1. Resistance
VCR (Constraint between Resistor Voltage and Current)
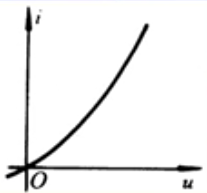
Linear resistance: The resistance of the VCR through a straight line from the origin of the coordinates. Nonlinear resistance: No linear resistance.
Time-varying resistance: The resistance of the VCR changes over time.
Time-varying resistance: no time-varying resistance
Two special cases of linear resistance: open circuit and short circuit
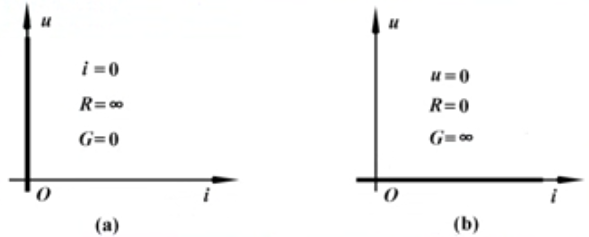
(a) The picture shows an open circuit, no matter what the voltage is, the current is always 0.
(b) The picture shows a short circuit, no matter how much current, the voltage is always 0.

It can be deduced from the above formula:
When R > 0 or G > 0, P >= 0, must absorb power,
When R < 0 or G < 0, P <= 0, must consume power, indicating that negative resistance can emit power
The resistance that consumes power is called active resistance, otherwise it is called passive resistance. (It can be judged according to the quadrant of the coordinate axis where the ui image is located)
2. Independent voltage source and independent current source
2-1. Independent voltage source

symbol:
The characteristic of an independent voltage source is that its terminal voltage is determined by its characteristics and has nothing to do with the position of the voltage source in the circuit.
The current of the independent voltage source is related to the external circuit it is connected to , and is determined by its voltage and the external circuit.
2-2. Independent current source

symbol: