This article is compiled from the sharing content of Tencent Cloud expert engineer Wang Jiluo at the Shenzhen Qcon Conference in December 2020- the challenges and practices of cloud edge-end integration in edge computing scenarios .
Everyone must have heard of edge computing, but how to extend the business to the edge to achieve greater business value?
Regarding this issue, Tencent Cloud started thinking about it a few years ago and set out to build a hyper-converged platform that integrates the edge and the end of the cloud. The purpose is to make it easier for the business to land on the edge.
Today, we will start from the following three parts to share with you some of Tencent Cloud's experience in building a hyper-converged platform:
-
The first part: Mainly introduces the role of edge computing, what challenges exist at the edge of business landing, and why there is cloud edge-end integration;
-
The second part: mainly introduces some practical experience and progress of Tencent Cloud in building a hyper-converged platform;
- Part 3: Introduce 3 edge business landing cases.
Cloud computing development trend
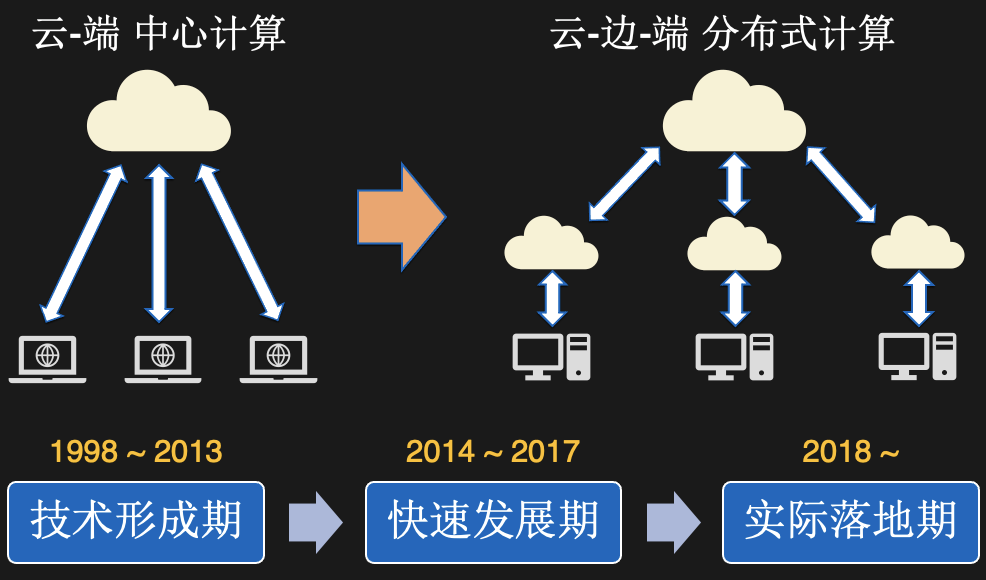
When it comes to cloud computing, everyone will immediately think of central cloud computing. Central cloud computing is a centralized architecture. The computing resources are located in the central computer room and maintained by cloud vendors. So, what are the benefits of this model?
-
The business side no longer needs to manage the underlying resources, and can focus on the business itself, reducing management costs;
- Business parties can apply, use, and return underlying resources flexibly and efficiently, which improves resource utilization as a whole and reduces resource use costs.
On the other hand, edge computing is a kind of distributed computing. Computing resources are scattered closer to the data source to achieve the purpose of providing services nearby. From the perspective of time, the development of edge computing can be divided into three stages:
-
Technology formation period, 1998-2013. It can be traced back to the content distribution network (CDN), the main purpose is to cache data in a location close to the user, so as to shorten the data download time and improve the user experience.
-
Period of rapid development, 2014-2017. As meeting the needs of the Internet of Everything, it has attracted close attention from academia and industry at home and abroad, and various institutions have issued related white papers.
- Actual landing period, 2018 -? With the development of 5G, more and more landing scenarios appear. Entering the government work guidance report, it is basically foreseeable that edge computing will begin to explode.
What is the use of edge computing

Earlier we talked about what edge computing is. Some people will have this question: Since we already have central cloud computing, why do we need edge computing? What value can edge computing bring?
In fact, with the continuous development of technology, the scope of cloud computing has continuously expanded from the center to the edge, and has evolved into an architectural model of collaborative work between the central cloud, edge cloud and end devices .
Why did this change happen? Mainly because the needs and scenarios are constantly changing, especially many traditional industries have put forward more new needs in the process of information transformation, such as: industrial manufacturing, port logistics, transportation energy and so on.
Take intelligent manufacturing as an example. The essence of intelligent manufacturing is equipment intelligence and informationization. The workflow of the entire system is: collecting data, processing data, and directing production. This brings up two problems:
-
High real-time requirements. Many industrial data have very strong real-time nature, and the expiration time is very short, often only a few milliseconds. This requires the entire process of data collection, data processing, and production guidance to be completed within a few milliseconds. If you upload to the cloud for processing, and then return the control command from the cloud, the entire process will take a long time. Obviously, it will not meet the timeliness requirements and will cause serious consequences, such as insufficient precision of the manufactured products or a relatively high rate of defective products. Therefore, processing data nearby is the core of intelligent manufacturing.
- How to deal with massive data. Intelligent industrial control equipment and sensors continuously generate industrial products and environmental data, which brings high transmission and storage costs. These costs even exceed the profits brought by intelligence, and they become obstacles to the transformation of industry to intelligence. On the other hand, more than 90% of these data are invalid data. If useful data can be screened out as early as possible and invalid data can be removed, transmission and storage costs can be reduced.
Take another example of high-definition video. 4K high-definition video requires at least 40M bandwidth. Bandwidth capacity and cost are important factors that we must consider. Compared with the central computer room, the total bandwidth capacity of the edge computer room is larger and the unit price is cheaper. Class services are very suitable for deployment at the edge.
In general, edge computing can bring benefits in four aspects: larger capacity, lower latency, lower cost, and support for localized processing.
Edge computing architecture
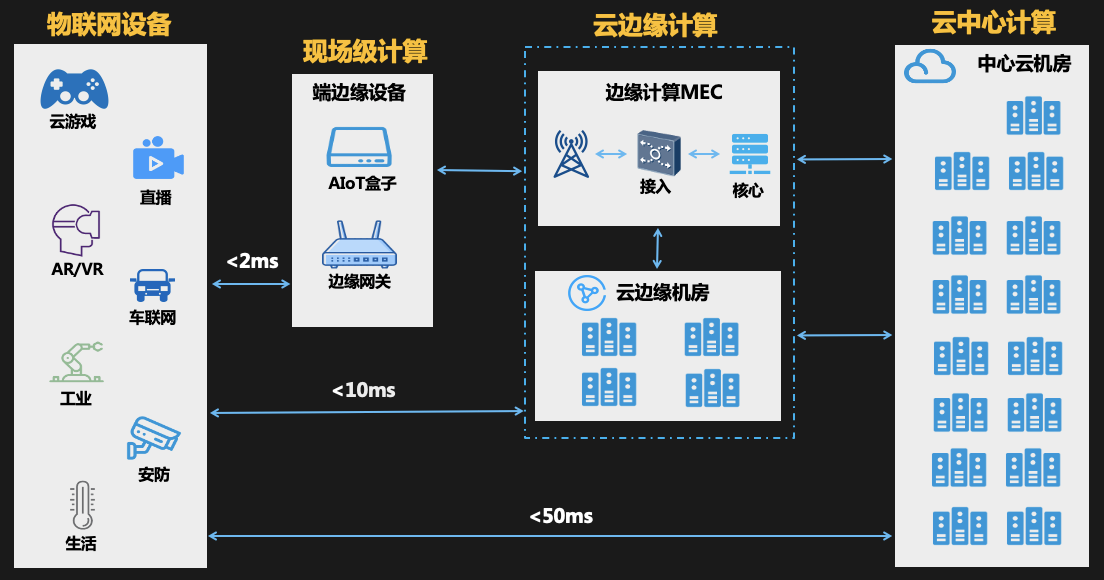
Earlier we talked about cloud computing gradually evolving into a collaborative work model of central cloud-edge cloud-end devices. What about the architecture under the new model?
Taking Tencent Cloud as an example, the central cloud usually refers to the IDC computer room, and the edge cloud will be the ec, oc, mec computer room in turn. Field devices are generally located near the data source, such as: home gateway, traffic light intersection, port/park/mine .
Generally, the delay between the IoT device and the edge device can be controlled within 2 ms, which is suitable for processing business data with extremely high real-time requirements, such as industrial control services.
The delay with the edge cloud can be controlled within 10ms, which can meet the business scenarios of real-time audio and video, ARVR, and cloud games.
This is the general architecture of edge computing.
The challenge
Let's take a look at the new challenges that edge computing scenarios will bring.
-
The heterogeneity is serious. It is reflected in both software and hardware. For example, central cloud and edge cloud usually use x86 and linux standard releases, while edge resources are likely to be cheaper or customized software and hardware due to the need to consider cost and special business requirements. Program.
-
The scale is huge. According to various authoritative organizations, the number of global IoT devices will exceed 100 billion in 2025, distributed all over the world. How to manage such a large-scale equipment is also a very challenging task
-
The environment is complicated. The equipment located in the cloud computer room is okay. Many terminal equipment is often located in harsh environments. For example, many equipment in steel mills are in high temperature environments for a long time, and the equipment deployment environment for water conservancy monitoring is often relatively humid. The device network environment is also various, wired, wireless, wireless and there are WIFI, 4G5G network, zigbee and so on.
- The standards are not uniform. There are no standards in many places, or there are many standards but no recognized standard, especially in terms of management methods.
The consequences of these challenges are:
-
The efficiency drops. Including R&D testing, delivery deployment, upgrade operation and maintenance, etc.
-
Difficulty in management. The scale is very large, the environment in all aspects is very complicated, and there are many standards. It has become difficult to manage our resources well.
- Reliability is reduced. The edge environment is very harsh, and how to ensure service quality in the harsh environment is also a problem
The significance of cloud edge integration
There are so many challenges in the edge scene, and the impact is that it is very difficult to implement the business. This problem directly hinders the development of the industry. In order to lower the threshold for business landing and promote the smooth development of the industry, it is necessary to integrate the cloud and the end.
Integration is reflected in many aspects:
-
Unified management. First of all, we must unify the complex and changeable underlying resource management solutions to minimize unnecessary business perception of underlying details, such as hardware architecture, operating system, network environment, and so on. The second is that the management capabilities provided should be as unified as possible with the central cloud, such as monitoring alarms, publishing operation and maintenance and other basic capabilities commonly used in various businesses.
-
Cloud edge collaboration. In the edge computing scenario, it is natural to sink the business from the center to the edge, but it is not enough. It is usually necessary for the edge and the cloud to work together. For example, it is very necessary to collect useful data from the edge to the center for analysis and processing, and then continue to feed it back to the edge. Taking the AI scenario as an example, we can put inference on the edge, then collect data from the edge for training in the center, and then distribute the trained model to the edge. In addition, the capabilities on the cloud also need to form linkages, such as collecting useful data on the edge, presenting and reprocessing it on the cloud.
- Resource Scheduling. In the edge computing scenario, resources are very scattered, and the load varies greatly with time and space. How to adjust resources reasonably and effectively according to the differences in time and space is also a very meaningful thing to achieve the best effect of resource use. Reasonable resource scheduling can make the system more efficient, stable and low-cost.
The mission of the hyper-converged platform
Above we discussed the challenges of edge computing and the significance of cloud edge-end integration. Tencent Cloud began investing resources in this area a few years ago. After years of accumulation, it has gradually built a hyper-converged platform covering all aspects. Next, I will share with you Next Tencent Cloud’s practice in the construction of hyper-converged platforms.
In the early stages of construction, the question that everyone thinks about most is what a hyper-converged platform is and what benefits we hope the hyper-converged platform will bring to the business. After a long period of exploration, we have determined the mission of the hyper-converged platform: to make edge resources as easy to manage as central cloud resources.
To put it simply, shield the underlying complexity from the platform level, and align all the basic capabilities as much as possible with the central cloud, so that the business will not feel too much difference when using it, and the business side can focus more and focus on specific business research and development. , And finally make everything simple and efficient.
How to achieve this effect
direction:
-
Completely self-study. Starting from scratch is very costly; it is not universal and difficult to promote.
- Embrace cloud native. Cloud native is an ecosystem that encompasses all aspects of capabilities. Based on these capabilities, instead of recreating wheels, we can focus on solving the particularities of edge scenes to achieve a multiplier effect.
Program:
-
Use native Kubernetes. It is not aimed at edge computing scenarios, and there will be some problems when using it directly at the edge.
-
Magic change Kubernetes. The threshold is high, the cost is high, and compatibility issues cannot be ignored.
- Enhance Kubernetes. Comply with Kubernetes standard, flexible, open, low learning cost, easy to use.
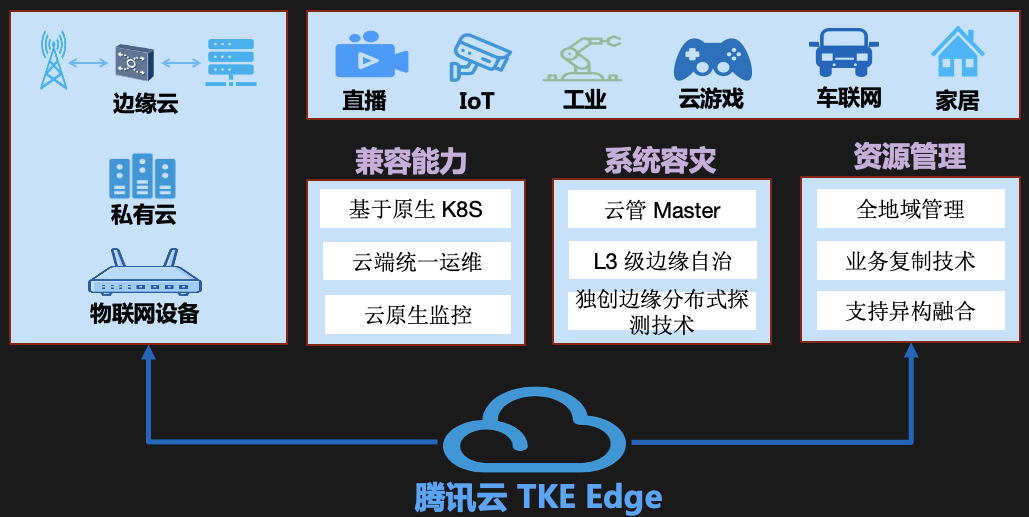
TKE Edge
TKE Edge is an edge computing container system developed by Tencent Cloud based on native Kubernetes. Its main purpose is to shield the intricate edge computing physical environment and provide a unified and standard resource management and scheduling solution for the business. Some of its capabilities have been open sourced as the SuperEdge project.
TKE Edge has several features:
- Kubernetes is native. Extend Kubernetes' powerful container orchestration and scheduling capabilities to the edge in a non-intrusive manner. It natively supports Kubernetes, is fully compatible with all Kubernetes APIs and resources, and has no additional learning costs.
- Edge autonomy. Provides L3 edge autonomy. When the edge node and the cloud network are unstable or offline, the edge node can work autonomously, eliminating the adverse effects of unreliable network.
- Distributed node health monitoring. It is the industry's first open source container management system that provides edge-side health monitoring capabilities. SuperEdge can continue to guard the process on the edge side and collect node fault information to realize faster and more accurate problem discovery and reporting. In addition, its distributed design can also realize multi-region and multi-range monitoring and management .
