Strings and tuples are very similar and cannot be easily modified once they are defined
If you have to modify it, you can use slices and concatenations
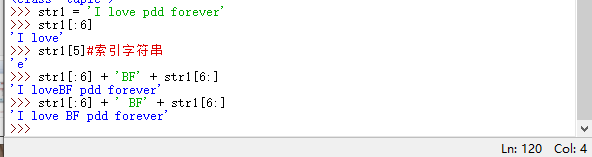
so that the old string str1 is still there, and it will be overwritten after assignment. Python's garbage collection mechanism will remove strings without tags.
Built-in methods for strings
| method | meaning |
|---|---|
| capitalize() | Change the first character of the string to uppercase and all other characters to lowercase |
| casefold() | All letters of the new string become lowercase |
| center(width, fillchar=’ ') | Return a new string with characters centered (width <= string length, new string = original string; width> string width, all characters are centered, left and right are filled with the characters specified by the fillchar parameter) |
| count(sub[, start[, end]]) | Returns the number of non-overlapping occurrences of sub in the string. The optional parameters start and end are used to specify the start and end positions |
| endswith(suffix[, start[, end]]) | If the string ends with the substring specified by suffix, then return True, otherwise return False; the optional parameters start and end are used to specify the start and end positions |
| expandtabs([tabsize=8]) | Return a new string using spaces to replace tabs. If the tabsize parameter is not specified, then 1 tab = 8 spaces by default |
| find(sub[, start[, end]]) | Find the sub substring in the string and return the lowest index value of the match; the optional parameters start and end are used to specify the start and end positions; if the substring fails to match, return -1 |
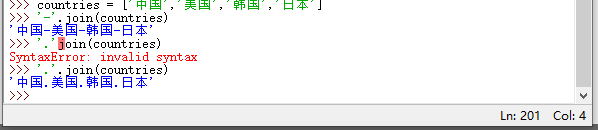
| join(iterable) | Concatenate multiple strings and return a new string; use the string calling this method as the separator and insert it into the middle of each string specified by the iterable parameter; |
| encode(encoding=‘utf-8’, errors=‘strict’) | Encode the string in the encoding format specified by the encoding parameter. The errors parameter specifies the solution when an encoding error occurs: the default'strict' means that if an error occurs, a UnicodeEncodeError will be thrown. Other available parameter values are'ignore','replace' and'xmlcharrefreplace' |
| format(*args, **kwargs) | Return a new formatted string; use positional parameters (args) and keyword arguments (kwargs) to replace |
| format_map(mapping) | Return a new formatted string; use mapping parameters (mapping) to replace |
| index(sub[, start[, end]]) | Find the sub substring in the string and return the lowest index value of the match; the optional parameters start and end are used to specify the start and end positions; if the substring fails to match, a ValueError exception is thrown |
| isalnum () | If there is at least one character in the string and all characters are letters or numbers, it returns True, otherwise it returns False |
| isalpha () | If there is at least one character in the string and all characters are letters, it returns True, otherwise it returns False |
| isascii () | If all the characters in the string are ASCII, it returns True, otherwise it returns False; the ASCII character encoding range is U+0000 ~ U+007F, and the empty string is also ASCII |
| isdecimal () | If there is at least one character in the string and all characters are decimal numbers, it returns True, otherwise it returns False |
| isdigit() | If there is at least one character in the string and all characters are numbers, it returns True, otherwise it returns False |
| Identifier () | If the string is a valid Python identifier, it returns True, otherwise it returns False; call keyword.iskeyword(s) to check whether the string is a reserved identifier (such as "if" or "for") |
| islower() | If the string contains at least one case-sensitive English letter, and these letters are all lowercase, return True, otherwise return False |
