Shell script application
sehll's basic information
The role of the shell
(1) The role of the shell-command interpreter "translator"
- Between the system kernel and the user, responsible for explaining the command line
(2) the user's login shell - The shell program used by default after login,
一般为 /bin/bash - The internal commands and operating environment of different shells will be different
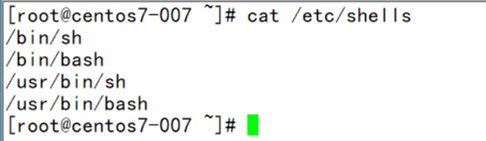
(3) [root@localhost ~]# cat /etc/shells (display all shells)
Write the first shell script
(1) Write script code
-
Use vi or vim editor
-
One Linux command per line, written in order of execution
[root@localhost ~]# vi first.sh(一般shell脚本的后缀都是.sh)
writes(推荐使用vim编辑器,因为会变颜色,写的时候写错了不会变颜色)(you can use yum -y install vim to install if you don’t have it, generally Centos systems with a graphical interface will have it, the command line You have to install it yourself)

(2) Grant executable permissions -
Having a property to make the script executable
(没有可执行的权限就无法运行脚本)
[root @ localhost ~] # chmod + x first.sh ( using chmod added to the script execute permission)
(3) executing the script file
method: ./ script file path(使用./时最好就直接进入脚本所在目录执行即可)
Method Two: sh script file path
Method three: source script file path -
Script execution
(使用./时时必须要求有x可执行权限的使用sh或source可以不用,但是还是要养成习惯给一个x权限)
method: [root @ localhost ~] # ./first.sh

Method Two: [root @ localhost ~] # sh /first.sh

Method three: [the root @ localhost ~] # Source /first.sh

(. 4) More complete script composition (usually written like this) -
The first line of the script statement declares the running environment of the script
-
The line with comment information starting with # is a comment line, what do you usually do when writing this script, etc.
-
Executable statement
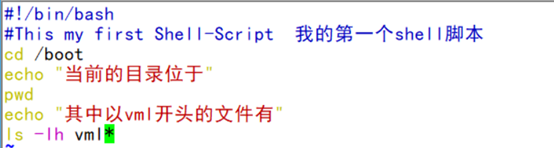
Example: [root@localhost ~]# vi /first.sh
#!/bin/bash #This(脚本声明,在/bin/bash下运行)
is my first shell script(注释信息)
cd /boot(下面都是可执行语句)
echo "The current directory is located:"
pwd
echo "Vml The files at the beginning include: "(输出友好的提示信息)
ls -lh vml*(ls -lh 长格式更加人性化方式显示出以vml开头的文件)
[root@localhost ~]#chmod +x first.sh (add executable permissions)
[root@localhost ~]# ./first.sh (execute script)

Redirection and pipe operation
(1) Interactive hardware equipment
- Standard input: Receive user input data from the device
- Standard output: output data to the user through the device
- Standard error: report execution error information through this device
[type] [device file] [file description number] [default device]
standard input; /dev/stdin; 0; keyboard
standard output; /dev/stdout; 1; display
standard error Output; /dev/stderr; 2; display
(2) redirection operation
[type] [operator] [purpose]
redirect input; <; read data from the specified file instead of
redirecting output from keyboard input ;> ; the output保存to the specified file(会覆盖原文件)
to redirect the output; >>; the output追加to the specified file(不会覆盖原文件默认加到指定文件的末尾)
standard error output; 2>; error information保存to the specified file(会覆盖原文件)
standard error output; 2 >>; error information追加to the specified File(不会覆盖原文件默认加到指定文件的末尾)
mixed output; &>; save the contents of standard output and standard error to the same file(就是不管是对的还是错的只要是执行问前一个命令后的所有结果都保存到指定文件,会覆盖原文件)
(one> is to overwrite two >> is to append)
Redirect example:
- uname -p > kernel.txt
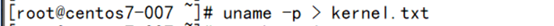
cat kernel.txt
uname -p

- uname -r >> kernel.txt

cat kernel.txt

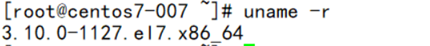
- echo “123456” > pass.txt
(利用重定向去设置用户密码)
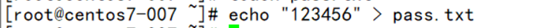
cat pass.txt
useradd tom

passwd --stdin tom < pass.txt

- tar jcf /nonedir/etc.tgz /etc

tar jcf /nonedir/etc.tgz /etc 2>error.log (enter the error information into the error.log file)

cat error.log

Pipe symbol "|"
- Output the result of the command on the left as the processing target of the command on the right
- Format: cmd1 | cmd2 |… | cmdn
(cmd执行的命令,可以使用管道符|一直执行)
[root@localhost ~]# grep "bash$" /etc/passwd

[root@localhost ~]# grep "bash$" /etc/passwd | awk -F:'{print $1,$7}' (利用管道符和awk行处理器筛选出数据中的第一个和第七个字段 -F是用什么分割,这里是使用的是 :分割的)

Example: Use the pipe character and the awk line processor to extract the mac address to/mount the usage
- df -hT | grep “/$” | awk'{print $6}' (the usage of mounting with / ending)
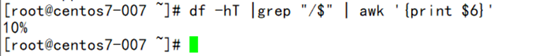
- ip a | grep "ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff$" | awk'[print $2}' (extract the mac address through grep, awk)
