- 文章如有错误或疏漏之处还请不吝赐教
- 本文假定读者已经掌握一门编程语言的基础,不适宜从未接触编程的同学
本文开始讲解java中的GUI编程(以swing为例)

先看一些例子:
package chapt2;
import java.awt.*;
import javax.swing.*;
public class test extends JFrame{
private JLabel lbl;
public test(){
super("Test");
lbl = new JLabel("Hello,swing");
getContentPane().add(lbl);
setSize(300,200);
setDefaultCloseOperation(EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new test().setVisible(true);
}
}

package chapt2;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
import javax.swing.*;
import javax.swing.border.*;
public class test extends JFrame {
JButton b1 = new JButton("JButton 1");
JButton b2 = new JButton("JButton 2");
JTextField t = new JTextField(20);
public test() {
b1.setToolTipText("Press Button will show msg");
b1.setIcon( new ImageIcon( "cupHJbutton.gif") );
getContentPane().setLayout( new FlowLayout() );
getContentPane().add(b1);
getContentPane().add(b2);
getContentPane().add(t);
setSize(400,300);
setDefaultCloseOperation(EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
ActionListener al = new ActionListener() {
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e){
String name =
((JButton)e.getSource()).getText();
t.setText(name + " Pressed");
}
};
b1.addActionListener(al);
b2.addActionListener(al);
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
new test().setVisible(true);
}
}

package chapt2;
import javax.swing.*;
public class test {
/**{
* 创建并显示GUI。出于线程安全的考虑,
* 这个方法在事件调用线程中调用。
*/
private static void createAndShowGUI() {
// 确保一个漂亮的外观风格
JFrame.setDefaultLookAndFeelDecorated(true);
// 创建及设置窗口
JFrame frame = new JFrame("HelloWorldSwing");
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
// 添加 "Hello World" 标签
JLabel label = new JLabel("Hello World");
frame.getContentPane().add(label);
// 显示窗口
frame.pack();
frame.setVisible(true);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 显示应用 GUI
javax.swing.SwingUtilities.invokeLater(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
createAndShowGUI();
}
});
}
}
package chapt2;
import javax.swing.JButton;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
import javax.swing.JLabel;
import javax.swing.JPanel;
import javax.swing.JPasswordField;
import javax.swing.JTextField;
public class test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建 JFrame 实例
JFrame frame = new JFrame("Login Example");
// Setting the width and height of frame
frame.setSize(350, 200);
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
/* 创建面板,这个类似于 HTML 的 div 标签
* 我们可以创建多个面板并在 JFrame 中指定位置
* 面板中我们可以添加文本字段,按钮及其他组件。
*/
JPanel panel = new JPanel();
// 添加面板
frame.add(panel);
/*
* 调用用户定义的方法并添加组件到面板
*/
placeComponents(panel);
// 设置界面可见
frame.setVisible(true);
}
private static void placeComponents(JPanel panel) {
/* 布局部分我们这边不多做介绍
* 这边设置布局为 null
*/
panel.setLayout(null);
// 创建 JLabel
JLabel userLabel = new JLabel("User:");
/* 这个方法定义了组件的位置。
* setBounds(x, y, width, height)
* x 和 y 指定左上角的新位置,由 width 和 height 指定新的大小。
*/
userLabel.setBounds(10,20,80,25);
panel.add(userLabel);
/*
* 创建文本域用于用户输入
*/
JTextField userText = new JTextField(20);
userText.setBounds(100,20,165,25);
panel.add(userText);
// 输入密码的文本域
JLabel passwordLabel = new JLabel("Password:");
passwordLabel.setBounds(10,50,80,25);
panel.add(passwordLabel);
/*
*这个类似用于输入的文本域
* 但是输入的信息会以点号代替,用于包含密码的安全性
*/
JPasswordField passwordText = new JPasswordField(20);
passwordText.setBounds(100,50,165,25);
panel.add(passwordText);
// 创建登录按钮
JButton loginButton = new JButton("login");
loginButton.setBounds(10, 80, 80, 25);
panel.add(loginButton);
}
}

- JFrame – java的GUI程序的基本思路是以JFrame为基础,它是屏幕上window的对象,能够最大化、最小化、关闭。
- JPanel – Java图形用户界面(GUI)工具包swing中的面板容器类,包含在javax.swing 包中,可以进行嵌套,功能是对窗体中具有相同逻辑功能的组件进行组合,是一种轻量级容器,可以加入到JFrame窗体中。。
- JLabel – JLabel 对象可以显示文本、图像或同时显示二者。可以通过设置垂直和水平对齐方式,指定标签显示区中标签内容在何处对齐。默认情况下,标签在其显示区内垂直居中对齐。默认情况下,只显示文本的标签是开始边对齐;而只显示图像的标签则水平居中对齐。
- JTextField –一个轻量级组件,它允许编辑单行文本。
- JPasswordField – 允许我们输入了一行字像输入框,但隐藏星号(*) 或点创建密码(密码)
- JButton – JButton 类的实例。用于创建按钮类似实例中的 “Login”。
Swing 组件都采用 MVC(Model-View-Controller,即模型-视图-控制器)的设计,实现 GUI 组件的显示逻辑和数据逻辑的分离,从而允许程序员自定义 Render 来改变 GUI 组件的显示外观,以提供更多的灵活性。Swing 围绕 JComponent 组件构建,JComponent 则由 AWT 的容器类扩展而来。