| isnumeric() | If there is at least one character in the string and all characters are numbers, it returns True, otherwise it returns False |
| printable () | If the string is printable, it returns True, otherwise it returns False |
| isspace() | If there is at least one character in the string and all characters are spaces, return True, otherwise return False |
| list () | If the string is a titled string (all words start with uppercase, the rest of the letters are lowercase) then return True, otherwise return False |
| isupper() | If the string contains at least one case-sensitive English letter, and these letters are all uppercase, return True, otherwise return False |
| join(iterable) | Concatenate multiple strings and return a new string; use the string calling this method as the separator and insert it into the middle of each string specified by the iterable parameter; |
| bright (width) | Return a new string with characters left aligned (width <= string length, new string = original string; width> string width, all characters are left aligned, and the right side is filled with the characters specified by the fillchar parameter) |
| lower() | Return a new string with all English letters converted to lowercase |
| lstrip(chars=None) | Return a new string with the left blank characters removed; the chars parameter can be used to specify the string to be removed |
| partition(sep) | Search for the separator specified by the sep parameter in the string. If found, return a 3-tuple ('the part before sep','sep','the part after sep'); if not found, return (' Original string','','') |
| removeprefix(prefix) | If the prefix substring specified by the prefix parameter exists, it returns a new string with the prefix removed; if it does not exist, it returns a copy of the original string |
| removesuffix(suffix) | If the suffix substring specified by the suffix parameter exists, it returns a new string with the suffix removed; if it does not exist, it returns a copy of the original string |
| replace(old, new, count=-1) | 返回一个将所有 old 参数指定的子字符串替换为 new 的新字符串;count 参数指定替换的次数,默认是 -1,表示替换全部 |
| rfind(sub[, start[, end]]) | 在字符串中自右向左查找 sub 子字符串,返回匹配的最高索引值;可选参数 start 和 end 用于指定起始和结束位置;如果未能匹配子字符串,返回 -1 |
| rindex(sub[, start[, end]]) | 在字符串中自右向左查找 sub 子字符串,返回匹配的最高索引值;可选参数 start 和 end 用于指定起始和结束位置;如果未能匹配子字符串,抛出 ValueError 异常 |
| rjust(width, fillchar=’ ') | 返回一个字符右对齐的新字符串(width <= 字符串长度,新字符串 = 原字符串;width > 字符串宽度,所有字符右对齐,左侧使用 fillchar 参数指定的字符填充) |
| rpartition(sep) | 在字符串中自右向左搜索sep参数指定的分隔符,如果找到,返回一个 3 元组 (‘在sep前面的部分’, ‘sep’, ‘在sep后面的部分’);如果未找到,则返回 (’’, ‘’, ‘原字符串’) |
| rsplit(sep=None, maxsplit=-1) | 将字符串自右向左进行分割,并将结果以列表的形式返回;sep 参数指定一个字符串作为分隔的依据,默认是任意空白字符;maxsplit 参数用于指定分割的次数(注意:分割 2 次的结果是 3 份),默认是不限制 |
| rstrip(chars=None) | 返回一个去除右侧空白字符的新字符串;通过 chars 参数可以指定将要去除的字符串 |
| split(sep=None, maxsplit=-1) | 将字符串进行分割,并将结果以列表的形式返回;sep 参数指定一个字符串作为分隔的依据,默认是任意空白字符;maxsplit参数用于指定分割的次数(注意:分割 2 次的结果是 3 份),默认是不限制 |
| splitlines(keepends=False) | 将字符串按行分割,并将结果以列表的形式返回;keepends 参数指定是否包含换行符,True 是包含,False 是不包含 |
| startswith(prefix[, start[, end]]) | 如果存在 prefix 参数指定的前缀子字符串,则返回 True,否则返回 False;可选参数 start 和 end 用于指定起始和结束位置;prefix 参数允许以元组的形式提供多个子字符串 |
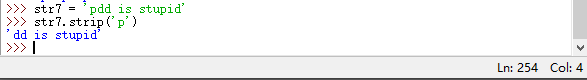
| strip(chars=None) | 返回一个去除左右两侧空白字符的新字符串;通过 chars 参数可以指定将要去除的字符串 |
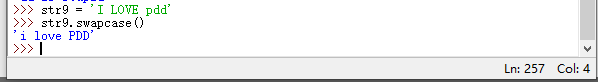
| swapcase() | 返回一个大小写字母翻转的新字符串 |
| title() | 返回标题化(所有的单词都是以大写开始,其余字母均小写)的字符串。 |
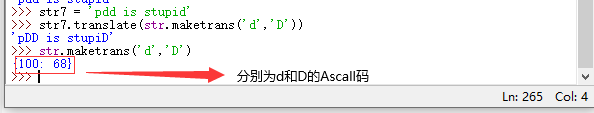
| translate(table) | 返回一个根据 table 参数转换后的新字符串;table 参数应该提供一个转换规则(可以由 str.maketrans(‘a’, ‘b’) 进行定制,例如 “FishC”.translate(str.maketrans(“FC”, “15”)) -> ‘1ish5’) |
| upper() | 返回一个所有英文字母都转换成大写后的新字符串 |
| zfill(width) | 返回一个左侧用 0 填充的新字符串(width <= 字符串长度,新字符串 = 原字符串;width > 字符串宽度,所有字符右对齐,左侧使用 0 进行填充) |
capitalize():将字符串的第一个字符修改为大写,其他字符全部改为小写
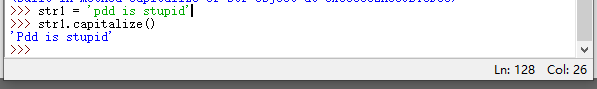
casefold() :新字符串的所有字母变为小写