- Built-in edge orchestration capabilities. It can automatically deploy microservices in multiple regions to facilitate the management of microservices running in multiple regions. At the same time, closed-loop services in the grid can effectively reduce the operating load and improve the fault tolerance and availability of the system .
- Intranet penetration. It can ensure that Kubernetes nodes can be continuously operated and maintained with or without a public network, and also supports Transmission Control Protocol (TCP), Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP), and Hypertext Transfer Security Protocol (HTTPS).
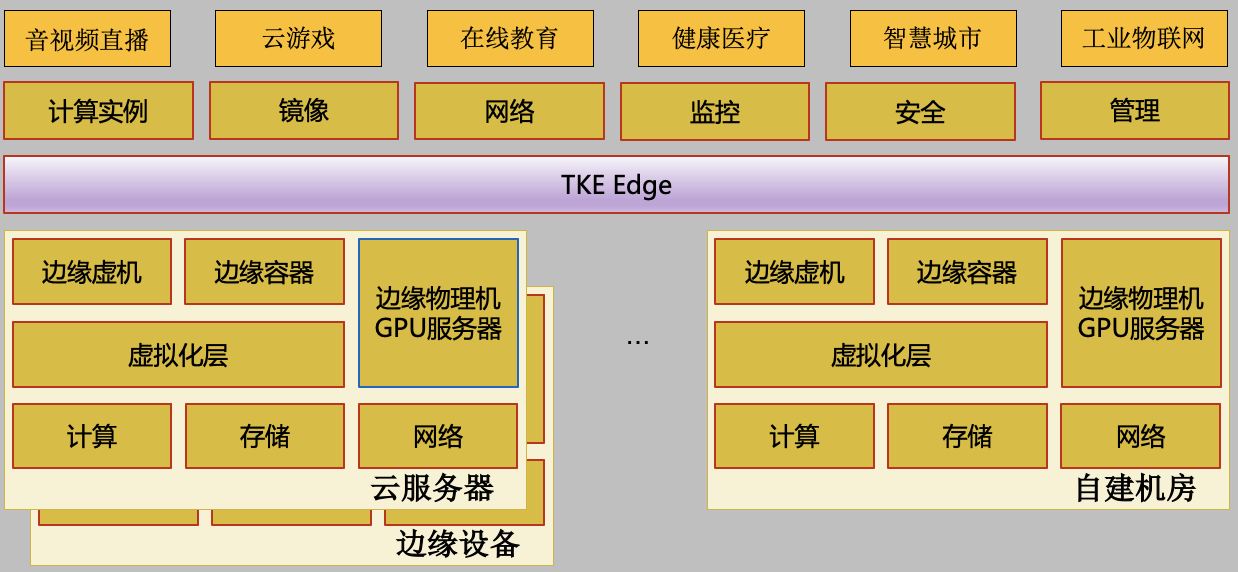
Hyper-converged platform
The hyper-converged platform is based on the underlying IaaS, with TKE Edge as the bonding, and integrates a large number of capabilities and services on Tencent Cloud. The platform has three characteristics:
- Openness. On the IaaS resource side, in addition to access to Tencent's resources, users can also easily access the user's existing computing resources: such as servers from other cloud vendors, user-built computer rooms, smart devices, and so on.
- Integration. The platform integrates a large number of basic service capabilities on the cloud, such as cloud monitoring, cloud logs, cloud operation and maintenance, etc., which can meet most of the needs of use; in addition, it also opens up Tencent Cloud resources, edge computing machines, Tencent Cloud intelligent gateway devices, and so on.
- Ease of use. The use of functions is basically consistent with the use of the central cloud, and there is no need to learn additional use knowledge.
