有的非I/O
if (ioRatio == 100) {
try {
processSelectedKeys();
} finally {
// Ensure we always run tasks.
runAllTasks();
}
} else {
//如果不是100,那就是I/O处理了时间为t1,非I/O处理的时间为t1*(100 - ioRatio) / ioRatio,
//当然默认情况下I/O处理了时间为t1,则非I/O处理的时间也只能为t1
final long ioStartTime = System.nanoTime();
try {
processSelectedKeys();
} finally {
// Ensure we always run tasks.
final long ioTime = System.nanoTime() - ioStartTime;
runAllTasks(ioTime * (100 - ioRatio) / ioRatio);
}
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
handleLoopException(t);
}
// Always handle shutdown even if the loop processing threw an exception.
try {
if (isShuttingDown()) {
closeAll();
if (confirmShutdown()) {
return;
}
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
handleLoopException(t);
}
}
}
分析这句
selectStrategy.calculateStrategy(selectNowSupplier, hasTasks())

selectStrategy是DefaultSelectStrategy
final class DefaultSelectStrategy implements SelectStrategy {
static final SelectStrategy INSTANCE = new DefaultSelectStrategy();
private DefaultSelectStrategy() { }
//hasTasks为false,那表示taskQueue里没任务,即没非IO任务,那就执行IO任务.
//那为什么hasTasks为true要selectSupplier.get()?这个在后面会解答
public int calculateStrategy(IntSupplier selectSupplier, boolean hasTasks) throws Exception {
return hasTasks ? selectSupplier.get() : SelectStrategy.SELECT;
}
DefaultSelectStrategy的定义如下
private final IntSupplier selectNowSupplier = new IntSupplier() {
@Override
public int get() throws Exception {
return selectNow();
}
};
int selectNow() throws IOException {
try {
//这方法不会阻塞会立即返回
//返回的值是指有多少个channel ready for handle
return selector.selectNow();
} finally {
// restore wakup state if needed
if (wakenUp.get()) {
selector.wakeup();
}
}
}
合起来的逻辑就是先看下 taskQueue有没任务,有的话就去查下selector里的有没可操作的集合。由于最开始addTask()加入了server channel 的注册,所以hasTasks()为true. 而selector里并没有channel注册,所以selector.selectNow()返回是0。这样的话,就会直接走到
runAllTasks(ioTime * (100 - ioRatio) / ioRatio);
register 属于非I/O的处理,也就是会在runAllTasks里处理。
请看下面runAllTasks()的注释
//取消息然后再`safeExecute(task)`直接运行。运行完channel就注册到了selector上了。
protected boolean runAllTasks(long timeoutNanos) {
fetchFromScheduledTaskQueue();
Runnable task = pollTask();
if (task == null) {
afterRunningAllTasks();
return false;
}
final long deadline = ScheduledFutureTask.nanoTime() + timeoutNanos;
long runTasks = 0;
long lastExecutionTime;
for (;;) {
//跟进去就是task.run(),注意不是start()
safeExecute(task);
...
}
afterRunningAllTasks();
this.lastExecutionTime = lastExecutionTime;
return true;
}
runAllTasks执行完后,ServerSocketChannel就注册到selector里了。
前面说过runAllTasks()是处理非I/O任务,那接下来就是processSelectedKeys()处理I/O逻辑的如下代码
private void processSelectedKeys() {
//debug 发现selectedKeys非空,那这个是怎么来的?
if (selectedKeys != null) {
processSelectedKeysOptimized(selectedKeys.flip());
} else {
processSelectedKeysPlain(selector.selectedKeys());
}
}
第一个疑问就是selectedKeys非空,这个是哪里赋值进去的?
在获取JDK的Selector的时候,用selectedKeys 替换并引用了SelectorImpl里定义的selectedKeys和publicSelectedKeys, 如果看过
JAVA NIO的基本类里的Selector,就知道Selector维护了3种set,其中的一种就是selectedKeys,在执行了select()或selectNow()或select(long)的时候,会把可以操作的注册凭证(SelectionKey)集合放到selectedKeys这个字段里。
替换的代码如下
private Selector openSelector() {
final Selector selector;
try {
selector = provider.openSelector();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new ChannelException("failed to open a new selector", e);
}
if (DISABLE_KEYSET_OPTIMIZATION) {
return selector;
}
final SelectedSelectionKeySet selectedKeySet = new SelectedSelectionKeySet();
Object maybeSelectorImplClass = AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction<Object>() {
@Override
public Object run() {
try {
return Class.forName(
"sun.nio.ch.SelectorImpl",
false,
PlatformDependent.getSystemClassLoader());
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
return e;
} catch (SecurityException e) {
return e;
}
}
});
if (!(maybeSelectorImplClass instanceof Class) ||
// ensure the current selector implementation is what we can instrument.
!((Class<?>) maybeSelectorImplClass).isAssignableFrom(selector.getClass())) {
if (maybeSelectorImplClass instanceof Exception) {
...
}
return selector;
}
final Class<?> selectorImplClass = (Class<?>) maybeSelectorImplClass;
Object maybeException = AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction<Object>() {
@Override
public Object run() {
try {
//要替换的字段为selectedKeys
Field selectedKeysField = selectorImplClass.getDeclaredField("selectedKeys");
//要替换的字段为publicSelectedKeys
Field publicSelectedKeysField = selectorImplClass.getDeclaredField("publicSelectedKeys");
selectedKeysField.setAccessible(true);
publicSelectedKeysField.setAccessible(true);
//执行替换 selectedKeysField.set(selector, selectedKeySet);
//执行替换 publicSelectedKeysField.set(selector, selectedKeySet);
return null;
} catch (NoSuchFieldException e) {
...
}
}
});
if (maybeException instanceof Exception) {
...
} else {
selectedKeys = selectedKeySet;
logger.trace("instrumented a special java.util.Set into: {}", selector);
}
return selector;
}
public abstract class SelectorImpl extends AbstractSelector {
protected Set<SelectionKey> selectedKeys = new HashSet();
private Set<SelectionKey> publicSelectedKeys;
}
这也解释前面的疑问为什么hasTasks=true的时候,为啥不直接给个固定的值,例如hasTasks ? 0 : SelectStrategy.SELECT;,而要去selectSupplier.get()下。
因为selectSupplier.get()会把NioEventLoop.selectedKeys这个指向了SelectorImpl.selectedKeys。
原来的selectedKeys是hashset,而替换后的是下面的类,也继承了AbstractSet,所以可以直接替换。只是引用就好了,为什么还要替换?为什么搞2个数组keysA,keysA?为啥还有flip()暂时没搞明白
这个类还是挺简单的,重写了add方法
final class SelectedSelectionKeySet extends AbstractSet<SelectionKey> {
private SelectionKey[] keysA;
private int keysASize;
private SelectionKey[] keysB;
private int keysBSize;
private boolean isA = true;
SelectedSelectionKeySet() {
keysA = new SelectionKey[1024];
keysB = keysA.clone();
}
@Override
public boolean add(SelectionKey o) {
if (o == null) {
return false;
}
if (isA) {
int size = keysASize;
keysA[size ++] = o;
keysASize = size;
if (size == keysA.length) {
doubleCapacityA();
}
} else {
int size = keysBSize;
keysB[size ++] = o;
keysBSize = size;
if (size == keysB.length) {
doubleCapacityB();
}
}
return true;
}
private void doubleCapacityA() {
SelectionKey[] newKeysA = new SelectionKey[keysA.length << 1];
System.arraycopy(keysA, 0, newKeysA, 0, keysASize);
keysA = newKeysA;
}
private void doubleCapacityB() {
SelectionKey[] newKeysB = new SelectionKey[keysB.length << 1];
System.arraycopy(keysB, 0, newKeysB, 0, keysBSize);
keysB = newKeysB;
}
SelectionKey[] flip() {
if (isA) {
isA = false;
keysA[keysASize] = null;
keysBSize = 0;
return keysA;
} else {
isA = true;
keysB[keysBSize] = null;
keysASize = 0;
return keysB;
}
}
@Override
public int size() {
if (isA) {
return keysASize;
} else {
return keysBSize;
}
}
}
public int calculateStrategy(IntSupplier selectSupplier, boolean hasTasks) throws Exception {
return hasTasks ? selectSupplier.get() : SelectStrategy.SELECT;
}
知道了为什么selectedKeys非空,并且哪里来后。那代码就会进入processSelectedKeysOptimized(selectedKeys.flip());
private void processSelectedKeys() {
if (selectedKeys != null) {
processSelectedKeysOptimized(selectedKeys.flip());
} else {
processSelectedKeysPlain(selector.selectedKeys());
}
}
分析processSelectedKeysOptimized
private void processSelectedKeysOptimized(SelectionKey[] selectedKeys) {
//死循环,当没任务的时候跳出
for (int i = 0;; i ++) {
final SelectionKey k = selectedKeys[i];
if (k == null) {
break;
}
final Object a = k.attachment();
if (a instanceof AbstractNioChannel) {
processSelectedKey(k, (AbstractNioChannel) a);
} else {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
NioTask<SelectableChannel> task = (NioTask<SelectableChannel>) a;
processSelectedKey(k, task);
}
...
}
}
private void processSelectedKey(SelectionKey k, AbstractNioChannel ch) {
final AbstractNioChannel.NioUnsafe unsafe = ch.unsafe();
if (!k.isValid()) {
final EventLoop eventLoop;
try {
eventLoop = ch.eventLoop();
} catch (Throwable ignored) {
...
return;
}
if (eventLoop != this || eventLoop == null) {
return;
}
unsafe.close(unsafe.voidPromise());
return;
}
try {
int readyOps = k.readyOps();
// We first need to call finishConnect() before try to trigger a read(...) or write(...) as otherwise
// the NIO JDK channel implementation may throw a NotYetConnectedException.
if ((readyOps & SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT) != 0) {
// remove OP_CONNECT as otherwise Selector.select(..) will always return without blocking
// See https://github.com/netty/netty/issues/924
int ops = k.interestOps();
ops &= ~SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT;
k.interestOps(ops);
unsafe.finishConnect();
}
// Process OP_WRITE first as we may be able to write some queued buffers and so free memory.
if ((readyOps & SelectionKey.OP_WRITE) != 0) {
// Call forceFlush which will also take care of clear the OP_WRITE once there is nothing left to write
ch.unsafe().forceFlush();
}
// Also check for readOps of 0 to workaround possible JDK bug which may otherwise lead
// to a spin loop
if ((readyOps & (SelectionKey.OP_READ | SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT)) != 0 || readyOps == 0) {
unsafe.read();
if (!ch.isOpen()) {
// Connection already closed - no need to handle write.
return;
}
}
} catch (CancelledKeyException ignored) {
unsafe.close(unsafe.voidPromise());
}
}
线程栈分析
上面的源码从线程栈分析会更加明确
telnet 127.0.0.1 8888 后,线程调用代码栈如下。
"boss-1-1@1468" prio=5 tid=0xd nid=NA runnable
java.lang.Thread.State: RUNNABLE
at io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap$ServerBootstrapAcceptor.channelRead(ServerBootstrap.java:254)
at io.netty.channel.AbstractChannelHandlerContext.invokeChannelRead(AbstractChannelHandlerContext.java:373)
at io.netty.channel.AbstractChannelHandlerContext.invokeChannelRead(AbstractChannelHandlerContext.java:359)
at io.netty.channel.AbstractChannelHandlerContext.fireChannelRead(AbstractChannelHandlerContext.java:351)
at io.netty.channel.DefaultChannelPipeline$HeadContext.channelRead(DefaultChannelPipeline.java:1334)
at io.netty.channel.AbstractChannelHandlerContext.invokeChannelRead(AbstractChannelHandlerContext.java:373)
at io.netty.channel.AbstractChannelHandlerContext.invokeChannelRead(AbstractChannelHandlerContext.java:359)
at io.netty.channel.DefaultChannelPipeline.fireChannelRead(DefaultChannelPipeline.java:926)
at io.netty.channel.nio.AbstractNioMessageChannel$NioMessageUnsafe.read(AbstractNioMessageChannel.java:93)
at io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoop.processSelectedKey(NioEventLoop.java:651)
at io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoop.processSelectedKeysOptimized(NioEventLoop.java:574)
at io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoop.processSelectedKeys(NioEventLoop.java:488)
at io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoop.run(NioEventLoop.java:450)
at io.netty.util.concurrent.SingleThreadEventExecutor$5.run(SingleThreadEventExecutor.java:873)
at io.netty.util.concurrent.DefaultThreadFactory$DefaultRunnableDecorator.run(DefaultThreadFactory.java:144)
at java.lang.Thread.run(Thread.java:748)
下面进行解析
1.