center(width, fillchar=’ ') : 返回一个字符居中的新字符串(width <= 字符串长度,新字符串 = 原字符串;width > 字符串宽度,所有字符居中,左右使用 fillchar 参数指定的字符填充)

count(sub[, start[, end]]): 返回 sub 在字符串中不重叠的出现次数,可选参数 start 和 end 用于指定起始和结束位置

endswith(suffix[, start[, end]]): 如果字符串是以 suffix 指定的子字符串为结尾,那么返回 True,否则返回 False;可选参数 start 和 end 用于指定起始和结束位置

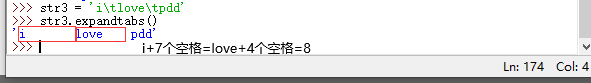
expandtabs([tabsize=8]) :返回一个使用空格替换制表符的新字符串,如果没有指定 tabsize 参数,那么默认 1 个制表符 = 8 个空格
find(sub[, start[, end]]) :在字符串中查找 sub 子字符串,返回匹配的最低索引值;可选参数 start 和 end 用于指定起始和结束位置;如果未能匹配子字符串,返回 -1

index(sub[, start[, end]]) :在字符串中查找 sub 子字符串,返回匹配的最低索引值;可选参数 start 和 end 用于指定起始和结束位置;如果未能匹配子字符串,抛出 ValueError 异常
join(iterable) :连接多个字符串并返回一个新字符串;以调用该方法的字符串作为分隔符,插入到 iterable 参数指定的每个字符串的中间;
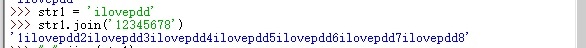
join()方法代替加号来拼接字符串
istitle():如果字符串是标题化字符串(所有的单词都是以大写开始,其余字母均小写)则返回 True,否则返回 False

lstrip(chars=None):返回一个去除左侧空白字符的新字符串;通过 chars 参数可以指定将要去除的字符串
rstrip(chars=None):返回一个去除右侧空白字符的新字符串;通过 chars 参数可以指定将要去除的字符串

partition(sep) 在字符串中搜索 sep 参数指定的分隔符,如果找到,返回一个 3 元组 (‘在sep前面的部分’, ‘sep’, ‘在sep后面的部分’);如果未找到,则返回 (‘原字符串’, ‘’, ‘’)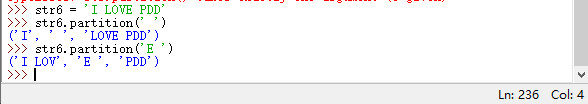
replace(old, new, count=-1) 返回一个将所有 old 参数指定的子字符串替换为 new 的新字符串;count 参数指定替换的次数,默认是 -1,表示替换全部