常用的swing包:
| 包名称 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| javax.swing | 提供一组“轻量级”组件,尽量让这些组件在所有平台上的工作方式都相同 |
| javax.swing.border | 提供围绕 Swing 组件绘制特殊边框的类和接口 |
| javax.swing.event | 提供 Swing 组件触发的事件 |
| javax.swing.filechooser | 提供 JFileChooser 组件使用的类和接口 |
| javax.swing.table | 提供用于处理 javax.swing.JTable 的类和接口 |
| javax.swing.text | 提供类 HTMLEditorKit 和创建 HTML 文本编辑器的支持类 |
| javax.swing.tree | 提供处理 javax.swingJTree 的类和接口 |
javax.swing.event 包中定义了事件和事件监听器类
当在树组件中需要节点扩展(或折叠)的通知时,则要实现 Swing 的TreeExpansionListener 接口,并把一个 TreeExpansionEvent 实例传送给 TreeExpansionListener 接口中定义的方法,而 TreeExpansionListener 和 TreeExpansionEvent 都是在 swing.event 包中定义的。
虽然 Swing 的表格组件(JTable)在 javax.swing 包中,但它的支持类却在 javax.swing.table 包中。表格模型、图形绘制类和编辑器等也都在 javax.swing.table 包中。
与 JTable 类一样,Swing 中的树 JTree(用于按层次组织数据的结构组件)也在 javax.swing 包中,而它的支持类却在 javax.swing.tree 包中。javax.swing.tree 包提供树模型、树节点、树单元编辑类和树绘制类等支持类。
创建图形用户界面程序的第一步是创建一个容器类以容纳其他组件,常见的窗口就是一种容器。容器本身也是一种组件,它的作用就是用来组织、管理和显示其他组件。
Swing 中容器可以分为两类:顶层容器和中间容器。
顶层容器是进行图形编程的基础,一切图形化的东西都必须包括在顶层容器中。顶层容器是任何图形界面程序都要涉及的主窗口,是显示并承载组件的容器组件。在 Swing 中有三种可以使用的顶层容器,分别是 JFrame、JDialog 和 JApplet。
1.JFrame:用于框架窗口的类,此窗口带有边框、标题、关闭和最小化窗口的图标。带 GUI 的应用程序至少使用一个框架窗口。
2.JDialog:用于对话框的类。
3.JApplet:用于使用 Swing 组件的 Java Applet 类。
中间容器是容器组件的一种,也可以承载其他组件,但中间容器不能独立显示,必须依附于其他的顶层容器。常见的中间容器有 JPanel、JScrollPane、JTabbedPane 和 JToolBar。
1.JPanel:表示一个普通面板,是最灵活、最常用的中间容器。
2.JScrollPane:与 JPanel 类似,但它可在大的组件或可扩展组件周围提供滚动条。
3.JTabbedPane:表示选项卡面板,可以包含多个组件,但一次只显示一个组件,用户可在组件之间方便地切换。
4.JToolBar:表示工具栏,按行或列排列一组组件(通常是按钮)。





JFrame & JPanel

在图 1 中显示有“大家好”的 Swing 组件需要放到内容窗格的上面,内容窗格再放到 JFrame 顶层容器的上面。菜单栏可以直接放到顶层容器 JFrame 上,而不通过内容窗格。内容窗格是一个透明的没有边框的中间容器。

JPanel 是一种中间层容器,它能容纳组件并将组件组合在一起,但它本身必须添加到其他容器中使用。JPanel 类的构造方法如下。
- JPanel():使用默认的布局管理器创建新面板,默认的布局管理器为 FlowLayout。
- JPanel(LayoutManagerLayout layout):创建指定布局管理器的 JPanel 对象。

Swing布局管理器
BorderLayout(边框布局管理器)是 Window、JFrame 和 JDialog 的默认布局管理器。边框布局管理器将窗口分为 5 个区域:North、South、East、West 和 Center。其中,North 表示北,将占据面板的上方;Soufe 表示南,将占据面板的下方;East表示东,将占据面板的右侧;West 表示西,将占据面板的左侧;中间区域 Center 是在东、南、西、北都填满后剩下的区域,如图 1 所示。

BorderLayout 布局管理器的构造方法如下所示。
- BorderLayout():创建一个 Border 布局,组件之间没有间隙。
- BorderLayout(int hgap,int vgap):创建一个 Border 布局,其中 hgap 表示组件之间的横向间隔;vgap 表示组件之间的纵向间隔,单位是像素。
package chapt2;
import java.awt.*;
import javax.swing.*;
public class test
{
public static void main(String[] agrs)
{
JFrame frame=new JFrame(); //创建Frame窗口
frame.setSize(400,200);
frame.setLayout(new BorderLayout()); //为Frame窗口设置布局为BorderLayout
JButton button1=new JButton ("上");
JButton button2=new JButton("左");
JButton button3=new JButton("中");
JButton button4=new JButton("右");
JButton button5=new JButton("下");
frame.add(button1,BorderLayout.NORTH);
frame.add(button2,BorderLayout.WEST);
frame.add(button3,BorderLayout.CENTER);
frame.add(button4,BorderLayout.EAST);
frame.add(button5,BorderLayout.SOUTH);
frame.setBounds(300,200,600,300);
frame.setVisible(true);
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
}
}

FlowLayout(流式布局管理器)是 JPanel 和 JApplet 的默认布局管理器。FlowLayout 会将组件按照从上到下、从左到右的放置规律逐行进行定位。与其他布局管理器不同的是,FlowLayout 布局管理器不限制它所管理组件的大小,而是允许它们有自己的最佳大小。
FlowLayout 布局管理器的构造方法如下。
- FlowLayout():创建一个布局管理器,使用默认的居中对齐方式和默认 5 像素的水平和垂直间隔。
- FlowLayout(int align):创建一个布局管理器,使用默认 5 像素的水平和垂直间隔。其中,align 表示组件的对齐方式,对齐的值必须是 FlowLayoutLEFT、FlowLayout.RIGHT 和 FlowLayout.CENTER,指定组件在这一行的位置是居左对齐、居右对齐或居中对齐。
- FlowLayout(int align, int hgap,int vgap):创建一个布局管理器,其中 align 表示组件的对齐方式;hgap 表示组件之间的横向间隔;vgap 表示组件之间的纵向间隔,单位是像素。
package chapt2;
import java.awt.*;
import javax.swing.*;
public class test
{
public static void main(String[] agrs)
{
JFrame jFrame=new JFrame("Java第四个GUI程序"); //创建Frame窗口
JPanel jPanel=new JPanel(); //创建面板
JButton btn1=new JButton("1"); //创建按钮
JButton btn2=new JButton("2");
JButton btn3=new JButton("3");
JButton btn4=new JButton("4");
JButton btn5=new JButton("5");
JButton btn6=new JButton("6");
JButton btn7=new JButton("7");
JButton btn8=new JButton("8");
JButton btn9=new JButton("9");
jPanel.add(btn1); //面板中添加按钮
jPanel.add(btn2);
jPanel.add(btn3);
jPanel.add(btn4);
jPanel.add(btn5);
jPanel.add(btn6);
jPanel.add(btn7);
jPanel.add(btn8);
jPanel.add(btn9);
//向JPanel添加FlowLayout布局管理器,将组件间的横向和纵向间隙都设置为20像素
jPanel.setLayout(new FlowLayout(FlowLayout.LEADING,20,20));
jPanel.setBackground(Color.gray); //设置背景色
jFrame.add(jPanel); //添加面板到容器
jFrame.setBounds(300,200,300,150); //设置容器的大小
jFrame.setVisible(true);
jFrame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
}
}
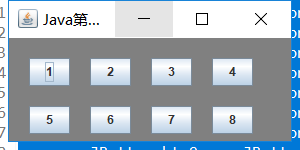
package chapt2;
import java.awt.*;
import javax.swing.*;
public class test extends JFrame {
JButton[] buttons = new JButton[8];
public test(){
for( int i=0; i<buttons.length; i++)
buttons[i] = new JButton( "Button"+(i+1) );
setLayout(new FlowLayout(FlowLayout.LEFT, 10, 5 ));
for( int i=0; i<buttons.length; i++)
add( buttons[i] );
setSize(300,200);
setDefaultCloseOperation(EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
setVisible(true);
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
new test();
}
}

CardLayout(卡片布局管理器)能够帮助用户实现多个成员共享同一个显不空间,并且一次只显示一个容器组件的内容。
CardLayout 布局管理器将容器分成许多层,每层的显示空间占据整个容器的大小,但是每层只允许放置一个组件。CardLayout 的构造方法如下。
- CardLayout():构造一个新布局,默认间隔为 0。
- CardLayout(int hgap, int vgap):创建布局管理器,并指定组件间的水平间隔(hgap)和垂直间隔(vgap)。
package chapt2;
import java.awt.*;
import javax.swing.*;
public class test
{
public static void main(String[] agrs)
{
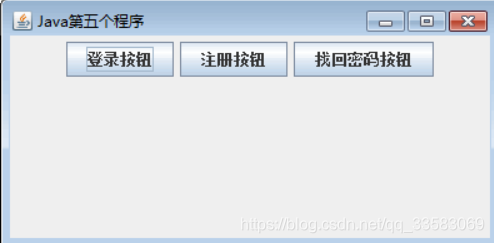
JFrame frame=new JFrame("Java第五个程序"); //创建Frame窗口
JPanel p1=new JPanel(); //面板1
JPanel p2=new JPanel(); //面板2
JPanel cards=new JPanel(new CardLayout()); //卡片式布局的面板
p1.add(new JButton("登录按钮"));
p1.add(new JButton("注册按钮"));
p1.add(new JButton("找回密码按钮"));
p2.add(new JTextField("用户名文本框",20));
p2.add(new JTextField("密码文本框",20));
p2.add(new JTextField("验证码文本框",20));
cards.add(p1,"card1"); //向卡片式布局面板中添加面板1
cards.add(p2,"card2"); //向卡片式布局面板中添加面板2
CardLayout cl=(CardLayout)(cards.getLayout());
cl.show(cards,"card1"); //调用show()方法显示面板2
frame.add(cards);
frame.setBounds(300,200,400,200);
frame.setVisible(true);
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
}
}

上述代码创建了一个卡片式布局的面板 cards,该面板包含两个大小相同的子面板 p1 和 p2。需要注意的是,在将 p1 和 p2 添加到 cards 面板中时使用了含有两个参数的 add() 方法,该方法的第二个参数用来标识子面板。当需要显示某一个面板时,只需要调用卡片式布局管理器的 show() 方法,并在参数中指定子面板所对应的字符串即可,这里显示的是 p1 面板
如果将“cl.show(cards,“card1”)”语句中的 card1 换成 card2,将显示 p2 面板的内容,此时运行结果如图 7所示。

GridLayout(网格布局管理器)为组件的放置位置提供了更大的灵活性。它将区域分割成行数(rows)和列数(columns)的网格状布局,组件按照由左至右、由上而下的次序排列填充到各个单元格中。
GridLayout 的构造方法如下。
- GridLayout(int rows,int cols):创建一个指定行(rows)和列(cols)的网格布局。布局中所有组件的大小一样,组件之间没有间隔。
- GridLayout(int rows,int cols,int hgap,int vgap):创建一个指定行(rows)和列(cols)的网格布局,并且可以指定组件之间横向(hgap)和纵向(vgap)的间隔,单位是像素。
提示:GridLayout 布局管理器总是忽略组件的最佳大小,而是根据提供的行和列进行平分。该布局管理的所有单元格的宽度和高度都是一样的。
package chapt2;
import java.awt.*;
import javax.swing.*;
public class test
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
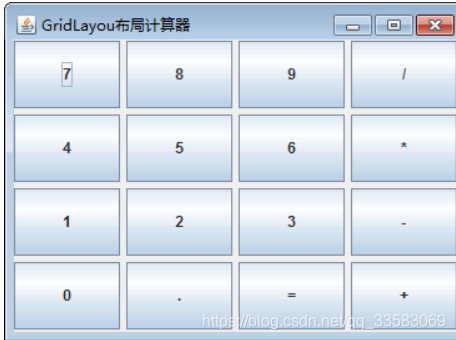
JFrame frame=new JFrame("GridLayou布局计算器");
JPanel panel=new JPanel(); //创建面板
//指定面板的布局为GridLayout,4行4列,间隙为5
panel.setLayout(new GridLayout(4,4,5,5));
panel.add(new JButton("7")); //添加按钮
panel.add(new JButton("8"));
panel.add(new JButton("9"));
panel.add(new JButton("/"));
panel.add(new JButton("4"));
panel.add(new JButton("5"));
panel.add(new JButton("6"));
panel.add(new JButton("*"));
panel.add(new JButton("1"));
panel.add(new JButton("2"));
panel.add(new JButton("3"));
panel.add(new JButton("-"));
panel.add(new JButton("0"));
panel.add(new JButton("."));
panel.add(new JButton("="));
panel.add(new JButton("+"));
frame.add(panel); //添加面板到容器
frame.setBounds(300,200,200,150);
frame.setVisible(true);
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
}
}
网格包布局管理器(不考)
GridBagLayout(网格包布局管理器)是在网格基础上提供复杂的布局,是最灵活、 最复杂的布局管理器。GridBagLayout 不需要组件的尺寸一致,允许组件扩展到多行多列。每个 GridBagLayout 对象都维护了一组动态的矩形网格单元,每个组件占一个或多个单元,所占有的网格单元称为组件的显示区域。
GridBagLayout 所管理的每个组件都与一个 GridBagConstraints 约束类的对象相关。这个约束类对象指定了组件的显示区域在网格中的位置,以及在其显示区域中应该如何摆放组件。除了组件的约束对象,GridBagLayout 还要考虑每个组件的最小和首选尺寸,以确定组件的大小。
为了有效地利用网格包布局管理器,在向容器中添加组件时,必须定制某些组件的相关约束对象。GridBagConstraints 对象的定制是通过下列变量实现的。
- gridx 和 gridy
用来指定组件左上角在网格中的行和列。容器中最左边列的 gridx 为 0,最上边行的 gridy 为 0。这两个变量的默认值是 GridBagConstraints.RELATIVE,表示对应的组件将放在前一个组件的右边或下面。 - gridwidth 和 gridheight
用来指定组件显示区域所占的列数和行数,以网格单元而不是像素为单位,默认值为 1。 - fill
指定组件填充网格的方式,可以是如下值:GridBagConstraints.NONE(默认值)、GridBagConstraints.HORIZONTAL(组件横向充满显示区域,但是不改变组件高度)、GridBagConstraints.VERTICAL(组件纵向充满显示区域,但是不改变组件宽度)以及 GridBagConstraints.BOTH(组件横向、纵向充满其显示区域)。 - ipadx 和 ipady
指定组件显示区域的内部填充,即在组件最小尺寸之外需要附加的像素数,默认值为 0。 - insets
指定组件显示区域的外部填充,即组件与其显示区域边缘之间的空间,默认组件没有外部填充。 - anchor
指定组件在显示区域中的摆放位置。可选值有 GridBagConstraints.CENTER(默认值)、GridBagConstraints.NORTH、GridBagConstraints.
NORTHEAST、GridBagConstraints.EAST、GridBagConstraints.SOUTH、GridBagConstraints.SOUTHEAST、GridBagConstraints.WEST、GridBagConstraints.SOUTHWEST 以及 GridBagConstraints.NORTHWEST。 - weightx 和 weighty
用来指定在容器大小改变时,增加或减少的空间如何在组件间分配,默认值为 0,即所有的组件将聚拢在容器的中心,多余的空间将放在容器边缘与网格单元之间。weightx 和 weighty 的取值一般在 0.0 与 1.0 之间,数值大表明组件所在的行或者列将获得更多的空间。
package chapt2;
import java.awt.*;
import javax.swing.*;
public class test
{
//向JFrame中添加JButton按钮
public static void makeButton(String title,JFrame frame,GridBagLayout gridBagLayout,GridBagConstraints constraints)
{
JButton button=new JButton(title); //创建Button对象
gridBagLayout.setConstraints(button,constraints);
frame.add(button);
}
public static void main(String[] agrs)
{
JFrame frame=new JFrame("拨号盘");
GridBagLayout gbaglayout=new GridBagLayout(); //创建GridBagLayout布局管理器
GridBagConstraints constraints=new GridBagConstraints();
frame.setLayout(gbaglayout); //使用GridBagLayout布局管理器
constraints.fill=GridBagConstraints.BOTH; //组件填充显示区域
constraints.weightx=0.0; //恢复默认值
constraints.gridwidth = GridBagConstraints.REMAINDER; //结束行
JTextField tf=new JTextField("13612345678");
gbaglayout.setConstraints(tf, constraints);
frame.add(tf);
constraints.weightx=0.5; // 指定组件的分配区域
constraints.weighty=0.2;
constraints.gridwidth=1;
makeButton("7",frame,gbaglayout,constraints); //调用方法,添加按钮组件
makeButton("8",frame,gbaglayout,constraints);
constraints.gridwidth=GridBagConstraints.REMAINDER; //结束行
makeButton("9",frame,gbaglayout,constraints);
constraints.gridwidth=1; //重新设置gridwidth的值
makeButton("4",frame,gbaglayout,constraints);
makeButton("5",frame,gbaglayout,constraints);
constraints.gridwidth=GridBagConstraints.REMAINDER;
makeButton("6",frame,gbaglayout,constraints);
constraints.gridwidth=1;
makeButton("1",frame,gbaglayout,constraints);
makeButton("2",frame,gbaglayout,constraints);
constraints.gridwidth=GridBagConstraints.REMAINDER;
makeButton("3",frame,gbaglayout,constraints);
constraints.gridwidth=1;
makeButton("返回",frame,gbaglayout,constraints);
constraints.gridwidth=GridBagConstraints.REMAINDER;
makeButton("拨号",frame,gbaglayout,constraints);
constraints.gridwidth=1;
frame.setBounds(400,400,400,400); //设置容器大小
frame.setVisible(true);
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
}
}