at io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoop.run(NioEventLoop.java:450)
run方法就是个死循环
2.
at io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoop.processSelectedKey(NioEventLoop.java:651)
at io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoop.processSelectedKeysOptimized(NioEventLoop.java:574)
at io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoop.processSelectedKeys(NioEventLoop.java:488)
runTask()里 selector.selectNow()后会填充上NioEventLoop.selectedKeys
3.
at io.netty.channel.DefaultChannelPipeline$HeadContext.channelRead(DefaultChannelPipeline.java:1334)
at io.netty.channel.AbstractChannelHandlerContext.invokeChannelRead(AbstractChannelHandlerContext.java:373)
at io.netty.channel.AbstractChannelHandlerContext.invokeChannelRead(AbstractChannelHandlerContext.java:359)
at io.netty.channel.DefaultChannelPipeline.fireChannelRead(DefaultChannelPipeline.java:926)
at io.netty.channel.nio.AbstractNioMessageChannel$NioMessageUnsafe.read(AbstractNioMessageChannel.java:93)
这个就是找到NioServerChannel里的pipeline,从pipeline里找到HeadContext,执行HeadContext.channelRead,它的调用如下
public ChannelHandlerContext fireChannelRead(final Object msg) {
invokeChannelRead(findContextInbound(), msg);
return this;
}
private AbstractChannelHandlerContext findContextInbound() {
AbstractChannelHandlerContext ctx = this;
do {
ctx = ctx.next;
} while (!ctx.inbound);
return ctx;
}
其实就是双向链表里的下一个context,
at io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap$ServerBootstrapAcceptor.channelRead(ServerBootstrap.java:254)
at io.netty.channel.AbstractChannelHandlerContext.invokeChannelRead(AbstractChannelHandlerContext.java:373)
at io.netty.channel.AbstractChannelHandlerContext.invokeChannelRead(AbstractChannelHandlerContext.java:359)
at io.netty.channel.AbstractChannelHandlerContext.fireChannelRead(AbstractChannelHandlerContext.java:351)
下一个context 找到就是ServerBootstrapAcceptor,这个ServerBootstrapAcceptor是在哪里加入到pipeline里的?
//初始化channel里
void init(Channel channel) throws Exception {
....