Edge resource construction

-
Edge computing (Edge Computing Machine, ECM). The product provides low-latency, high-availability, and low-cost edge computing services by sinking computing power from the central node to edge nodes close to users. Currently, 300+ nodes have been opened, covering the whole country. Product homepage: https://console.cloud.tencent.com/ecm
-
Integration center . The product uses Tencent Cloud’s self-developed Mini T-Block mobile data center infrastructure as a carrier, integrates 5G, edge computing, and the Internet of Things, and introduces Tencent Cloud edge computing IaaS/PaaS/SaaS platform product capabilities to support cloud 5G 2C and 2B services such as games, 4K live broadcast, and robotics, providing comprehensive innovative and deliverable 5G edge computing overall solutions.
- Edge intelligent gateway . This product is Tencent's industrial-grade equipment facing IoT edge application scenarios. It provides IoT device access, AI local analysis, edge-cloud collaboration and other functions. It has features such as small size, high reliability, multiple networks, ultra-quiet, and easy management. It is suitable for park security, smart retail, power inspection, smart street lights, smart transportation, water conservancy monitoring, industrial quality inspection and other scenarios.
Edge business landing case
Audio and video business practice
-
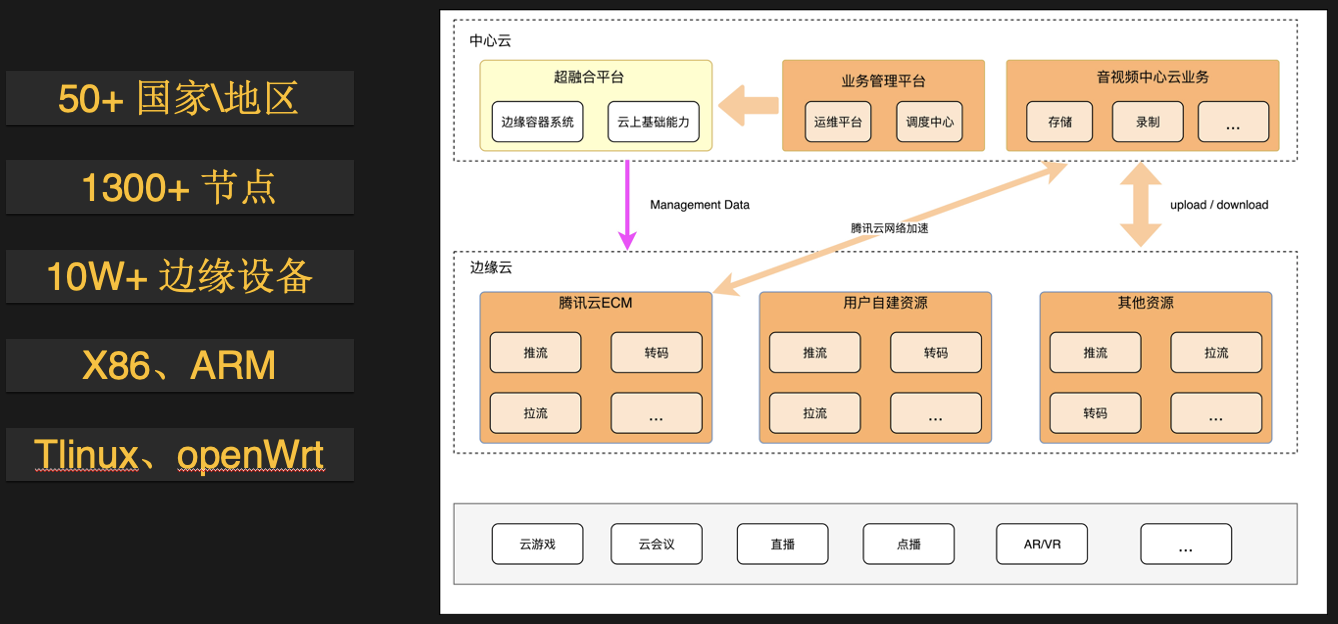
The amount of resources is extremely large, the distribution is extremely wide, and the heterogeneity is serious. It is necessary to consider adapting to different hardware environments during development. The workload of testing has increased exponentially, and it is quite troublesome to release and go online.