绝对布局

package chapt2;
import java.awt.*;
import javax.swing.*;
public class test {
public static void main(String args[]) {
Frame f = new Frame("Flow Layout");
Button[] buttons = new Button[8];
for( int i=0; i<buttons.length; i++){
buttons[i] = new Button( "button"+(i+1) );
buttons[i].setLocation( 120*i, 100 );
buttons[i].setSize(100,20);
}
f.setLayout(null);
for( int i=0; i<buttons.length; i++)
f.add( buttons[i] );
f.setSize(400,200);
f.setVisible(true);
}
}

盒布局管理器
BoxLayout(盒布局管理器)通常和 Box 容器联合使用,Box 类有以下两个静态方法。
- createHorizontalBox():返回一个 Box 对象,它采用水平 BoxLayout,即 BoxLayout 沿着水平方向放置组件,让组件在容器内从左到右排列。
- createVerticalBox():返回一个 Box 对象,它采用垂直 BoxLayout,即 BoxLayout 沿着垂直方向放置组件,让组件在容器内从上到下进行排列。


事件监听


编程练习:
在窗口中有1个”打开”按钮。
单击“打开”按钮,将按钮文本改成“关闭”。
单击“关闭”按钮,将按钮文本改成“打开”。
注意,获取按钮上的文本:button.getText()
package chapt2;
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
import java.awt.event.ActionListener;
import javax.swing.*;
public class test{
public static void main(String[] args) {
JFrame frame = new JFrame("test");
frame.setSize(600,300);
JPanel panel = new JPanel();
JButton btn = new JButton("打开");
panel.add(btn);
btn.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
JButton src = (JButton)e.getSource();
String str = src.getText();
if(str.equals("关闭")){
src.setText("打开");
}else{
src.setText("关闭");
}
}
});
frame.add(panel);
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
frame.setVisible(true);
}
}
在窗口中有一个“确定”按钮。
单击“确定”按钮后,将窗口的标题改为“单击了确定按钮”。
package chapt2;
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
import java.awt.event.ActionListener;
import javax.swing.*;
public class test{
public static void main(String[] args) {
JFrame frame = new JFrame("test");
frame.setSize(600,300);
JPanel panel = new JPanel();
JButton btn = new JButton("打开");
panel.add(btn);
btn.addActionListener(new myListener(frame));
frame.add(panel);
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
frame.setVisible(true);
}
}
class myListener implements ActionListener{
JFrame frame;
public myListener(JFrame frame) {
this.frame = frame;
}
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
JButton src = (JButton)e.getSource();
String str = src.getText();
frame.setTitle("单击了确定按钮");
}
}
some examples:
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
import javax.swing.*;
public class TestMultiListener {
public static void main(String args[]) {
JFrame f = new JFrame("Test");
JTextField msg = new JTextField(20);
Listener1 m1 = new Listener1(f);
Listener2 m2 = new Listener2(f, msg);
f.addWindowListener(m1);
f.addMouseMotionListener(m2);
f.add( msg, BorderLayout.SOUTH );
f.setSize(200,160);
f.setVisible(true);
}
}
class Listener1 implements WindowListener {
Listener1( JFrame f ){
this.f = f;
}
private JFrame f;
public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e){System.exit(0);}
public void windowOpened(WindowEvent e){}
public void windowIconified(WindowEvent e){}
public void windowDeiconified(WindowEvent e){}
public void windowClosed(WindowEvent e){}
public void windowActivated(WindowEvent e){}
public void windowDeactivated(WindowEvent e){}
}
class Listener10 extends WindowAdapter{
public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e){System.exit(0);}
}
class Listener2 implements MouseMotionListener {
Listener2( JFrame f, JTextField msg ){
this.msg = msg;
this.f = f;
}
private JTextField msg;
private JFrame f;
private boolean bDragged = false;
public void mouseMoved( MouseEvent e ){
msg.setText( "MouseMoved: "+ e.getX() + ", " + e.getY() );
if ( bDragged){
f.setCursor( new Cursor( Cursor.DEFAULT_CURSOR ) );
bDragged = false;
}
}
public void mouseDragged( MouseEvent e ){
msg.setText( "MouseDraged: "+ e.getX() + ", " + e.getY() );
if( ! bDragged ) {
f.setCursor( new Cursor( Cursor.CROSSHAIR_CURSOR ) );
bDragged = true;
}
f.getGraphics().drawLine( e.getX(), e.getY(), e.getX(), e.getY());
}
}
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
import javax.swing.*;
class MyFrame extends JFrame {
JButton btn = new JButton("start");
JLabel lbl = new JLabel("");
public MyFrame(){
this.setTitle("test InvokeLater");
this.setSize(300, 200);
lbl.setFont( new Font("Times New Rome",0,48) );
lbl.setHorizontalAlignment( SwingConstants.CENTER );
getContentPane().setLayout( new BorderLayout() );
getContentPane().add(btn, BorderLayout.NORTH );
getContentPane().add(lbl, BorderLayout.CENTER );
btn.addActionListener( e->{
new Thread( ()->{
for(int i=10; i>=0; i-- ){
final int j = i;
SwingUtilities.invokeLater(()->{
lbl.setText(""+j);
});
try{ Thread.sleep(200); }
catch(Exception ex){}
}
}).start();
});
this.setDefaultCloseOperation(EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
}
}
class InvokeLaterDemo{
public static void main( String... args){
SwingUtilities.invokeLater(()->{
new MyFrame().setVisible(true);
});
}
}
Java计算器
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
import javax.swing.*;
public class JCalculator extends JFrame implements ActionListener {
private final String[] str = {
"7", "8", "9", "/",
