Set working directory
- Work listVery important, because it is the default location for all input and output files, including reading and writing data files, opening and saving script files, and saving workspace mirroring, etc.
- It is much more convenient to operate in the directory where the file is located, or we don’t know where to look after saving a file.
- In R, if you use an absolute path, it will be more troublesome. For example, you need to give the full path of the file to open a file. If you put the file in the default path, you can find it by writing the file name
- So setting the default path will be much more convenient
Use functions in R must add parentheses
In R, constants, variables, functions, and graphics are all called objects , and objects can be represented by custom letters.
getwd () Display the current working directory, which is equivalent to the pwb command in Linux. The files generated by default are here
getwd() #显示当前工作目录,相当于Linux中的pwb命令,默认生成的文件都在这里
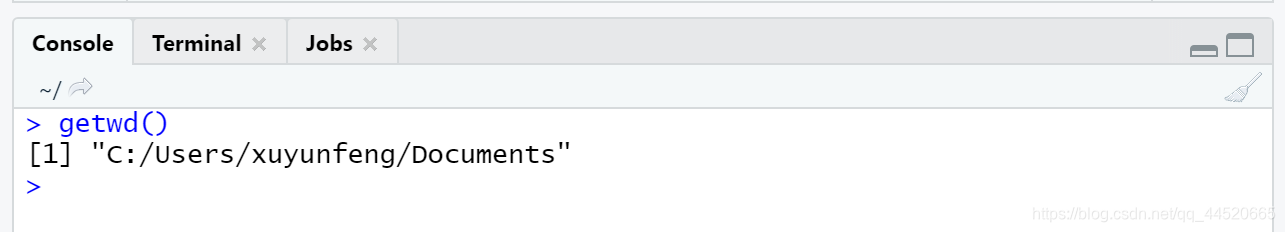
set () Modify the default working directory. In R data analysis, it is generally customary to set the working directory to the directory where the input file is located, and the output results are also saved in this directory, which is convenient for reading and writing operations
-For example, create a new Rdata directory on the desktop and set it as the R default working directory
setwd(dir = "C:/Users/xuyunfeng/Desktop/Rdata")
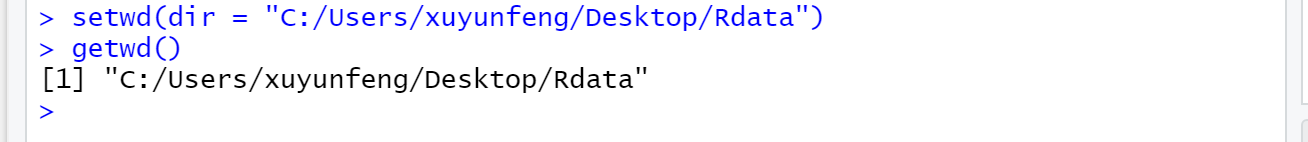
noteThe path in R uses /, and the path in Windows uses
If you want to completely modify the working directory used by R, you can also modifyrprofile.setFile (?? How to modify)
After modifying the working directory, you can uselist.files() View the files contained in the directory
list.files()

to you() You can also view the files contained in the directory
dir()

Basic operation
R performs calculations, R is a good calculator

Create variables and assign values to variables. In R language, there is no need to declare variables before assigning values. In R language, you can define a variable directly with characters, but the variable name cannot start with a number. You can use it after defining the variable Assignment operator:<-, Assign values to variablesAlt±Shortcut key output<-;-> means assign to the right (not recommended);<< means forcing assignment to a global variable instead of a local variable
sum(1,2,3,4,5)#sum求和
mean(c(1,2,3,4,5))#mean求平均值
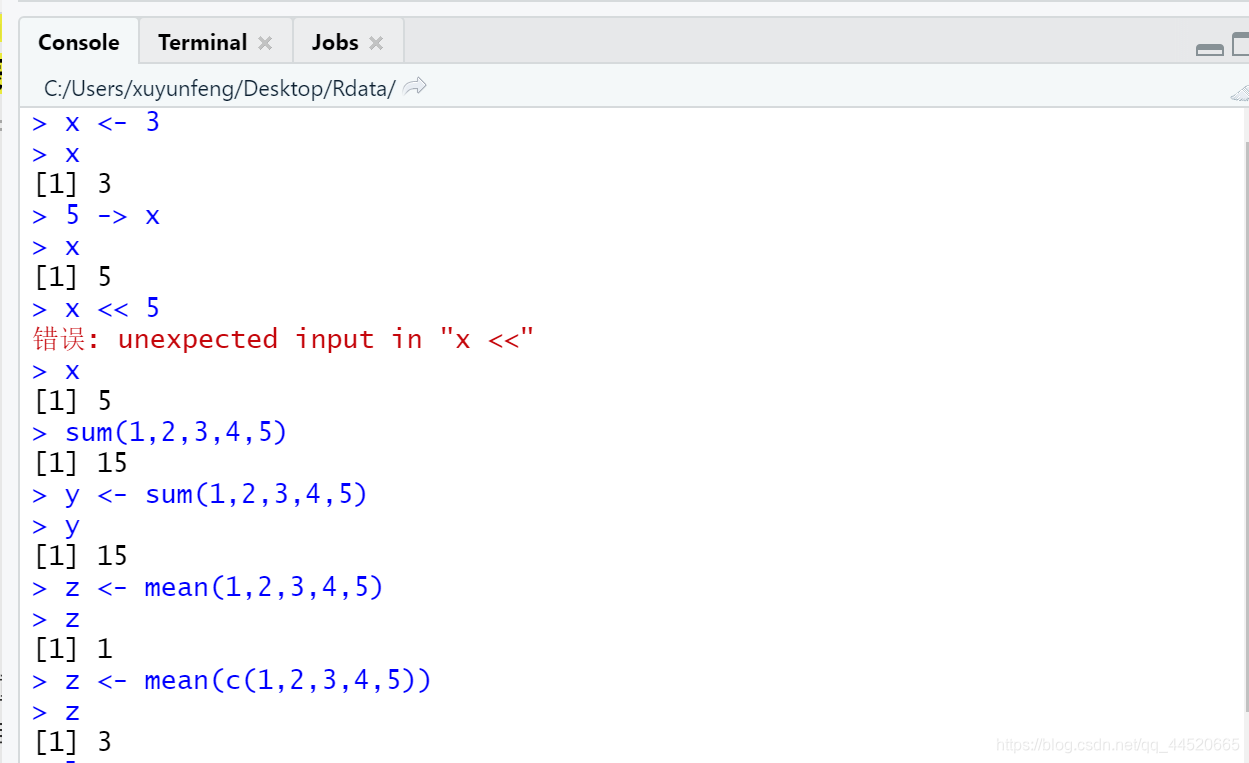
Mean is to average the first parameter, mean(c(1,2,3,4,5)) can be calculated as 3
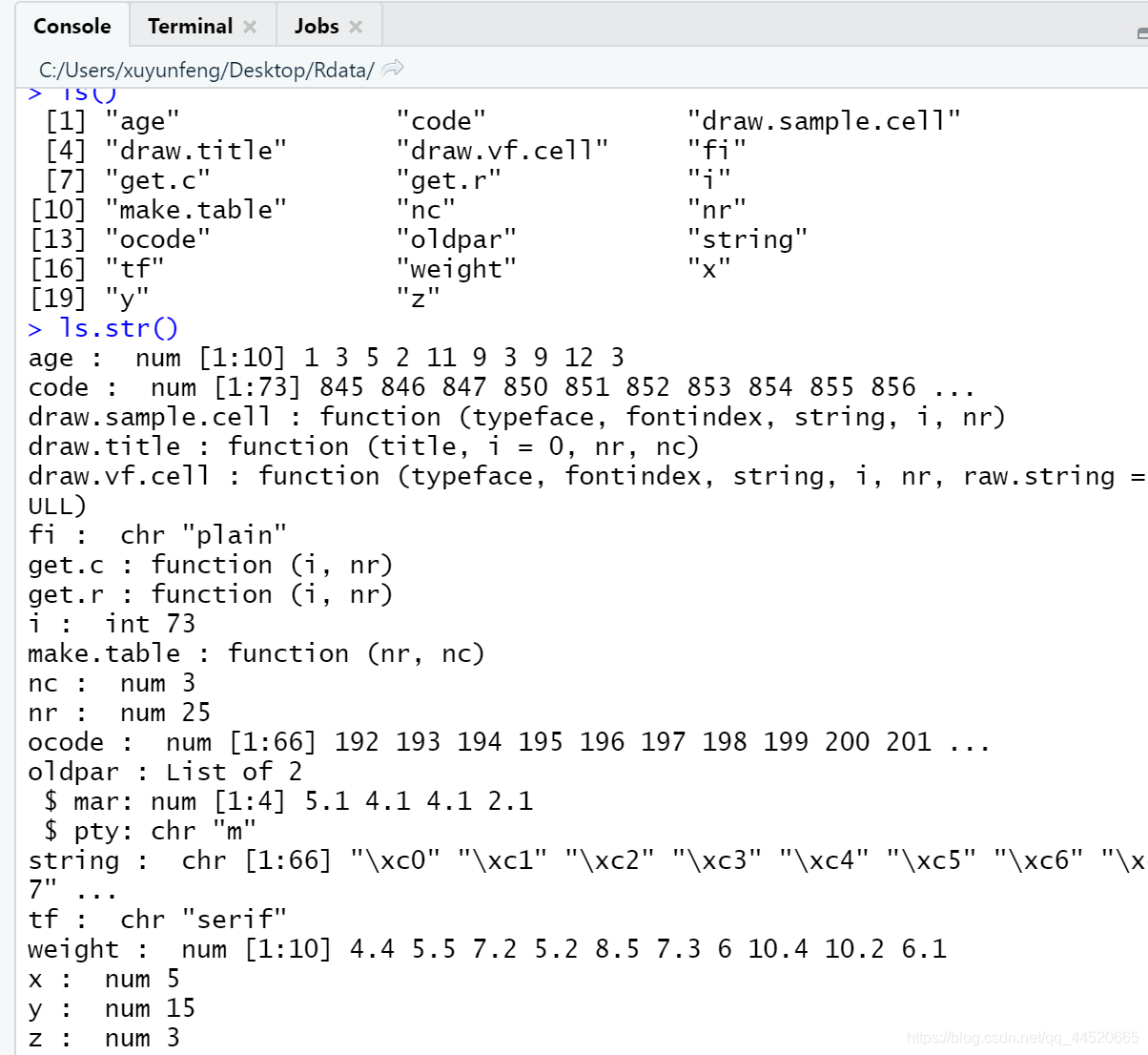
If there are more variables in the workspace, sometimes they will be forgotten, and then re-assign to x, the original value will be replaced, and you want to see which variables and functions that have been defined in the current workspace can be usedls ()orls.str function, The latter will list detailed information
- The ls() function cannot list files starting with ., and files starting with. are hidden files
ls.str()
ls()
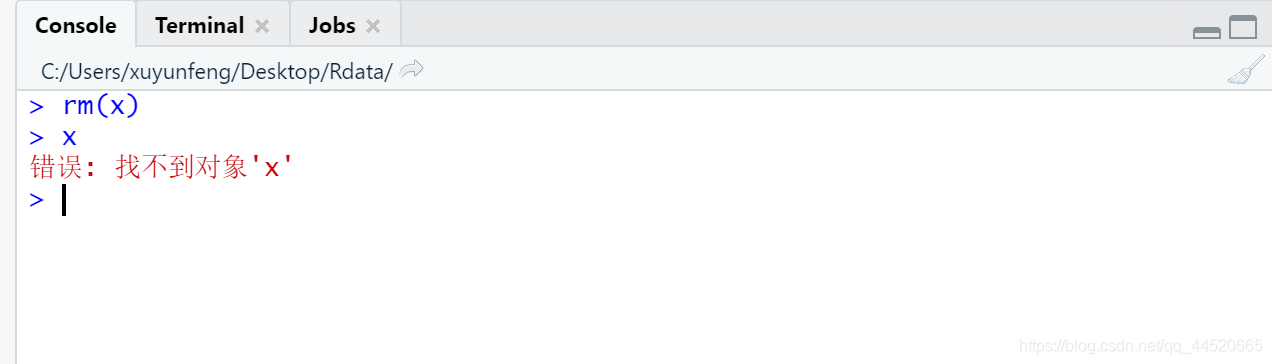
Delete unnecessary variables and functions in the workspace:rm() function, You can delete one or more objects
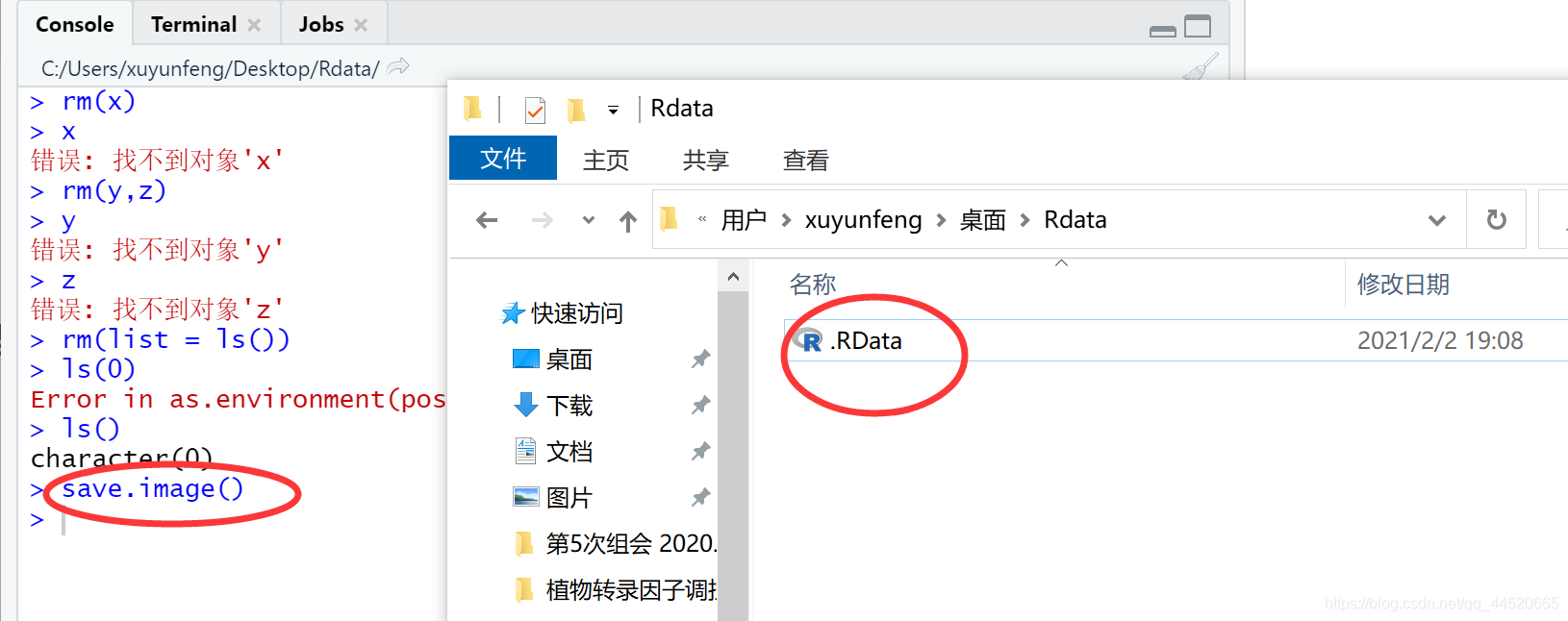
rm(list = ls()): Delete all objects in the workspace
rm(list = ls())#删除工作空间中所有的对象

Ctrl+L to clear the screen
After working in R for a period of time, in order to avoid the unexpected exit of the software due to power failure or crash, you can useThe save.image() function saves the workspace, This is equivalent to saving regularly in Word. The workspace saved by R software will only save data and drawing functions, etc. The drawn graphics will not be saved separately, because these pictures are in separate picture formats, and these pictures can be stored separately
After using the R software, you can pressq() exit