-
If a set of K8s is deployed in each computer room, one is that the cost of additional resource overhead cannot be ignored, and the other is that thousands of clusters are basically unmanageable.
- After accessing the hyper-converged platform, the heterogeneity of underlying resources is shielded to the greatest extent through containerization technology, and the number of clusters can be reduced from thousands to dozens. The development, testing, and release operation and maintenance costs have dropped significantly.
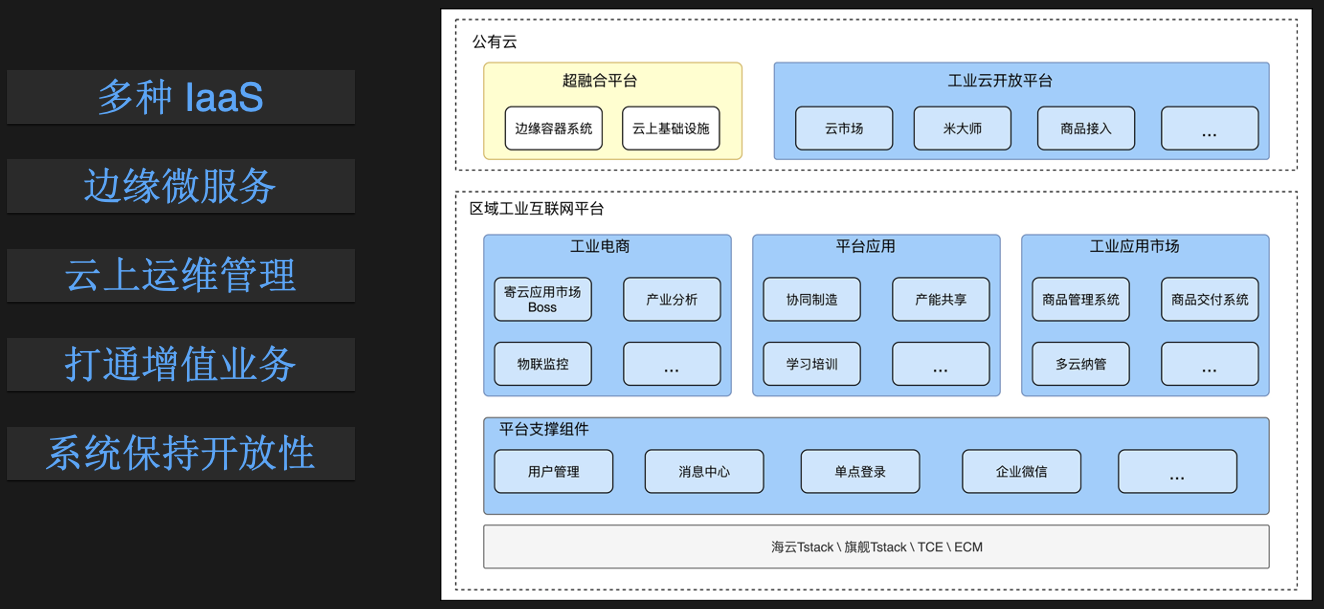
Industrial Cloud
The bottom of the industrial cloud is a private cloud computer room on which many management systems in the industrial field are deployed. Among them, delivery and operation and maintenance are their two biggest headaches. In the past, the delivery team was sent to the customer site for deployment. The delivery of a system takes as little as half a month. Basically, daily operation and maintenance, expansion, etc. need to be implemented on site, which is very inefficient and extremely costly.
After docking with the hyper-converged platform, their delivery is streamlined to only need to execute a command in the user environment, and daily operation and maintenance and other operations are all completed on the cloud.
The other is industrial value-added services. In the past, users selected the value-added services they needed, signed contracts, and deployed them on site. Customers paid for them. The process was cumbersome and the cycle was long. Now a cloud-based industrial e-commerce model has been made. Users add business to the shopping cart, and the business takes effect immediately after placing an order.