"4", "5", "6", "*",
"1", "2", "3", "-",
".", "0", "=", "+"};
JButton[] buttons = new JButton[str.length]; //buttons for numbers
JButton reset = new JButton("CE"); //button for reset
JTextField display = new JTextField("0"); //textfied for result
public JCalculator() {
super("Calculator");
Font font = new Font("Consolas", Font.BOLD, 18);
// add components
JPanel pnlHead = new JPanel(new BorderLayout());
pnlHead.add( display, BorderLayout.CENTER);
pnlHead.add( reset, BorderLayout.EAST);
display.setFont(font);
reset.setFont(font);
JPanel pnlBody = new JPanel(new GridLayout(4, 4));
for (int i = 0; i < str.length; i++) {
buttons[i] = new JButton(str[i]);
buttons[i].setFont(font);
pnlBody.add(buttons[i]);
}
getContentPane().setLayout(new BorderLayout());
getContentPane().add(BorderLayout.NORTH, pnlHead);
getContentPane().add(BorderLayout.CENTER, pnlBody);
// register listeners
for (int i = 0; i < str.length; i++)
buttons[i].addActionListener(this);
reset.addActionListener(this);
display.addActionListener(this);
// set frame properties
setDefaultCloseOperation(WindowConstants.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
setSize(300, 280);
setVisible(true);
}
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
Object source = e.getSource();
String cmd = e.getActionCommand();
if (source == reset)
handleReset();
else if ("0123456789.".indexOf(cmd) >= 0)
handleNumber(cmd);
else
handleOperator(cmd);
}
boolean isFirstDigit = true;
double number = 0.0;
String operator = "=";
public void handleNumber(String key) {
if (isFirstDigit)
display.setText(key);
else if (!key.equals("."))
display.setText(display.getText() + key);
else if (display.getText().indexOf(".") < 0)
display.setText(display.getText() + ".");
isFirstDigit = false;
}
public void handleReset() {
display.setText("0");
isFirstDigit = true;
operator = "=";
}
public void handleOperator(String cmd) {
double dDisplay = Double.valueOf(display.getText());
switch(operator){
case "+": number += dDisplay; break;
case "-": number -= dDisplay; break;
case "*": number *= dDisplay; break;
case "/": number /= dDisplay; break;
case "=": number = dDisplay; break;
}
display.setText(String.valueOf(number));
operator = cmd;
isFirstDigit = true;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SwingUtilities.invokeLater(()->{
new JCalculator();
});
}
}
java数字华容道
package chapt2;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
import java.awt.event.ActionListener;
import javax.swing.*;
import javax.swing.event.*;
public class test extends JFrame{
final int RC = 4;
final int N = RC*RC;
int[] num = new int[N];
JButton[] btn = new JButton[N];
JButton btnStart = new JButton("StartGame");
public test(){
setTitle("BlockMoveGame");
setSize(300,350);
setDefaultCloseOperation(EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
JPanel pnlBody = new JPanel();
JPanel pnlFoot = new JPanel();
pnlBody.setLayout(new GridLayout(RC,RC));
pnlFoot.add(btnStart);
getContentPane().setLayout(new BorderLayout());
getContentPane().add(pnlBody,BorderLayout.CENTER);
getContentPane().add(pnlFoot,BorderLayout.SOUTH);
for(int i=0;i<N;i++){
num[i] = i;
btn[i] = new JButton(""+(num[i]+1));
pnlBody.add(btn[i]);
btn[i].setVisible(true);
}
btn[N-1].setVisible(false);
btnStart.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
btnStart_Click();
}
});
for(int i=0;i<N;i++){
btn[i].addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
for(int j=0;j<N;j++)
if((JButton)e.getSource()==btn[j])
btn_Click(j);
}
});
}
}
public void btnStart_Click(){
for(int i=1;i<500;i++){
int j=(int)(Math.random()*N);
int k=(int)(Math.random()*N);
int t=num[j]; num[j] = num[k]; num[k]=t;
}
for(int i=0;i<N;i++){
btn[i].setText(""+(num[i]+1));
btn[i].setVisible(true);
}
int blank = findBlank();
btn[blank].setVisible(false);
}
int findBlank(){
for(int i=0;i<N;i++)if(num[i]==N-1)return i;
return -1;
}
void btn_Click(int index){
int blank = findBlank();
if(isNeighbor(blank,index)){
btn[index].setVisible(false);
btn[blank].setVisible(true);
int t = num[index];
num[index] = num[blank];
num[blank] = t;
btn[blank].setText(""+(num[blank]+1));
btn[index].setText(""+(num[index]+1));
btn[blank].requestFocus();
}
checkResult();
}
boolean isNeighbor(int a,int b){
boolean r = false;
if(a == b-RC || a == b+RC)r=true;
if((a==b-1||a==b+1)&&a/RC==b/RC)r=true;
return r;
}
void checkResult(){
for(int i=0;i<N;i++)if(num[i]!=i)return;
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(this, "You Win!");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SwingUtilities.invokeLater(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
new test().setVisible(true);
}
});
}
}
java记事本
package chapt2;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
import java.awt.event.ActionListener;
import java.io.*;
import javax.sound.midi.SysexMessage;
import javax.swing.*;
import javax.swing.event.*;
import java.util.logging.*;
public class test{
public static void main(String[] args) {
SwingUtilities.invokeLater(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