p.addLast(new ChannelInitializer<Channel>() {
@Override
public void initChannel(Channel ch) throws Exception {
final ChannelPipeline pipeline = ch.pipeline();
ChannelHandler handler = config.handler();
if (handler != null) {
pipeline.addLast(handler);
}
ch.eventLoop().execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
pipeline.addLast(new ServerBootstrapAcceptor(
currentChildGroup, currentChildHandler, currentChildOptions, currentChildAttrs));
}
});
}
});
}
在这个例子中我们只有3个context,如下
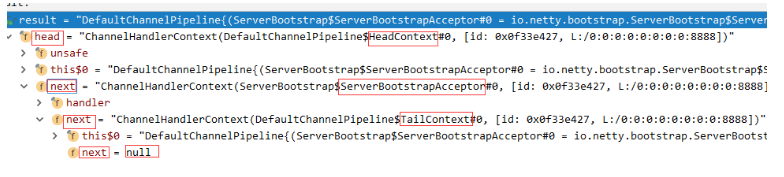
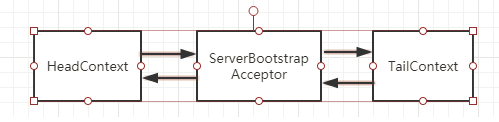
明白了在哪里设值后。
自然就会我们就会去分析ServerBootstrapAcceptor.channelRead方法所做的事情
1.断点 ServerBootstrapAcceptor 237行

child 是 io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioSocketChannel
child.pipeline().addLast(childHandler);
childHandler=rechard.learn.netty.demo.welcome.WelcomeServer$1 就是在WelcomeServer定义的
2. 断点 ServerBootstrapAcceptor 254

childGroup 就是worker EventLoopGroup
childGroup.register(child)进入到
public ChannelFuture register(Channel channel) {
return next().register(channel);
}
register后worker eventLoopGroup里的一个eventLoop线程就会启动
观察线程的变化
为了更好的观察,在welcomeServer里的2个EventLoopGroup 改成如下
EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(0,new DefaultThreadFactory("boss"));
EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(0,new DefaultThreadFactory("worker"));
server启动完,只有一个boss-1-1
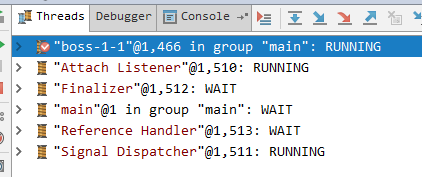
telnet 127.0.0.1 8888 后,可以看到多了一个worker-3-1

再开个cmd ,telnet 127.0.0.1 8888

Netty线程模型如下

总结
第一次运行到run()方法里
- taskQueue里有个server 的注册任务,所以hasTask()为true,而selector.selectNow()一定是返回0,这样就会走到swich的default里
- 先执行I/O处理事件即方法processSelectedKeys(),再执行非I/O处理事件即rurunAllTasks(long timeoutNanos)
- runAllTasks(long timeoutNanos)里去获取到taskQueue里的任务,即注册任务,注册到selector上。这样ServerSocketChannel就注册到了selector里了.
- telnet 127.0.0.1 8888 就会有个SocketChannel连接,selector在selectNow()里就会获取到这个SelectKey
- NioServerSocketChannel里的pipeline中的ServerBootstrapAcceptor.channelRead会处理这个连接的注册
- 处理注册是将该SocketChannel注册到childGroup里,这个过程和 NioServerSocketChannel的注册是一样的。
还剩下一个bind
bind方法
bind方法比较简单
正常的NIO服务端注册代码是如下
ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open()
Selector selector = Selector.open();
serverSocketChannel.socket().bind(new InetSocketAddress(8080));
serverSocketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
serverSocketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
但Netty其实是
private ChannelFuture doBind(final SocketAddress localAddress) {
//1.先注册channel到selector上
final ChannelFuture regFuture = initAndRegister();
final Channel channel = regFuture.channel();
if (regFuture.cause() != null) {
return regFuture;
}
//2.如果注册成功了
if (regFuture.isDone()) {
ChannelPromise promise = channel.newPromise();
//3.再绑定到localAddress
doBind0(regFuture, channel, localAddress, promise);
return promise;
} else {
...
}
}
doBind0 这个方法比较简单,就是把channel绑定到localAddress上。注意这个方法也不是直接绑定,而是作为一个非I/O任务加入到taskQueue里。
它的调用线程栈如下

下面的代码
protected void doBeginRead() throws Exception {
// Channel.read() or ChannelHandlerContext.read() was called
final SelectionKey selectionKey = this.selectionKey;
if (!selectionKey.isValid()) {
return;
}
readPending = true;
final int interestOps = selectionKey.interestOps();
if ((interestOps & readInterestOp) == 0) {
selectionKey.interestOps(interestOps | readInterestOp);
}
}
解释了为什么一开始设置成0,但后面其实又设置成了SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT。
//为什么这里是0而是SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT?
//在AbstractNioChannel.doBeginRead里会改,这个bind里再分析
protected void doRegister() throws Exception {
selectionKey = javaChannel().register(eventLoop().selector, 0, this);
}