Hybrid resource management
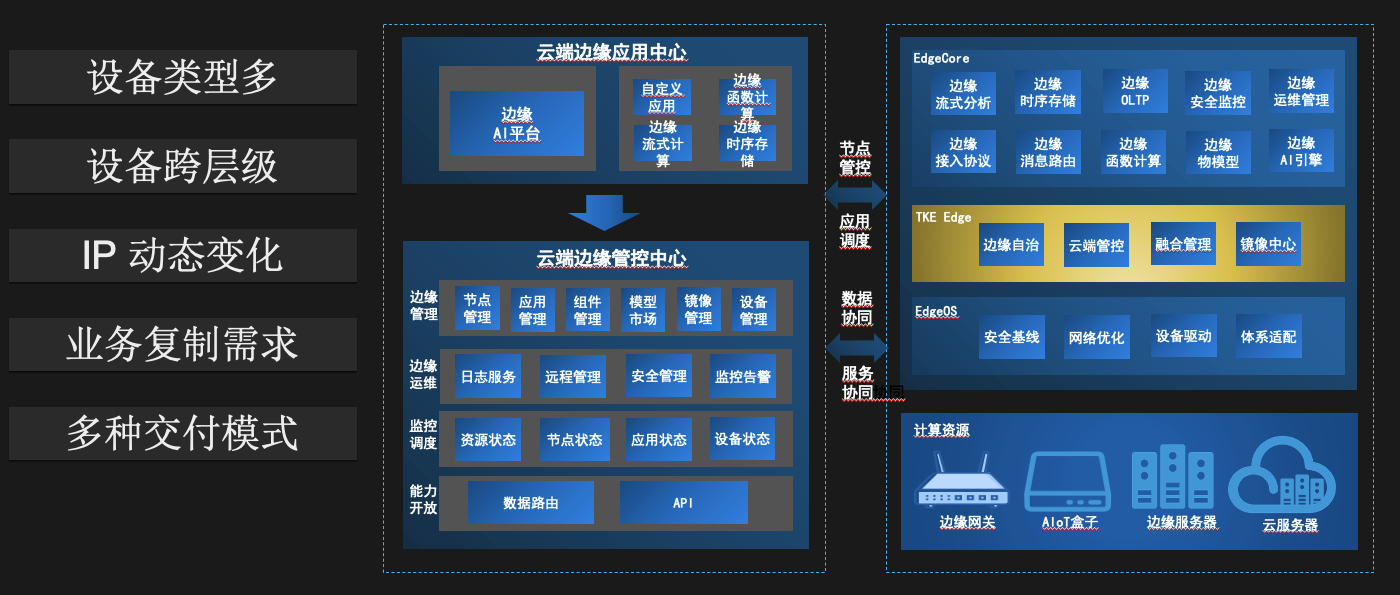
The feature of this scenario is that there are many types of resources, including cloud hosts, self-built computer rooms, and edge smart devices. The network environment is also very complex: 4/5G, one-way networks, all.
Taking vehicle-road collaboration as an example, there is usually a cloud center in an area, on which system management services related to vehicle-road collaboration are run; below the cloud center is an edge cloud small computer room, the number varies from a few to hundreds, mainly Data storage; below is the intersection smart device, which runs AI inference services, and is responsible for processing intersection camera video data;
The previous management method was to deploy a set of K8s in both the central cloud and the edge cloud. Due to limited resources, the junction smart device was not enough to deploy a complete Kubernetes cluster and was not containerized. The two main pain points in this scenario are:
- There are too many clusters, and management is a heavy burden. The other is that service updates and configuration upgrades are very troublesome and require one cluster operation, which is easy to miss.
- Since Junkou smart devices are not containerized, it is inconvenient for both service upgrades and online debugging.
Since the hyper-converged platform does not require the edge resources to be on the same intranet, it is convenient to manage the central cloud, edge cloud, and junction devices in the same cluster at the same time, which solves the two pain points mentioned above.