TextDAL dal = new FileTextDAL();
TextEditer f = new TextEditer(dal);
f.setSize(800,600);
f.setDefaultCloseOperation(WindowConstants.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
f.setVisible(true);
}
});
}
}
class TextEditer extends JFrame{
File file = null;
Color color = Color.black;
TextDAL dal = null;
JTextPane text = new JTextPane();
JFileChooser filechooser = new JFileChooser();
JColorChooser colorchooser = new JColorChooser();
JDialog about = new JDialog(this);
JMenuBar menubar = new JMenuBar();
JMenu[] menus = new JMenu[]{
new JMenu("File"),new JMenu("Edit"),new JMenu("Help")
};
JMenuItem menuitems[][] = new JMenuItem[][]{
{new JMenuItem("New"),new JMenuItem("Open"),new JMenuItem("Save"),new JMenuItem("Exit")},
{new JMenuItem("Copy"),new JMenuItem("Cut"),new JMenuItem("Paste"),new JMenuItem("Color")},
{new JMenuItem("About")}
};
JToolBar toolbar = new JToolBar();
JButton[] buttons = new JButton[]{new JButton("Copy"),new JButton("Cut"),new JButton("paste")};
public TextEditer(TextDAL dal){
this.dal = dal;
initTextPane();
initMenu();
initAboutDialog();
initToolBar();
}
void initTextPane(){getContentPane().add(new JScrollPane(text));}
void initMenu(){
for(int i=0;i<menus.length;i++){
menubar.add(menus[i]);
for(int j=0;j<menuitems[i].length;j++){
menus[i].add(menuitems[i][j]);
menuitems[i][j].addActionListener(action);
}
}
this.setJMenuBar(menubar);
}
void initAboutDialog(){
about.getContentPane().add(new JLabel("starEdit"));
about.setModal(true);
about.setSize(100,50);
}
void initToolBar(){
for(int i=0;i<buttons.length;i++)toolbar.add(buttons[i]);
buttons[0].addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {text.copy();}
});
buttons[1].addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {text.cut();}
});
buttons[2].addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {text.paste();}
});
this.getContentPane().add(toolbar,BorderLayout.NORTH);
toolbar.setRollover(true);
}
ActionListener action = new ActionListener() {
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
JMenuItem mi = (JMenuItem)e.getSource();
String id = mi.getText();
if(id.equals("New")){
text.setText("");
file = null;
}else if(id.equals("Open")){
if(file!=null)filechooser.setSelectedFile(file);
int returnVal = filechooser.showOpenDialog(TextEditer.this);
if(returnVal == JFileChooser.APPROVE_OPTION){
file = filechooser.getSelectedFile();
openFile();
}
}else if(id.equals("Save")){
if(file!=null)filechooser.setSelectedFile(file);
int returnVal = filechooser.showSaveDialog(TextEditer.this);
if(returnVal == JFileChooser.APPROVE_OPTION){
file = filechooser.getSelectedFile();
saveFile();
}
}
else if(id.equals("Exit"))System.exit(0);
else if(id.equals("Cut"))text.cut();
else if(id.equals("Copy"))text.copy();
else if(id.equals("Paste"))text.paste();
else if(id.equals("Color")){
color = JColorChooser.showDialog(TextEditer.this,"",color);
text.setForeground(color);
}
else if(id.equals("About")){
about.setSize(200,100);
about.setVisible(true);
}
}
};
void openFile(){String content = dal.read(file);text.setText(content);}
void saveFile(){String content = text.getText();dal.save(file,content);}
}
//------------- 关于数据存取、关于日志 ---------------
interface TextDAL{
String read(File file);
void save(File file,String text);
}
class FileTextDAL implements TextDAL{
Logger logger = Logger.getLogger(FileTextDAL.class.getName());
{
try{
FileHandler handler = new FileHandler("test.log");
handler.setFormatter(new SimpleFormatter());
logger.addHandler(handler);
}catch(IOException e){}
}
@Override
public String read(File file) {
logger.log(Level.INFO,"read","read "+file.getPath());
try{
FileReader fr = new FileReader(file);
int len = (int)file.length();
char[] buffer = new char[len];
fr.read(buffer,0,len);
fr.close();
return new String(buffer);
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
logger.log(Level.SEVERE,null,e);
}
return "";
}
@Override
public void save(File file, String text) {
logger.log(Level.INFO,"save","save "+file.getPath());
try{
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter(file);
fw.write(text);
fw.close();
}catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
logger.log(Level.SEVERE,null,e);
}
}
}
鼠标事件举例:

package chapt2;
import java.awt.Color;
import java.awt.Graphics;
import java.awt.event.MouseAdapter;
import java.awt.event.MouseEvent;
import javax.swing.*;
public class test extends MouseAdapter{
JFrame frame;
Graphics g;
JPanel pane;
public test() {
frame = new JFrame("Draw");
frame.setSize(300,200);
frame.setVisible(true);
pane = new JPanel();
frame.add(pane);
pane.setBackground(Color.YELLOW);
pane.addMouseListener(this);
}
@Override
public void mouseClicked(MouseEvent e) {
g = pane.getGraphics();
g.setColor(Color.blue);
g.fillOval(e.getX(), e.getY(), 10, 10);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new test();
}
}
Reference
1.https://www.runoob.com/w3cnote/java-swing-demo-intro.html
2.http://c.biancheng.net/swing/
3.PKU-Java程序设计
4.NCEPU-Java程序设计
5.《Java核心技术 卷I》