split(sep=None, maxsplit=-1) 将字符串进行分割,并将结果以列表的形式返回;sep 参数指定一个字符串作为分隔的依据,默认是任意空白字符;maxsplit参数用于指定分割的次数(注意:分割 2 次的结果是 3 份),默认是不限制

strip(chars=None) 返回一个去除左右两侧空白字符的新字符串;通过 chars 参数可以指定将要去除的字符串

swapcase() 返回一个大小写字母翻转的新字符串
translate(table) 返回一个根据 table 参数转换后的新字符串;table 参数应该提供一个转换规则(可以由 str.maketrans(‘a’, ‘b’) 进行定制,例如 “FishC”.translate(str.maketrans(“FC”, “15”)) -> ‘1ish5’)
Task
0. 还记得如何定义一个跨越多行的字符串吗(请至少写出两种实现的方法)?
【1】三重引号字符串
【2】转义字符\n
【3】
>>> str3 = ('待卿长发及腰,我必凯旋回朝。'
'昔日纵马任逍遥,俱是少年英豪。'
'东都霞色好,西湖烟波渺。'
'执枪血战八方,誓守山河多娇。'
'应有得胜归来日,与卿共度良宵。'
'盼携手终老,愿与子同袍。')
1. 三引号字符串通常我们用于做什么使用?
三引号字符串不赋值的情况下,通常当作跨行注释使用
2. file1 = open('C:\windows\temp\readme.txt','r') means to open the text file "C:\windows\temp\readme.txt" in read-only mode, but in fact this statement Will report an error, do you know why? How would you modify it?
"\T" and "\r" stand for "horizontal tab (TAB)" and "carriage return" respectively
>>> file1 = open(r'C:\windows\temp\readme.txt', 'r')
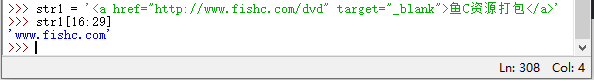
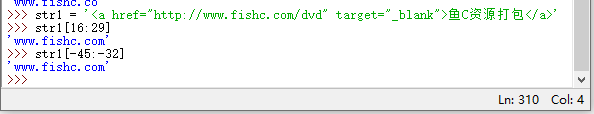
3. There is a string: str1 ='<a href="http://www.fishc.com/dvd" target="_blank">Fish C resource packaging', how to extract the substring:'www.fishc .com'
>>> str1 = '<a href="http://www.fishc.com/dvd" target="_blank">鱼C资源打包</a>'
>>> str1[16:29]
4. If you use a negative number as the index value for slicing operation, can you correctly visually detect the result according to the third question?
>>> str1 = '<a href="http://www.fishc.com/dvd" target="_blank">鱼C资源打包</a>'
>>> str1[-45:-32]
5. It's the string in question 3. What will be displayed in the sentence below?
>>> str1[20:-36]
‘fishc’
6. It is said that only fish oil with an IQ higher than 150 can unlock this string (reverted to a meaningful string): str1 ='i2sl54ovvvb4e3bferi32s56h;$c43.sfc67o0cm99'
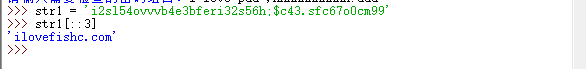
(I don’t know much,?????)
7. Please write a code for password security check: check.py (in thinking...)
# 密码安全性检查代码
#
# 低级密码要求:
# 1. 密码由单纯的数字或字母组成
# 2. 密码长度小于等于8位
#
# 中级密码要求:
# 1. 密码必须由数字、字母或特殊字符(仅限:~!@#$%^&*()_=-/,.?<>;:[]{}|\)任意两种组合
# 2. 密码长度不能低于8位
#
# 高级密码要求:
# 1. 密码必须由数字、字母及特殊字符(仅限:~!@#$%^&*()_=-/,.?<>;:[]{}|\)三种组合
# 2. 密码只能由字母开头
# 3. 密码长度不能低于16位
